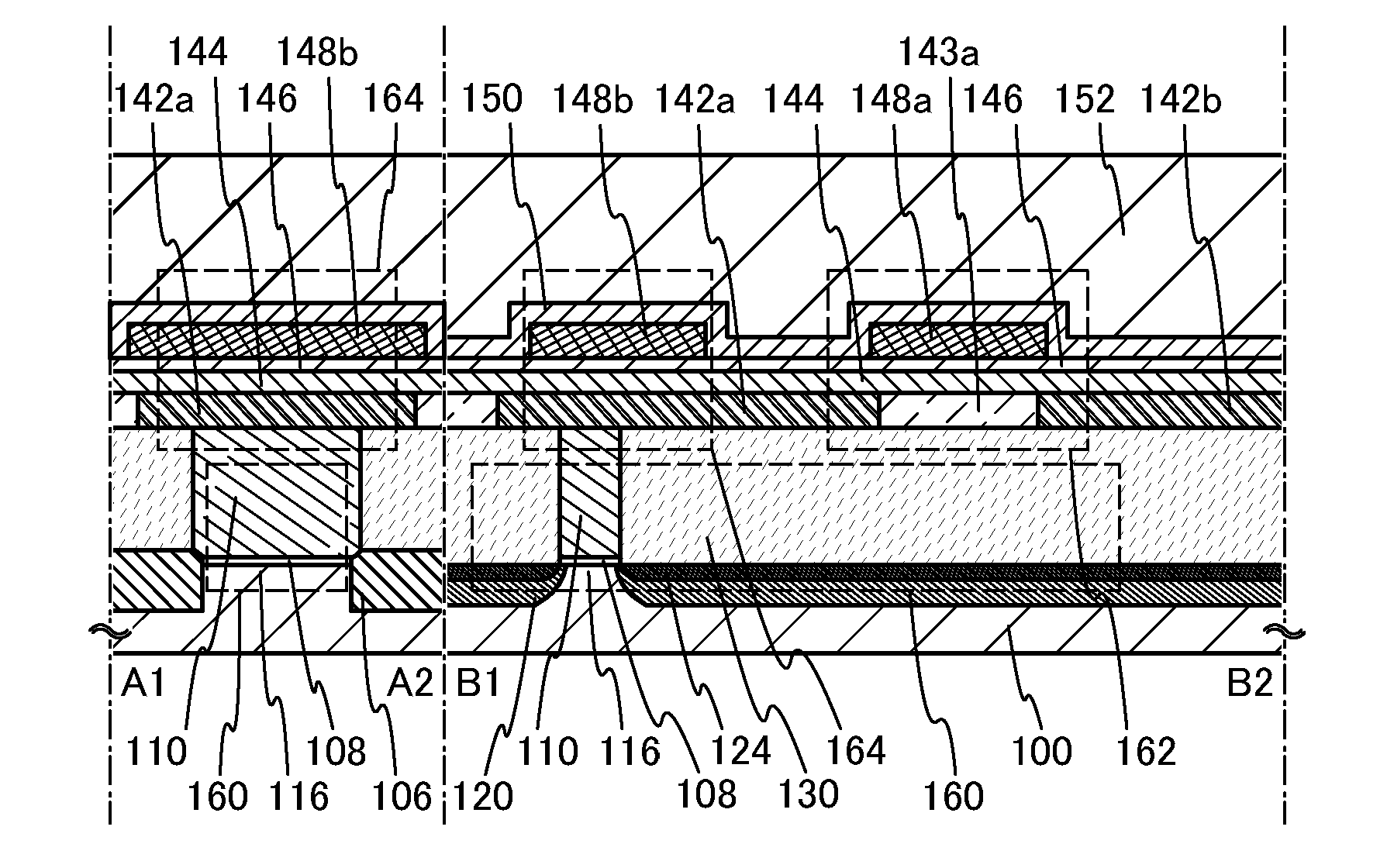
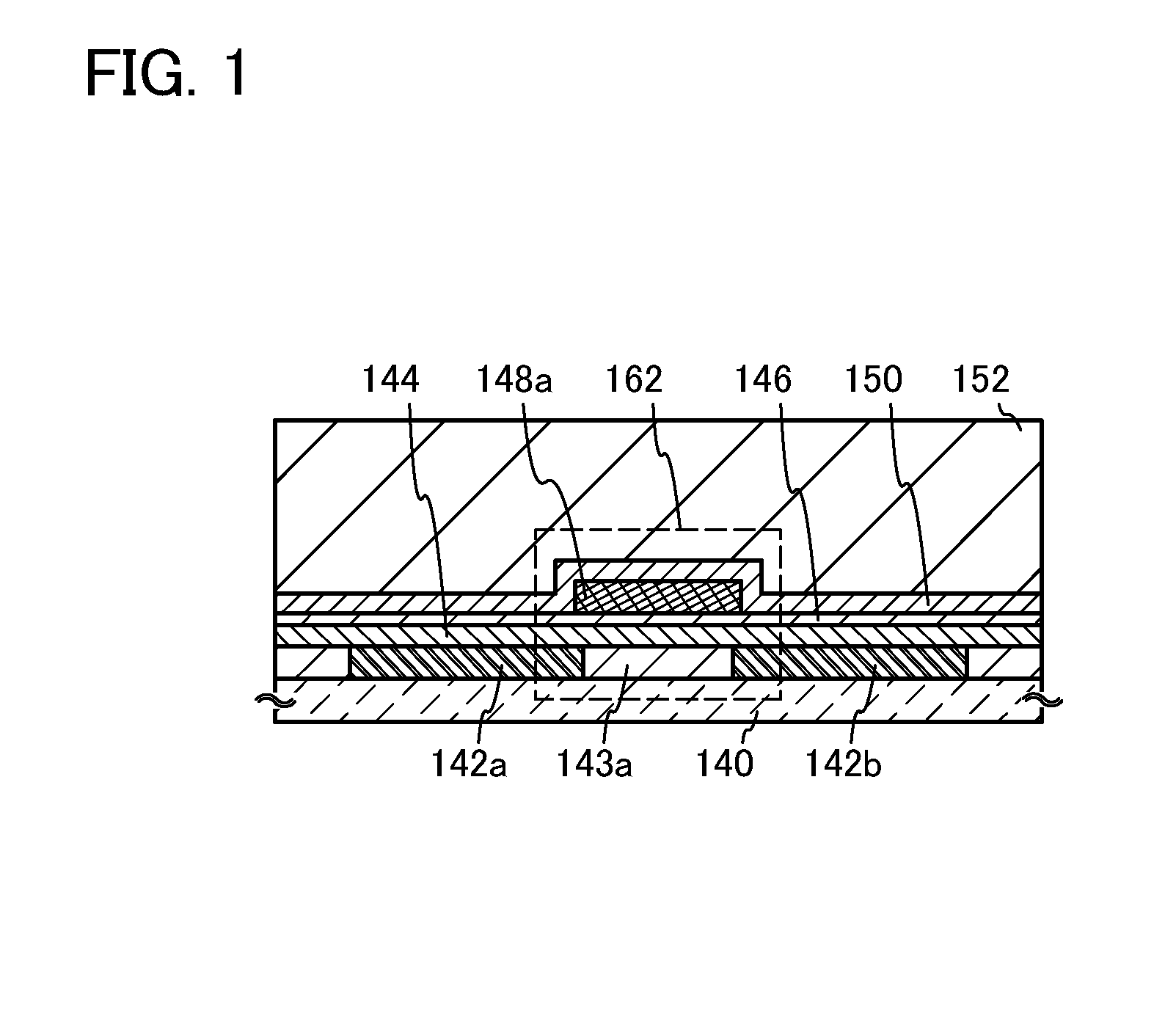
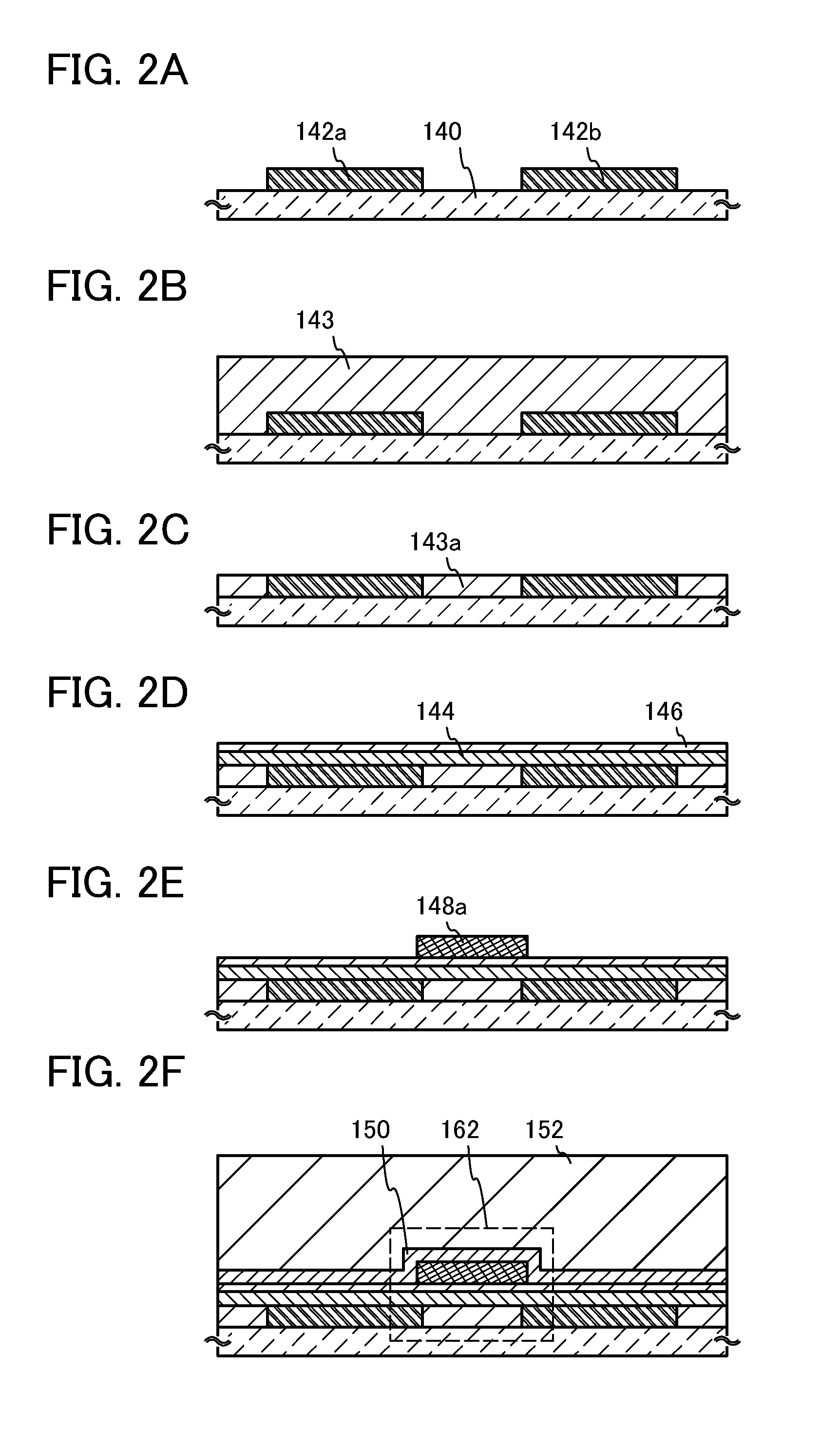
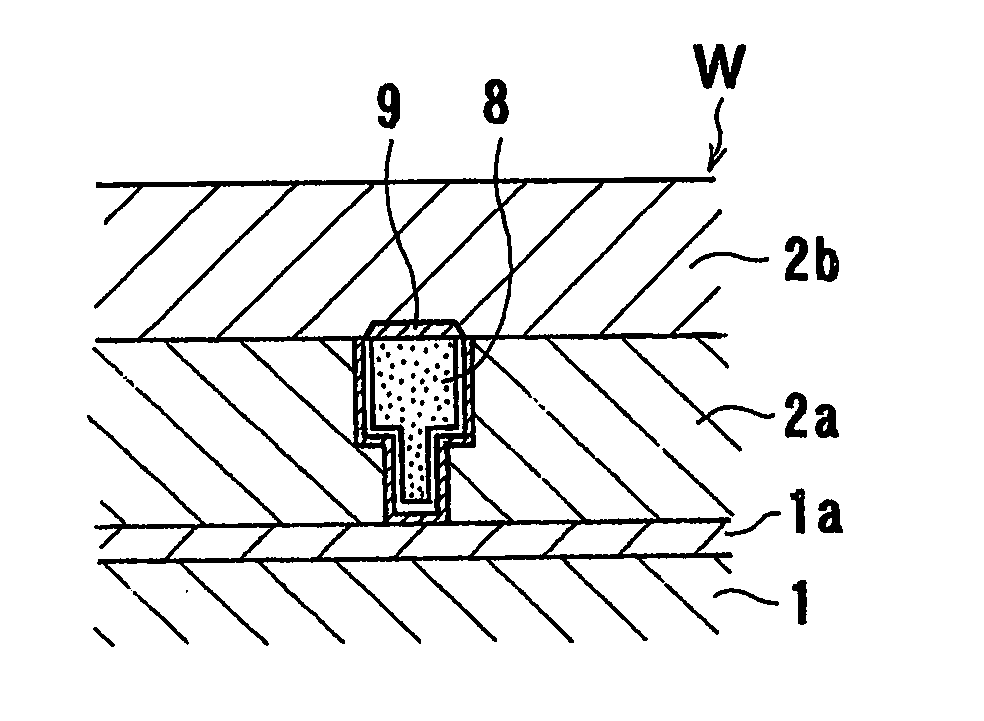
Patents
Literature
171results about How to "Improve surface flatness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
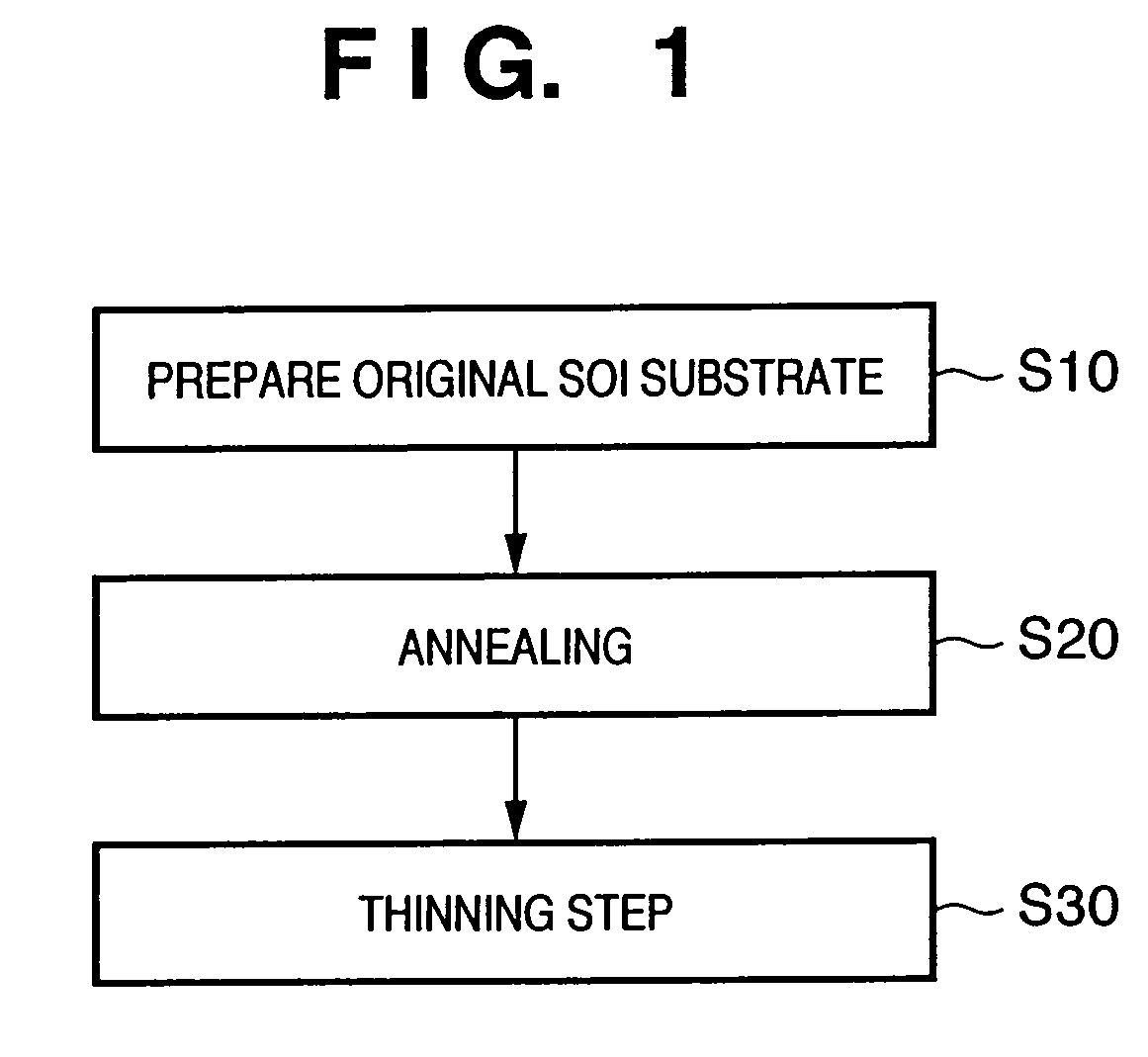
