Transgenic plants with modified sterol biosynthetic pathways
A plant, sterol technology, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Embodiment 1
[0094] EXAMPLES Example 1. Phytosterols
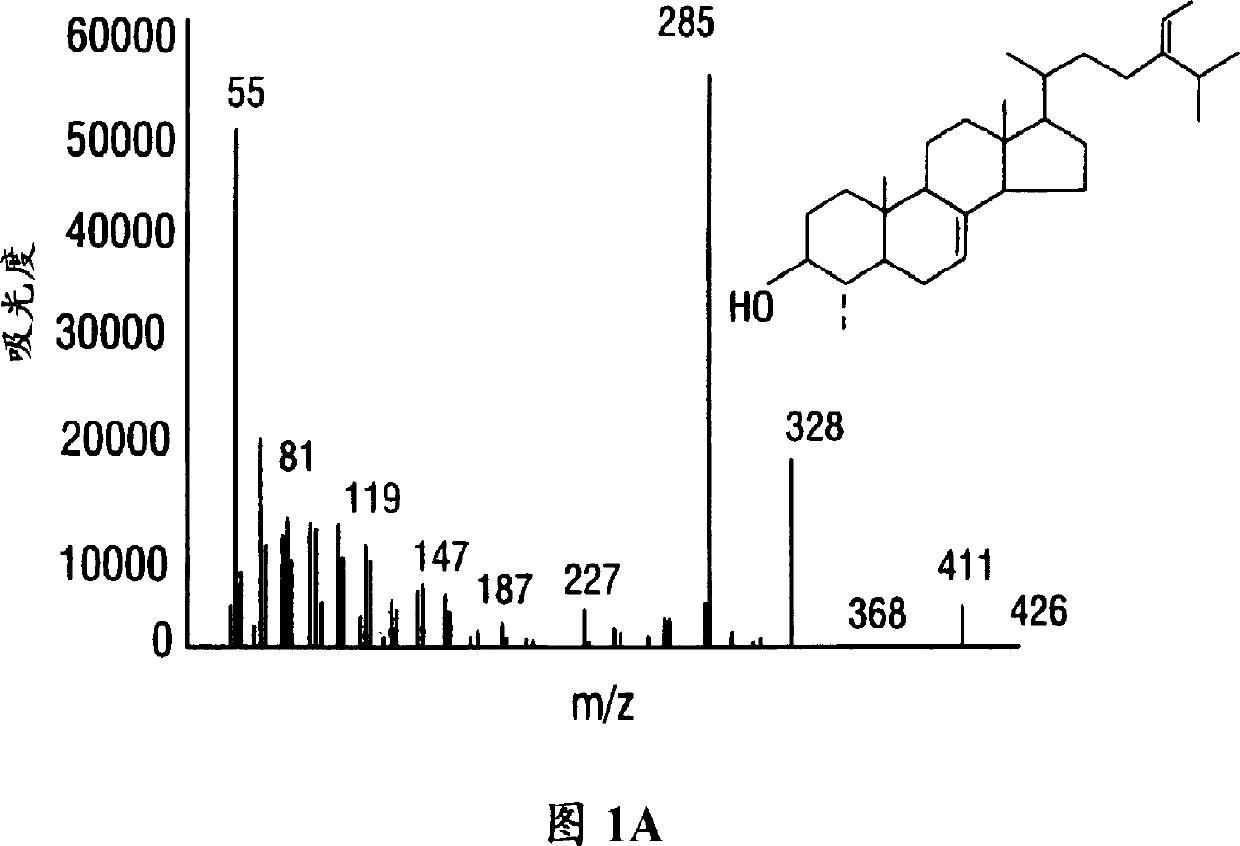
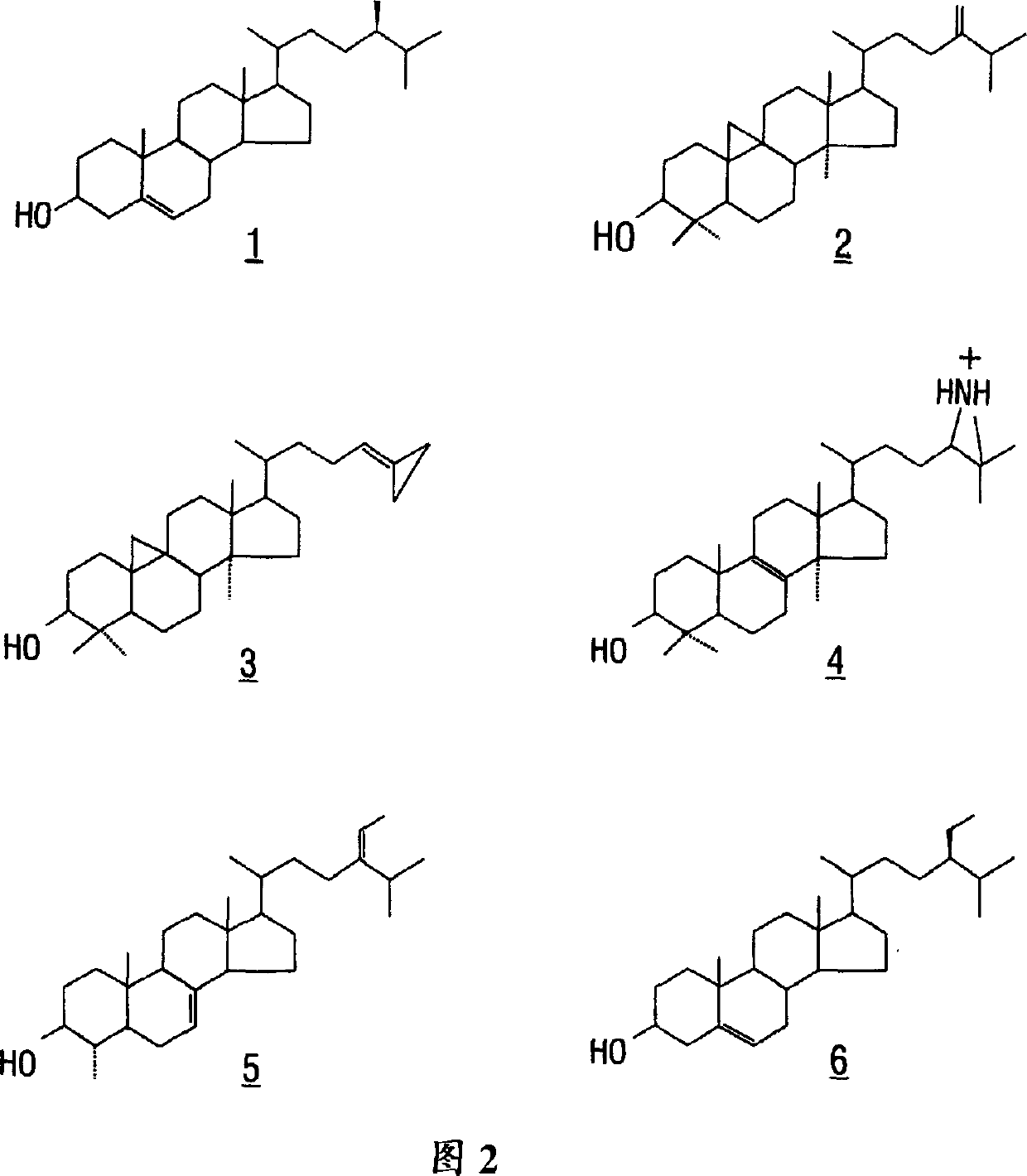
[0095] Sterol isomers were extracted from cotton and separated into homogeneous forms by chromatography. Identification of novel phytosterols with side chains not available to insects.
[0096] by mass spectrometry and 1 H and 13 C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments, found that sterols have structural specificity (Table 1) (Guo et al., 1995).
[0097] Initial studies showed that 4-day-old maize produced mono- or di-alkylated sterols at C-24. Maize can produce those sterols because the isolated 24(28)-methylene and 24(28)-ethylene sterols were obtained from maize seedling tissue and their structures were determined by mass and proton NMR Resonance spectroscopy was identified.
[0098] Table 1
[0099] Sterol Components of Corn
[0100] MS a TLC a Sterol bd plant source c
[0101] ...
