Compound semiconductor light-emitting device and method of producing same
A light-emitting device and compound technology, which is applied in the field of pn junction compound semiconductor light-emitting devices, can solve problems such as difficult to obtain ohmic contact, and achieve the effect of reliable formation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0169] The present invention will be described in detail by Example 1 below, in which a conductor layer made of undoped p-type boron arsenic phosphide and a light-transmitting substrate made of glass material are bonded together to form a pn junction compound semiconductor light emitting device.
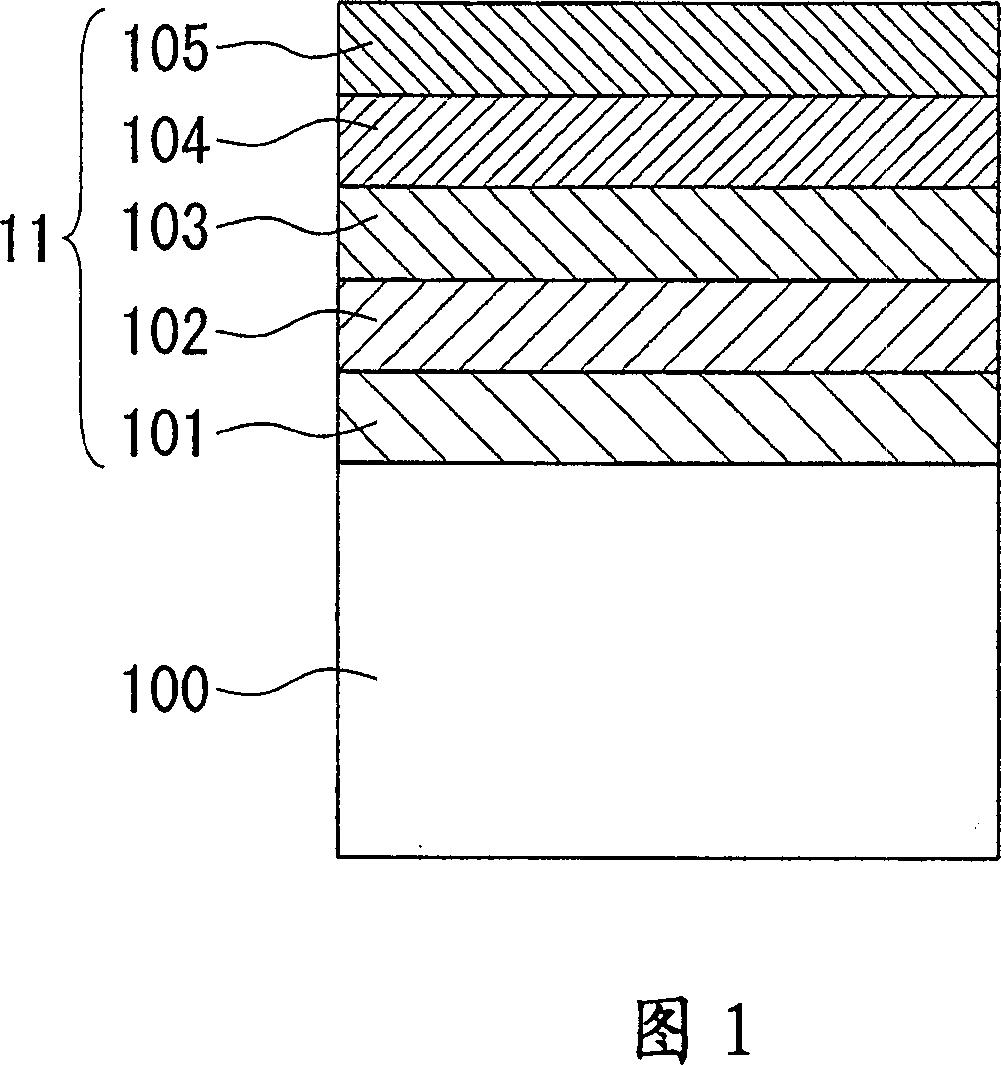
[0170] FIG. 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an exemplary stacked structure 11 having a pn junction double hetero (DH) junction structure and formed on a crystal substrate.
