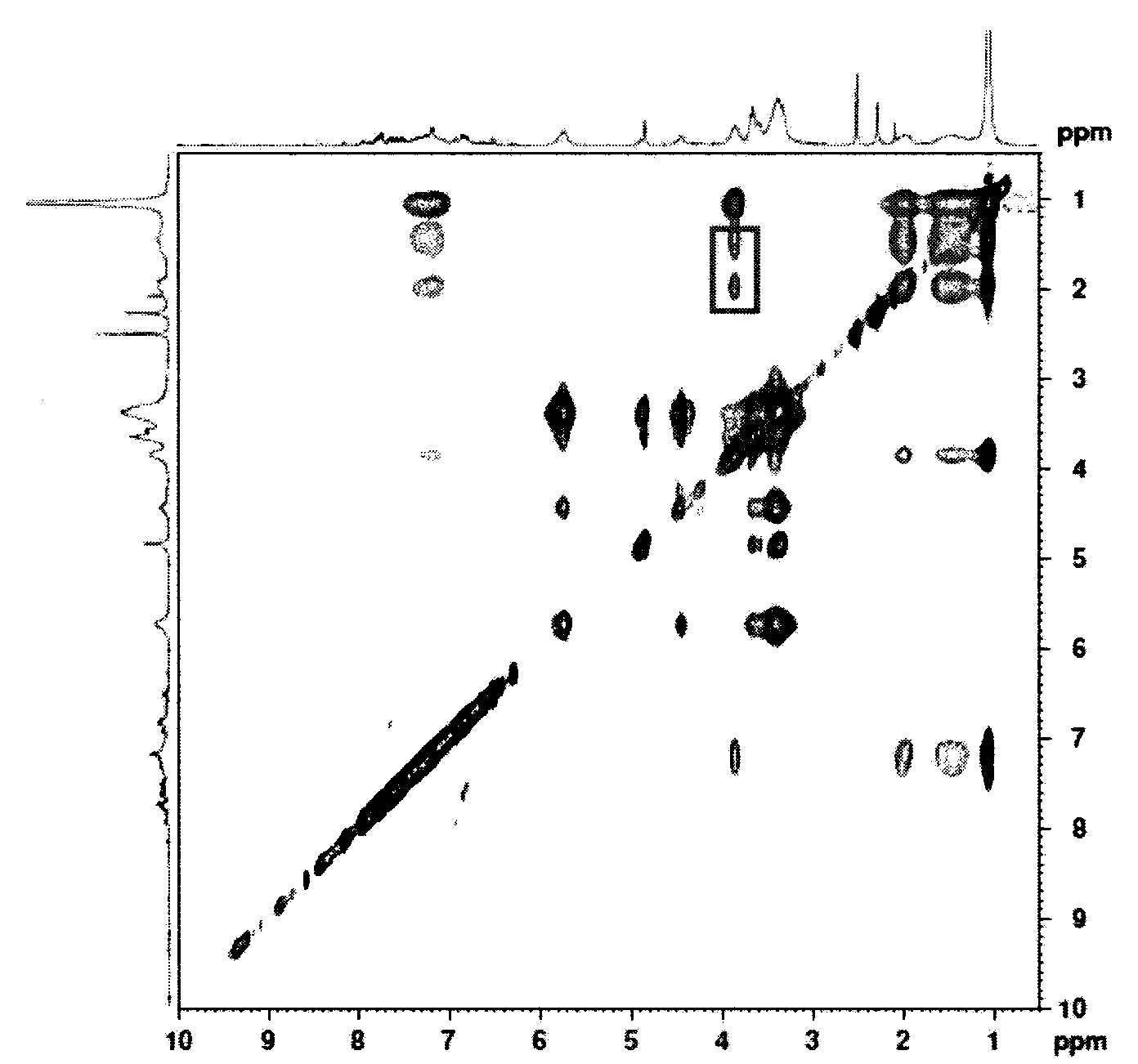
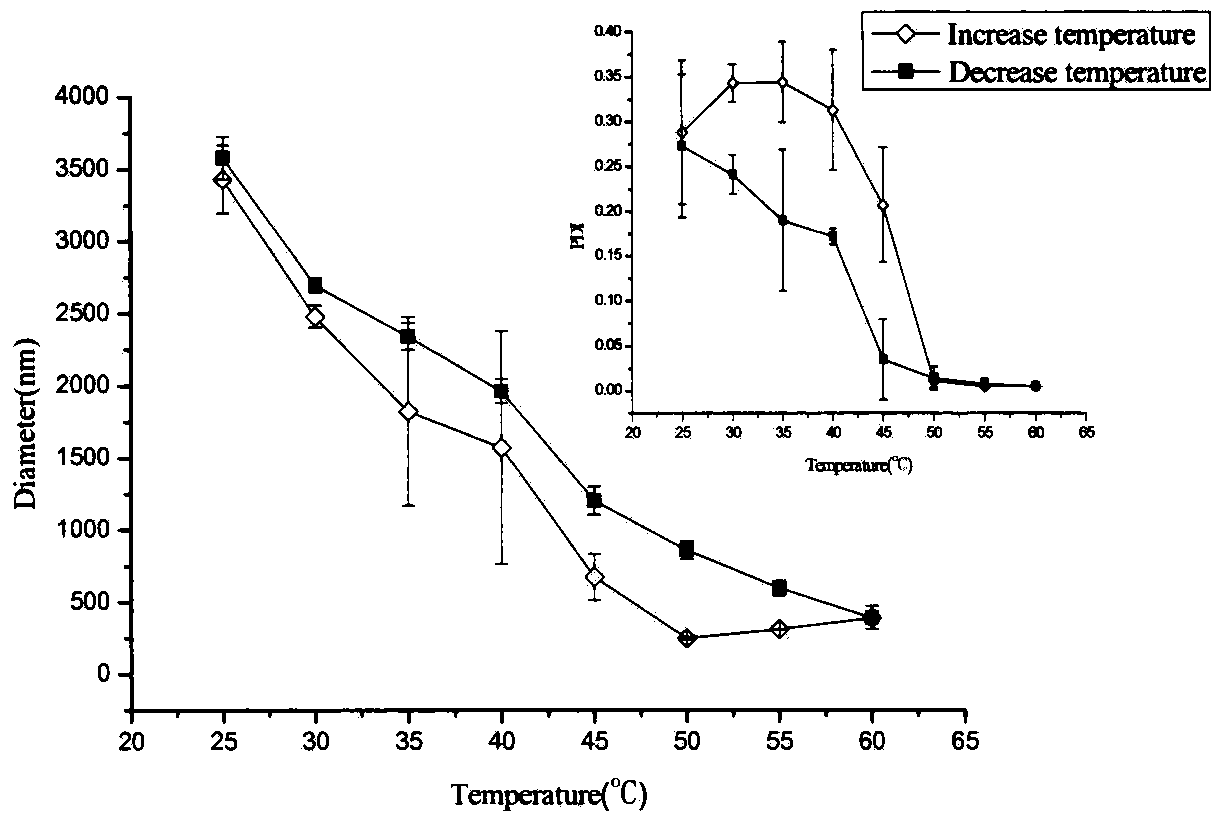
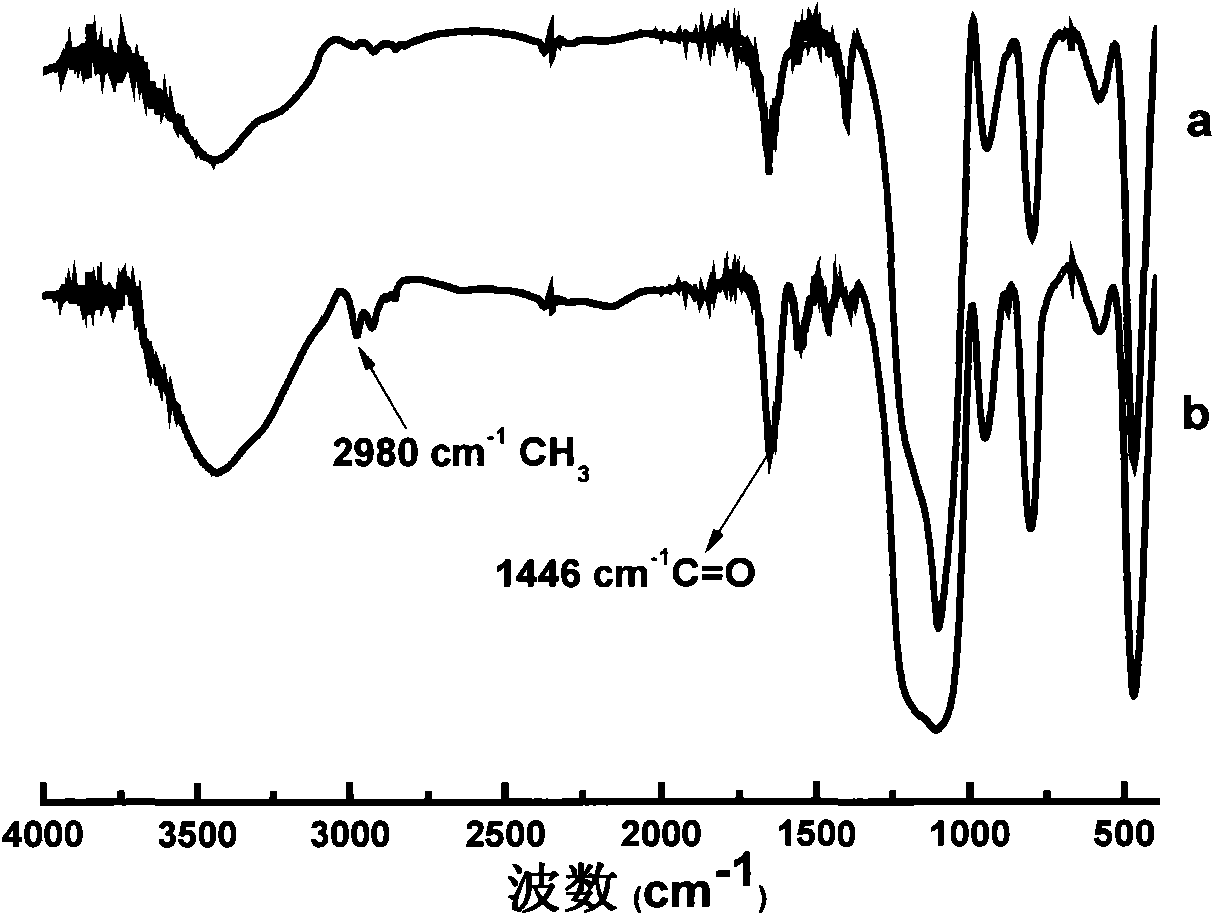
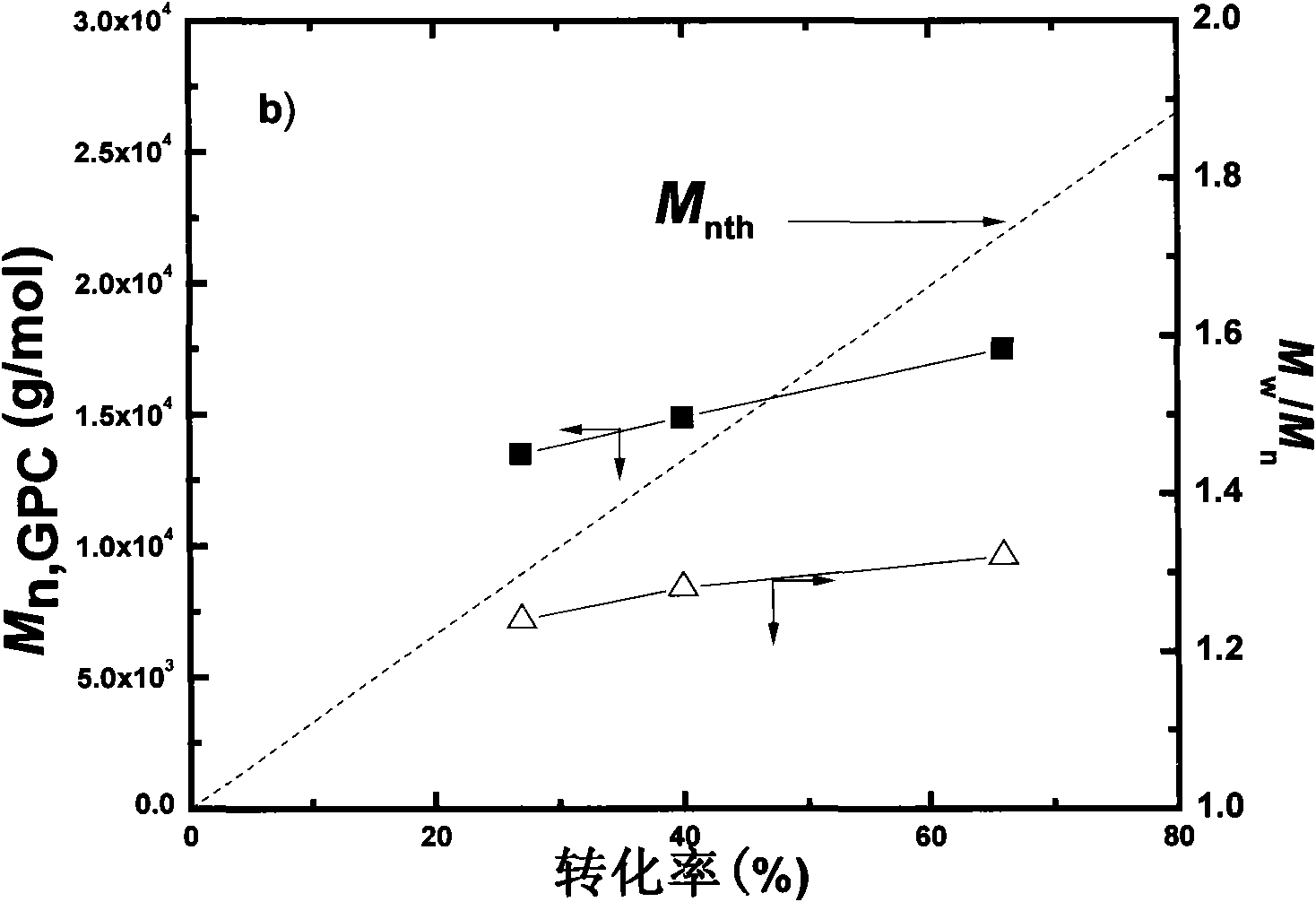
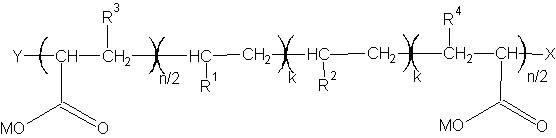
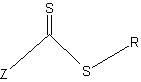
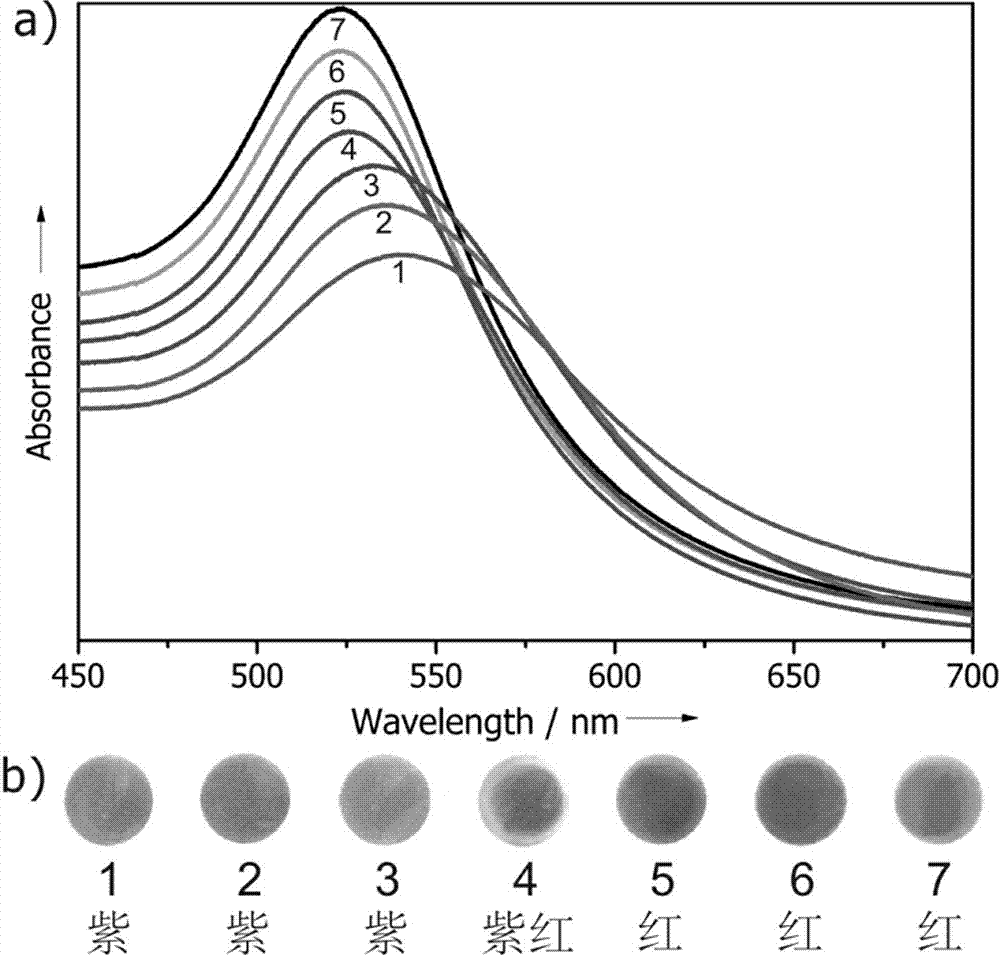
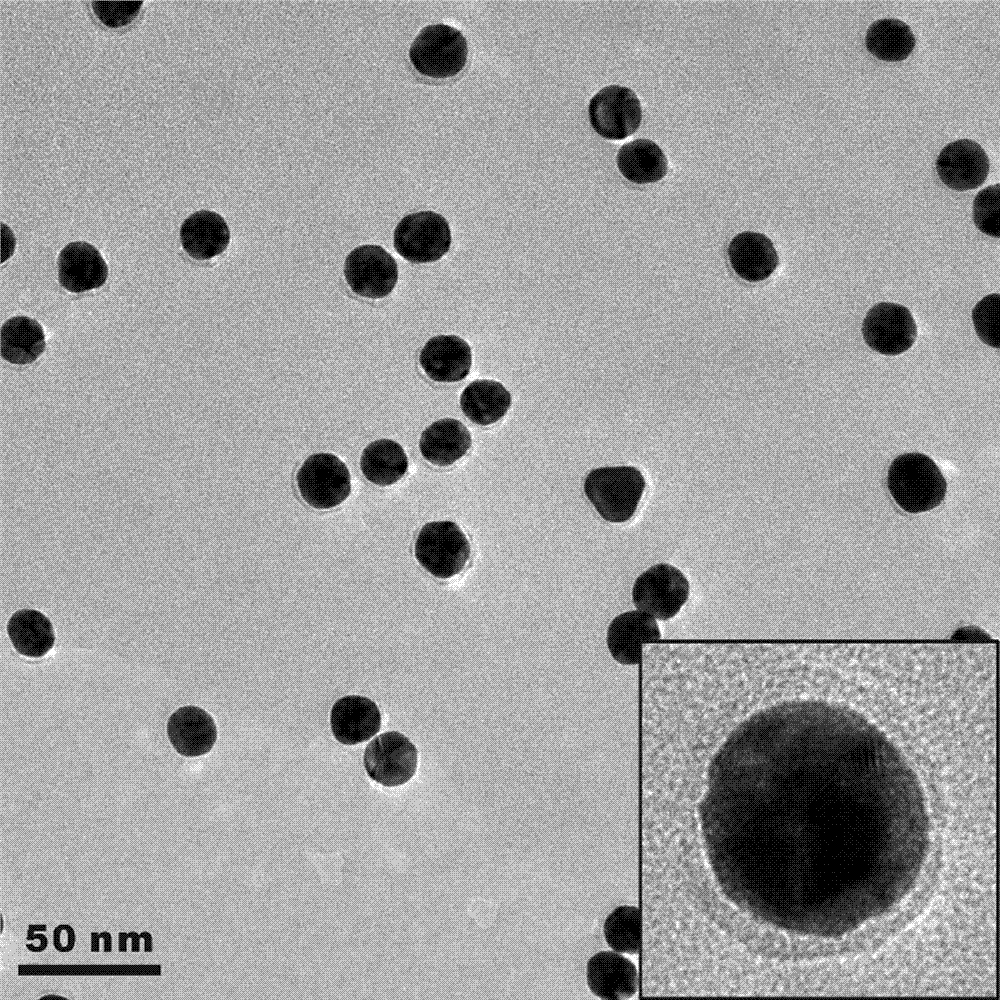
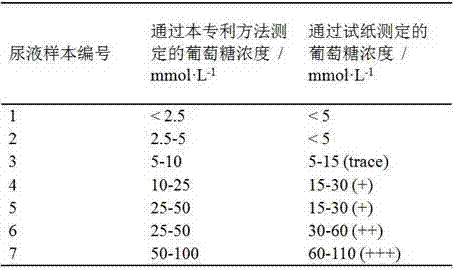
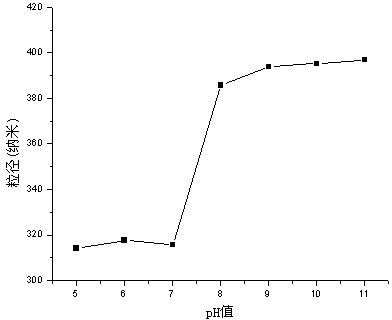
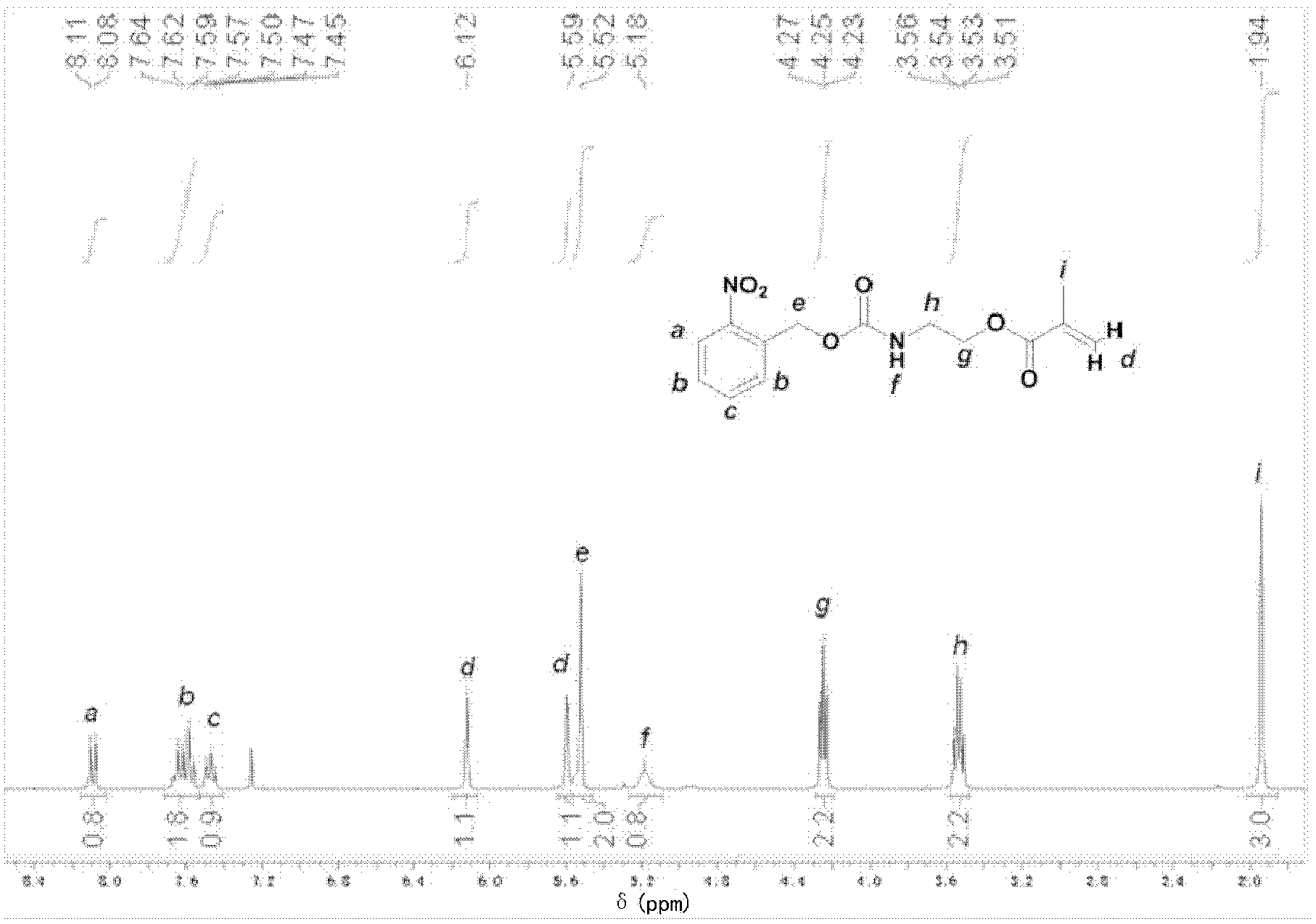
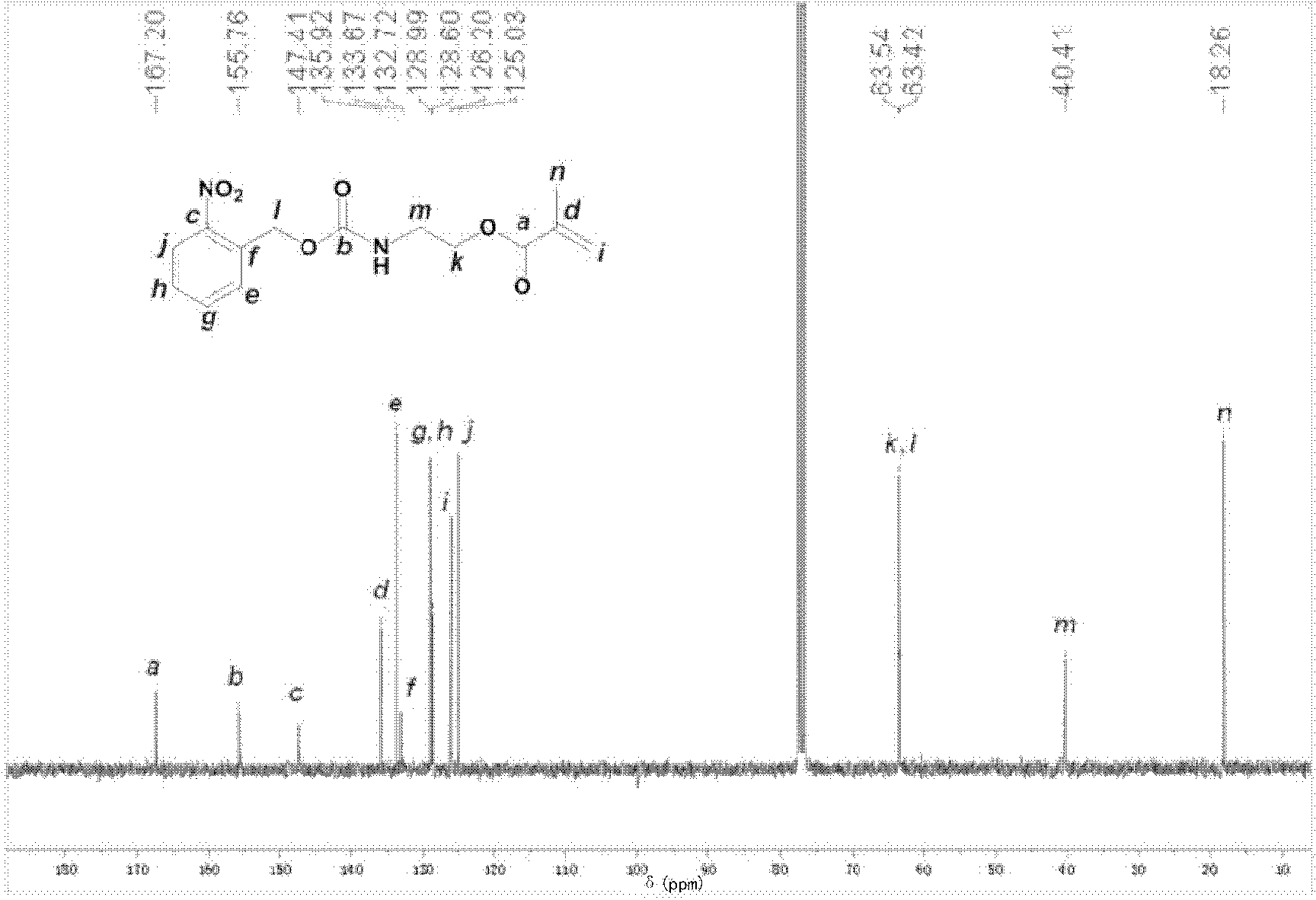
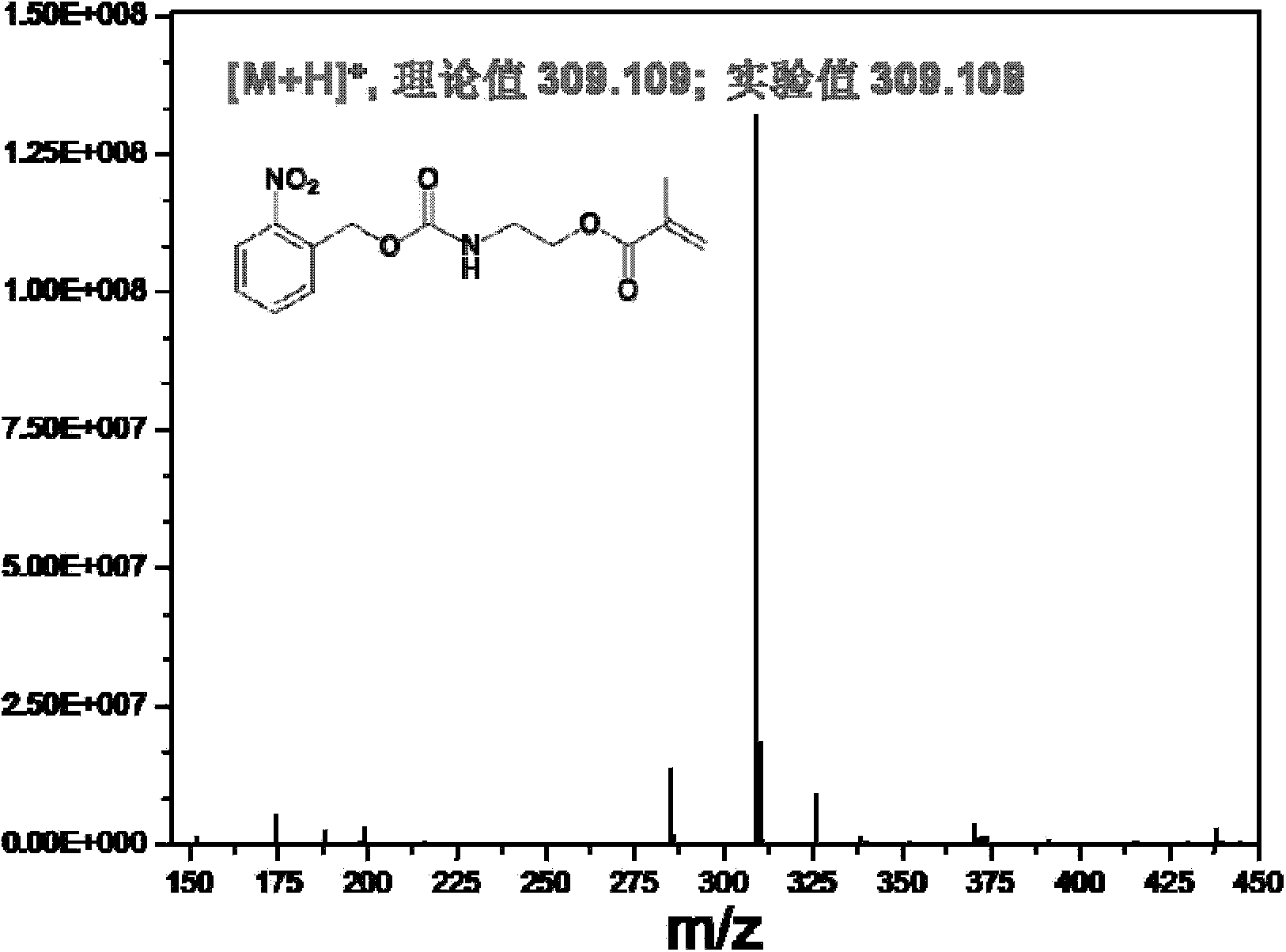
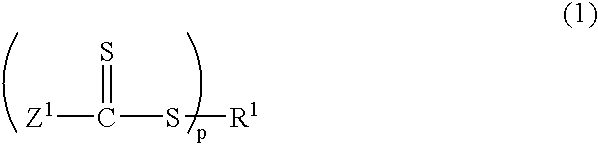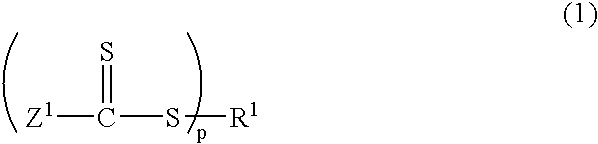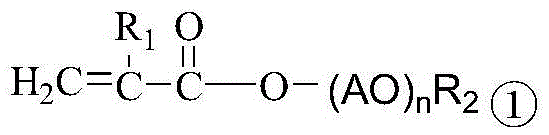