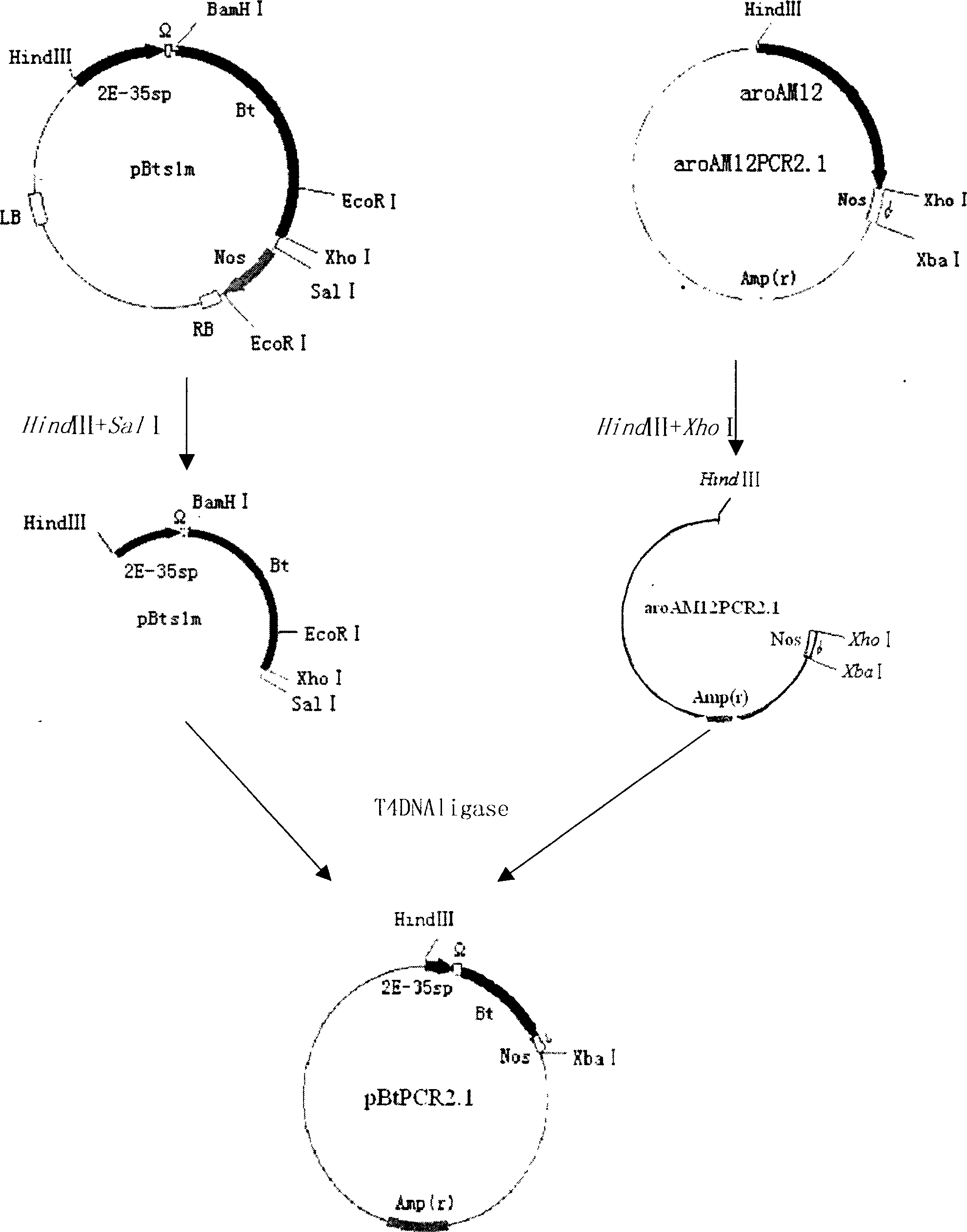
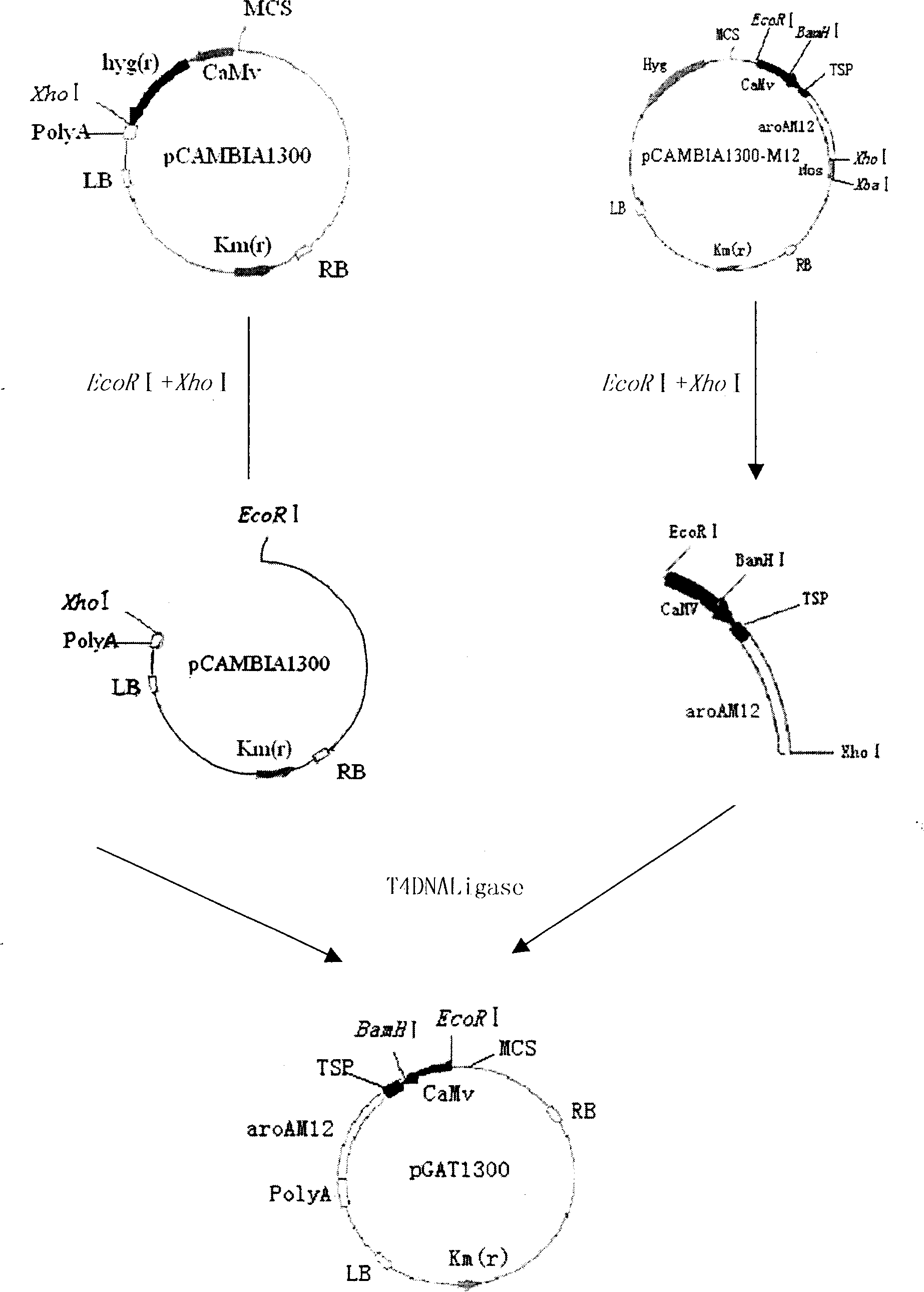
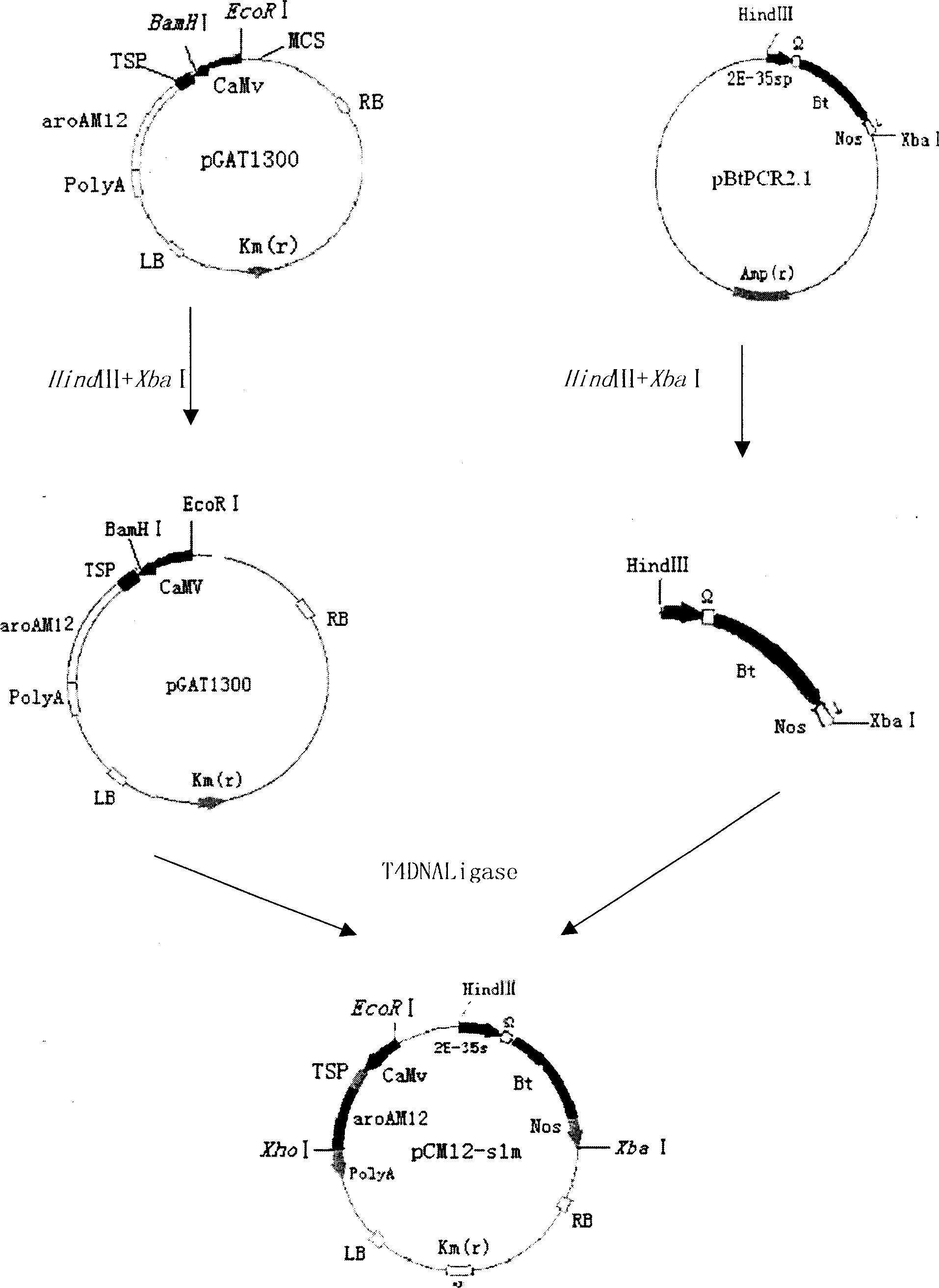
Method for screening transgenic plant and its used bivalent plant expression vector
A technology of transgenic plants and expression vectors, which is applied in the field of bivalent plant expression vectors, can solve the problems of single-action safety of screening markers, and achieve the effect of convenient screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0037] The ligation reaction was performed overnight at 16°C. Embodiment 2. Obtaining of Escherichia coli transformants
[0038] Preparation of E.coli XL-1-blue competent cells: ①Put a single colony of XL1-blue into 5mL LB liquid medium (see Table 2.1) without antibiotics, shake overnight at 37°C; ②Press 1% The amount of (v / v) was transferred to fresh LB liquid medium and shaken to OD at 37°C 600 =0.3; ③Add 50-100mL LB liquid culture medium (see Table 2.1 for LB preparation) into two sterile centrifuge tubes, place on ice for 30 minutes; ④Centrifuge at 4°C, 4000rpm (rev / min) for 10 minutes , remove the supernatant, and add 10 mL of pre-cooled 0.1% CaCl to each centrifuge tube 2 Resuspend the cells in the solution, and