Catalyst surface-characteristic comprehensive measuring device and application thereof
A technology of surface properties and catalysts, applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficulties, time-consuming, and large errors, and achieve the effect of simple structure, convenient operation, and small errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
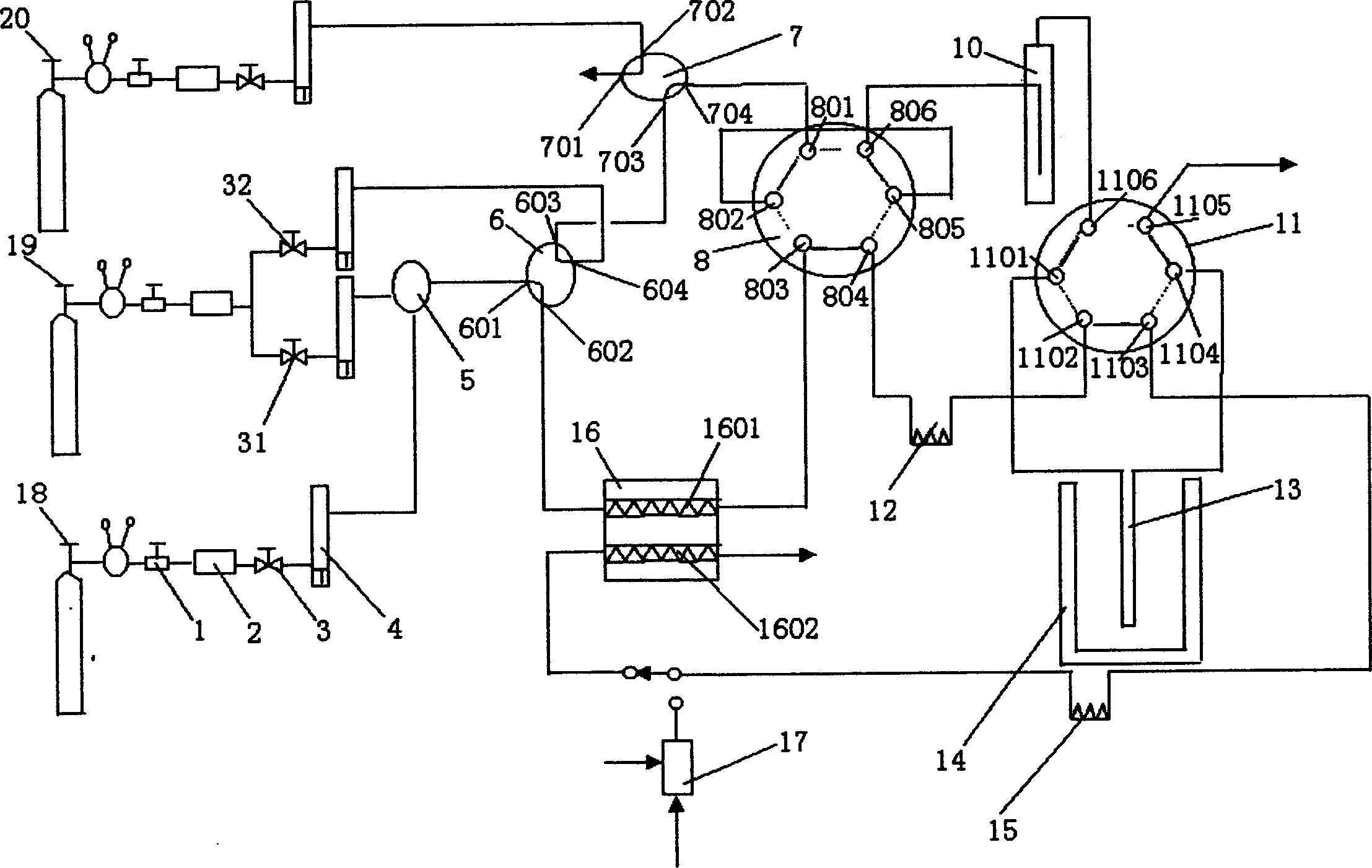
[0189] use as figure 1 The apparatus shown, performs TPR tests on Cu-containing hydrotalcite-like catalysts.