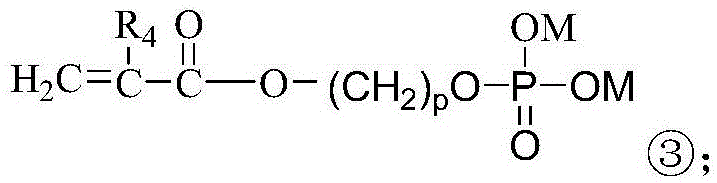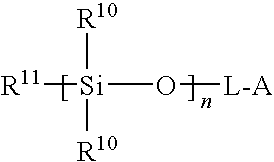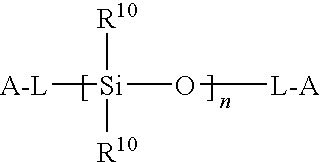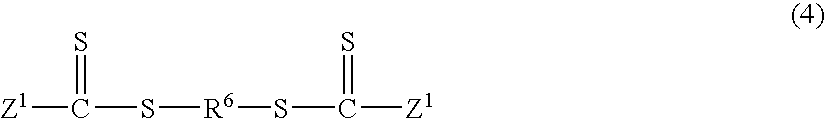Patents
Literature
433 results about "Reversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
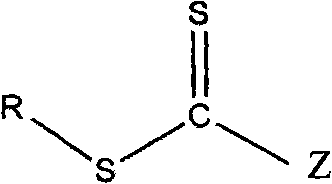
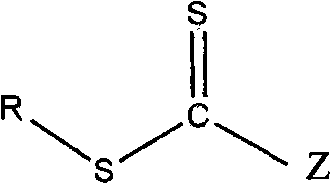
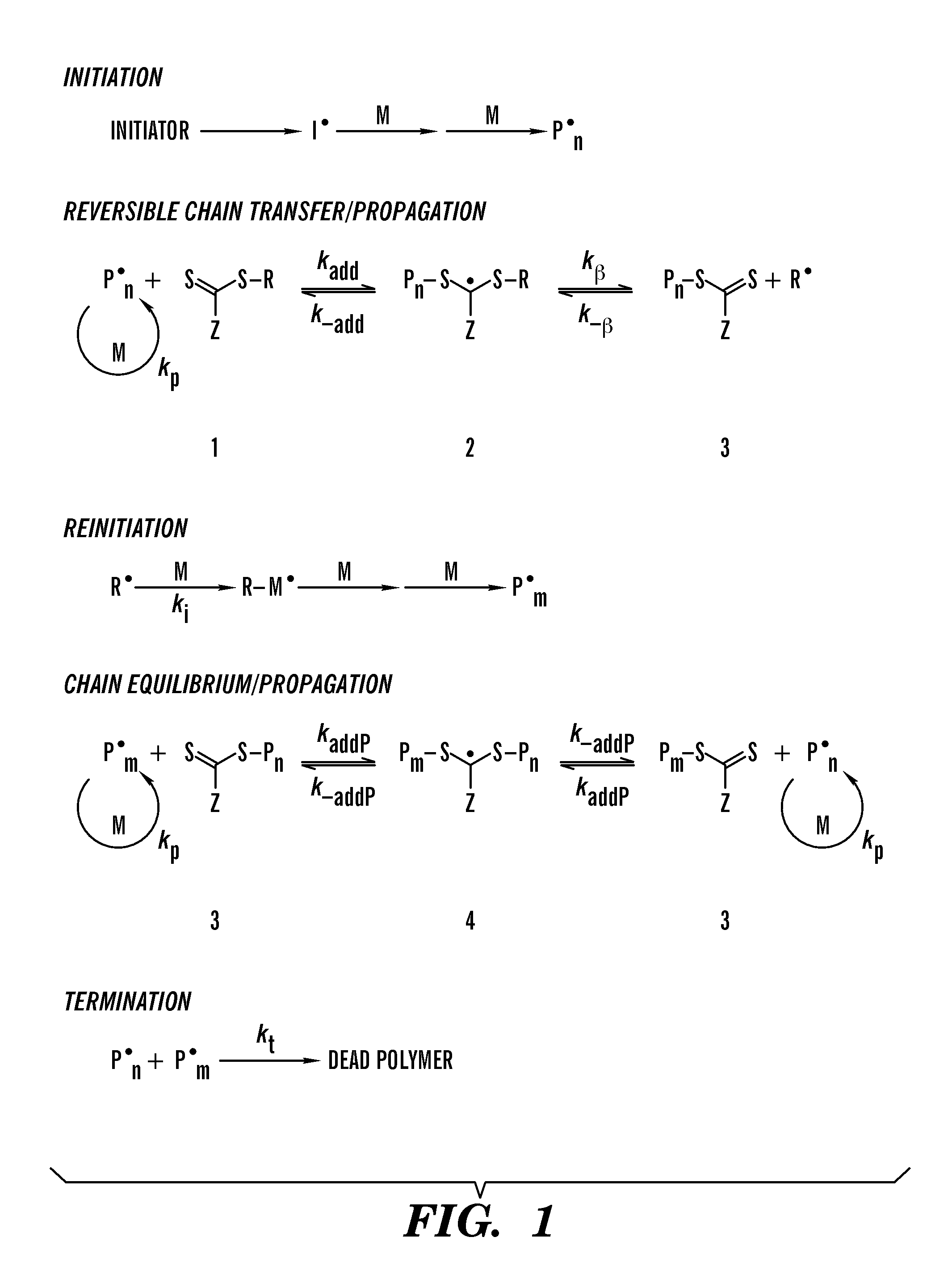
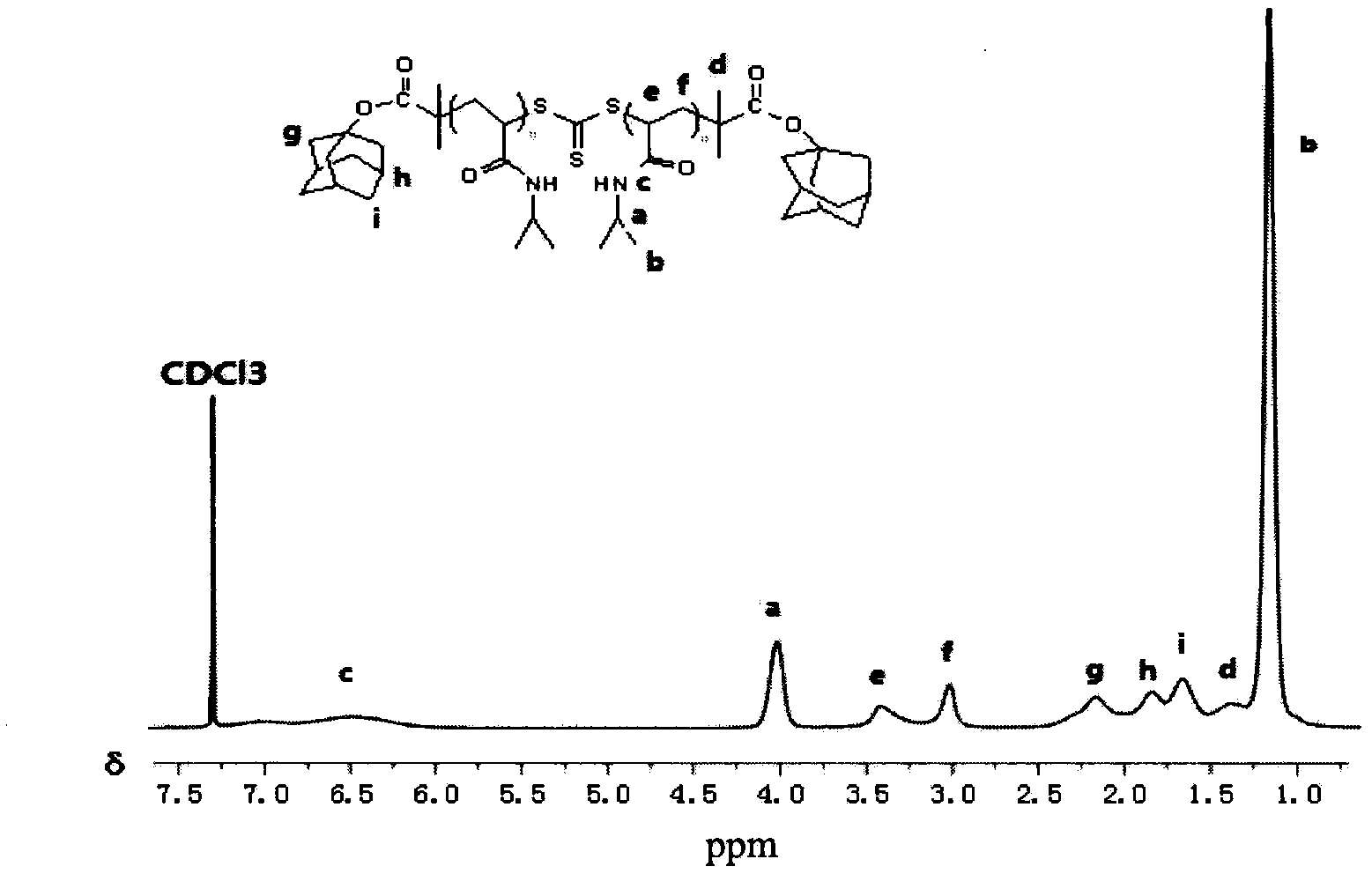
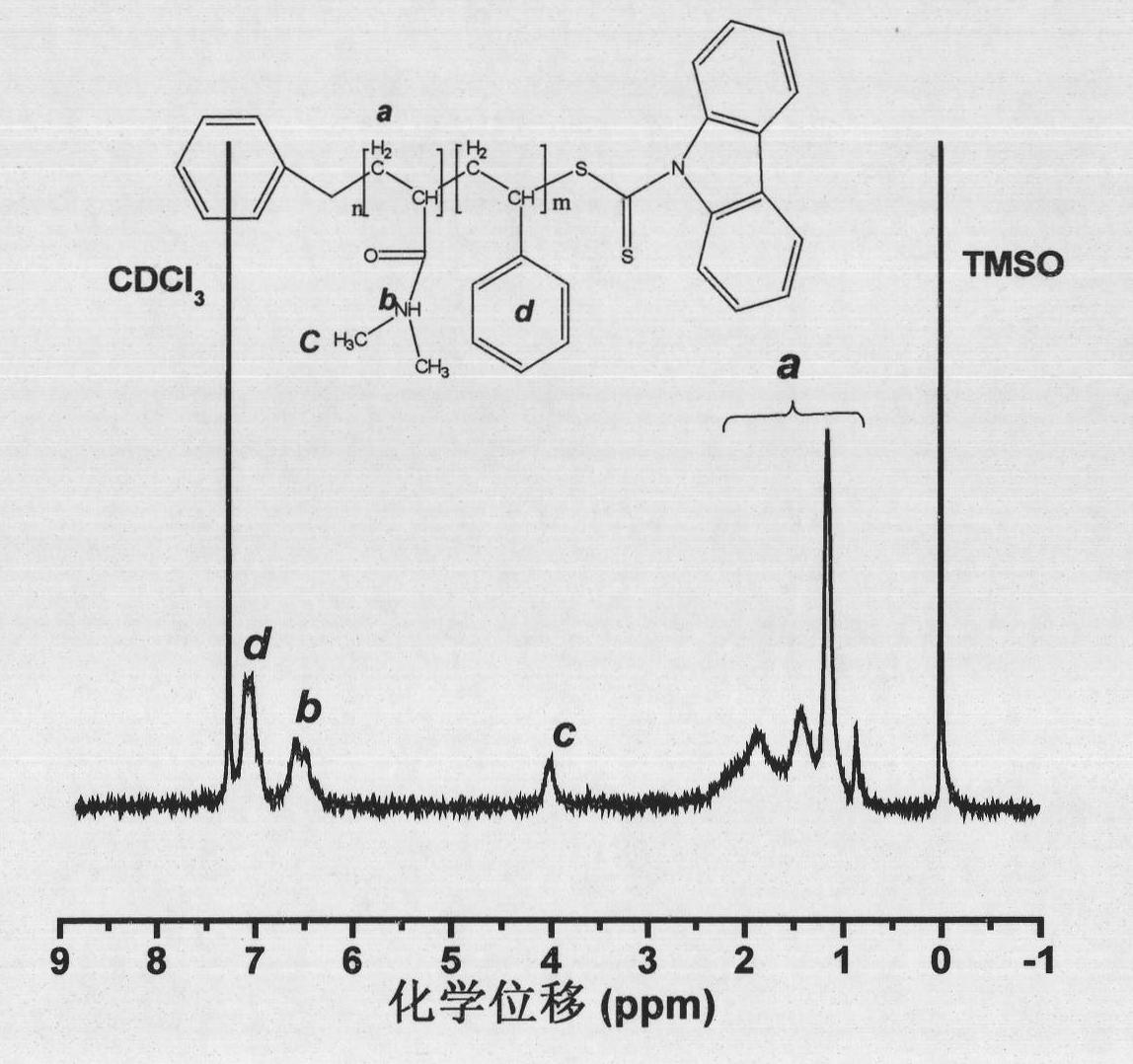
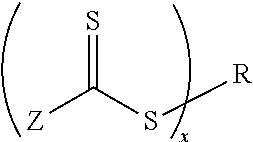
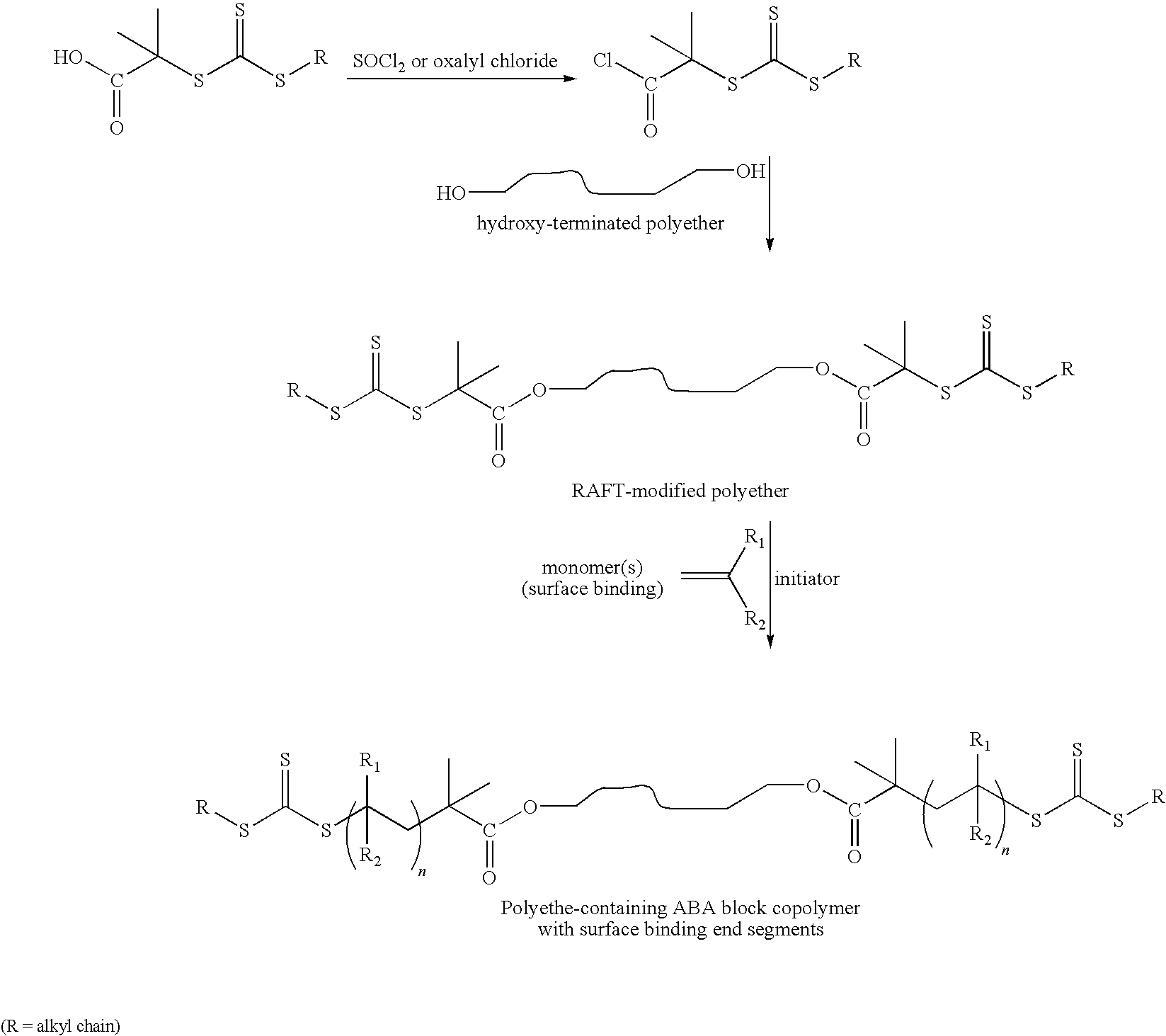
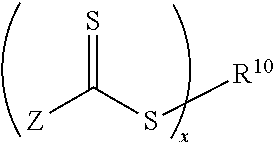
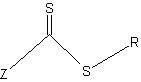
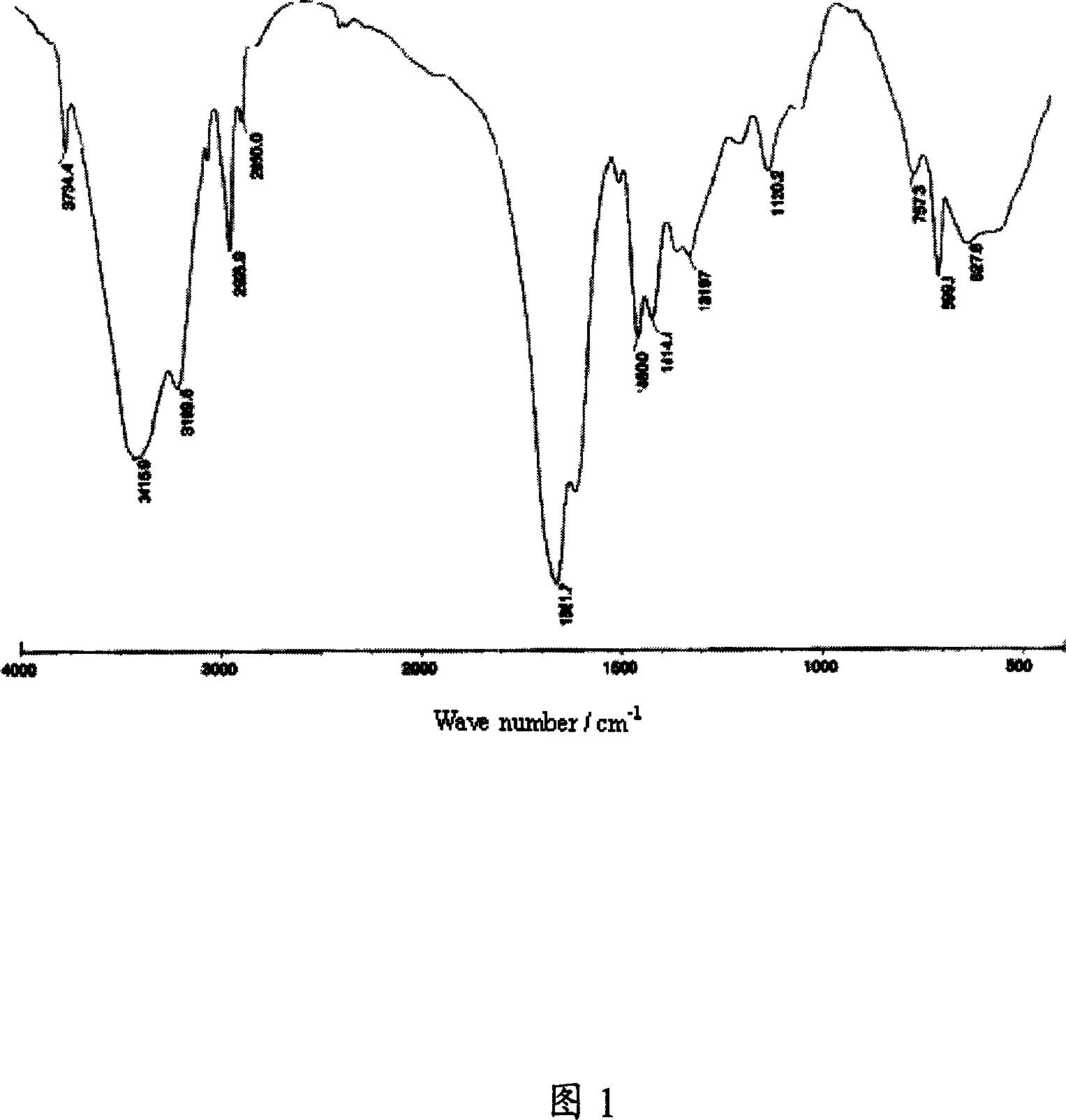
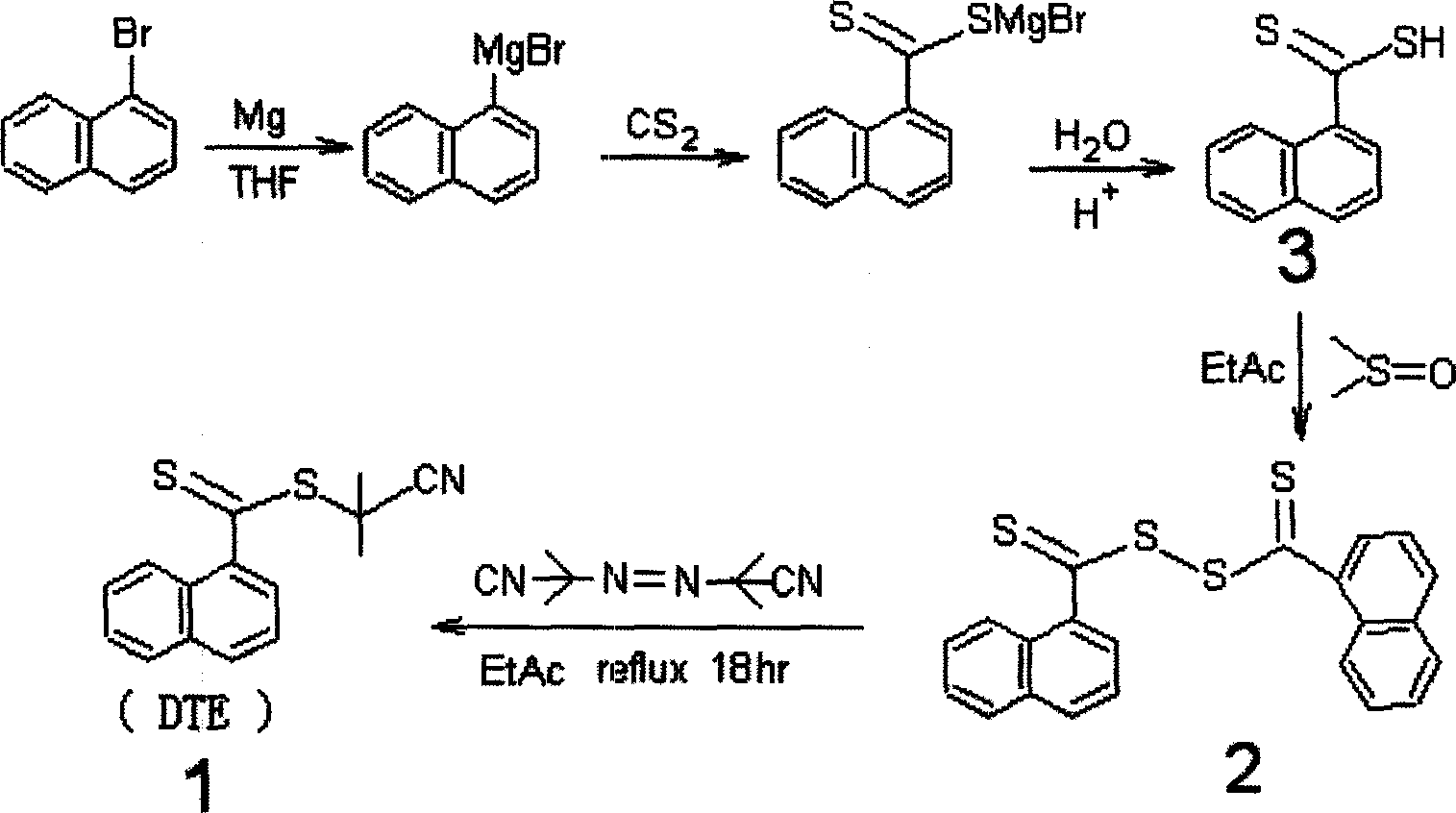
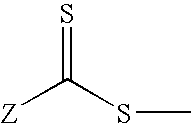
Reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer or RAFT polymerization is one of several kinds of reversible-deactivation radical polymerization. It makes use of a chain transfer agent in the form of a thiocarbonylthio compound (or similar, from here on referred to as a RAFT agent, see Figure 1) to afford control over the generated molecular weight and polydispersity during a free-radical polymerization. Discovered at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) of Australia in 1998, RAFT polymerization is one of several living or controlled radical polymerization techniques, others being atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and nitroxide-mediated polymerization (NMP), etc. RAFT polymerization uses thiocarbonylthio compounds, such as dithioesters, thiocarbamates, and xanthates, to mediate the polymerization via a reversible chain-transfer process. As with other controlled radical polymerization techniques, RAFT polymerizations can be performed with conditions to favor low dispersity (molecular weight distribution) and a pre-chosen molecular weight. RAFT polymerization can be used to design polymers of complex architectures, such as linear block copolymers, comb-like, star, brush polymers, dendrimers and cross-linked networks.
