Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer free radical polymerization method
A technology of addition-fragmentation and chain transfer, applied in the field of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer radical polymerization, which can solve the problems of rate retardation, decrease in polymerization reaction rate, long reaction time, etc., and achieve high polymerization rate and small molecular weight distribution index , the effect of convenient control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
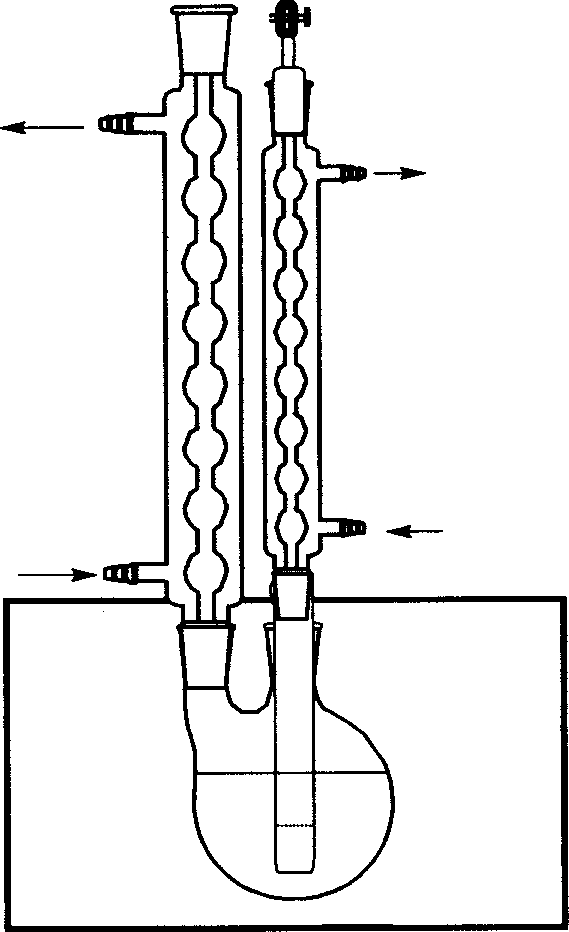
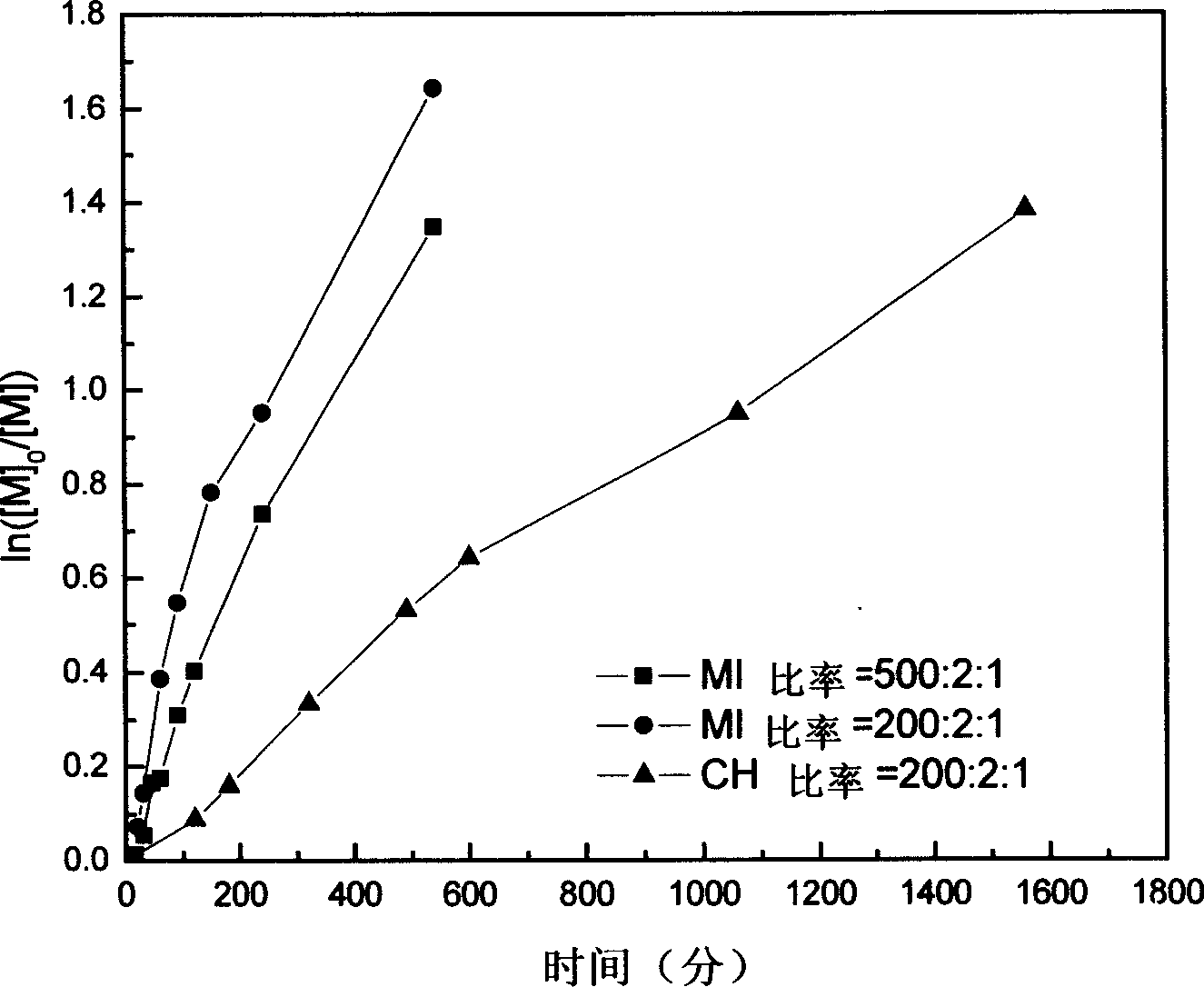
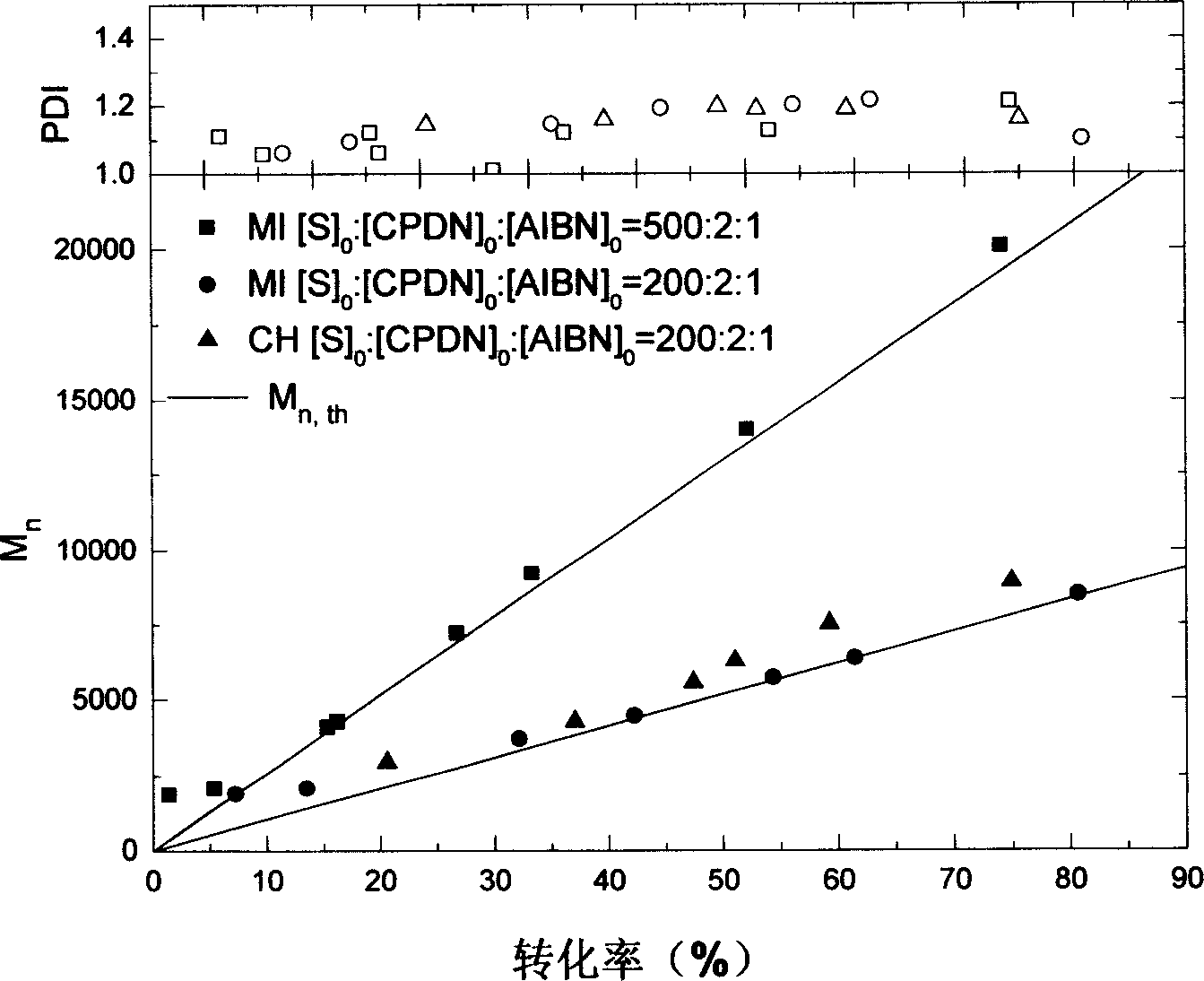
[0028] Embodiment one: see attached figure 1 to attach image 3 As shown, the polymerization of styrene was carried out by microwave radiation treatment with reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer radical polymerization.
[0029] A. Use CPDN as RAFT reagent and AIBN as initiator.
[0030] Monomer styrene (Styrene, St, Shanghai Reagent Company) was washed with alkali to colorless, then washed with deionized water until neutral, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and then used by distillation under reduced pressure. AIBN (Shanghai Reagent