Polyvalent bacteria capsule polysaccharide-protein conjugate combined vaccine
A technology of capsular polysaccharides and bacterial polysaccharides, applied in the direction of antibacterial drugs, bacterial antigen components, etc., to achieve the effects of relieving pain, improving immune coverage, and reducing immunization costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
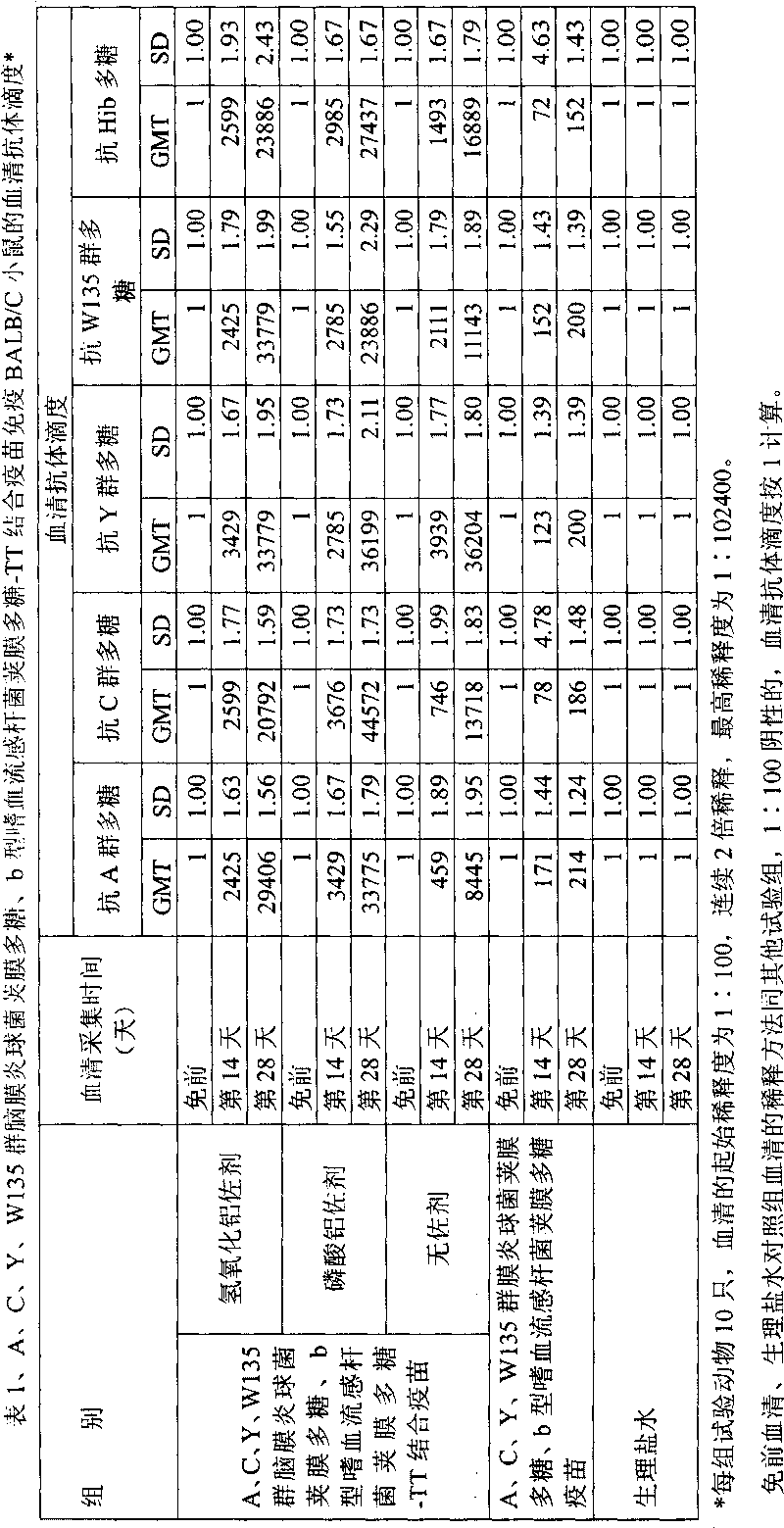
[0028] Extraction of capsular polysaccharide of meningococcus group A, C, Y, W135 and capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b
[0029] Proper medium can be selected for the production of polysaccharide vaccines. The liquid medium used for production does not contain components that can form precipitates with cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. The culture medium does not contain harmful or other allergen substances.
[0030] After inoculating the strains in a suitable medium, harvest after the logarithmic production phase or early in the stationary phase. It is advisable to add formaldehyde solution to the culture to sterilize or heat to sterilize, so as to ensure the safety of sterilization and not damage the polysaccharide of the bacteria. Centrifuge the sterilized single harvest (or combined harvest) to remove bacteria, collect the supernatant, concentrate the harvested supernatant to 1 / 8 of the original volume with an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecula...
