Method for synthesizing optically pure lactide by composite catalysis method
A composite catalyst and lactide technology, applied in the direction of organic chemistry and the like, can solve the problems of high lactide temperature, high energy consumption, long time, etc., and achieve the effects of high cost, low optical purity, and improved selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
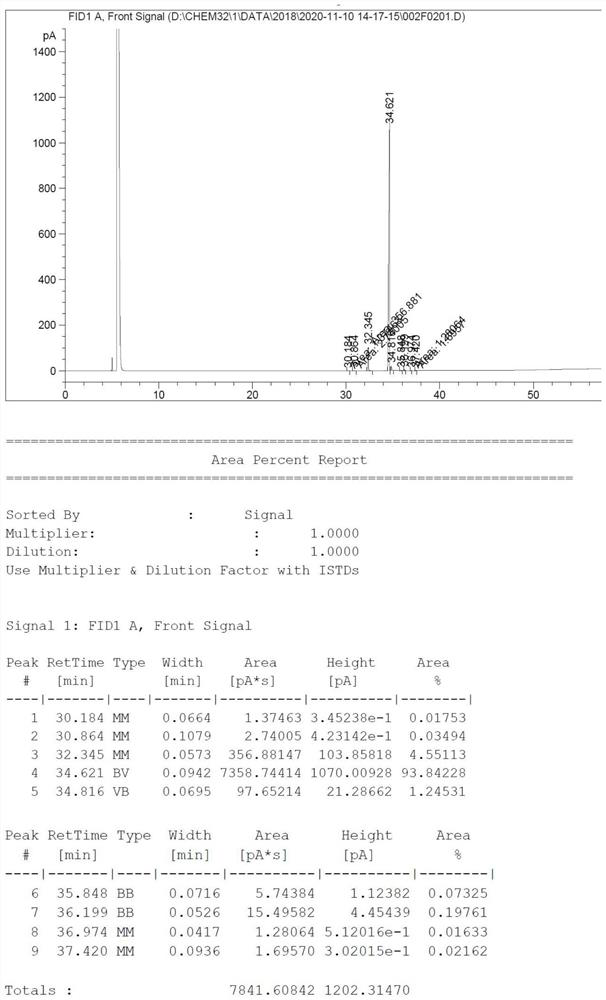
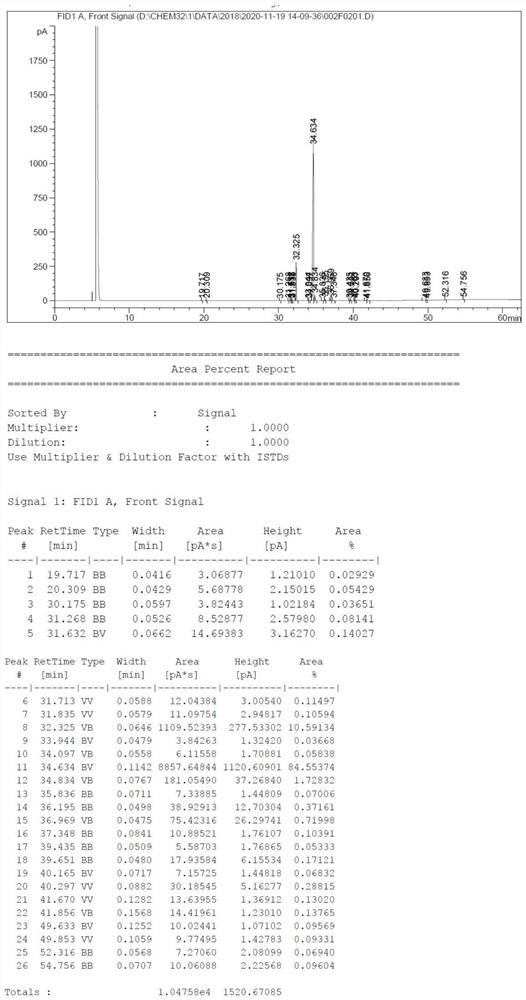
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of pure L-lactide, and this preparation method is as follows:
[0043] In a 1000mL three-necked flask, add 800g of L-lactic acid (chemical content 98.5%, moisture content 1.5%), 20g of D-sorbitol, 0.08g of creatinine (0.01%wt compared to L-lactic acid), 0.08 g of stannous octoate (0.01% wt compared to L-lactic acid), dehydrated by heating at 16 torr, 60-80 °C, dehydration for 2 h; 80-175 °C, dehydration for 10 h.
[0044]The molecular weight of the lactic acid oligomer was monitored to be between 1000 and 2000 Da. Then, the vacuum degree of the system was increased to 1.2 torr, and the temperature was increased to 200 °C for cracking, and the cracking was carried out for 3 hours to obtain 660 g of crude L-lactide. The crude product was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 160 g of filtrate.
[0045] About 500 g of the white solid obtained from the filter cake was placed in a 1000 mL beaker, and 300 g of ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of pure L-lactide, and this preparation method is as follows:
[0054] In a 5000mL three-necked flask, add 4000g of L-lactic acid (chemical content 98.5%, moisture content 1.5%), 100g of D-sorbitol, 0.4g of creatinine (0.01%wt compared to L-lactic acid), 0.4 g of stannous octoate (0.01%wt compared to L-lactic acid) was dehydrated by heating at 25torr, 60-80°C, dehydration for 3h; 80-175°C, dehydration for 10h.
[0055] The molecular weight of the lactic acid oligomer was monitored to be between 1000 and 2000 Da, and then the vacuum degree of the system was increased to 2.0 torr, and the temperature was increased to 200° C. for cracking for 5 hours to obtain 3300 g of crude L-lactide. The crude product was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 820 g of filtrate.
[0056] The obtained filter cake about 2480g of white solid was placed in a 5000mL beaker, and 1600g of 5% Na was added. 2 CO 3 The aqueous sol...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The present embodiment provides a kind of preparation method of pure D-lactide, and this preparation method is as follows:
[0065] In a 1000mL three-necked flask, add 800g of L-lactic acid (chemical content 98.5%, moisture content 1.5%), 20g of D-sorbitol, 0.08g of creatinine (0.01%wt compared to D-lactic acid), 0.08 g of stannous octoate (0.01%wt compared to D-lactic acid) was dehydrated by heating at 15torr, 60-80°C, dehydration for 2h; 80-175°C, dehydration for 10h.
[0066] The molecular weight of the lactic acid oligomer was monitored to be between 1000 and 2000 Da, then the vacuum degree of the system was increased to 1.0 torr, and the temperature was increased to 200 °C for cracking for 3 hours to obtain 640 g of crude D-lactide. The crude product was filtered under reduced pressure to obtain 135 g of filtrate.
[0067] About 505 g of the white solid obtained from the filter cake was placed in a 1000 mL beaker, and 300 g of 5% Na was added. 2 CO 3 The aqueous...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com