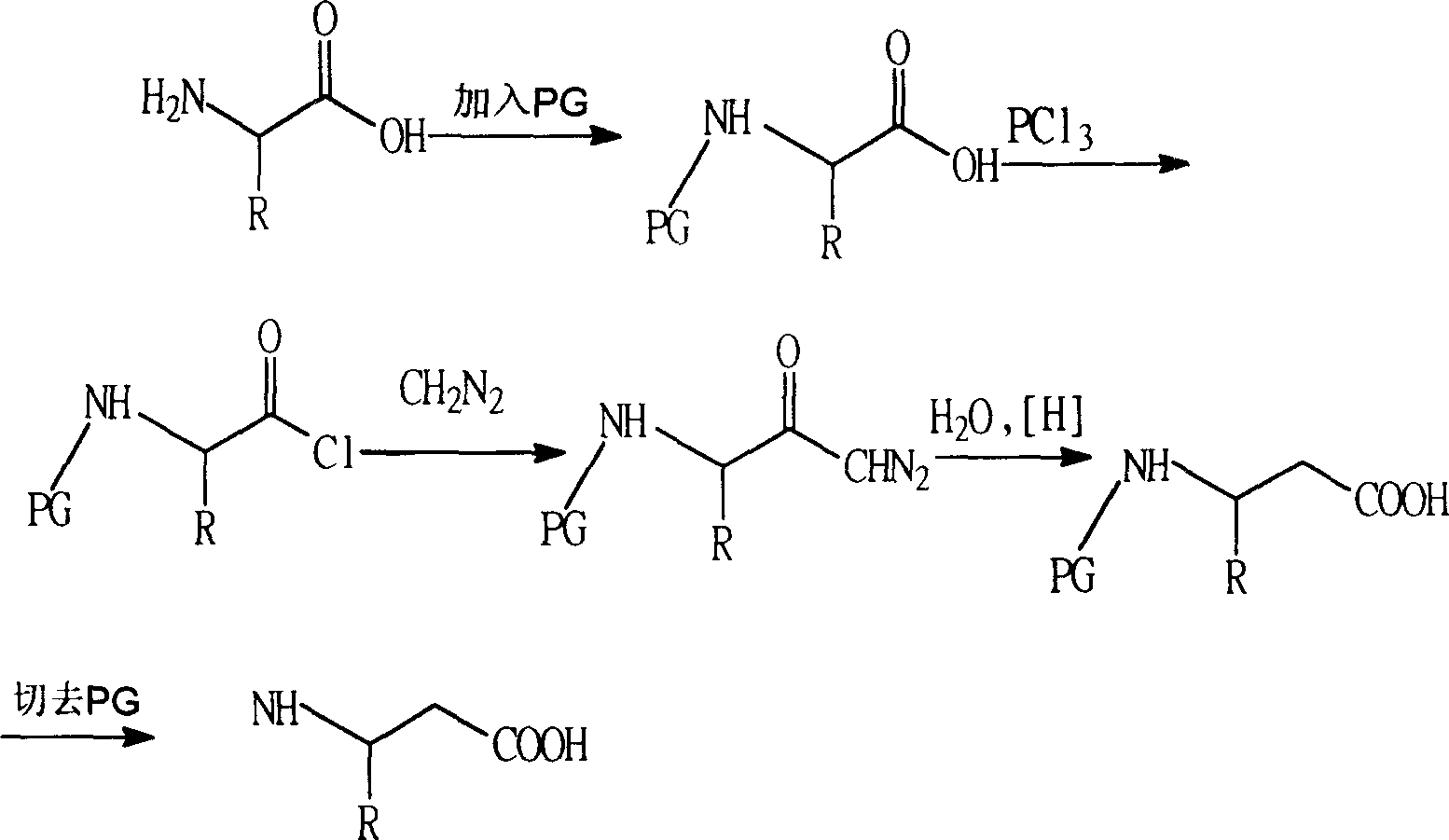
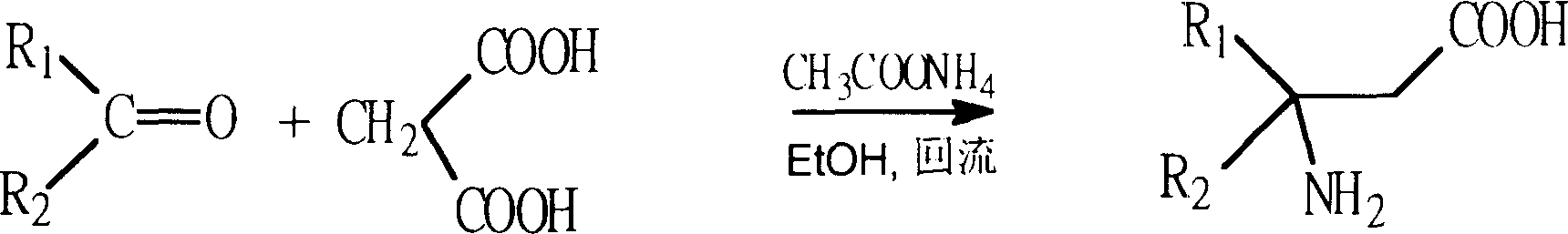Process for synthesizing beta-amino acid using ketone as raw material
A technology of amino acids and raw materials, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as difficult product separation and purification, high cost, unsafe operation, etc., achieve cheap raw materials, increase diversity, and synthesize Effects in simple steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Embodiment 1 (malonic acid method)
[0077] Preparation of β-substituted β-amino acids from cyclohexanone: 1-aminocyclohexyl-acetic acid
[0078] Put a large stirring magnet in a 500 ml round bottom bottle, add 49.0 g of malonic acid (molecular weight 104.06, 0.47 mol), 50.8 g of ammonium acetate (molecular weight 77.08, 0.66 mol) and 116 ml of hot ethanol, install and condense tube, heated to reflux with stirring on an oil bath at 100°C, and added 55 ml of cyclohexanone (specific gravity 0.947, 52.11 g; molecular weight 98.14, 0.53 mol). The reactant gradually dissolves and a large number of bubbles are released. The reaction liquid starts to be yellow, and the color gradually deepens as the reaction progresses, from yellow to deep yellow, yellowish brown, and finally brown. After 8 hours of reaction, the heating was stopped, and the reaction device was changed to a distillation device, and about half of the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and cooled to...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Embodiment 2 (ethyl cyanoacetate method)
[0081] Preparation of α-substituted β-amino acids from cyclohexanone: 2-cyclohexyl-3-amino-propionic acid