Embodiment 2
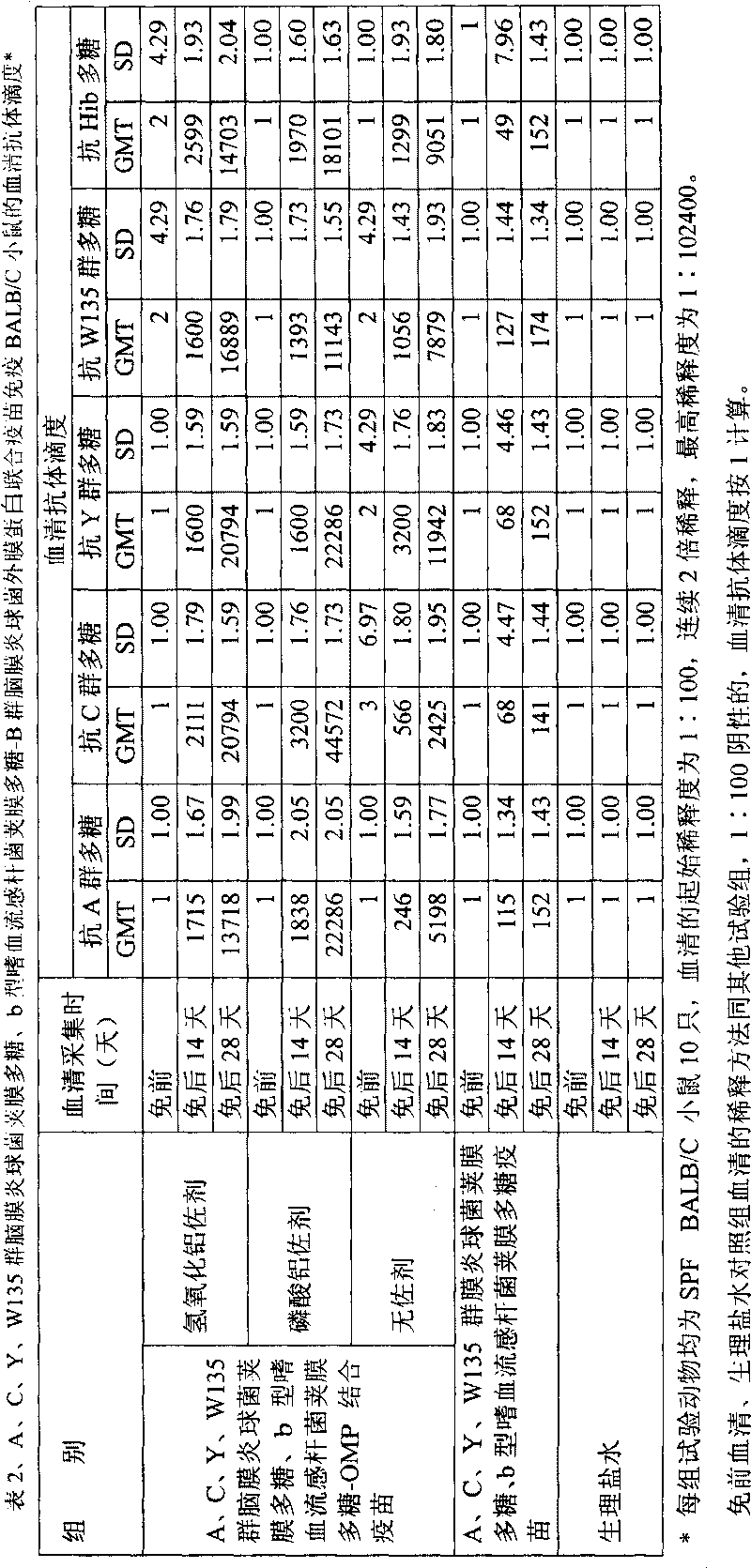
[0035] Lysis and purification of capsular polysaccharide
[0036] Dissolve 5 g of group A (or group C, Y, W135) Neisserial meningitidis capsular polysaccharide (or capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b, Hib) in 10 liters of 1 / 10 saturated sodium acetate buffer solution (pH5.5-6.0, adjust pH with acetic acid, room temperature), stir at room temperature, fully dissolve for 8-12 hours, until the solution is clear and transparent, add 50mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.5- 6.0) 38.33 liters, heat the circulating water in the jacket of the stainless steel reaction tank, maintain the temperature of the polysaccharide solution in the tank at 55-56 ° C, stir for 0.5 hours, add 1670 ml of 30% hydrogen peroxide to the tank, and crack the polysaccharide. The stirring speed is 100 rpm.
[0037] The polysaccharide cracking process is monitored by tracking the molecular weight of the polysaccharide. The molecular weight is determined by Shimadzu 20AT HPLC TSK3000W liquid ch...
