Fragile diamond abrasive particle and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of diamond grains and diamonds, applied in the field of diamond abrasive grains, can solve expensive problems, achieve continuous performance, realize the effect of machined surface quality, continuous grinding and polishing performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] §Improved brittleness of diamond particles for resin bonding
[0064] Commercially available diamond for resin bonding (Tomei Diamond Co. powder IRV3, #170 / 200, brittleness: 54.4; bulk density: 1.62 g / cm) 3 ) was used as the starting material, and was processed as follows for the purpose of improving brittleness.
[0065] [1] With CO 2 Oxidation
[0066] 20 grams of the starting material were weighed, placed in a ceramic dish and heated in a tube furnace at 980°C for 12 hours while carbon dioxide gas was flowing at a rate of 40 mL / min. The diamond particles recovered from the furnace showed a brittleness of 65.8 and 1.37 g / cm 3 bulk density; cracks were observed within the particles and surface corrosion was observed on the particles. A 21% increase in brittleness and an 18% decrease in bulk density were observed due to the rough surface.
[0067] [2] Use H 2 O oxidation
[0068] 20 grams of the above starting material was placed in a ceramic dish and heated in a...
Embodiment 2
[0073] § Improvement of diamond particles for metal bonding
[0074] Commercially available diamond particles for metal bonding (Tomei Diamond Co. powder IMS, #325 / 400, brittleness: 20.0) were used as starting materials, and were treated as follows for the purpose of increasing brittleness.