Polyurethane polymer
InactiveUS20040171765A1Good chemical resistanceImprove chlorine resistanceMonocomponent polyurethanes artificial filamentHeat resistanceReversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization
Provided is a polyurethane polymer which is excellent in oil resistance, weatherability, light resistance, heat resistance, hot water resistance, hydrolysis resistance, strength, chlorine resistance, and chemical resistance, and which can be produced simply and economically. The polyurethane polymer is produced by polymerizing at least two components: a vinyl polymer (A) having a mercapto group at each end of the molecular chain produced by a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method, and an organic polyisocyanate (B). Also provided are polyurethane-based materials containing the polyurethane polymer, and polyurethane elastic fiber.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Implementation method of reversible addition fragmentation chain emulsion polymerization
The invention discloses an implementation method of reversible addition fragmentation chain emulsion polymerization. 20-40 parts by weight of water, 0.1-2 parts by weight of bipolar macromolecule reversible addition fragmentation chain reagent, 1-20 parts by weight of monomer and 0.005-0.2 part by weight of micromolecule reversible addition fragmentation chain reagent are added into a reactor, stirring to be uniform is carried out, stirring is carried out, nitrogen is led in, heating is carried out until the temperature is increased to be 50-80 DEG C, 0.004-0.08 part by weight of water soluble initiator is added, initiated polymerization is carried out for 10-60min, 0-2 parts by weight of alkaline aqueous solution is added, and polymerization is continued for 0.5-5h. The invention utilizes bipolar macromolecule reversible addition fragmentation chain reagent with special structure as emulsifier and chain transfer agent, micromolecule reversible addition fragmentation chain is combined with emulsion polymerization, alkali is replenished, so as to improve the stability of emulsion; besides, process is simple, energy consumption is low, reaction time is short, conversion rate is high, no traditional emulsifier is adopted, molecular weight is consistent with design value, and molecular weight distribution is less than 2.0, thus having good industrialization prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Thermoplastic elastomers via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of triglycerides
ActiveUS20140343192A1Convenience to mergeCompetitive costVinyl aromatic copolymer adhesivesBituminous coatingsPolymer scienceThermoplastic elastomer
The present invention relates to a thermoplastic block copolymer comprising at least one PA block and at least one PB block. The PA block represents a polymer block comprising one or more units of monomer A, and the PB block represents a polymer block comprising one or more units of monomer B. Monomer A is a vinyl, acrylic, diolefin, nitrile, dinitrile, acrylonitrile monomer, a monomer with reactive functionality, or a crosslinking monomer. Monomer B is a radically polymerizable triglyceride or mixtures thereof, typically in the form of a plant or animal oil. The present invention also relates to a method of preparing a thermoplastic block copolymer or novel thermoplastic statistical copolymers by polymerizing a radically polymerizable monomer with a radically polymerizable triglyceride or mixtures thereof via reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization (RAFT), in the presence of an free radical initiator and a chain transfer agent.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for preparing porous material by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of high internal phase emulsion
The invention discloses a method for preparing a porous material by the reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of a high internal phase emulsion. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing a vinyl monomer, a polyvinyl monomer, a surfactant and a chain transfer reagent to form an oil phase; dissolving an electrolyte and a water-soluble initiator in deionized water to form a water phase; dropwise adding the water phase into the oil phase and stirring to form an emulsion system, and continuously stirring and carrying out pre-emulsification to form the high internal phase emulsion; transferring the high internal phase emulsion into a reactor, heating up to the temperature of 60-70 DEG C so as to initiate polymerization, stopping reaction after the polymerization is carried out for 24-48 hours, and cooling to room temperature; and carrying out extraction by adopting deionized water and a good solvent, and putting products into a vacuum baking oven and carrying out vacuum drying to obtain the porous polymeric material. According to the method, the chain transfer reagent and an activated / controllable free radical polymerization method are applied to a high internal phase emulsion template method, the open-cell porous material is successfully prepared, the method is simple and environment-friendly in process, and the mechanical properties of the material are greatly improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polyurethane polymer
Provided is a polyurethane polymer which is excellent in oil resistance, weatherability, light resistance, heat resistance, hot water resistance, hydrolysis resistance, strength, chlorine resistance, and chemical resistance, and which can be produced simply and economically. The polyurethane polymer is produced by polymerizing at least two components: a vinyl polymer (A) having a mercapto group at each end of the molecular chain produced by a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method, and an organic polyisocyanate (B). Also provided are polyurethane-based materials containing the polyurethane polymer, and polyurethane elastic fiber.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Preparation method of double-sensitivity cyclodextrin supermolecule aggregate
The invention discloses a preparation method of a double-sensitivity cyclodextrin supermolecule aggregate, belonging to the technical field of functional materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing a host molecule-photosensitive 4-hydroxycinnamic acid-cyclodextrin (4HCA-CD) by using 4-hydroxycinnamic acid (4HCA) to modify beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD); using trithioester with adamantine (AD) at tail end as a chain transfer agent, and preparing temperature-sensitive object polymer-double-arm adamantine-poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)-adamantine (AD-PNIPAM-AD) by using a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer free radical polymerization (RAFT) method; constructing a double-sensitivity supermolecule inclusion complex 4HCA-CD / AD-PNIPAM-AD by utilizing comprehensive performance of a beta-CD dewatering cavity and AD; and self-assembling the 4HCA-CD / AD-PNIPAM-AD to form the supermolecule aggregate which is capable of realizing reversible conversion in shape and size by changing light and temperature. The supermolecule aggregate prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has good light / temperature double sensitivities and is capable of carrying out smart response onto external stimulus, so that the supermolecule aggregate has a wide application prospect in the fields of drug loading, controlled release, and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle
InactiveCN101775112AAvoid reunionReduce quenchingLuminescent compositionsPotassium hydroxideBenzyl chloride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a nano particle core by a routine method, then packing the magnetic nano particle with a layer of silicon dioxide, performing cholromethylation on the silicon dioxide by utilizing a chloromethyl silane coupling agent, and leading benzyl chloride wrapped on the surface of the nano particle to react with carbon disulfide in the dimethylsulfoxide solution of potassium hydroxide so as to obtain a magnetic fluorescence nano particle the surface of which is modified with an RAFT reagent; and (2) utilizing the magnetic fluorescence nano particle obtained in step (1), a thermo-sensitive monomer, a sacrificed RAFT reagent and an initiating agent to form a polymerizing system and dissolving in solvent, carrying out reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) living radical polymerization, and then performing separating to obtain the magnetic fluorescence dual functional thermo-sensitive nano particle with a nuclear shell structure. RAFT polymerization is directly carried out on the surface of the magnetic silicon oxide nano particle, thus facilitating the magnetic fluorescence dual functional nuclear shell structure to keep the stability of the structure and performance in the actual application process.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Biomedical devices
InactiveUS20100315588A1Prevent limit adsorptionMaintain clarityProsthesisOptical partsHydrophilic polymersThio-
Biomedical devices such as contact lenses formed from a polymerization product of a mixture comprising (a) a hydrophilic polymer comprising one or more hydrophilic units and one or more thio carbonyl thio fragments of a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (“RAFT”) agent; and (b) one or more biomedical device-forming monomers are disclosed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Preparation method of novel organic-inorganic hybridization micropore separation membrane
ActiveCN103990384AInhibition of reunion behaviorGood dispersionSemi-permeable membranesNon solventReversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization
The invention discloses a preparation method of a novel organic-inorganic hybridization micropore separation membrane. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grafting a polymer on the surface of nano silicon dioxide through reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer to obtain polymer-grafted-silicon dioxide organic-inorganic hybridization nanometer particles, dispersing the polymer-grafted-silicon dioxide organic-inorganic hybridization nanometer particles in a quaternization reagent solution, stirring for 0.5-24 hours, realizing quaternization of the grafted polymer to obtain quaternization hybridization nanometer particles; with the quaternization hybridization nanometer particles as a dispersing phase, and a polymer membrane material as a main phase, preparing the organic-inorganic hybridization micropore separation membrane through a non-solvent inductive phase separation method. According to the preparation method, the agglomeration behavior of inorganic nanometer particles can be effectively inhibited, the dispersibility of the inorganic nanometer particles in a polymer matrix is promoted, the interaction of an organic phase and an inorganic phase is increased, the stability of the inorganic nanometer particles in the polymer matrix is improved, and multiple performances of hydrophilia, permselectivity, anti-fouling performance and antibacterial property of the separation membrane can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Active/controllable graphene oxide surface ion imprinted polymer, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104262536ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionMetal ions in aqueous solutionFunctional monomer
The invention provides an active / controllable graphene oxide surface ion imprinted polymer, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of preparation and separation of materials, wherein the graphene oxide surface ion imprinted polymer is prepared from a coupling agent, a functional monomer, a cross-linking agent and an initiator by using graphene oxide as a substrate and metal ions as a template in a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization manner. The problems to be solved in the invention are as follows: the thickness of a surface polymer layer is uncontrollable; template molecules cannot be thoroughly eluted because of being embedded deeply; and the adsorption rate is low, etc; the graphene oxide surface ion imprinted polymer is mainly used for adsorbing corresponding metal ions in aqueous solution and has good absorption effect at room temperature and obvious selective separation effect; and the graphene oxide surface ion imprinted polymer can be reused frequently.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Block copolymer
InactiveUS20040236020A1Improve flame retardant performanceImprove heat resistanceElastomerPolymer science
Provided are a block copolymer including a polymer block containing acrylonitrile or methacrylonitrile as a principal constituent, which is excellent in heat resistance, weatherability, oil resistance, flame retardancy, and low-temperature resistance and which can be economically produced; and a thermoplastic resin composition and an elastomer composition each containing the block copolymer. The block copolymer is produced by reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization in the presence of a thiocarbonylthio group-containing compound.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Method for preparing sulfate-resistant polycarboxylate water-reducing agents and application thereof
ActiveCN105713150AReduce pollutionThe synthesis method is simplePhosphateReversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization
The invention provides a method for preparing sulfate-resistant polycarboxylate water-reducing agents and application thereof. The sulfate-resistant polycarboxylate water-reducing agents comprise monomers a, monomers b and monomers c which are subjected to reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. The method and the application have the advantages that strong adsorption groups and phosphate groups are introduced into block polycarboxylate main chain structures definitely distributed on sequence structures, accordingly, block polycarboxylate is high in adsorption capacity, and the sulfate resistance of the block polycarboxylate can be improved; the sulfate-resistant polycarboxylate water-reducing agents are low in dosage and slump loss, high in water-reducing rate and good in cement adaptability and is sulfate-resistant, the method for synthesizing the sulfate-resistant polycarboxylate water-reducing agents is simple, is low in production cost and little in environmental pollution and has low technological requirements, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU SOBUTE NEW MATERIALS +1
Agricultural macromolecular surfactant and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102308798ARealize intelligent controlRealize adjustableBiocideAnimal repellantsHydrophilic monomerPolymer science
The invention discloses an agricultural macromolecular surfactant and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of surfactants. According to the invention, the block-type macromolecular surfactant is prepared by performing solution or emulsion polymerization on hydrophilic monomer and lipophilic monomer in a manner of employing a reversible addition fragmentation chain free radical copolymerization technology under the action of an initiator and a chain transfer agent, wherein the polymerization temperature is 50-150 DEG C and the polymerization pressure is 0.1-10 MPa. The macromolecular surfactant is applied in environment-friendly pesticide preparations. Hydrophilic groups with high charge density are bonded with the two ends of the macromolecular surfactant, and a hydrophobic long carbon chain is bonded with the other end of the macromolecular surfactant. According to the invention, the molecular weight and the molecular chain segment sequence structure of the macromolecular compound are intelligently controlled, and the molecular weight distribution is narrow. When being used in a pesticide preparation, the surfactant disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small dosage and good emulsion dispersion stability.