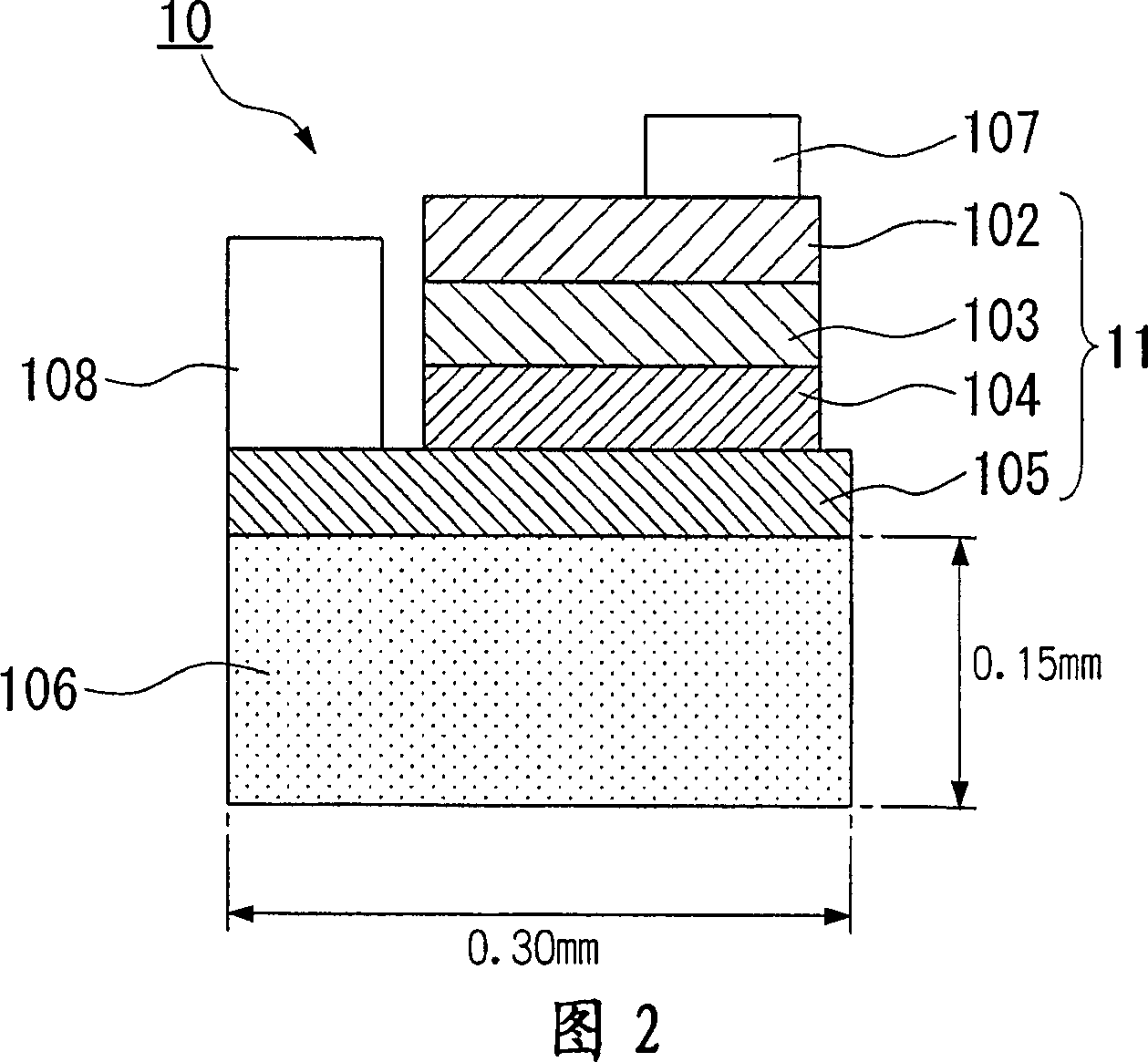
[0171] First, the laminated structure 11 for forming a pn junction compound semiconductor light emitting device 10 (hereinafter this device may be referred to as an LED chip) is formed through the following procedures.
[0172] The stacked structure 11 is formed by sequentially stacking the following layers on the (100) crystal plane of a zinc (Zn)-doped p-type gallium arsenide (GaAs) single crystal substrate 100: a zinc-doped p-type GaAs buffer layer 101, Aluminum gallium indium phosphide mixed crystal ...
example 2
[0206] The difference between the LED chip 20 and the LED of Example 1 is that an undoped n-type boron phosphide layer is provided as the conductor layer 205 .
[0207] The present invention will be described by Example 2 below. The same constituent members as employed in Example 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals.