[0082] (1) Preparation of enester: 103 milliliters of cyclohexanone (specific gravity 0.947, 97.5 grams; molecular weight 98.14, 0.99 moles) and 100 milliliters of ethyl cyanoacetate (specific gravity 1.061, 106.1 grams; molecular weight 113.12, 0.94 moles) were added to the flask In the mixture, add 3 milliliters of diethylamine dropwise under stirring, and leave it for 48 hours (it must be left for a long enough time, and turbidity can be observed, which is the reason for the reaction to produce water). Then add 100 milliliters of water to the reaction system, separate the oil layer, then wash the oil layer in the separatory funnel with water, dry the oil layer, and obtain the oily thing that is 50 grams of enester (molecular weight 193.24, 0.26 mole), and the condensation yield is 27.7%.
[0083] (2) Catalytic hydrog...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3 (cyanoacetic acid method)
[0092] Preparation of α-substituted β-amino acids from cyclohexanone: 2-cyclohexyl-3-amino-propionic acid
[0093] (1) Preparation of enoic acid: 57 milliliters of cyclohexanone (specific gravity 0.947, 54 grams; molecular weight 98.14, 0.54 moles), 42.5 grams of cyanoacetic acid (molecular weight 85.16, 0.50 moles), 2 grams of ammonium acetate and 100 milliliters of benzene were added Then add 100 ml of benzene to the reaction system, transfer it to a separatory funnel, add 200 ml of ether, and wash with water twice (except ammonium acetate); the oil layer is distilled Ethyl ether and benzene were removed, and the residue was solidified and washed with benzene or petroleum ether to obtain a white solid, enoic acid, weighing 35 grams (molecular weight: 165.19, 0.21 mol), with a yield of 42%.
[0094] (2) Catalytic hydrogenation reaction
[0095] (a) Double bond reduction
[0096] At room temperature, in a reactor, the 35 gram ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com