Owner:YANGZHOU SPED CHEM
Preparation method and application SiO2/GO surface metal ion imprinted polymer
InactiveCN104530334ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPolymer scienceReversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization
The invention provides a preparation method and application a SiO2 / GO surface metal ion imprinted polymer and belongs to the technical field of material preparation and separation. Particularly, silica / graphene oxide is used as a base, metal ions serve as a template, coupling agents, functional nonomers, cross-linking agents and initiators are used, reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization serves as a polymerization mode, and the SiO2 / GO surface metal ion imprinted polymer is prepared; the problems that the thickness of the surface polymer cannot be controlled, adsorption sites are not uniformly distributed, template molecules cannot be thoroughly eluted because they are wrapped too deep, the adsorption speed is low, the synthesis steps of chain transfer agents are complex, and time is consumed are solved; the SiO2 / GO surface metal ion imprinted polymer is mainly used for selectively separating corresponding metal ions in a water solution, the selective separation effect is remarkable, and the polymer can be reused many times.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Water-based electrode binding agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106281147AImprove mechanical propertiesGood compatibilityCell electrodesGraft polymer adhesivesWater basedPollution
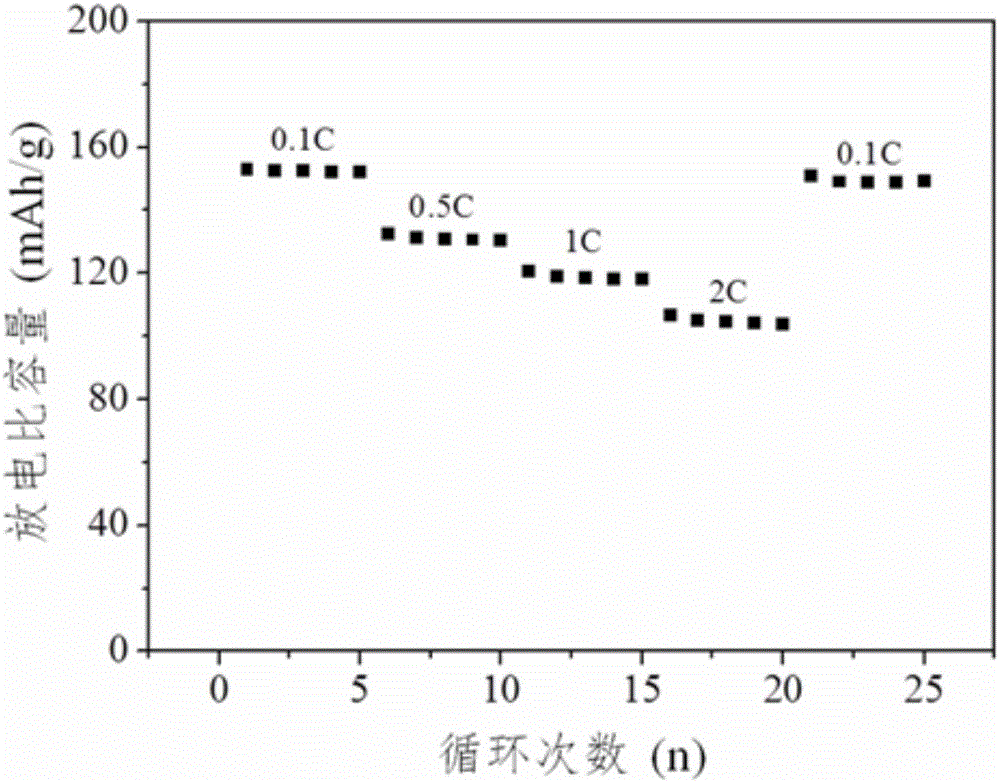
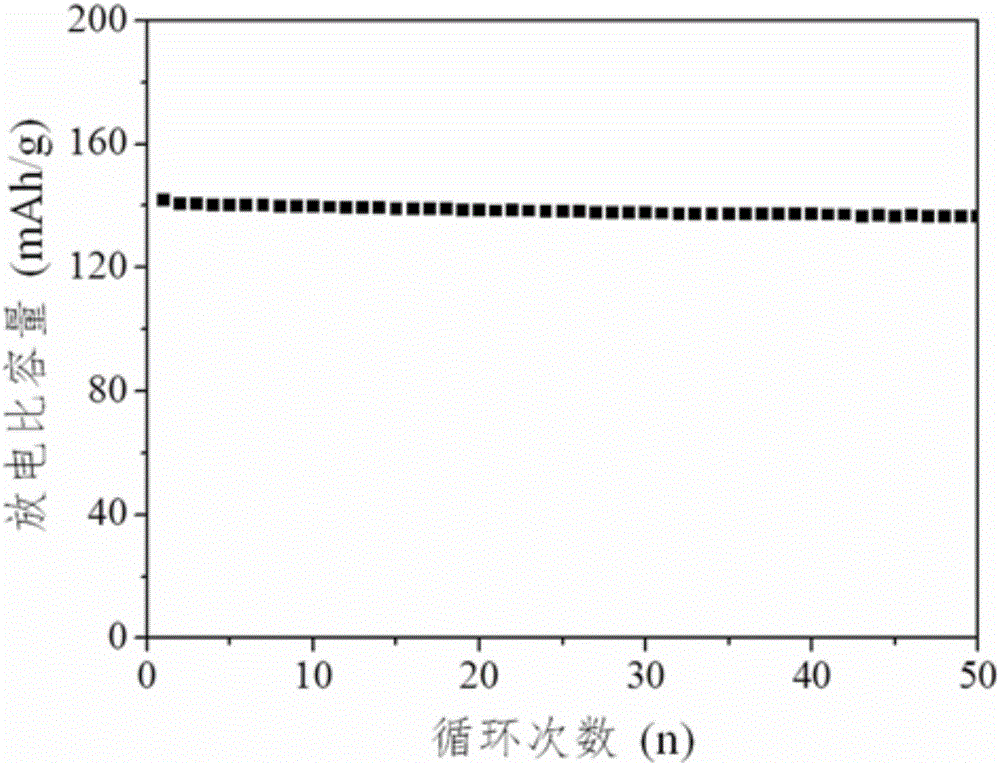
The invention discloses a water-based electrode binding agent and a preparation method thereof. According to the water-based electrode binding agent, an emulsion polymerization system is adopted, and a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer free-radical polymerization technology is used for preparing butyl acrylate / styrene / methyl acrylate block copolymer latex which is used as the electrode binding agent. A preparation process has the advantages of energy saving and environment protection; compared with a traditional binding agent polyvinylidene fluoride, the water-based electrode binding agent has the advantages of low price, simple process, no pollution and the like; the discharge specific capacity of a used electrode in a lithium iron phosphate electrode can reach 153.4mAh / g, and the discharge specific capacity in a graphite electrode can reach 358.6mAh / g; and therefore, the water-based electrode binding agent has great application prospects.
Owner:浙江杰特维新材料有限公司
Preparation method for amphiphilic segmented copolymer with pH value and temperature sensitivities
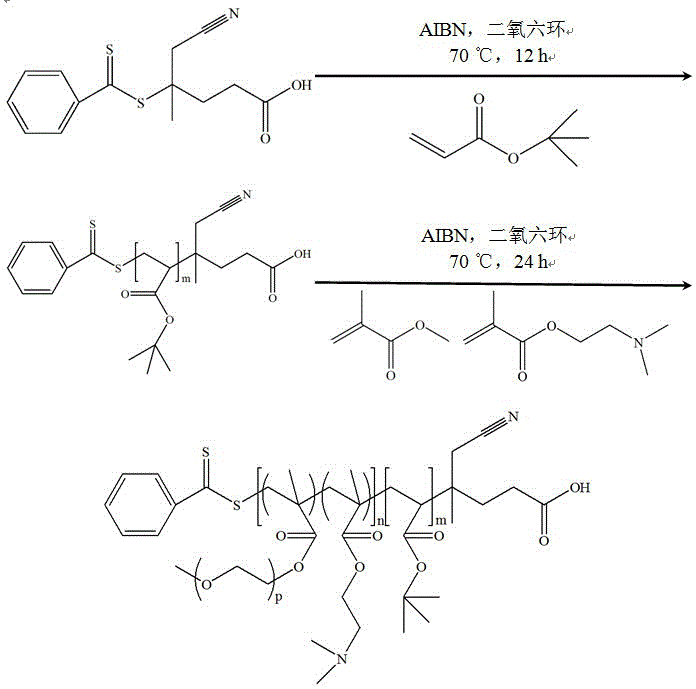
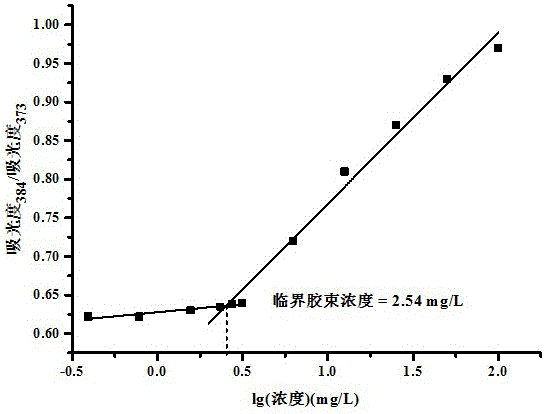
The invention relates to a preparation method for an amphiphilic segmented copolymer with pH value and temperature sensitivities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by adopting a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization process, synthesizing a macromolecular chain transfer agent namely tert-butyl polyacrylate, and subjecting the tert-butyl polyacrylate with dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate and ethylene glycol monomethyl ether methacrylate to the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization process again so as to synthesize the amphiphilic segmented copolymer P(tBA)-b-P(DMAEMA-co-PEGMA. The segmented copolymer provided by the invention can self-assemble to form micelles in an aqueous solution, and has pH value and temperature sensitivities, wherein the micelles have a critical pH value of 7 and a critical temperature of 37.5 DEG C. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of high yield, relatively wide applicable monomer range, low requirements on reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, greenness and environmental friendliness; and the amphiphilic segmented copolymer prepared by using the method provided by the invention has double pH value and temperature sensitivities and broad application prospects, and can be applied to the chemical production fields like dye adsorption, the environment protection fields like heavy metal pollution treatment, and the biomedical fields like controllable release of insoluble drugs.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Nanometer composite heat resisting fluid loss reducing agent and its prepn
InactiveCN101020814AImprove thermal stabilityGood physical and mechanical propertiesDrilling compositionPolymer scienceFiltration
The present invention discloses one kind of nanometer composition heat resisting filtration reducing agent and its preparation process. The nanometer composition filtration reducing agent is synthesized through a reverse addition-fracturing chain transferring (RAFT) process, and has nanometer montmorillonite layer dispersed inside amphiphilic block polymer base. The organic combination between rigid and stable montmorillonite and flexible block polymer makes the nanometer composition filtration reducing agent possess high physical and mechanical performance and high heat stability. It is used as drilling fluid treating agent and has obvious filtration reducing effect at high temperature and high pressure.
Owner:CNPC DRILLING RES INST
Hydrophilic bactericidal anti-contamination reverse osmosis membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108057348AImprove anti-pollution performanceGrowth inhibitionMembranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisReverse osmosisPolyamide
The invention provides a hydrophilic bactericidal anti-contamination reverse osmosis membrane and a preparation method thereof. A bactericidal high-molecular polymer and an antibacterial polymer are grafted on the surface of a reverse osmosis membrane through a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT) living polymerization method, so that the hydrophilic bactericidalanti-contamination reverse osmosis membrane is obtained, the method utilizes free amino groups on the surface of a polyamide functional layer to link a RAFT chain transfer agent in situ through an amide condensation reaction, and functional layers with different thicknesses and different molecular weights are controllably grafted, such as an amphoteric ion functional layer with hydrophilic properties and a quaternary ammonium salt functional layer with bactericidal performance. The anti-contamination reverse osmosis membrane prepared by the method still has excellent anti-contamination characteristics without sacrificing the performance of the original membrane, the long-term anti-contamination ability of the original membrane in a complex operating environment is improved, and the purposes of inhibiting the growth of bacteria and reducing attachment of microorganisms on the membrane are achieved.
Owner:VONTRON TECH CO LTD
Biomedical devices
ActiveUS20100317809A1High oxygen permeabilityLow modulusTissue regenerationIntraocular lensPolymer scienceThio-
Biomedical devices such as silicone hydrogels formed from a polymerization product of a mixture comprising (a) a siloxane-containing homopolymer comprising one or more thio carbonyl thio fragments of a reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) agent; and (b) one or more biomedical device-forming monomers are disclosed.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Preparation method of temperature and CO2 double-responsive block copolymer nano micelle
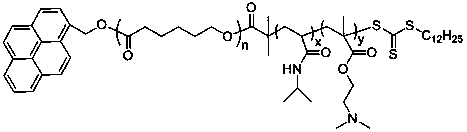
The invention relates to a preparation method of a temperature and CO2 double-responsive block copolymer nano micelle. The preparation method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of initiating caprolactone ring-opening polymerization by utilizing pyrene methanol under the protection of inert gas, then, carrying out esterification reaction by utilizing terminal hydroxyl of polycaprolactone and terminal carboxyl of a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymeric chain transfer agent, thereby obtaining a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerized macromolecular chain transfer agent; and carrying out reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide and an N,N-dimethylacrylic acid dimethylamino ethyl ester monomer by taking azodiisobutyronitrile as the initiator under the protection of inert gas so as to obtain Py-PCL-b-(NIPAM-coDMAEMA) block copolymer, dissolving the Py-PCL-b-(NIPAM-coDMAEMA) block copolymer in water, thereby obtaining a steady temperature and CO2 responsive nano-micelle. The temperature and CO2 double-responsive block copolymer nano-micelle disclosed by the invention has biodegradability, biocompatibility and bioactivity simultaneously; the steady nano micelle self-assembled in water has temperature and CO2 double-responsive characteristic; the preparation method disclosed by the invention has wide application prospect in the fields, such as drug-controlled release carriers, biological intelligent switches, soft tissue engineering bracket materials and biological sensors; the preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and practicable and has good popularization and application values; all the raw materials can be industrially produced.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Omega-functionalized polymers, junction-functionalized block copolymers, polymer bioconjugates, and radical chain extension polymerization
InactiveUS20110305660A1Maximal diversitySpecial deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer scienceBioconjugation
Polymeric compounds having spatially controlled bioconjugation sites are described. Functionalization is achieved by selective co-terminal chain extension of polymer chains by radical polymerization, such as reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization.