ice-bath for 30 minutes. ⑤ Centrifuge at 4°C and 4000rpm for 10 minutes, remove the supernatant, and suspend the bacteria in 2 mL of pre-cooled 0.1% CaCl 2 Add 300 μL of sterile glycerol to the solution, mix well, add 100 μL of XLl-blue competent cells t...
Embodiment 3
[0046] After complete dissolution, adjust the pH to 7.2 with 5mol / L NaOH, then add deionized water to a total volume of 1L, and then autoclave. Example 3. Transformation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens
[0047] Preparation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens LBA4404 competent cells: ① Pick LBA4404 colonies from the YEB solid medium (see Table 3.1) plate containing streptomycin (str) and rifampicin (Rif), inoculate into 5ml containing the corresponding antibiotic In the YEB liquid medium (according to Table 3.1, without adding agar), shake overnight at 200 rpm at 28°C. ② Dilute to 50ml with YEB liquid medium, then culture at 28°C and 200rpm for 6-12 hours until OD 600 The value is around 0.6. ③ Place on ice for 5 minutes, then centrifuge at 4°C, 2000rpm for 7 minutes. ④Take 1ml of ice-cold CaCl with a concentration of 20mmol / L 2 Resuspend the precipitate in the solution and mix well. ⑤ Divide into 10 portions, 100 μl each, and store in a -70°C refrigerator for later use.
[004...
Embodiment 4
[0055] The engineering bacterium that embodiment 3 obtains is infected tobacco explant (blade, cut into 0.5 * 0.5cm size) 5 minutes, blot dry with the filter paper through autoclaving, move into MS+6-BA (6-benzoladenine, 6 -benzylpurine) 1 mg / L+NAA (naphthalene acetic acid, naphthalene acetic acid) 0.1 mg / L+3% sucrose+0.7% agar in the dark for 48 hours. Rinse 3 times with sterile water, blot dry with sterile filter paper, and then transfer to MS+6-BA (1mg / L)+NAA (0.1mg / L) differentiation medium containing cephalosporin (400mg / L), Culture at 28±2°C under diffuse light conditions to induce differentiation. Culture for 1 week, and then transfer to the differentiation medium containing the selective agent glyphosate [MS+6-BA (1 mg / L)+NAA (0.1 mg / L)+glyphosate (30 μmol / L)]. Continue to cultivate for a period of time (3 weeks), when the shoots grow to 2-3cm, cut off the resistant shoots and move them into the MS+NAA (0.1mg / L) rooting medium that does not contain glyphosate to induc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-denatured | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com