Embodiment 3
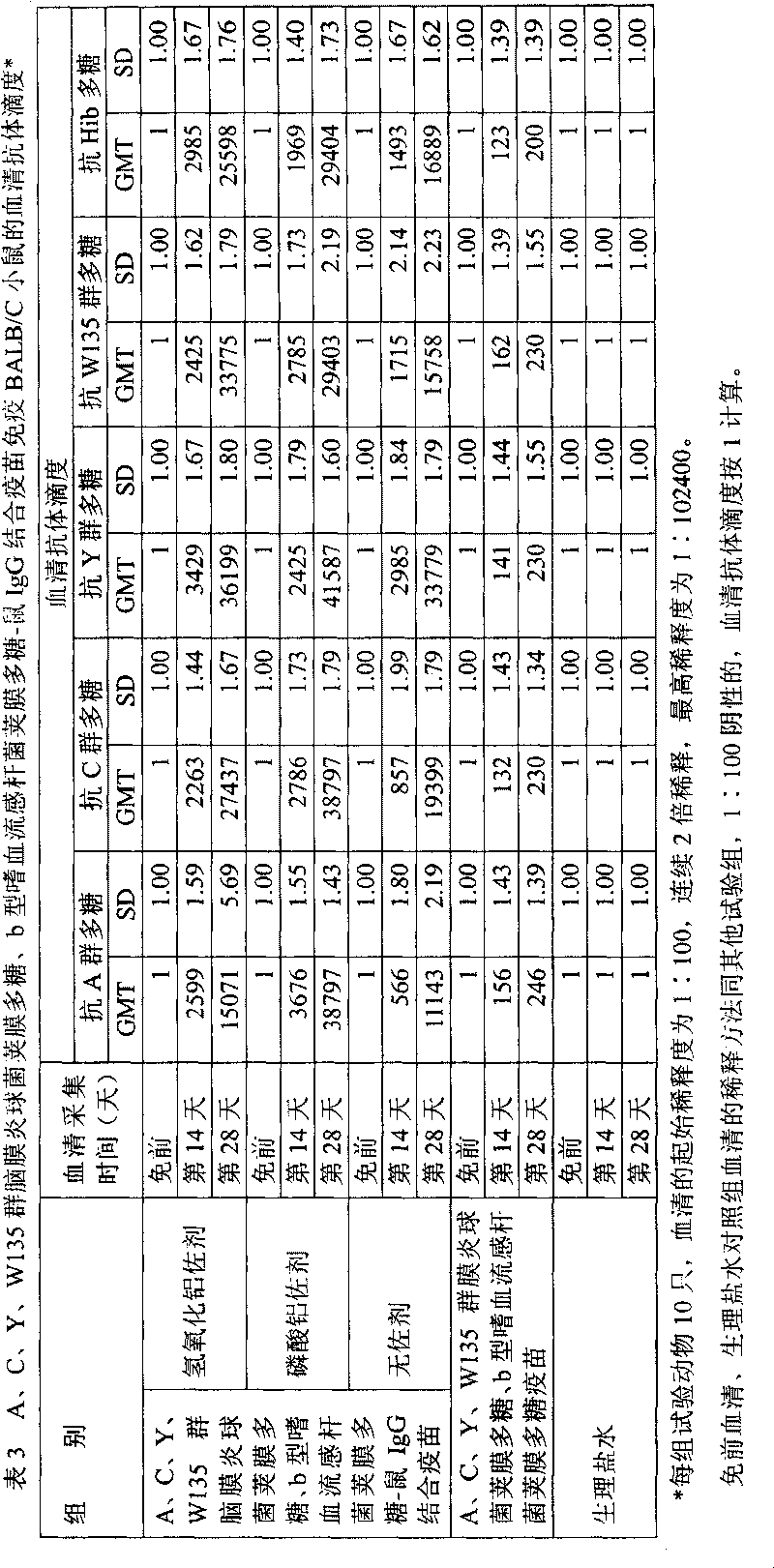
[0040] Coupling and Purification of Polysaccharide and Tetanus Toxoid
[0041] 1. Activate polysaccharide
[0042] Take 400mg (4mg / ml, 100ml) of meningococcal capsular polysaccharide (or Hib) polysaccharide of group A (or group C, group Y, group W135), adjust the pH to 10.8 with 0.5M NaOH, add 200mg of cyanogen bromide, and use 0.5M NaOH to maintain the pH at about 10.8±0.5 for 1 hour (22°C). Then use 0.5M HCl to adjust the pH to 8.8, add 1450mg adipic hydrazide (ADH), and react for 6 minutes; use 0.5M NaOH to adjust the pH to 8.5, and maintain the pH within the range of 8.5±0.5 for 15 minutes; Stir gently for 12 hours. Dialyze with pre-cooled 0.05M NaCl solution for 48 hours (4-8°C), during which time the solution was changed 5 times (or ultrafiltration with 3KD polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane). Filter the activated polysaccharide-AH derivative with a 0.45 μm filter membrane.
[0043] 2. Coupling of activated polysaccharides and tetanus toxoid (TT) (operated und...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com