Owner:GENEVANT SCI GMBH +1
Glycine betaine ester intelligent hydrogel relatively controllable in structure and preparation method and application
InactiveCN103059215AControl structureControl molecular weightSurgeryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSmart hydrogelsBetaine
The invention discloses a glycine betaine ester intelligent hydrogel relatively controllable in structure and a preparation method and application. The glycine betaine ester intelligent hydrogel relatively controllable in structure comprises, by weight, 0.2-0.9 part of carboxylic acid glycine betaine esters, 0.3-1 part of N- isopropyl acrylamide, 0.005-0.01part of initiators, 0.03-0.07 part of cross-linking agents, 0.01 part of reversible additive fragment transfer (RAFT) reagents and 5-9 parts of solvents. Solution polymerization or emulsion polymerization is carried out by means of an RAFT free radical polymerization method. An obtained glycine betaine ester intelligent hydrogel which is relatively controllable in structure and molecular weight has the good performance of sterilization, self-cleaning, soil release and the like. The glycine betaine ester intelligent hydrogel can be applied to a controllable drug sustained-release system and artificial cartilages, implantable biological materials of internal biosensors, and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing accurate polymer network
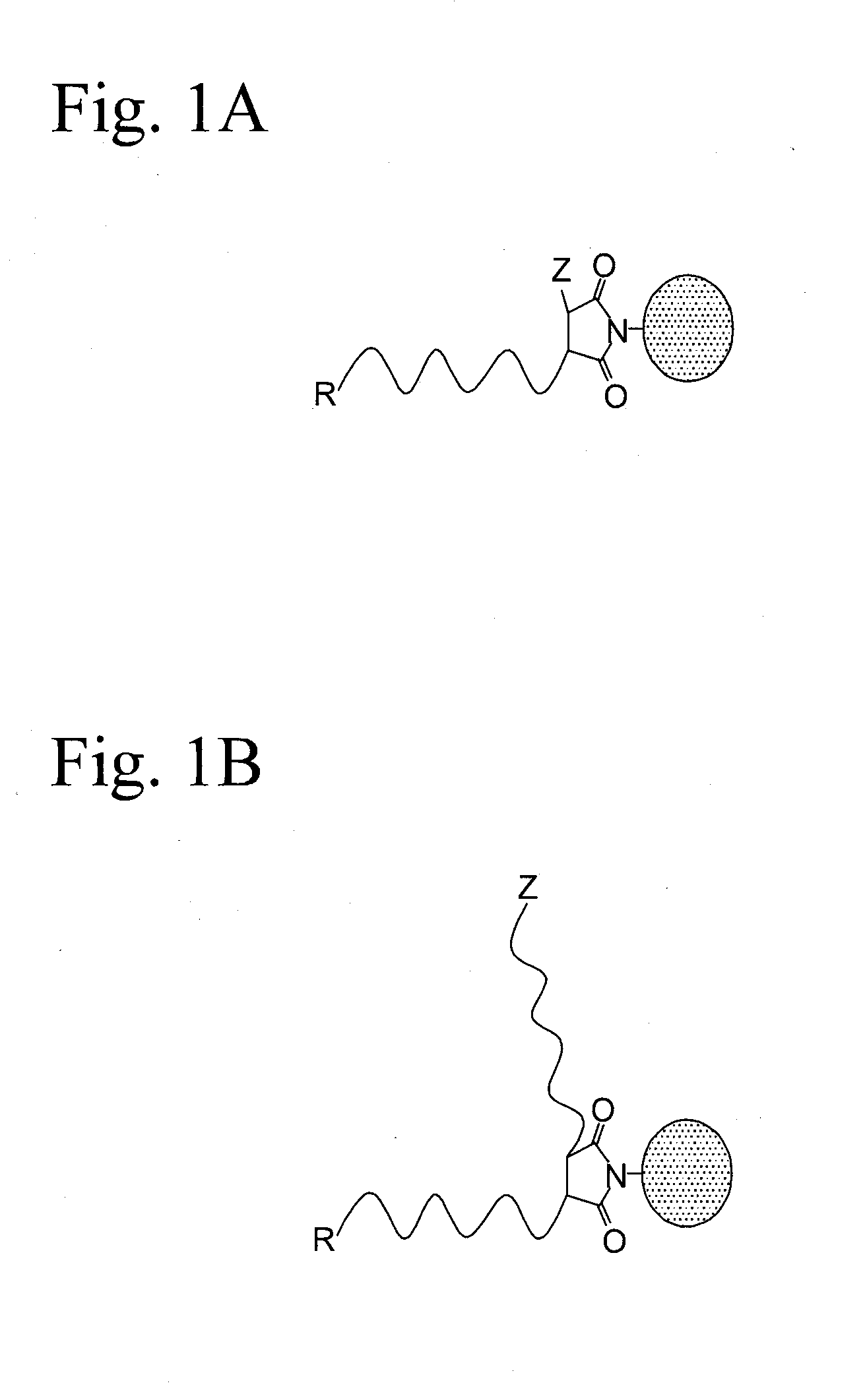
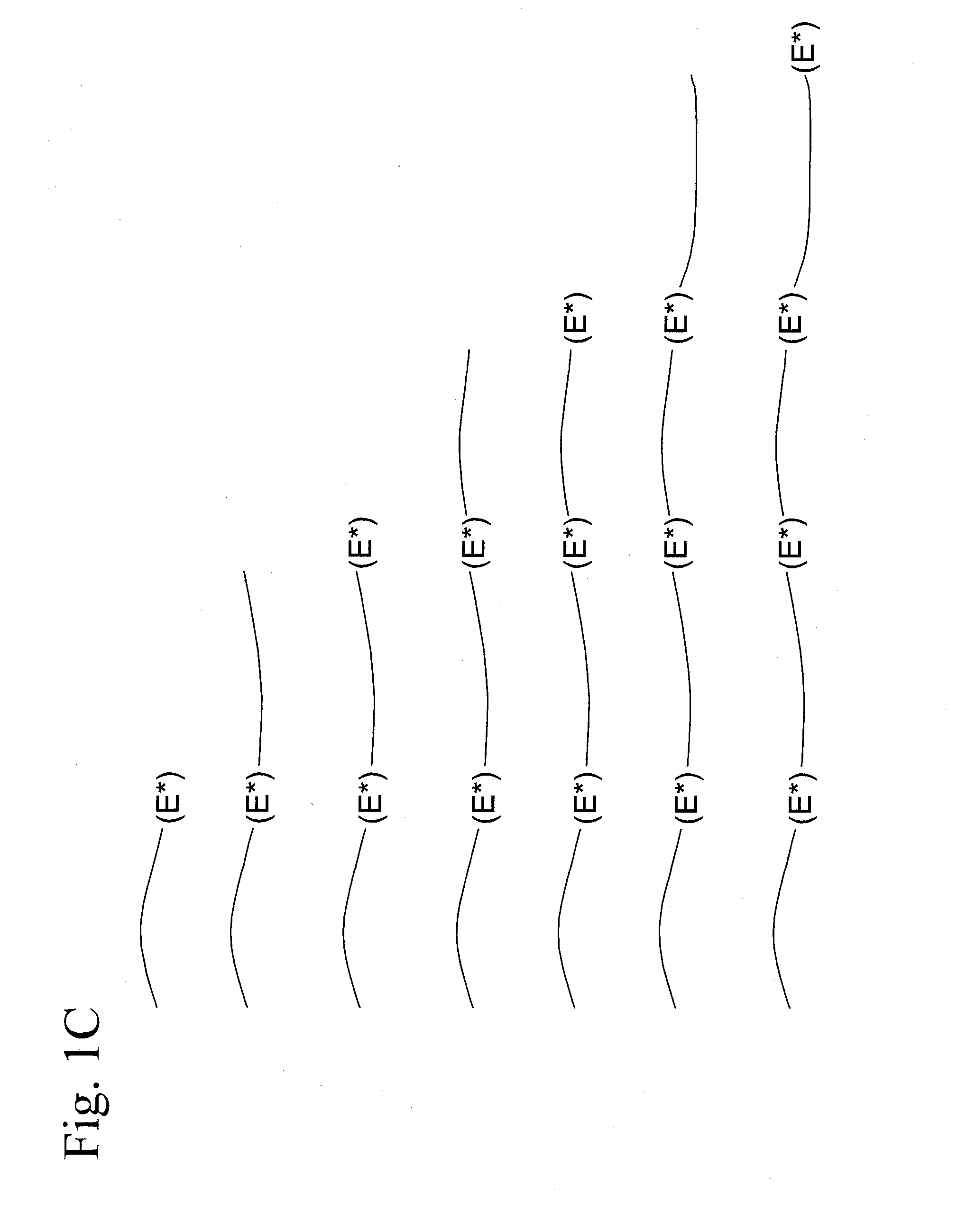
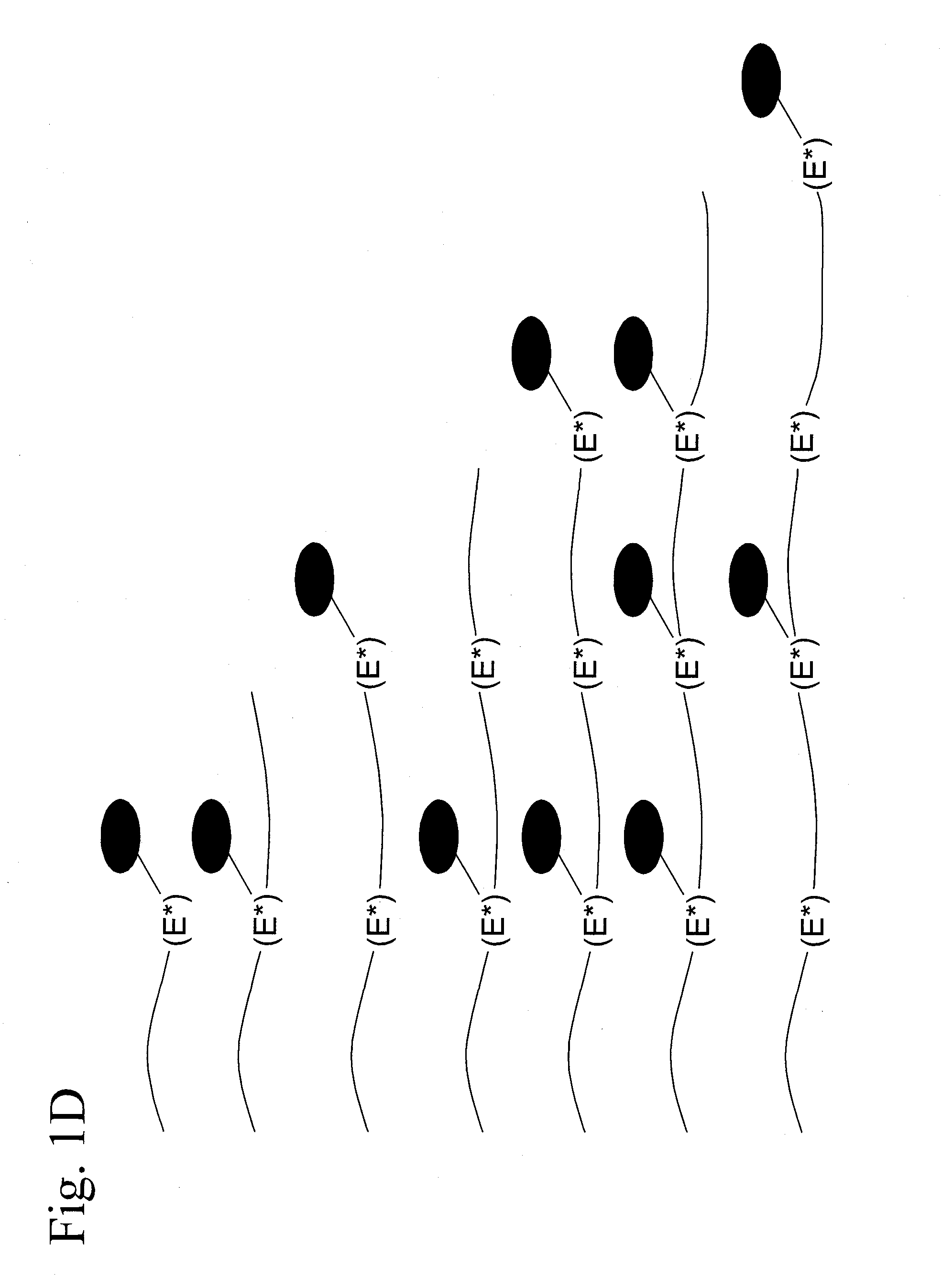
The invention discloses a method for preparing an accurate polymer network. The number of azide functional groups at the tail end of a polymer is controlled accurately by using a method combining reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) and click chemistry, so that the number of crosslinking points is controlled and a regular polymer cross-linked network structure is prepared. In the method disclosed by the invention, gel in the polymer network is generated by performing a click reaction on two or more accurately-controlled functional end group azide or alkyne functional groups (E) at the tail end of a polymer chain and two or more end alkynyl or azide functional groups (E) via multiple steps of RAFT. The method has the advantages of accurate controllability of the number of crosslinking points and density of a polymer cross-linked network structure and suitability for various polymer network structures containing different functional groups.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Glucose responsive gold nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102962471APrevent spontaneous aggregationAvoid interferenceMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhenylboronic acidNanoparticles dispersion
The invention discloses a glucose responsive gold nanoparticle and a preparation method and an application thereof. The method adopts the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method to prepare isopropyl acrylamide-acrylyl sulfourea amino phenylboronic acid copolymer that which is modified to the surface of the gold nanoparticle to obtain the gold nanoparticle covered by the copolymer. The gold nanoparticle obtained through the method in disclosed by the invention can generate response with the glucose molecule in a solution; the developing system dispersed by the gold nanoparticle is driven through by the glucose molecule to change the colour of the gold nanoparticle solution at high temperature, so as to realize visual identification and detection for the glucose. The method in disclosed by the invention can be widely used for the field of nanometre bioanalysis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing hydrophilic temperature and pH dual-sensitive graphene through thiol-ene click chemistry method
InactiveCN103407992ANo pollution in the processUniform and stable dispersionGrapheneChemical reactionClick chemistry
The present invention relates to a method for preparing hydrophilic temperature and pH dual-sensitive graphene through a thiol-ene click chemistry method. According to the method, graphene oxide is synthesized, a chemical modification method is adopted to prepare unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond group-containing graphene oxide, a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method is adopted to synthesize a temperature and pH dual-sensitive block polymer, the temperature and pH dual-sensitive block polymer is reduced into thiol group-containing temperature and pH dual-sensitive diblock polymer under a strong reduction agent effect, a thiol-ene click chemistry reaction is adopted to prepare hydrophilic temperature and pH dual-sensitive graphene oxide, and reduction is performed under a strong reduction agent to obtain the hydrophilic temperature and pH dual-sensitive graphene. The method has advantages of simple process, no environmental pollution, high product quality, high input-output ratio, low cost, wide application prospects, and the like. The obtained product can be used in the fields of lithium ion batteries, biosensors, supercapacitors, solar cells, metal ion absorption, stress sensors, hydrogen storage materials and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Preparation method of segmented copolymer material with temperature and pH (Potential of Hydrogen) sensitivity
The invention relates to a preparation method of a segmented copolymer material P(MMA-co-DMAEMA)-b-PPEGMA with temperature and pH (Potential of Hydrogen) sensitivity. According to the method, a copolymer poly(methyl methacrylate-co-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) is synthesized by adopting a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization method firstly; the synthesized poly(methyl methacrylate-co-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) as a macromolecular chain transfer agent is subjected to RAFT (Reversible Additive Fragment Transfer) polymerization with polyethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate, so as to obtain the segmented copolymer material P(MMA-co-DMAEMA)-b-PPEGMA with the temperature and pH sensitivity. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity and convenience, high preparation yield, no pollution to environment and the like; the prepared polymer material has high functionality and narrow molecular weight distribution, can be applied to organic dye adsorption and heavy metal adsorption, and medicine fields including in-vivo transportation of difficultly-soluble anti-cancer medicines and the like.