Company) was recrystallized twice with ethanol and then dried under vacuum at room temperature for use. Chain transfer agent (RAFT reagent) CPDN was synthesized according to literature method (Zhu J.; Zhu X.L.; Cheng Z.P.; Lu J.M., Liu F., Polymer, 2002, 43, 7037-7042). The rest of the reagents were all products from Shanghai Reagent Factory, and were used after being processed by the usual method.
[0031] The styrene RAFT p...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Example 2: Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate under microwave irradiation.
[0082] A. Use CPDN as RAFT reagent and AIBN as initiator
[0083] Monomer methyl methacrylate (Shanghai Reagent Company) was purified by vacuum distillation after alkali washing, water washing and drying. Initiator AIBN is refined by ethanol recrystallization. RAFT reagent CPDN was synthesized according to literature.
[0084] Microwave radiation polymerization: prepare the polymerization reaction solution with methyl methacrylate, CPDN, and AIBN at a ratio of 500:2:1 and place it in the polymerization reaction tube, vacuum degassing-nitrogen flushing, repeat three times, and then seal the tube under nitrogen atmosphere . Add 300ml of n-hexane (the normal boiling point is 69°C, the actual measured value under the experimental conditions is 72°C) into a 500mL two-neck bottle, irradiate with 450W power until the solvent refluxes, pu...
Embodiment 3
[0135] Example 3: Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer radical polymerization of methyl acrylate under microwave irradiation.
[0136] Monomer methyl acrylate (Shanghai Reagent Company) was purified by vacuum distillation after alkali washing, water washing and drying. Initiator AIBN is refined by ethanol recrystallization. RAFT reagent CPDN was synthesized according to literature.
[0137] Microwave radiation polymerization: Methyl acrylate, CPDN, AIBN prepared a polymerization reaction solution in a ratio of 500:2:1, placed in a polymerization reaction tube, vacuum degassing-nitrogen flushing, repeated three times, and then sealed the tube under nitrogen atmosphere. Add 300ml of n-hexane (the normal boiling point is 69°C, the actual measured value under the experimental conditions is 72°C) into a 500mL two-neck bottle, irradiate with 450W power until the solvent refluxes, put it into the reaction tube, and set the time and power (450W), continuous irradiation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com