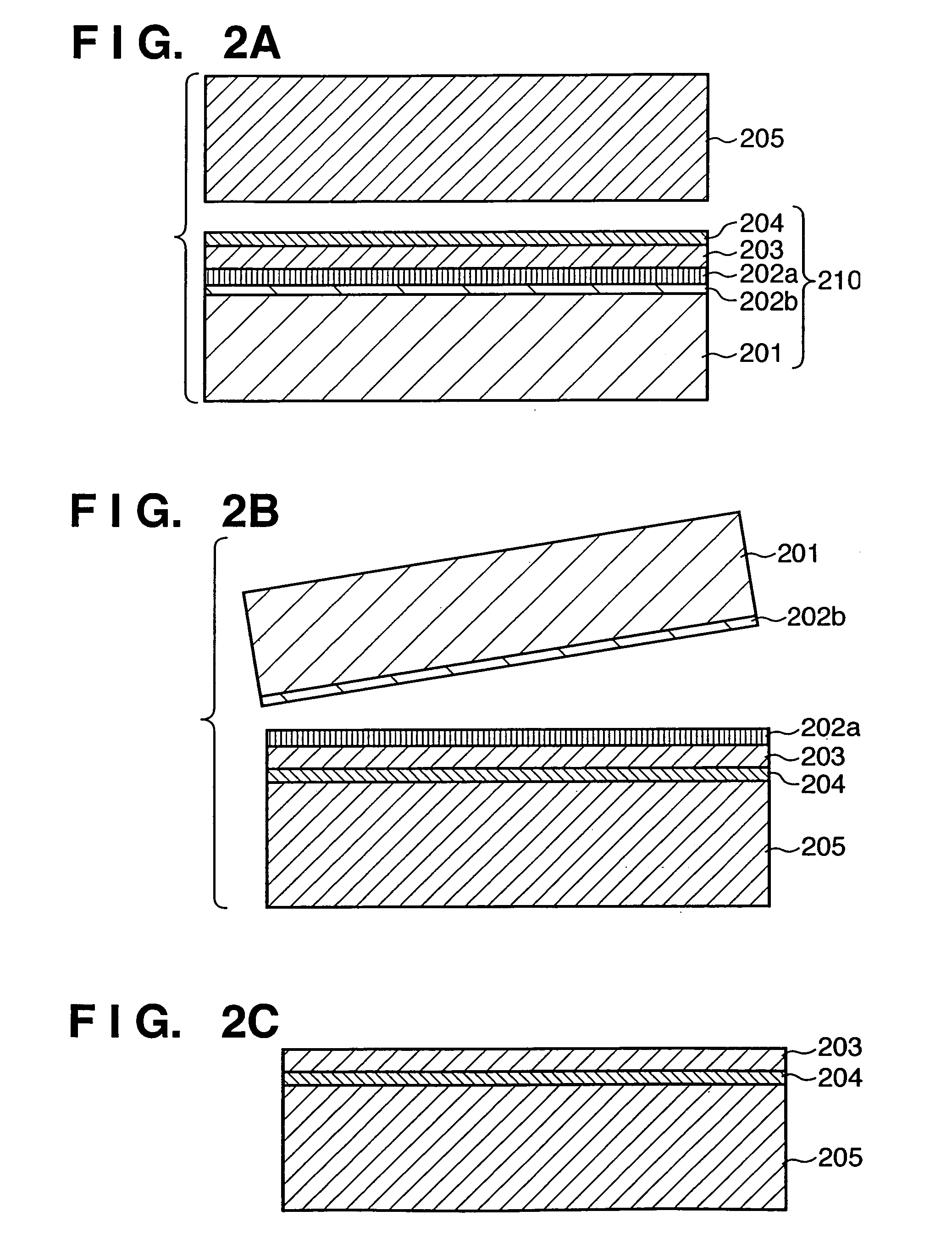
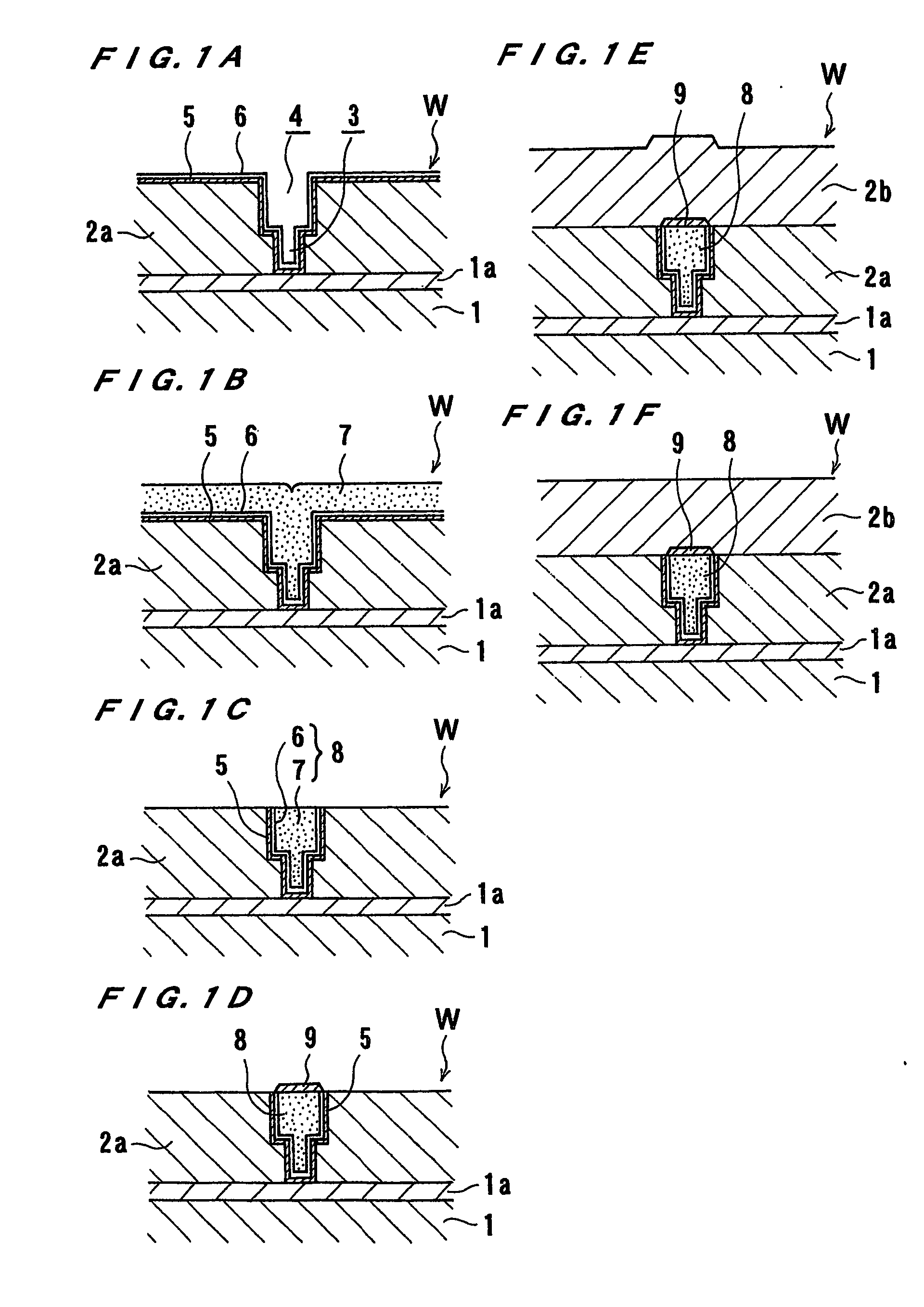
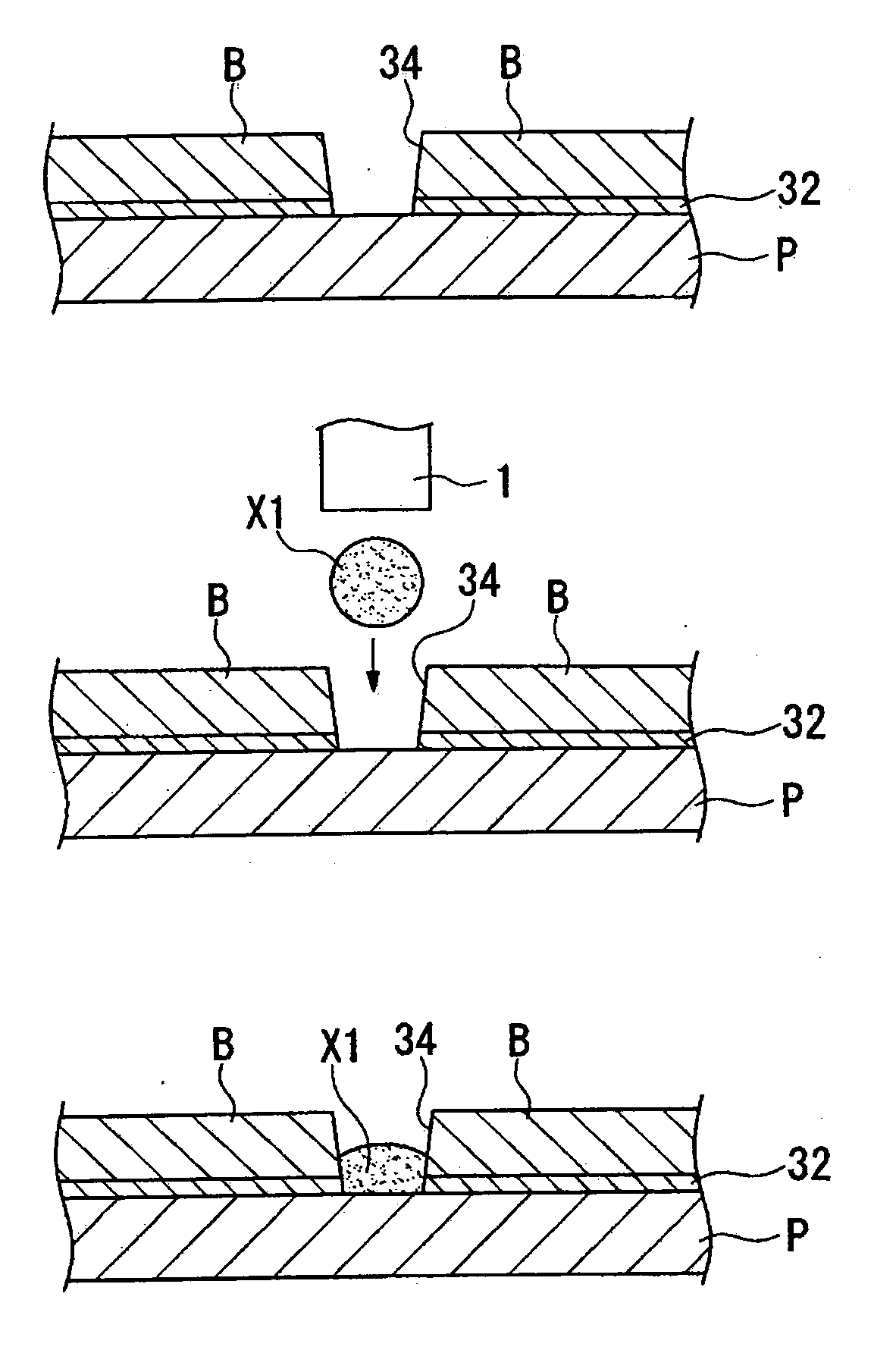
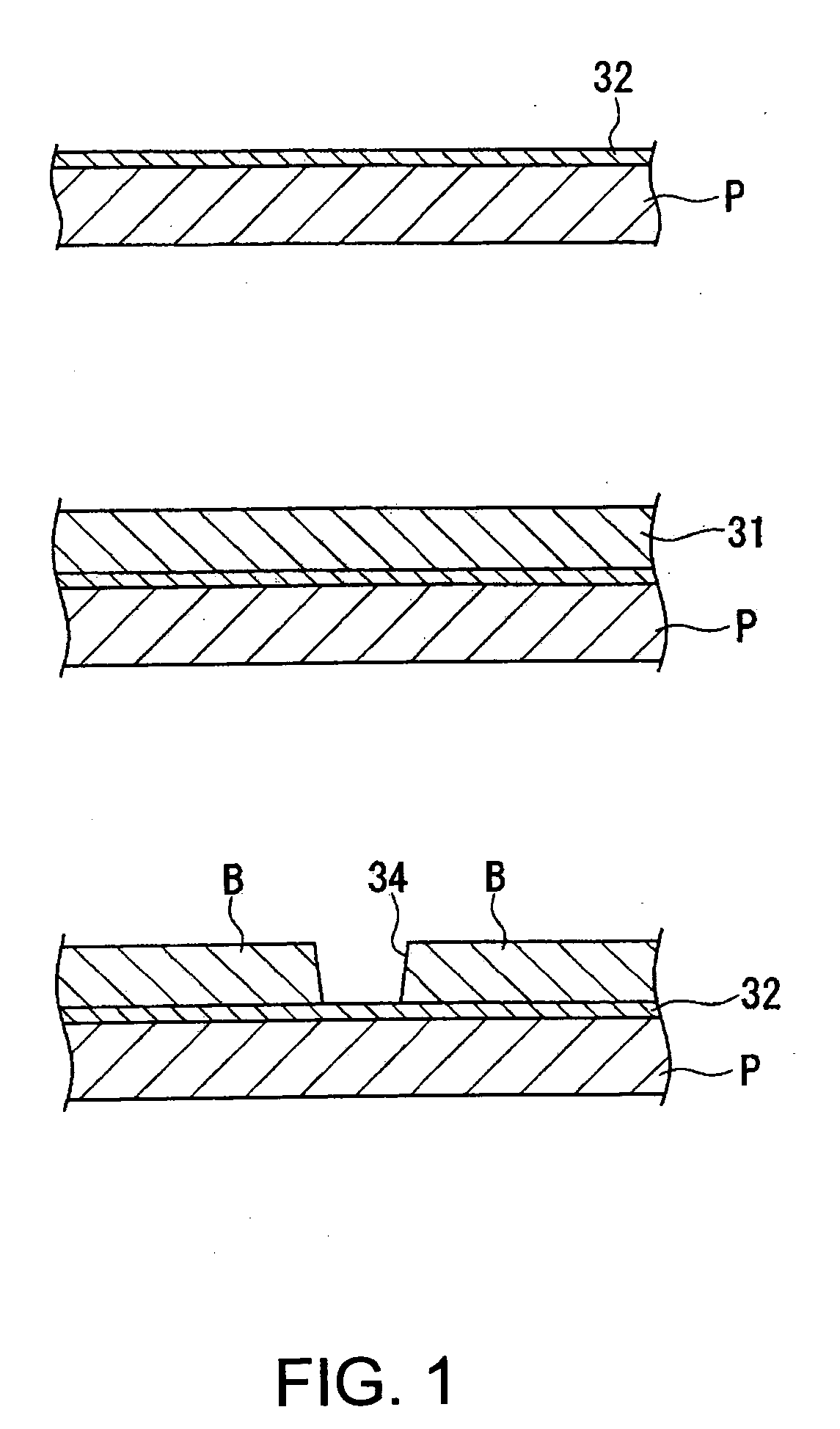
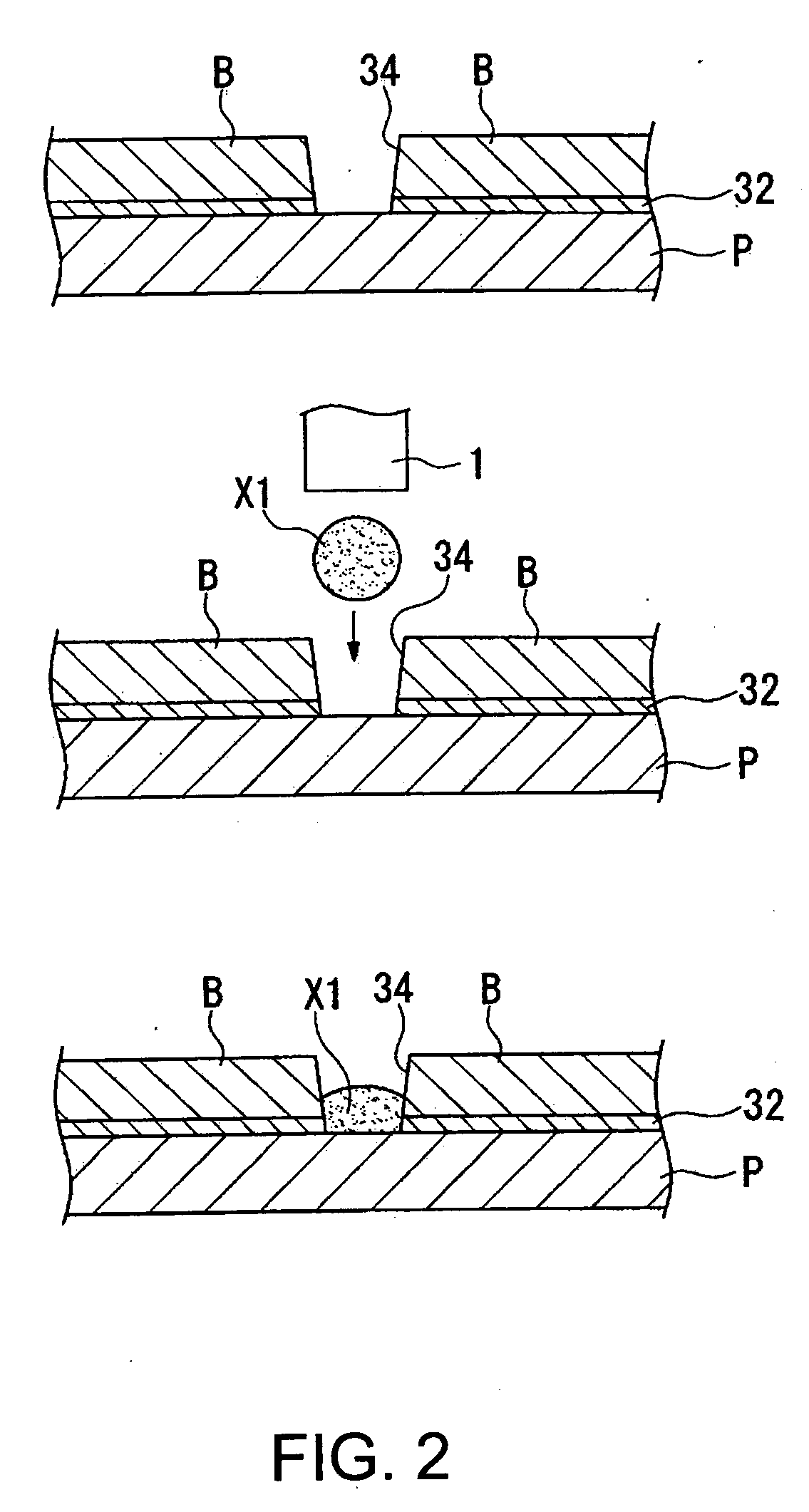
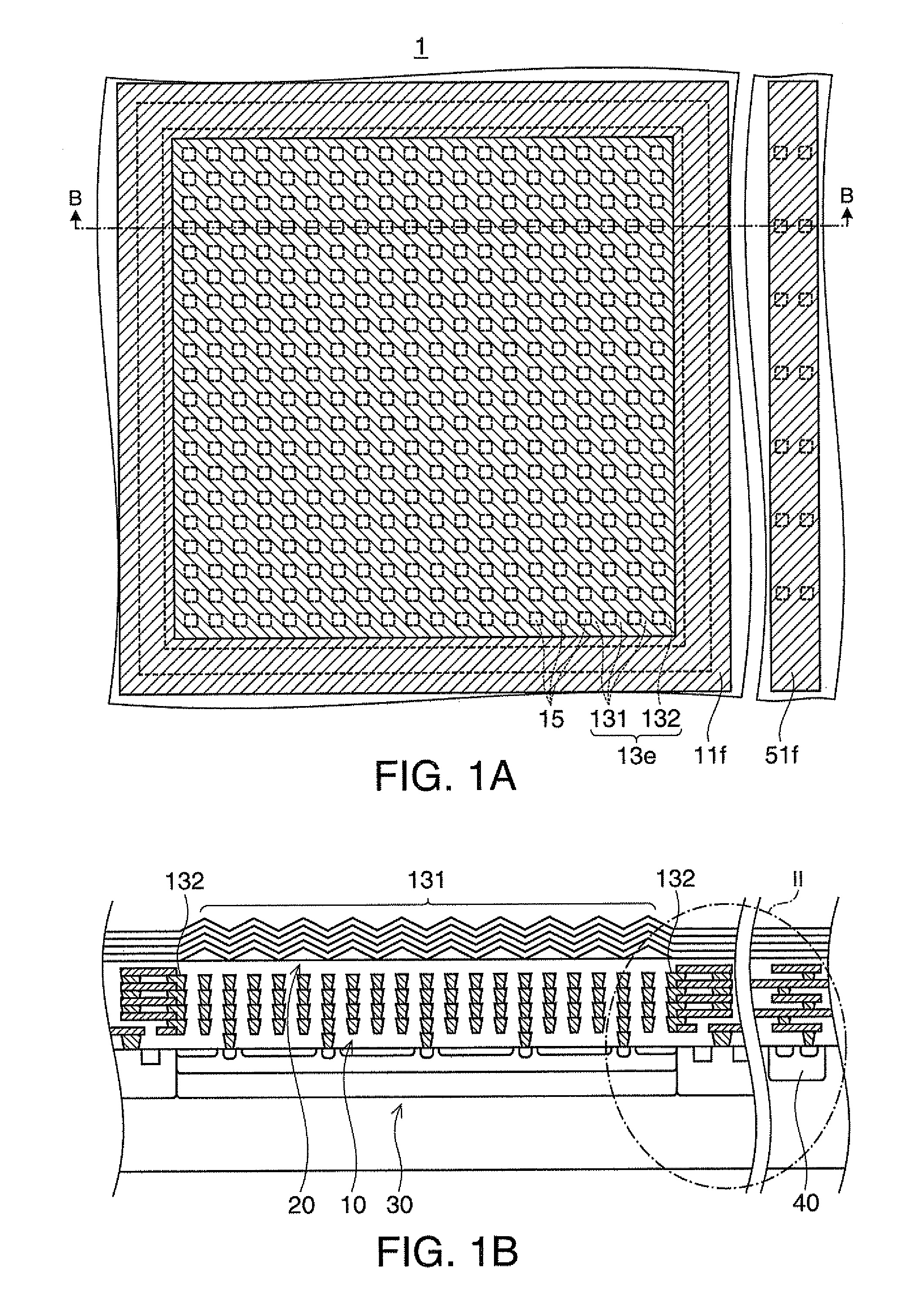
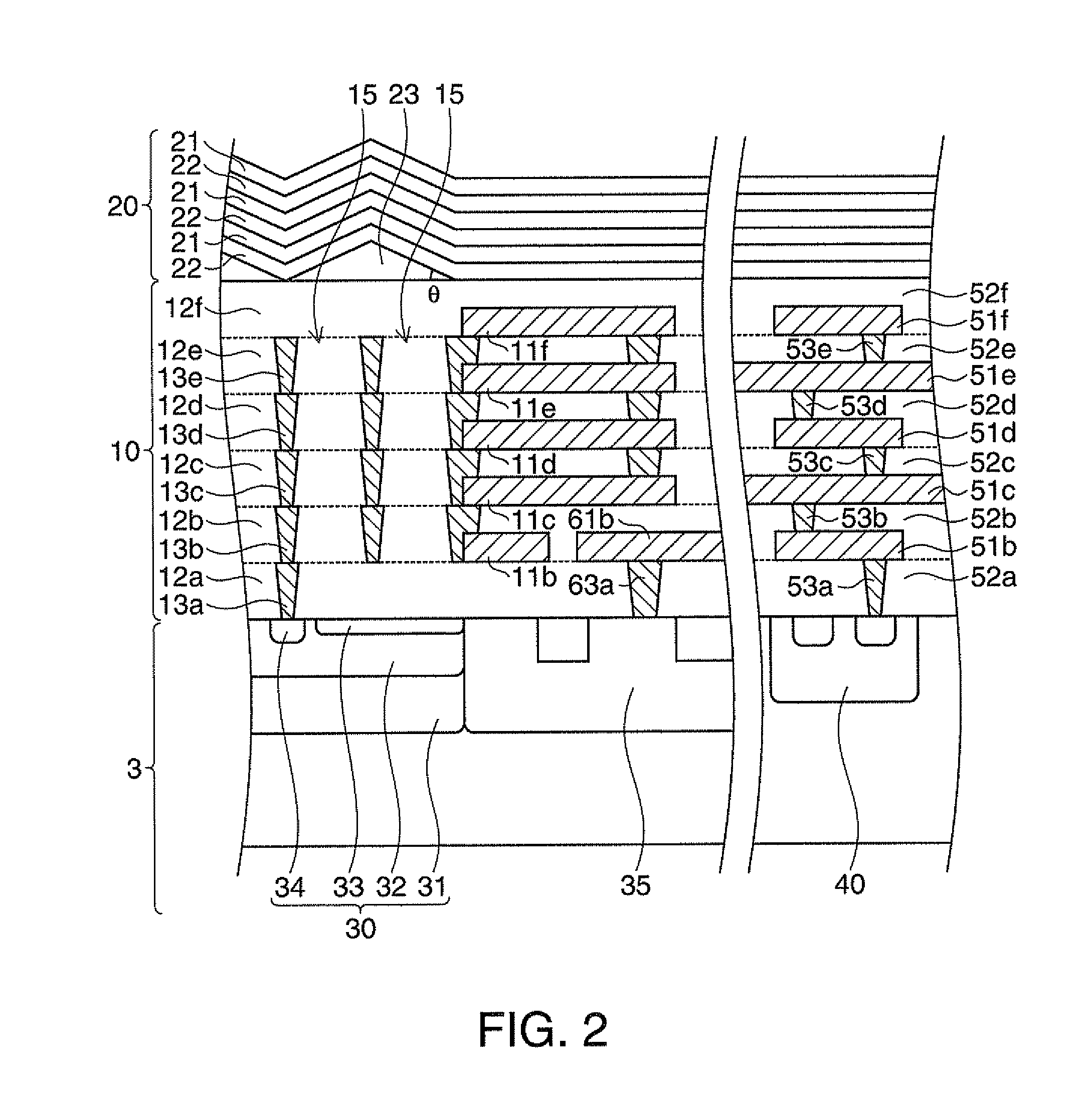