[0190] 1). Take 0.2g of Cu-containing hydrotalcite that has been calcined, and use reducing gas H 2 account for H 2 -5% of He gas mixture (total flow rate of gas mixture: 50ml / min);
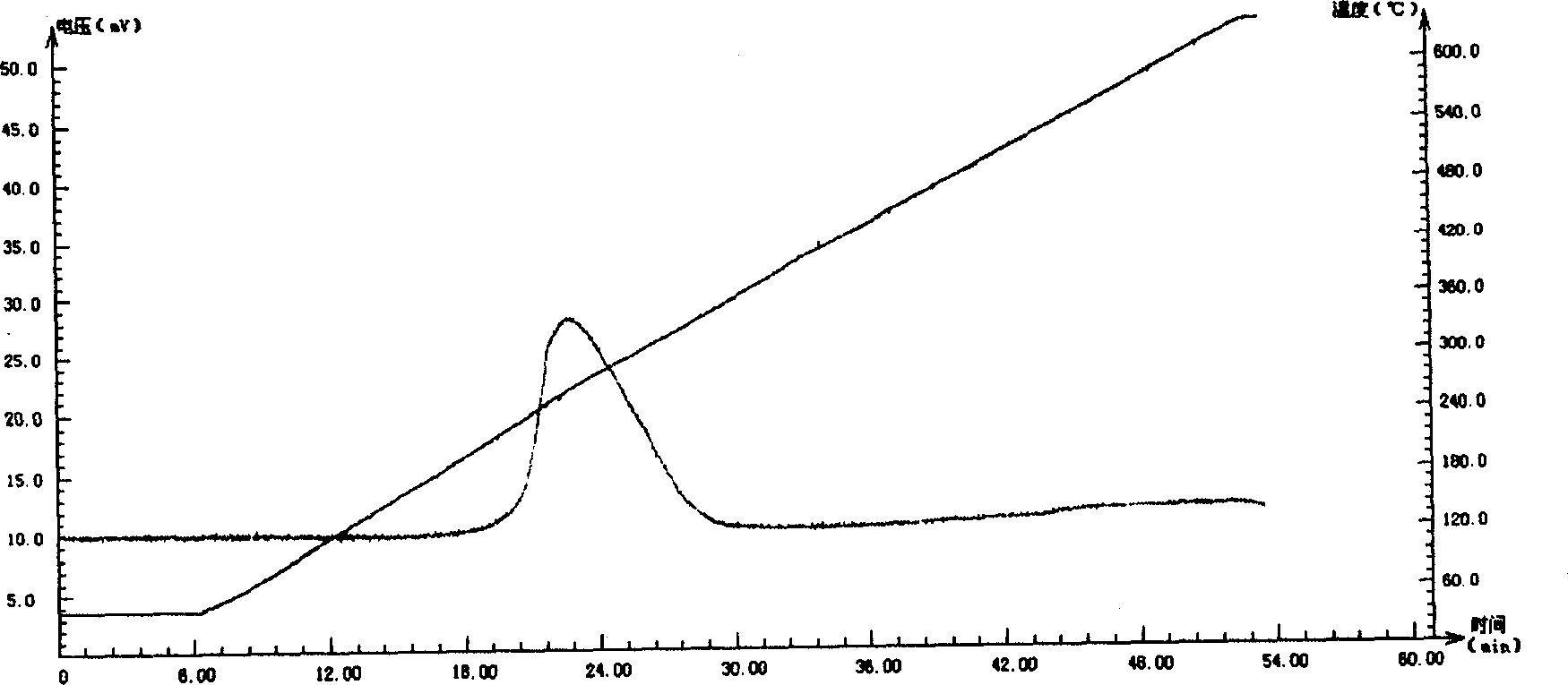
[0191] 2). After the baseline becomes stable, perform temperature-programmed reduction at a heating rate of 10°C / min. Its TPR spectrum is figure 2 .
[0192] As a comparison, the TPR test of CuO was done.
[0193] 1). Take 0.04g of dry CuO, reducing gas H 2 account for H 2 -5% of He gas mixture (total flow rate of gas mixture: 50ml / min);
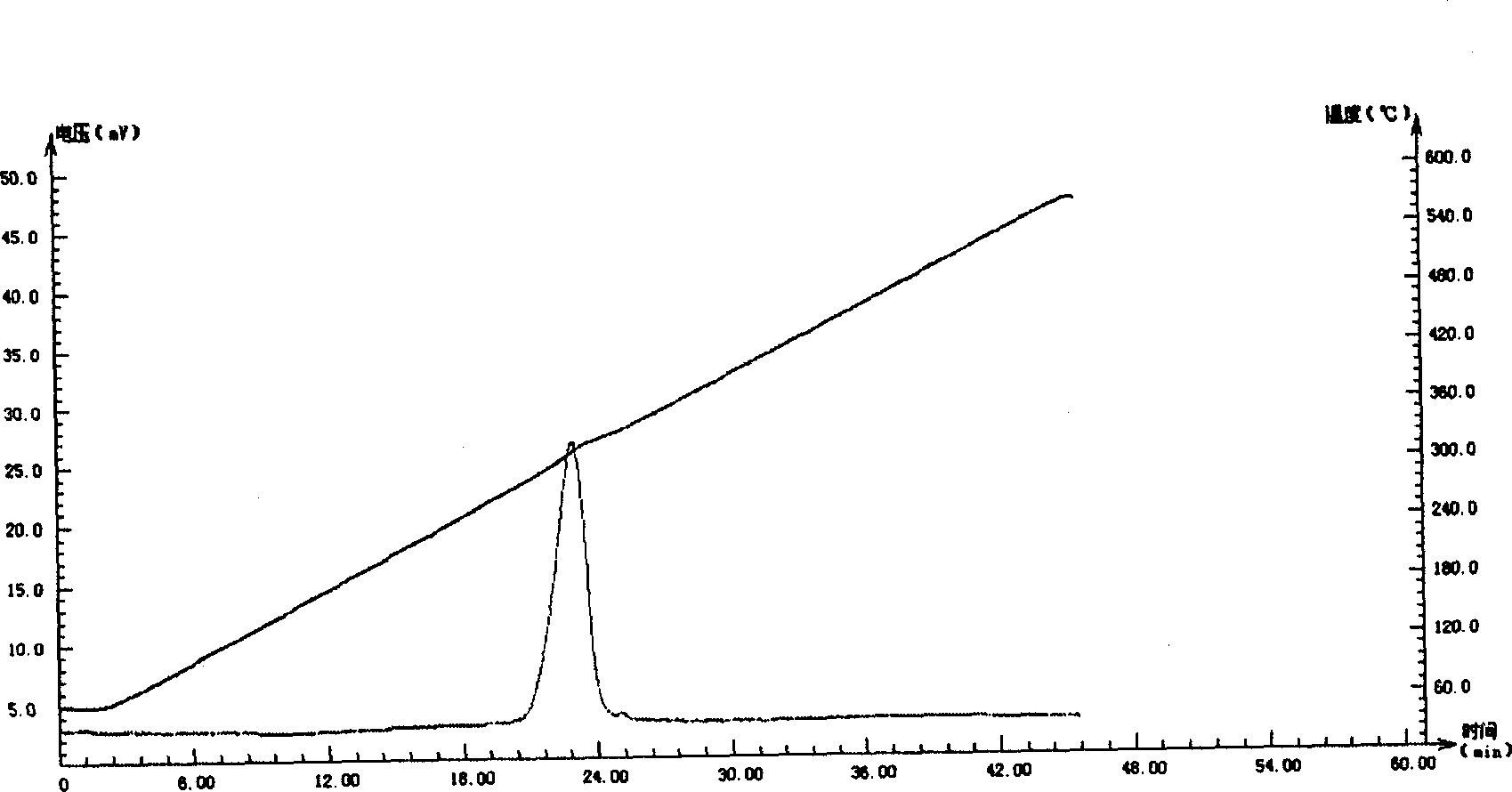
[0194] 2). After the baseline becomes stable, perform temperature-programmed reduction at a heating rate of 10°C / min. Its TPR spectrum is image 3 .
[0195] It can be seen from the figure that the TPR spectra of the Cu-containing hydrotalcite-like catalyst and CuO both have only one spectrum peak. The highest peak temperature of the former...
Embodiment 2
[0197] use as figure 1 The instrument shown, performs TPD testing on iron oxide catalysts.
[0198] 1) Iron trioxide catalyst 0.8g, reducing gas H 2 account for H 2 -5% of He mixed gas (total flow rate of mixed gas: 50ml / min); reduce at 450°C for 2h; then, close He, 2 (30ml / min), cool to room temperature (27°C).
[0199] 2) Close H 2 , turn on He (30ml / min) to purge to remove reversibly adsorbed H 2 , after the baseline becomes stable, conduct H at a rate of 25°C / min 2 desorption.
[0200] The direction of the peak can be adjusted by selecting the "positive\negative" switch of the detector. See TPD Spectrum Figure 4 .
[0201] Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the catalyst has only one broadened desorption peak, indicating that the energy distribution on the catalyst surface is relatively uniform; the highest peak temperature is 296 ° C, indicating that the H absorption 2 The active center is medium strength.
Embodiment 3
[0203] use as figure 1 The instrument shown, performs TPD tests on molybdenum-containing molecular sieve catalysts.
[0204] 1) Take 0.2 g of the catalyst that has been calcined at a high temperature, put it into the sample tube, purify it with He at 400 ° C for 1 h, and then cool it to 120 ° C. After the temperature is constant, use He to pass the NH 3 Vapor is introduced into the sample tube for adsorption.
[0205] 2) He (40ml / min) as carrier gas, purge to remove reversibly adsorbed NH 3 , after the baseline stabilized, the temperature-programmed desorption was performed at a rate of 10°C / min. See TPD Spectrum Figure 5 .
[0206] The spectrum shows that there are at least three kinds of adsorption centers on the surface of the catalyst (the highest peak temperature: 242°C, 325°C, 472°C), and the energy distribution on the surface is uneven, and the weak acid centers are the main ones.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com