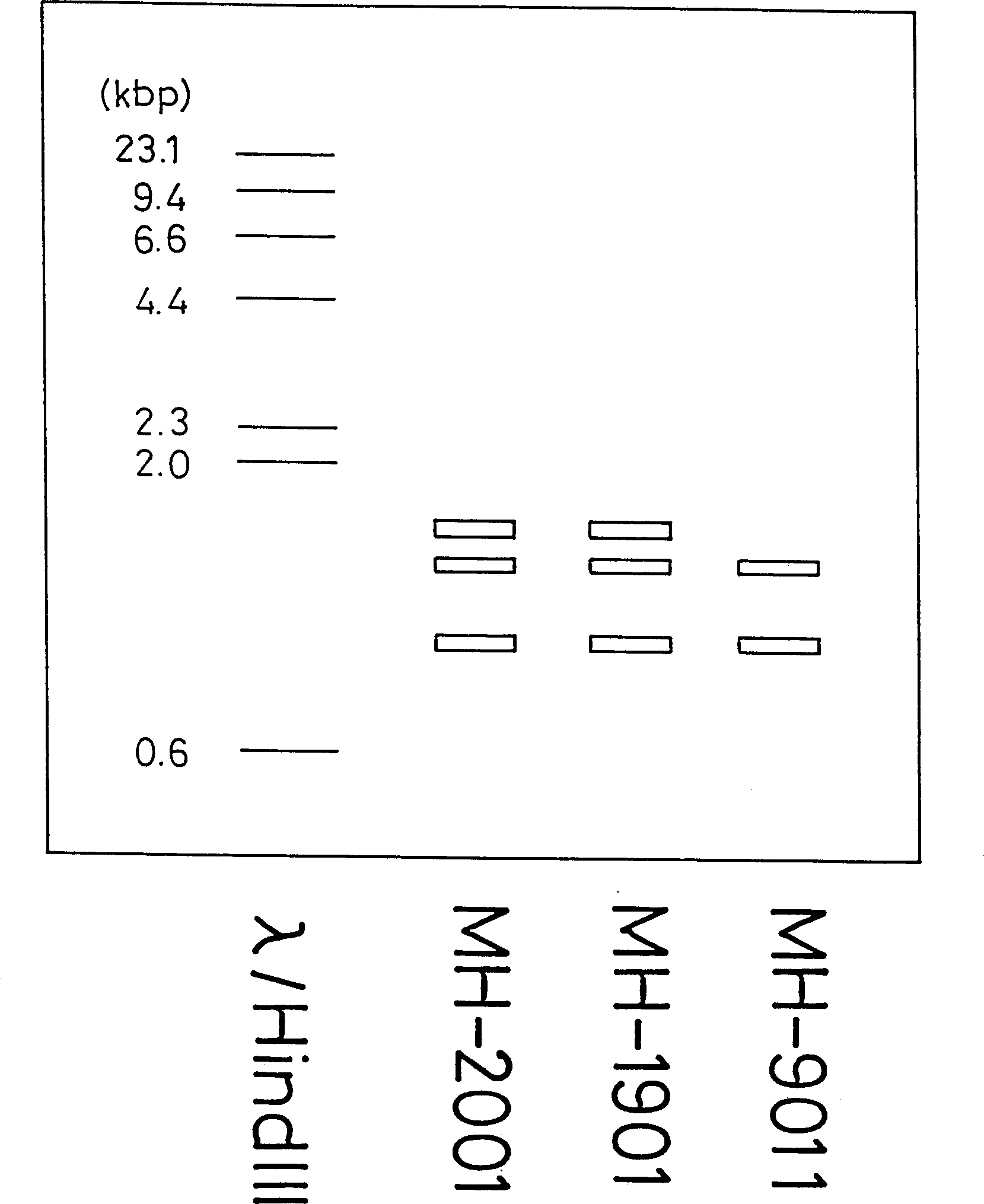New strains of drechslera monoceras and control compositions containing the same
A technology of Dess mold and composition, which is applied in the field of weed control composition, can solve the problems such as reduction, and achieve the effect of reducing environmental pollution and increasing herbicidal activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1: Isolation of Desseria monoceratum of the present invention
[0032] Naturally infected barnyardgrass is collected, and the pathogen is isolated from diseased tissues of the blades and sheaths of the leaves. Specifically, cut off a tissue part of 1 square centimeter with damage in the center, soak the cut part in 70% ethanol aqueous solution for 1-2 seconds, and then soak it in an aqueous solution of sodium hypochlorite with an effective chlorine concentration of about 2% for 10 seconds. minutes to sterilize the surface of the excised part. The sterilized diseased tissue portion was washed three times with sterile water, placed on an agar medium supplemented with antibiotics, and then incubated statically in an incubator. The top of the growing reticular mycelium was picked under a light microscope and transferred to nutrient medium for pure culture.
preparation Embodiment 1
[0070] Formulation Example 1: wettable powder
[0071] The conidia (1 × 10 9 ) and 90 g of a suspension of TOALITE (Toa Kasei Co., Ltd) on diatoms were thoroughly mixed, the mixture was fully dried in air at room temperature, and the dry matter was crushed. The resulting pulverized substance was mixed and kneaded with NewKalgen (Takemotooil & Fat Co., Ltd) as a surfactant, and the mixture was sieved to obtain a wettable powder of Desseria monocaria of the present invention.
preparation Embodiment 2
[0072] Formulation Example 2: Powder
[0073] The conidia (1 × 10 9 ) and the suspension of 90g TOALITE (Toa Kasei Co., Ltd) are fully mixed, then at room temperature, the mixture is fully dried in the air, the dry matter is crushed, and then sieved to obtain the powder of Desseria unicasei of the present invention.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com