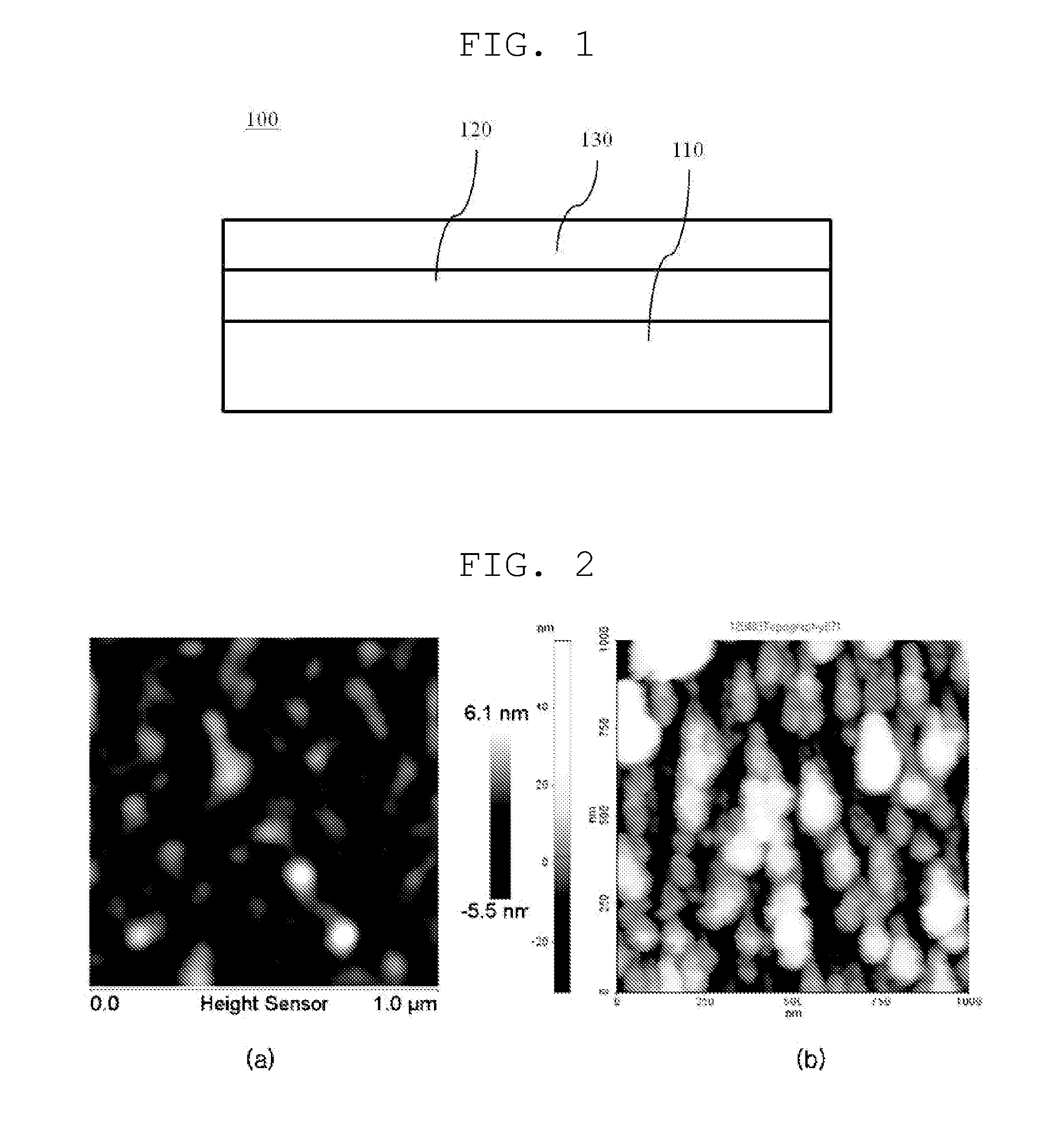
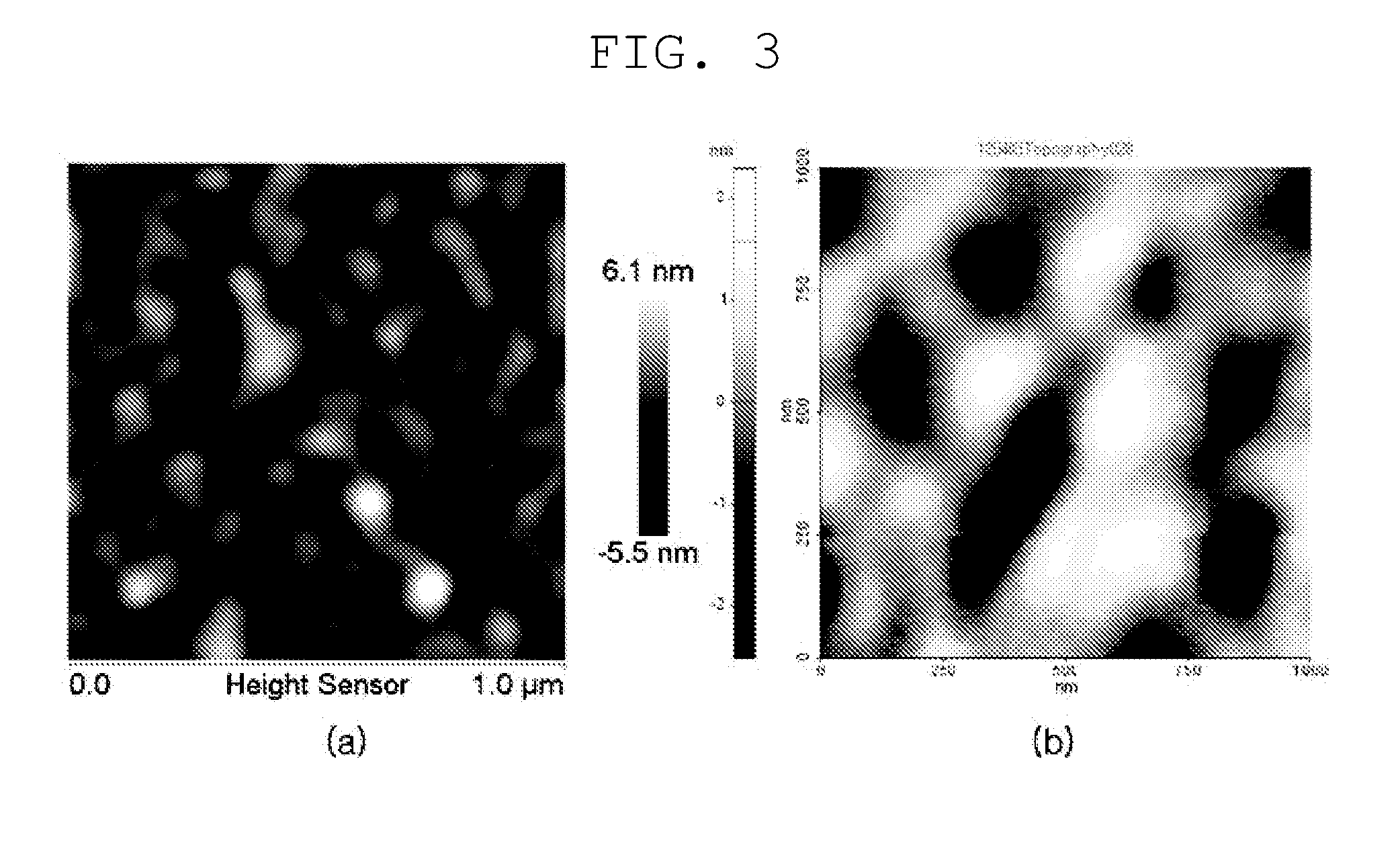
Substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070190746A1Easy thickness controlIncrease flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical solutionSoi substrate
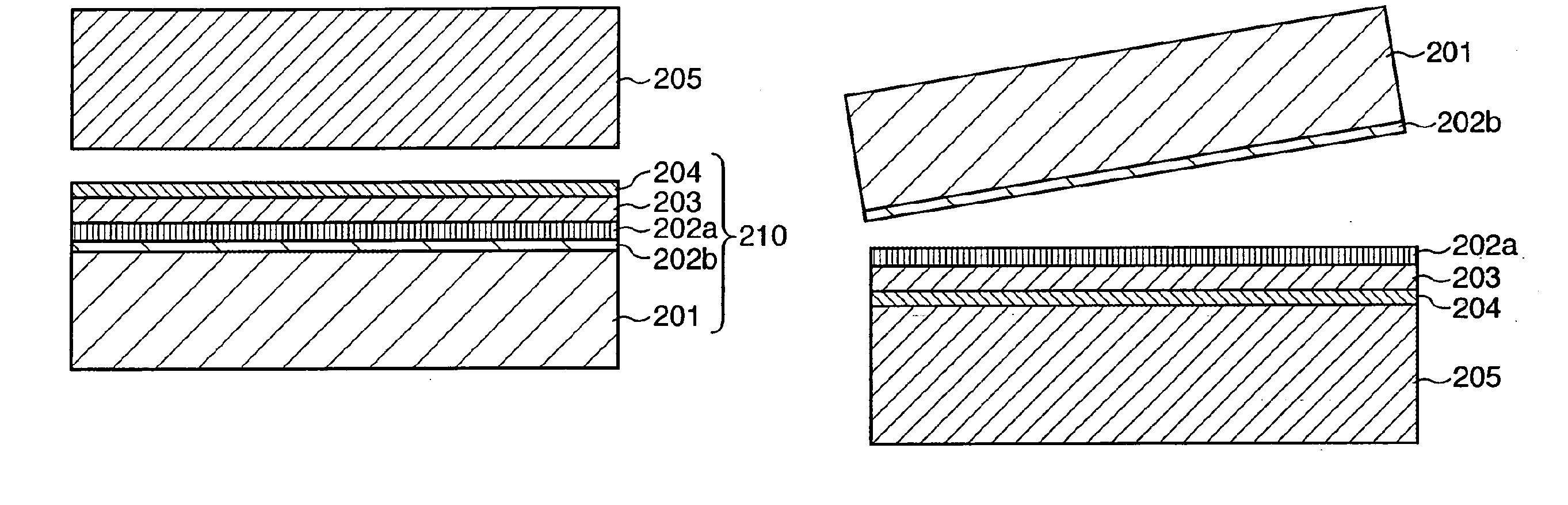