Owner:南京东焱氢能源科技有限公司
Amphipathic block polymer, polymersome, and preparation method and application of polymersome
ActiveCN103588940AStimulus Modulation of Biocatalytic ActivityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsOn/in organic carrierPolymer sciencePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to an amphipathic block polymer, a polymersome consisting of the amphipathic block polymer, and a preparation method and application of the polymersome. More specifically, the amphipathic block polymer is obtained from a hydrophilic chain segment and a hydrophobic chain segment by a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization method, wherein the hydrophilic chain segment is polyethylene glycol with the terminal group modified by tri-thioester and the molecular weight of the hydrophilic chain segment is 1,000 to 20,000 Da; the constitution of the hydrophobic chain segment is as shown in the following formula, m is equal to 1 to 11 and n is equal to 1 to 11. By adoption of the amphipathic block polymer, controllable and synchronous release of polymersome-loaded hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules is realized, and the biological catalytic activity of a polymersome-loaded enzyme reactor is regulated and controlled through stimulation. In addition, in the processing of triggering crosslinking by stimulation, the permeability of a sieve-shaped hydrophilic channel generated in a double-layer membrane of the polymersome and the membrane can be controlled by the duration time of stimulation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Curable composition
InactiveUS20050004318A1Low dyeabilityLow compression setReversible addition−fragmentation chain-transfer polymerizationPolymer chemistry
The present invention provides a curable composition that comprises a polymer (A) containing a cross-linkable silyl group and a condensation catalyst (B). The polymer (A) containing a cross-linkable silyl group is obtained by a process comprising the steps of conducting a radical polymerizable monomer in the presence of a thiocarbonylthio compound. For example, the polymer (A) is obtained by (i) initiating a reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization of a radical polymerizable monomer in the presence of a thiocarbonylthio compound, and (ii) adding an unsaturated compound containing a cross-linkable silyl group for copolymerization when a consumed amount of the radical polymerizable monomer by the polymerization has reached a level of 80% or more.
Owner:OHSHIRO NOBUAKI +2
Method for preparing gradient copolymer
InactiveCN101792496AMolecular weight controllableNarrow molecular weightOrganic chemistryCoatingsPolymer scienceChain structure
The invention provides a method for preparing a gradient copolymer. In the method, based on the special chain transfer function and self-emulsification function of an amphiphilic reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer agent (amphiphilic RAFT reagent), under a condition of no emulsifier, the gradient copolymer is made from comonomer units by using a thermolysis initiator for initiation and water as a disperse phase and spontaneously by adopting a once feed method when the reactivity ratio of comonomers is high or forcefully by adopting a reaction material supply method when the polymerization reactivity ratio of the two comonomers is small. The molecular chain of the copolymer prepared by the method has a gradient, namely along a molecular chain, the leading position is gradually transferred from one monomer unit to the other monomer unit. The gradient copolymer is used in fields of gradient functional coatings, polymer bulking agents, damping materials and the like. The method is simple, low in cost and pollution free, and makes the control of a molecular chain structure and a polymerization process easy.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Cation functional polymers with natural amino acid as side group, preparation method and application of polymer
InactiveCN103665222ARegular structureNarrow molecular weight distributionGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCytotoxicityPolylysine
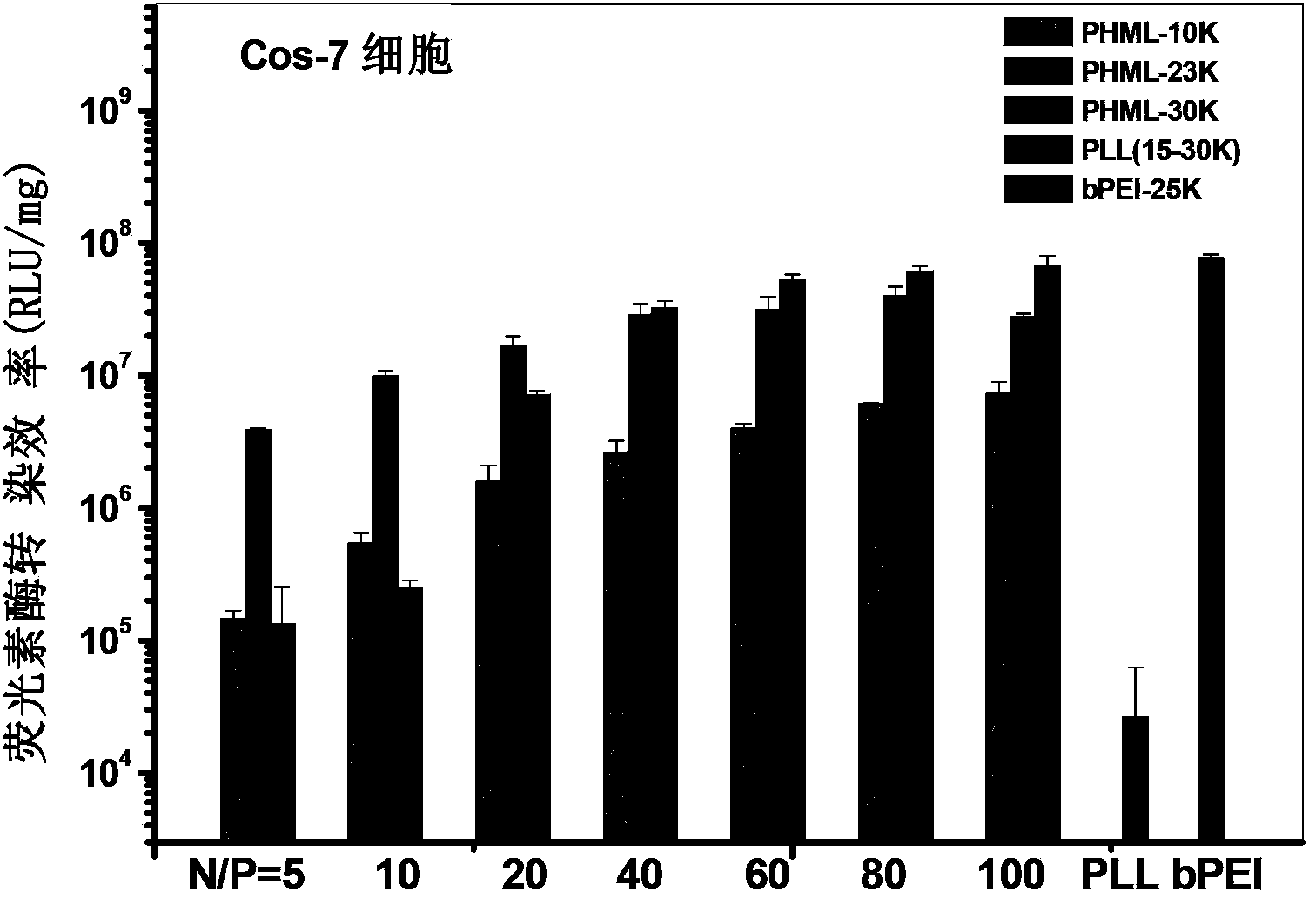
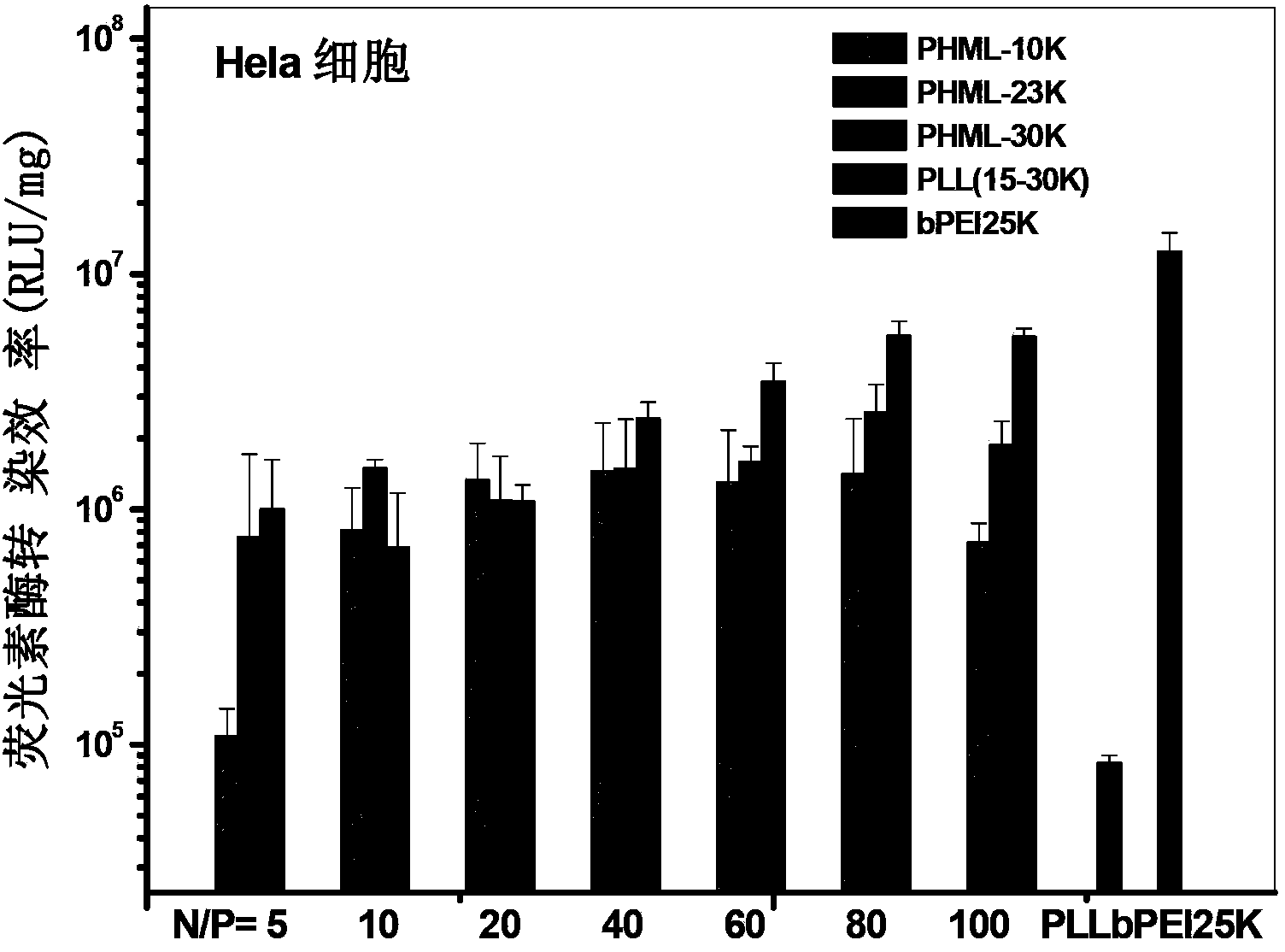
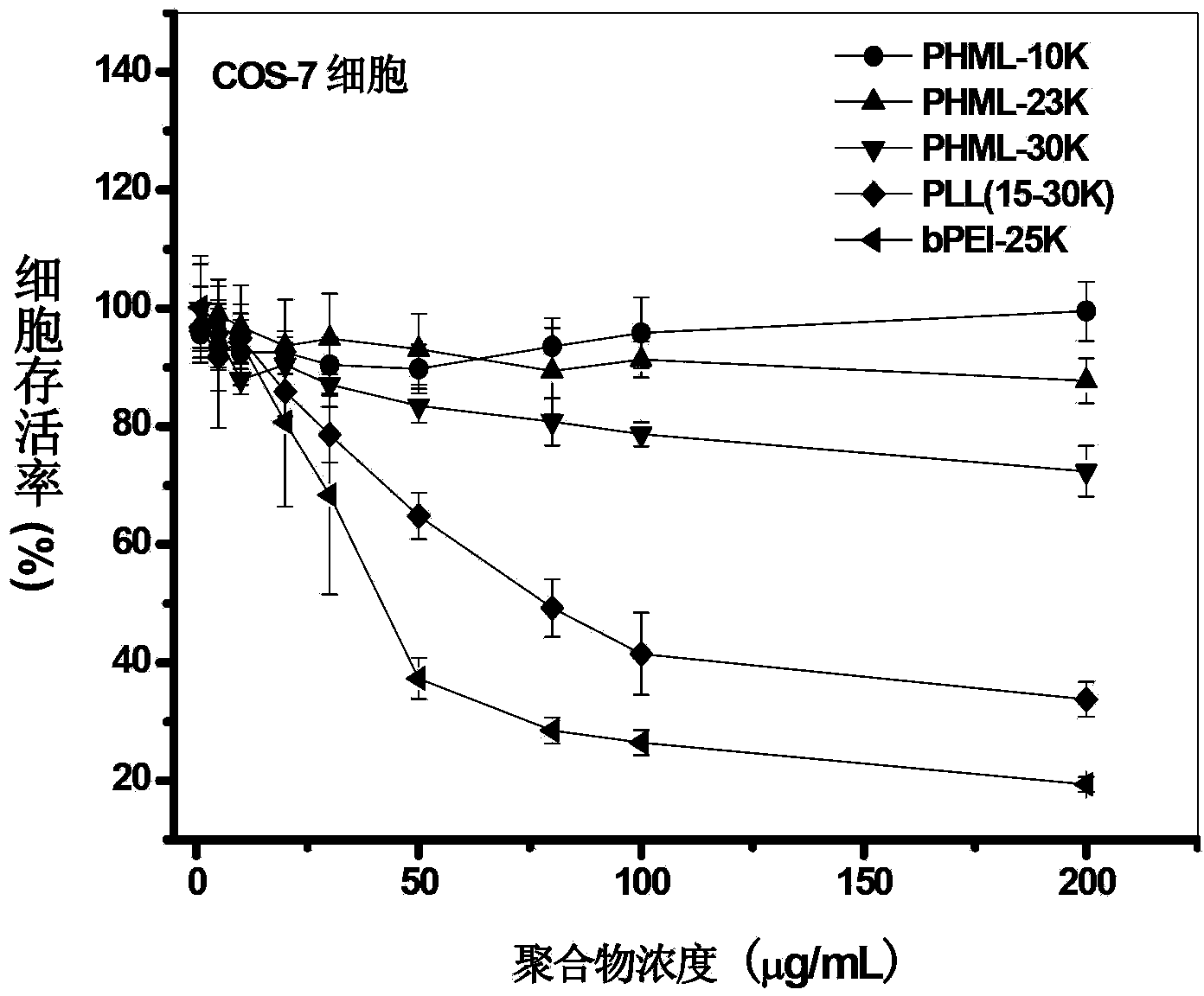
The invention relates to a class of cation functional polymers with natural amino acid as a side group, and a preparation method and an application of the polymer. A series of water-soluble cation functional polymers with amino acid side groups is prepared by performing controllable polymerization on Boc-amino acid functionalized acrylate monomers through reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization reaction, and removing the Boc protecting groups. The preparation method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the cost is low, polymer structure is regular, molecular weight distribution is narrow, raw materials are easy to obtain and the like. The class of water-soluble cation functional polymers with amino acid side groups is formed by taking natural amino acid as important building blocks, presents very low cytotoxicity by reference to commercial linear polylysine PLL (15-30K) and branched polyethyleneimine bPEI-25K in multiple cell lineages, present high-efficiency gene transfection in multiple cell strains when being used as a cation gene vector material, and has a good prospect in the low-toxicity and high-efficiency cation polymer gene vector application field.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com