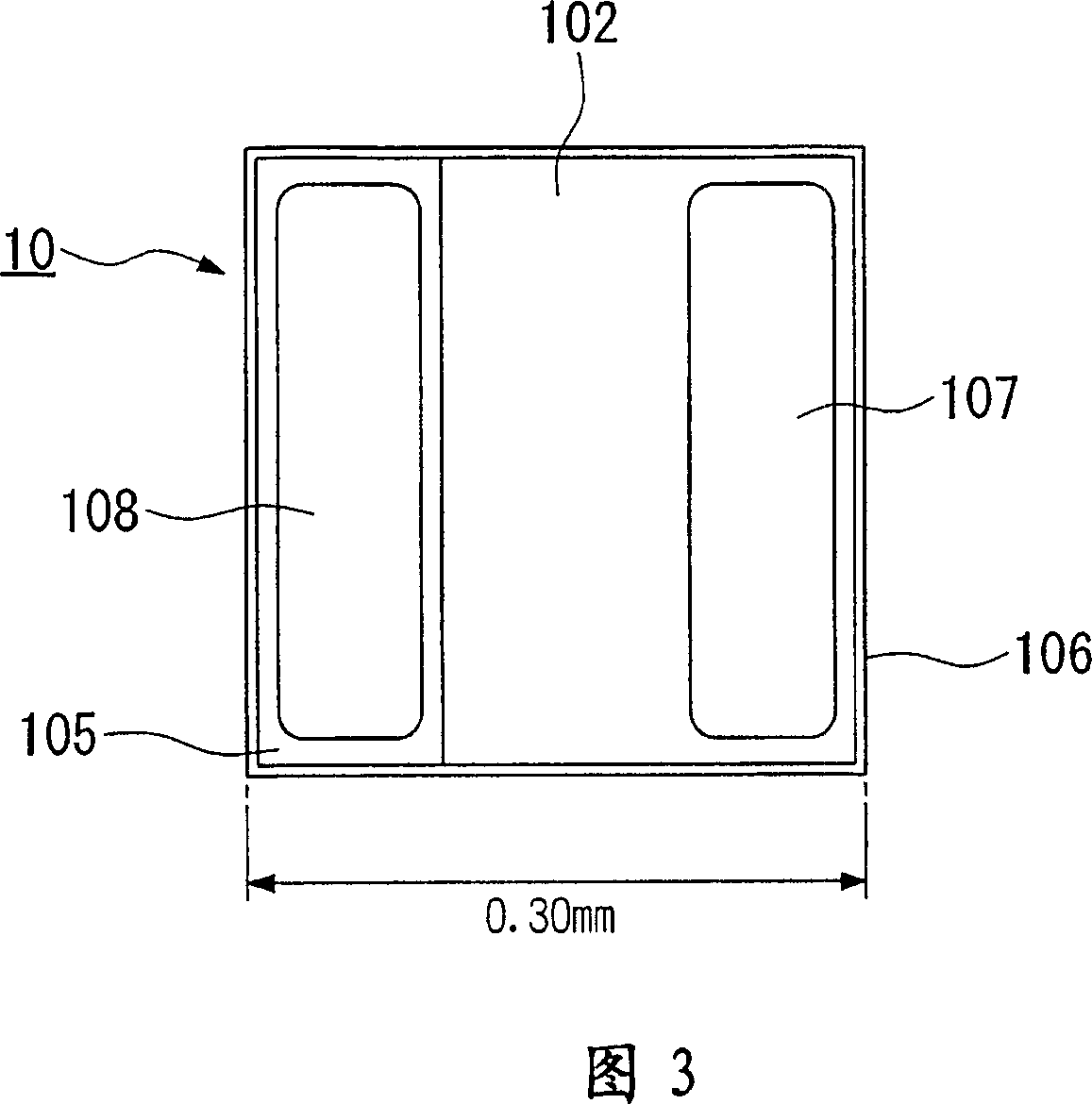
[0208] 5 is a schematic cross-sectional view of an exemplary LED lamp 22 including the LED chip 20 of Example 2. As shown in FIG.
[0209] In a similar manner to Example 1, the constituent layers 101 to 104 of the laminated structure 21 except the conductor layer 205 were formed on the single crystal substrate 100 .
[0210] Next, an undoped n-type boron phosphide (BP) layer is formed on the upper cladding layer 104 as the conductor layer 205 .
[0211] At 800 ° C, by atmospheric pressure (close to atmospheric pressure) metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) method, using triethylborane (molecular formula: (C 2 h 5 ) 3 B) as a source of bor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com