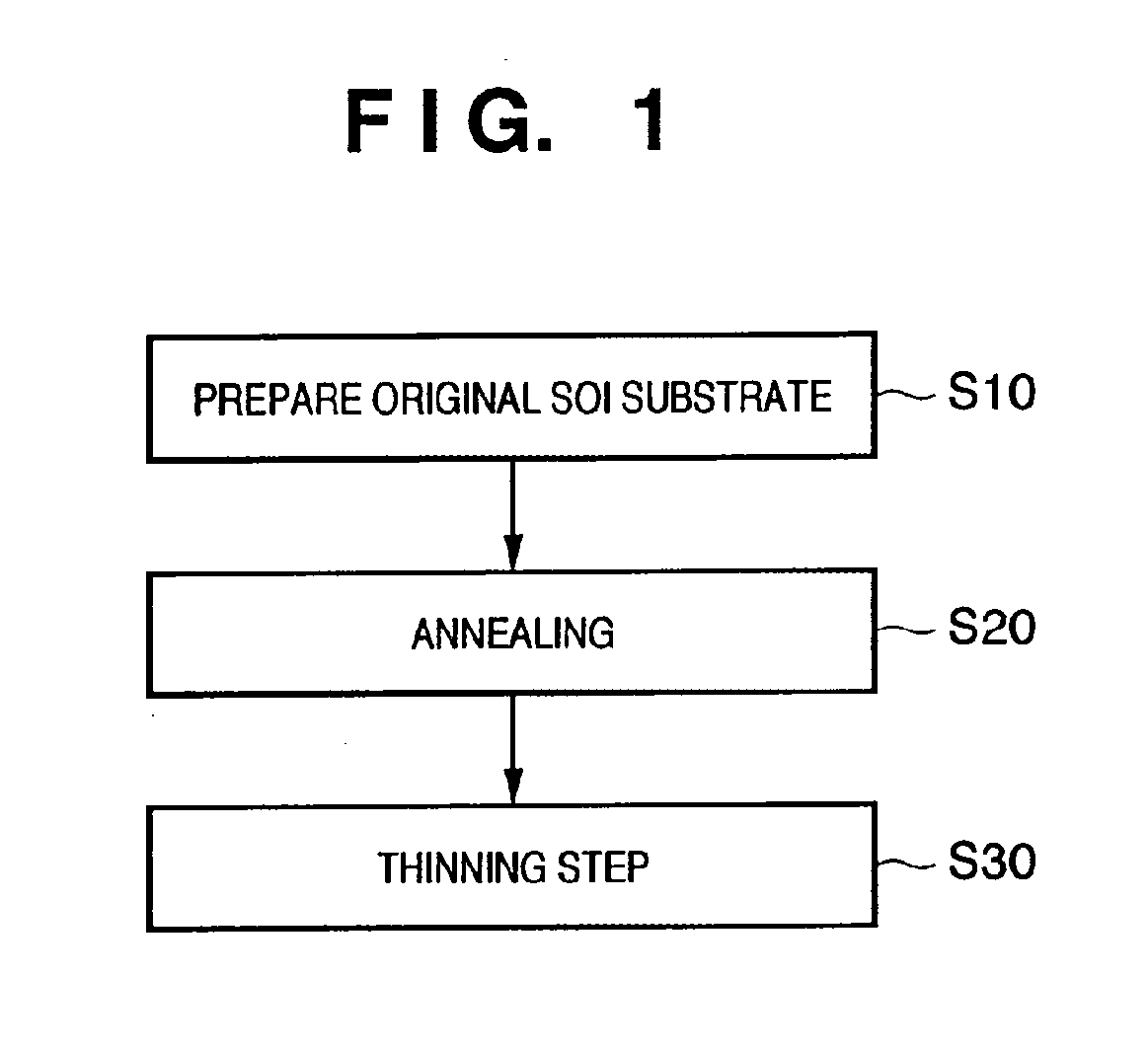
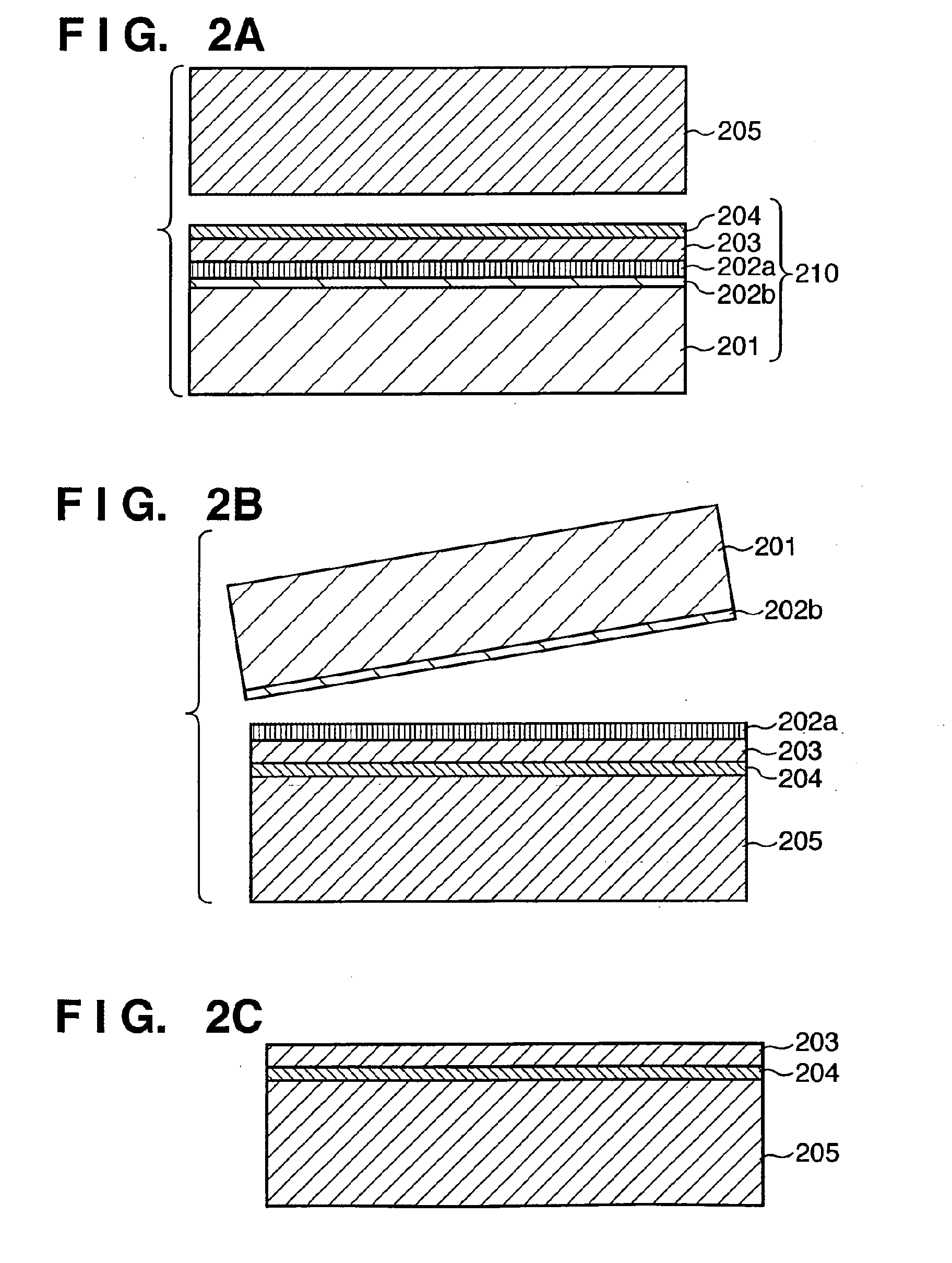
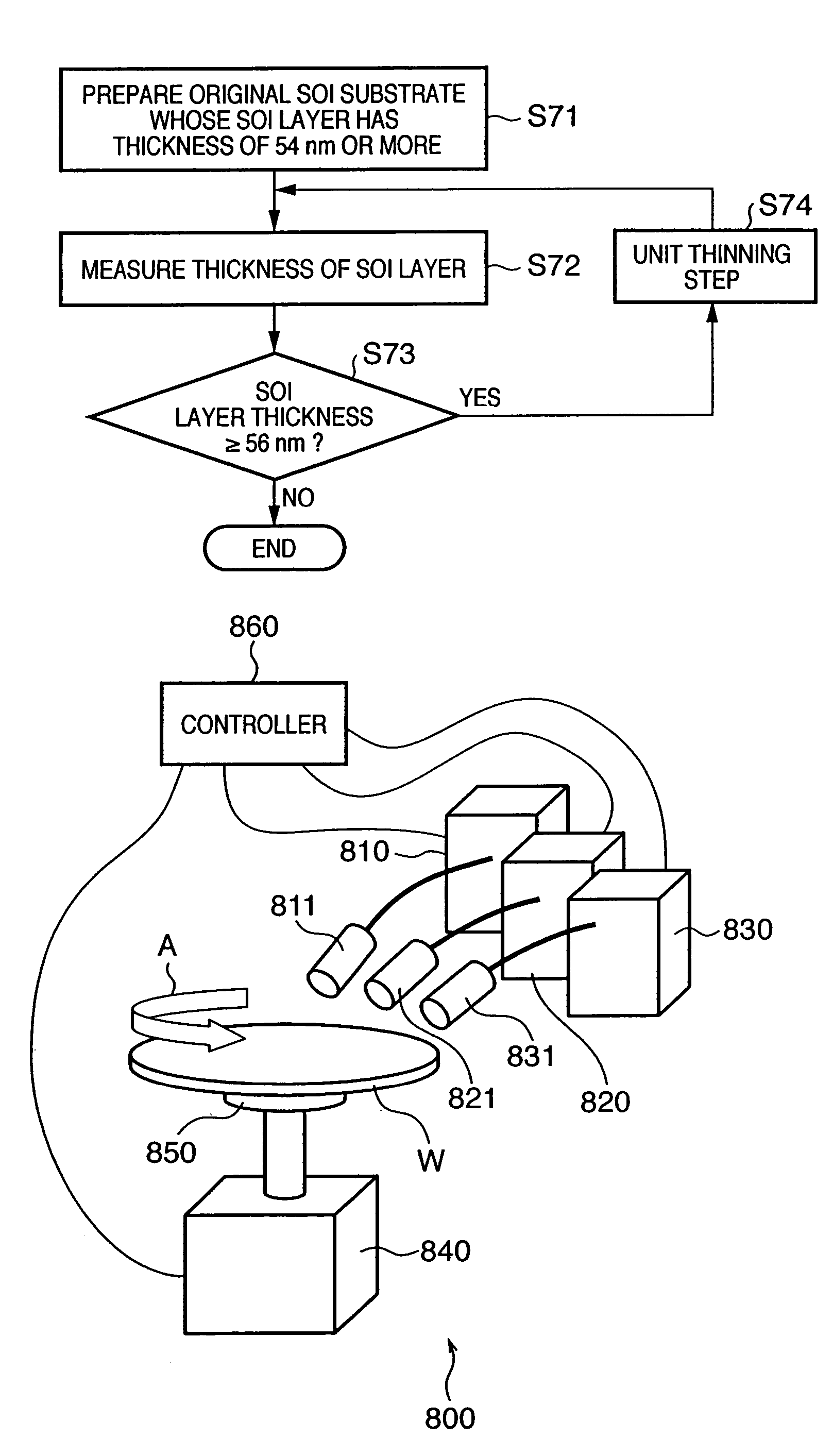
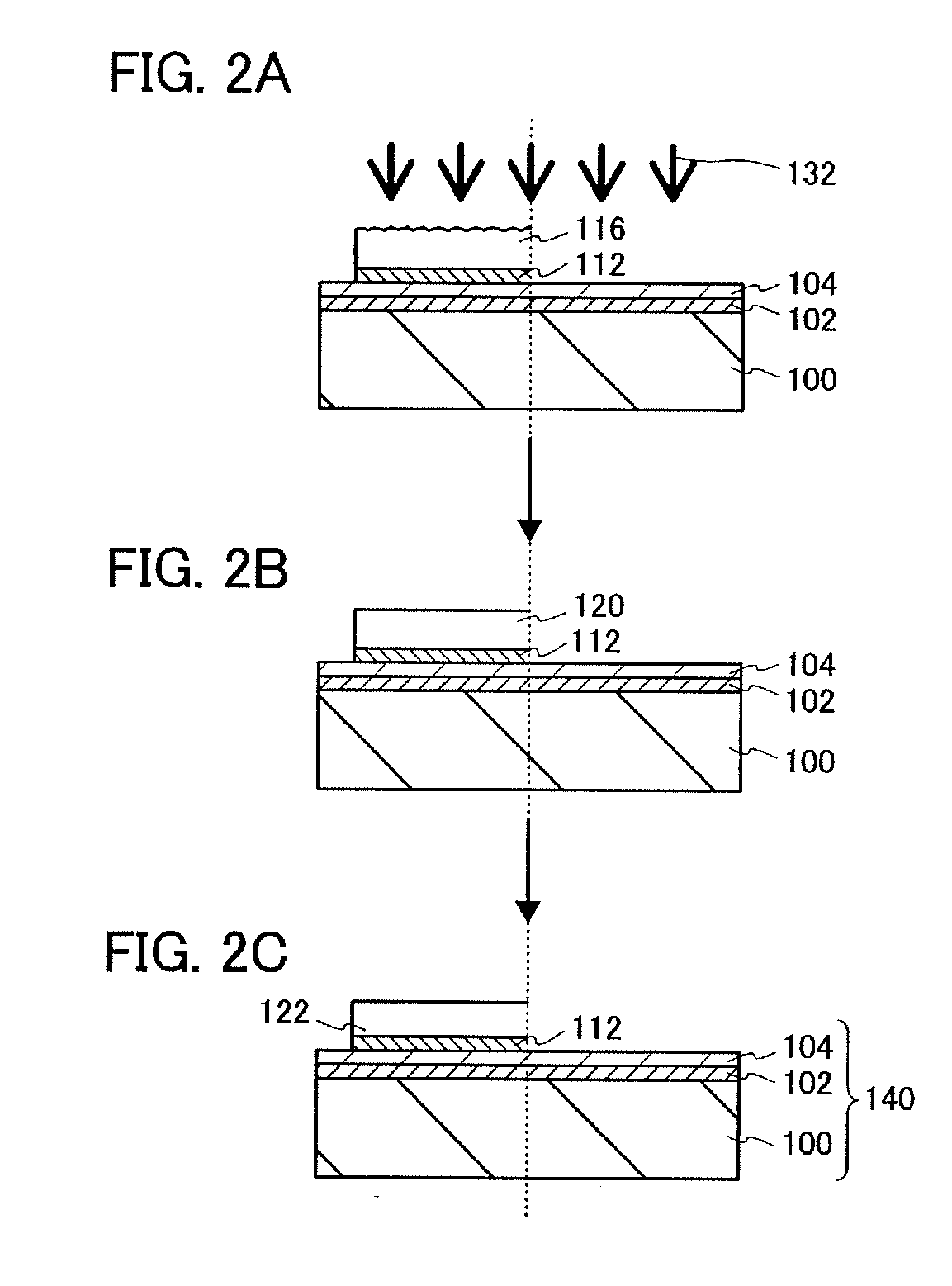
An SOI substrate which has a thick SOI layer is first prepared. Then, the SOI layer is thinned to a target film thickness using as a unit a predetermined thickness not more than that of one lattice. This thinning is performed by repeating a unit thinning step which includes an oxidation step of oxidizing the surface of the SOI layer by the predetermined thickness not more than that of one lattice and a removal step of selectively removing silicon oxide formed by the oxidation. The SOI layer of the SOI substrate is chemically etched by supplying a chemical solution to the SOI layer, and the film thickness of the etched SOI layer is measured. When the measured film thickness of the SOI layer has a predetermined value, a process of chemically etching the SOI layer ends.