[0075] A volume of initial diamond material was placed in an alumina crucible and heated at 1300°C for 6 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere. A sample of diamond particles was recovered after treatment with a grey appearance and a thin graphite layer formed on the surface. The brittleness rating was 35.0.
[0076] Two 20-gram samples were taken from the treated diamond. The first sample was in CO 2 Treated at 1000° C. for 2 hours in an atmosphere; a brittleness of 54.0 was thus obtained. The second sample was in H 2 The brittleness of 58.6 was obtained by treating at 1000°C for 2 hours in O vapor.
Embodiment 3
[0078] § Improvement of micron-sized diamond particles
[0079] [1] Surface oxidation using solid etchant
[0080] The initial diamond material used was a commercial product Tomei Diamond Co. micron-sized diamond powder (IRM5-10, D 50 Value (average particle size): 5.730 μm, specific surface area: 0.849 m 2 / g).
[0081] The regular attachment of the fine powder of oxide etchant to the diamond particles is ensured by a wet process: the diamond particles are first wetted with an acidic solution of metal salts (ferric chloride, magnesium chloride, etc.) to which base is added to induce metal hydrogen Oxide attachment. Then, the whole was dried and shaped into pellets as samples.
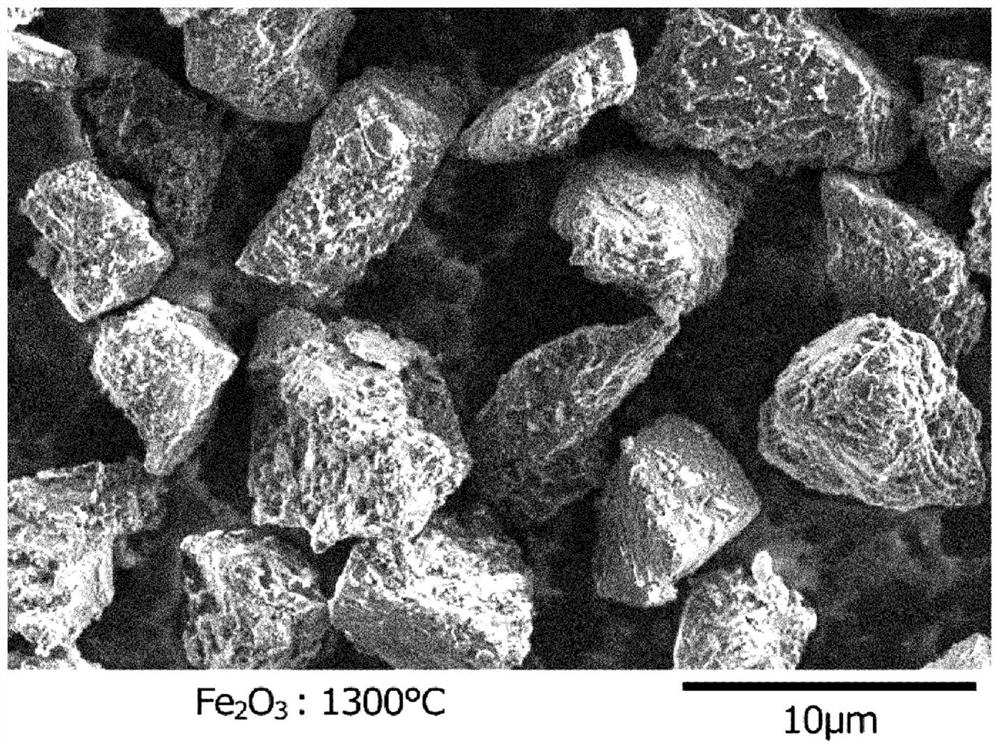
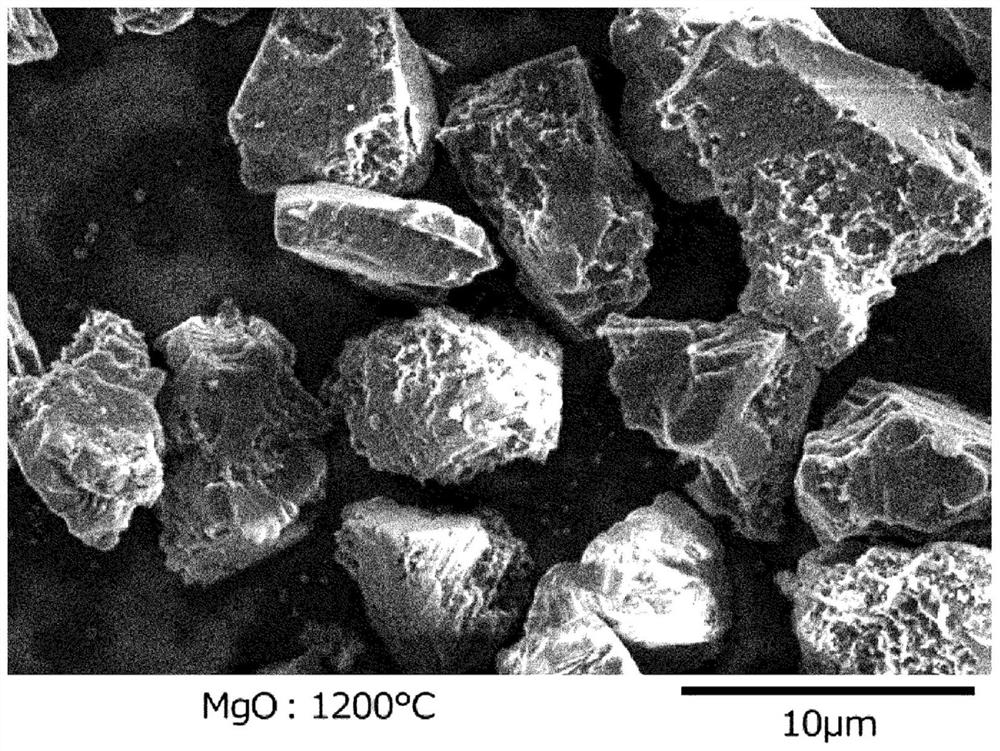
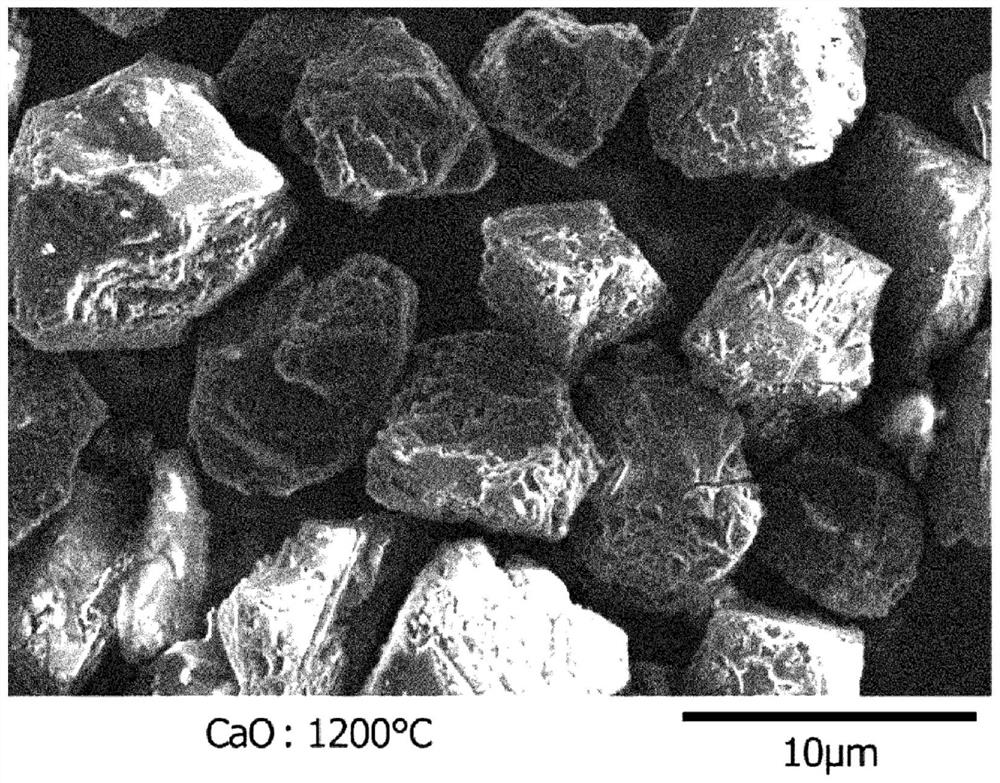
[0082] Each sample was placed in an alumina crucible and processed by holding at 1300°C or 1200°C for 2 hours in an inert atmosphere. For the recovered samples, metal components were removed by dissolving in dilute hydrochloric acid, rinsed with water and dried to collect diamond particles. The c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com