Embodiment 2
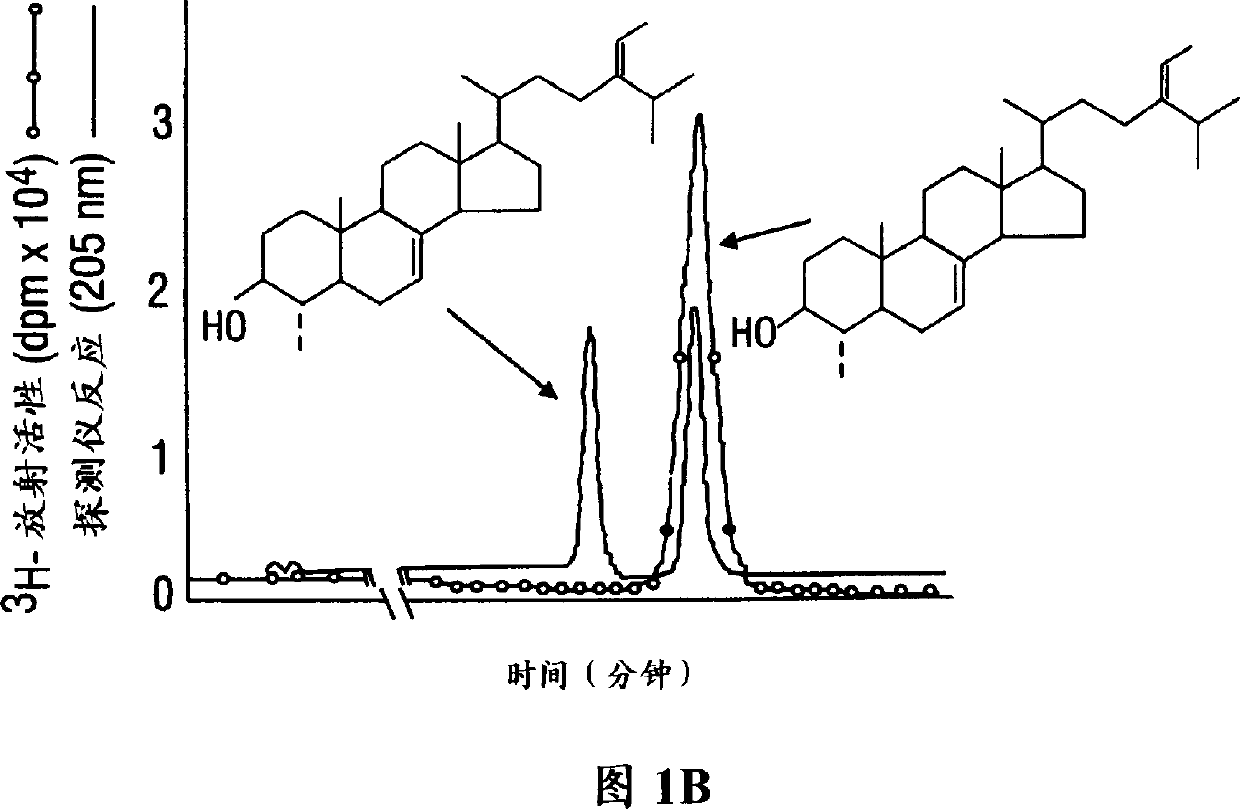
[0121] Figure 4 summarizes the kinetically favorable end-products Δ produced during seedling development into leaves and sheaths under dark-grown conditions. 5 -24-Alkylsterol pathway. Expression of SMT enzyme activity and data on sterol specificity early in the process of leaf and sheath production suggest that maize synthesizes at least two distinct SMT enzymes: SMT I Catalyzes the subsequent methyl conversion to generate Δ 24(28) -methylene sterol and Δ 24(28) - Ethylene sterol, while SMT II then catalyzes the conversion of the methyl group to Δ 23(24) -24-Methylsterol. Identification of sterols required for embodiment 2 plant growth
[0122] The phytosterols identified in Example 1 were individually tested for their ability to support growth. Due to the lack of phytosterol mutants available for this study, the yeast sterol auxotroph GL-7 was grown in the presence of the sterols identified in Example 1, see above (Li, 1996). This yeast mutant was used as a model syst...
Embodiment 3
[0123] Sterols can be classified according to their effects on growth processes. Growth-activating sterols include ergosterol. Sterols including cholesterol and sitosterol that are migrated to membrane and cellular structural components without affecting cell growth rate (Nes et al., 1993). The enzymatic research of embodiment 3 sterol converting enzyme
[0124] To illustrate the enzymatic basis for the sterols identified in Example 1, the sterol specificity of microsome-bound soluble SMTase from 4-day-old maize seedlings was determined. When using a microsome-bound enzyme system we found that cycloartenol was the preferred sterol acceptor and that 24(28)-methylene-4-methyl-7-encholestanol was methylated to generate 24 (28)-Ethylidene-4-methyl-7-encholestanol. Table 2 summarizes the specificity of soluble SMTases from maize seedlings for various sterol substrates.
[0125] Table 2
[0126] Sterol specificity of (S)-adenosyl-L-methionine: D 24 -Ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com