Owner:CANON KK
Substrate manufacturing method and substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS7256104B2Easy thickness controlIncrease flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical solutionSoi substrate
An SOI substrate which has a thick SOI layer is first prepared. Then, the SOI layer is thinned to a target film thickness using as a unit a predetermined thickness not more than that of one lattice. This thinning is performed by repeating a unit thinning step which includes an oxidation step of oxidizing the surface of the SOI layer by the predetermined thickness not more than that of one lattice and a removal step of selectively removing silicon oxide formed by the oxidation. The SOI layer of the SOI substrate is chemically etched by supplying a chemical solution to the SOI layer, and the film thickness of the etched SOI layer is measured. When the measured film thickness of the SOI layer has a predetermined value, a process of chemically etching the SOI layer ends.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device, semiconductor device and electronic appliance
InactiveUS20090134397A1Guaranteed high speed operationReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriver circuitDevice material
A non-single-crystal semiconductor layer is formed over a substrate, and then a single crystal semiconductor layer is formed over part of the non-single-crystal semiconductor layer. Thus, a semiconductor element of a region which requires a large area (e.g. a pixel region in a display device) can be formed using the non-single-crystal semiconductor layer, and a semiconductor element of a region which requires high speed operation (e.g. a driver circuit region in a display device) can be formed using the single crystal semiconductor layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Flash-preventing window ball grid array semiconductor package, method for fabricating the same, and chip carrier used in the semiconductor package
InactiveUS6870274B2High viscosityReduce flow rateTelevision system detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder ballEngineering
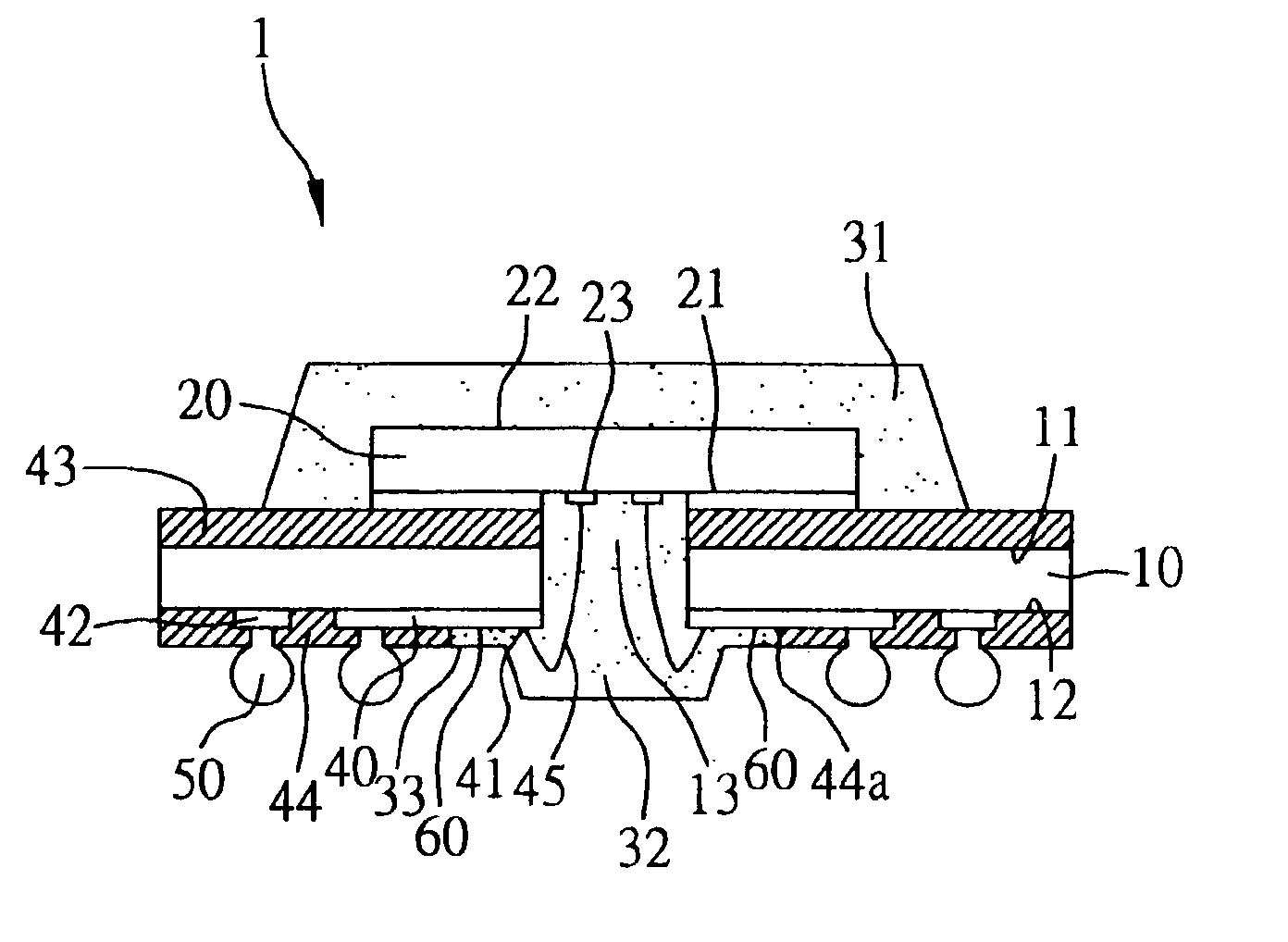
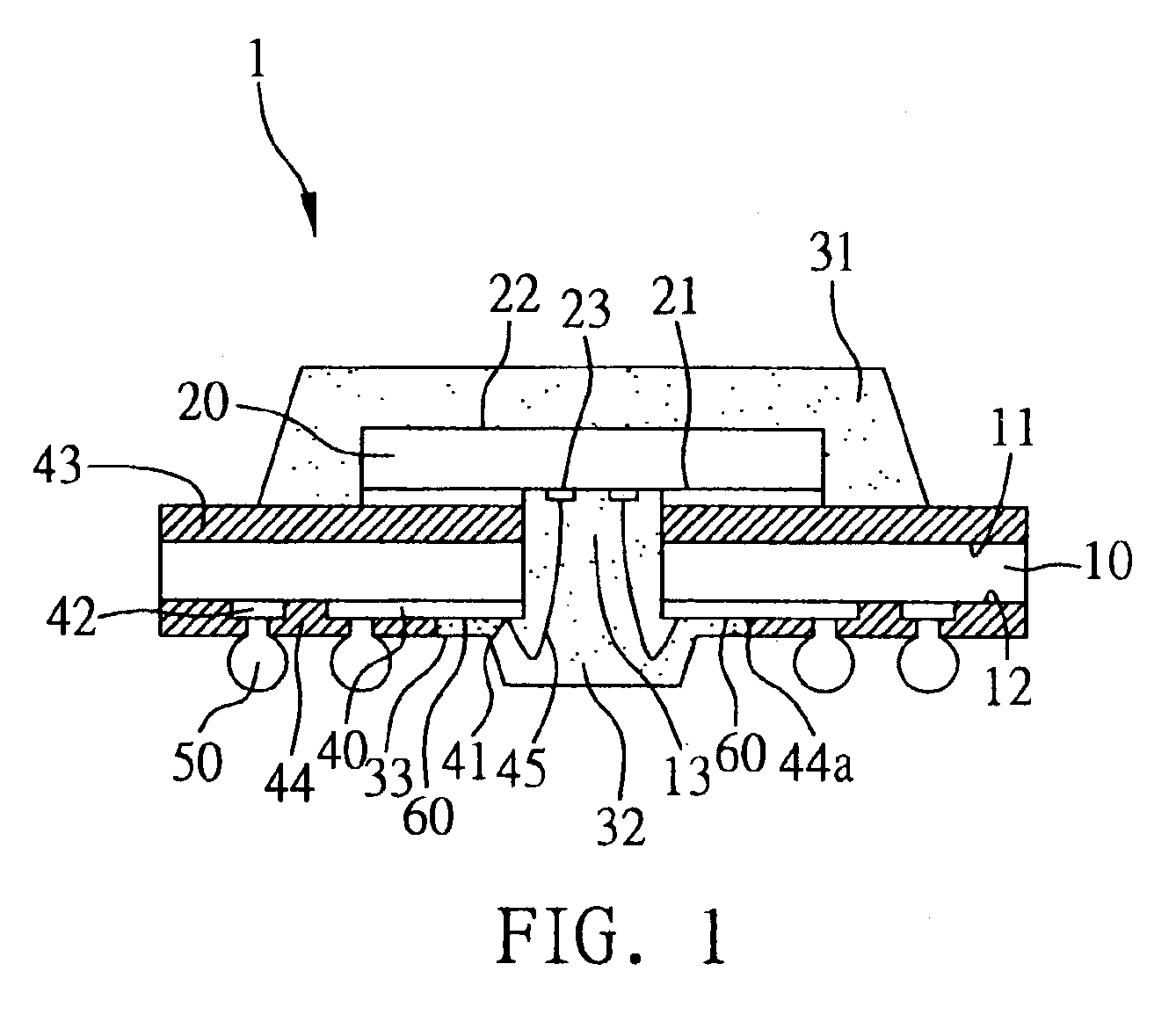
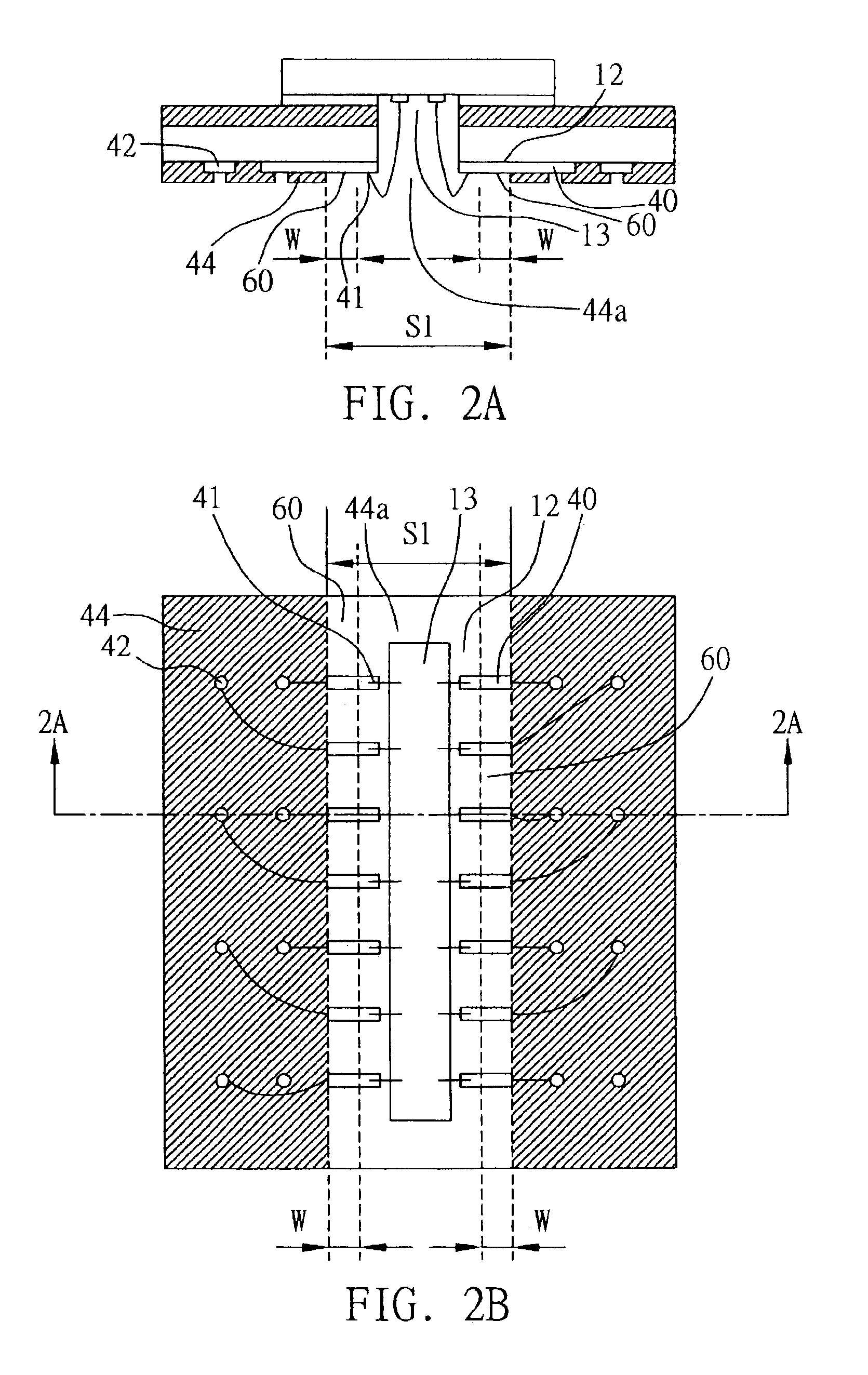
A flash-preventing window ball grid array semiconductor package, a method for fabricating the same, and a chip carrier used in the semiconductor package are provided. The chip carrier has a through hole and has a surface formed with a plurality of wire-bonding portions, ball-bonding portions and intended-exposing regions. A chip is mounted over the through hole and electrically connected to the wire-bonding portions by a plurality of bonding wires penetrating through the through hole. An encapsulation body encapsulates the chip and bonding wires. The intended-exposing regions serve as a narrow runner which is filled with an encapsulating material forming the encapsulation body, making the encapsulating material not flash over the ball-bonding portions. This allows a plurality of solder balls to be well bonded to the ball-bonding portions, thereby assuring the quality of electrical connection and the surface planarity of the semiconductor package.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110215326A1Inhibition effectImprove featuresTransistorSolid-state devicesMiniaturizationEngineering
Disclosed is a semiconductor device including: an insulating layer; a source electrode and a drain electrode embedded in the insulating layer; an oxide semiconductor layer in contact and over the insulating layer, the source electrode, and the drain electrode; a gate insulating layer over and covering the oxide semiconductor layer; and a gate electrode over the gate insulating layer, where the upper surfaces of the insulating layer, the source electrode, and the drain electrode exist coplanarly. The upper surface of the insulating layer, which is in contact with the oxide semiconductor layer, has a root-mean-square (RMS) roughness of 1 nm or less, and the difference in height between the upper surface of the insulating layer and the upper surface of the source electrode or the drain electrode is less than 5 nm. This structure contributes to the suppression of defects of the semiconductor device and enables their miniaturization.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
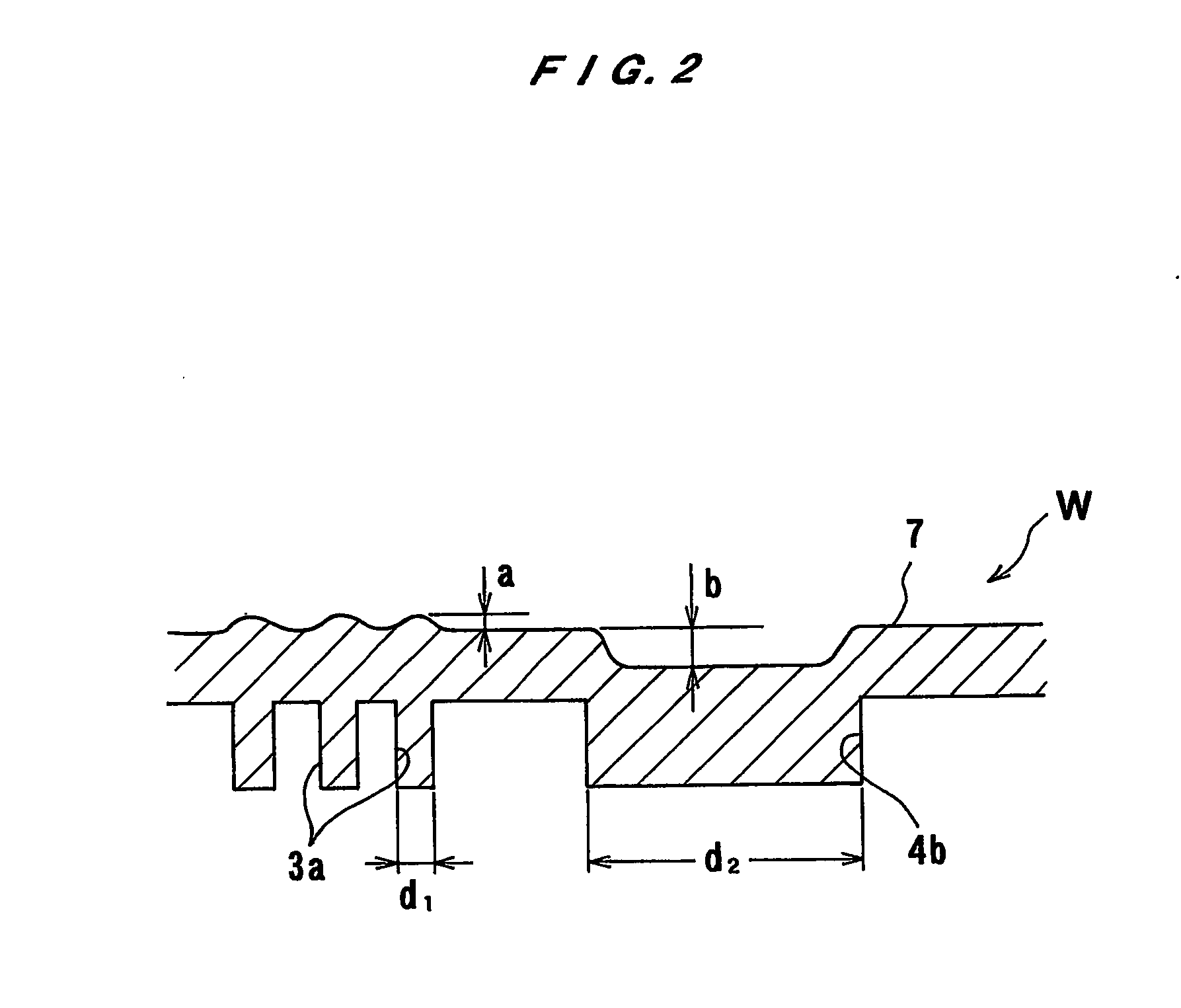
Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method
InactiveUS20060234508A1Reduce loadSufficient flatnessElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials scienceElectrolysis
There is provided a substrate processing apparatus which can process a substrate by using an electrolytic processing method, while reducing a load upon a CMP processing to the least possible extent. The substrate processing apparatus of the present invention includes: an electrolytic processing unit (36) for electrolytically removing the surface of the substrate W having a to-be-processed film formed in said surface, said unit including a feeding section (373) that comes into contact with said surface of the substrate W; a bevel-etching unit (48) for etching away the to-be-processed film remaining unprocessed at the portion of the substrate that has been in contact with the feeding section (373) in the electrolytic processing unit (36); a chemical mechanical polishing unit (34) for chemically and mechanically polishing the surface of the substrate.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Photosensitive polysiloxane composition and uses thereof
InactiveUS20150031808A1Improve surface flatnessHigh transparencyPhotosensitive material processingSilyleneSolvent
The invention relates to a photosensitive polysiloxane composition and a thin film formed by the aforementioned photosensitive polysiloxane composition. The thin film is a planarization film of a TFT substrate, an interlayer insulating film or an overcoat of a core material or a protective material in a waveguide. The invention is to provide a photosensitive polysiloxane composition having excellent surface flatness and high tapered angle of a pattern. The photosensitive polysiloxane composition comprises a polysiloxane (A), an o-naphthoquinone diazide sulfonic acid ester (B), an alkali-soluble resin containing a silyl group (C) and a solvent (D).
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Method for fabricating electro-optic light modulator
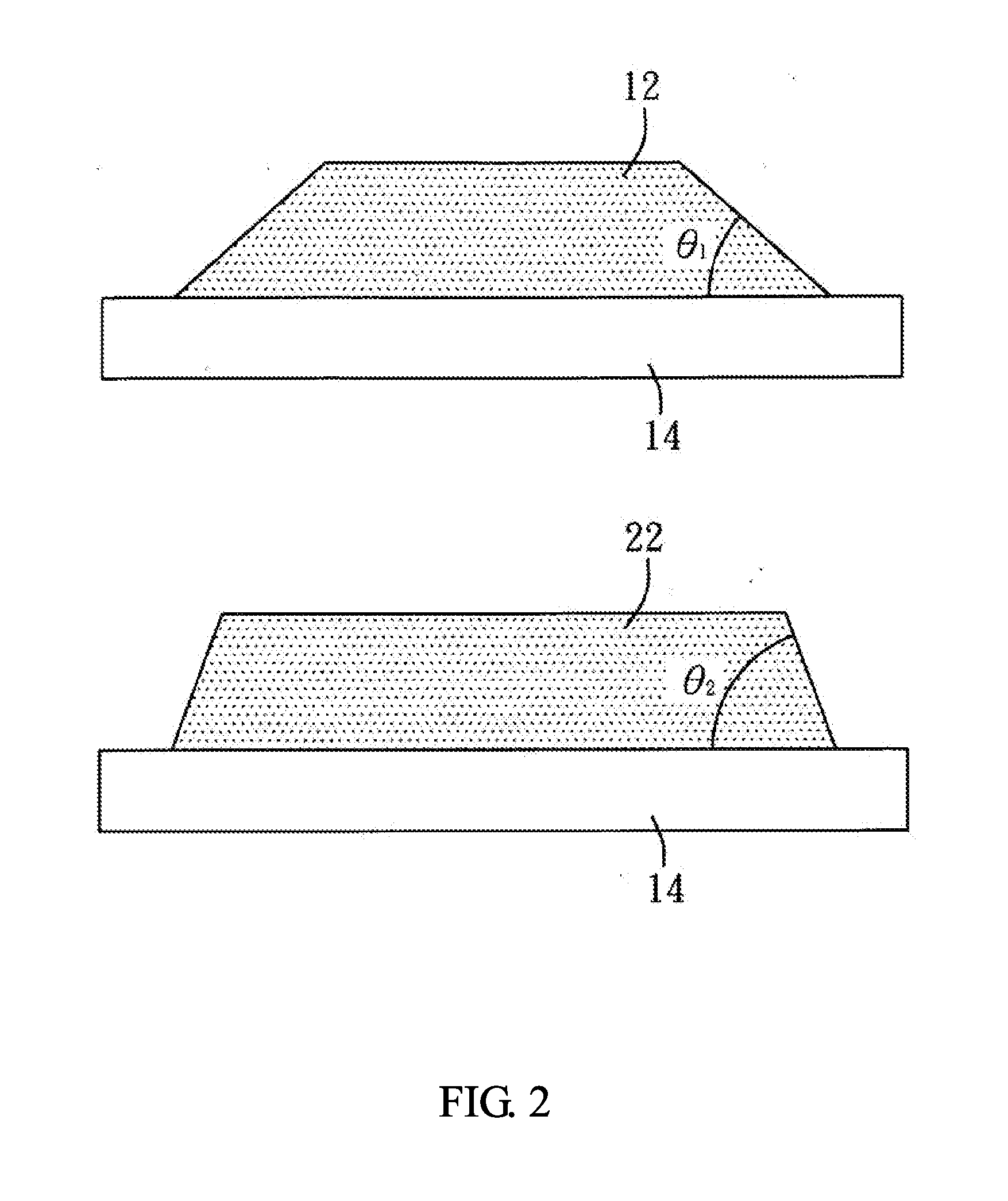
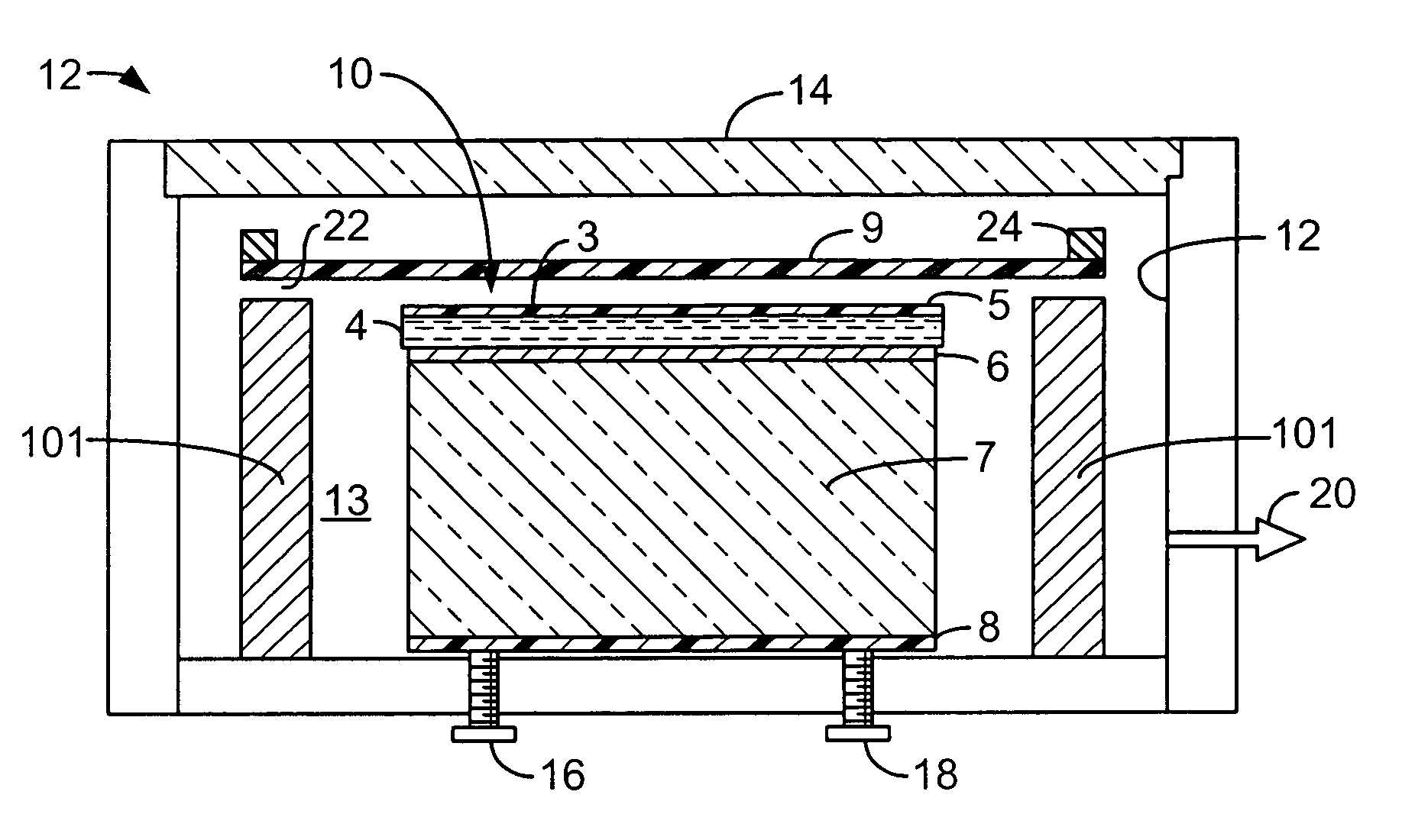
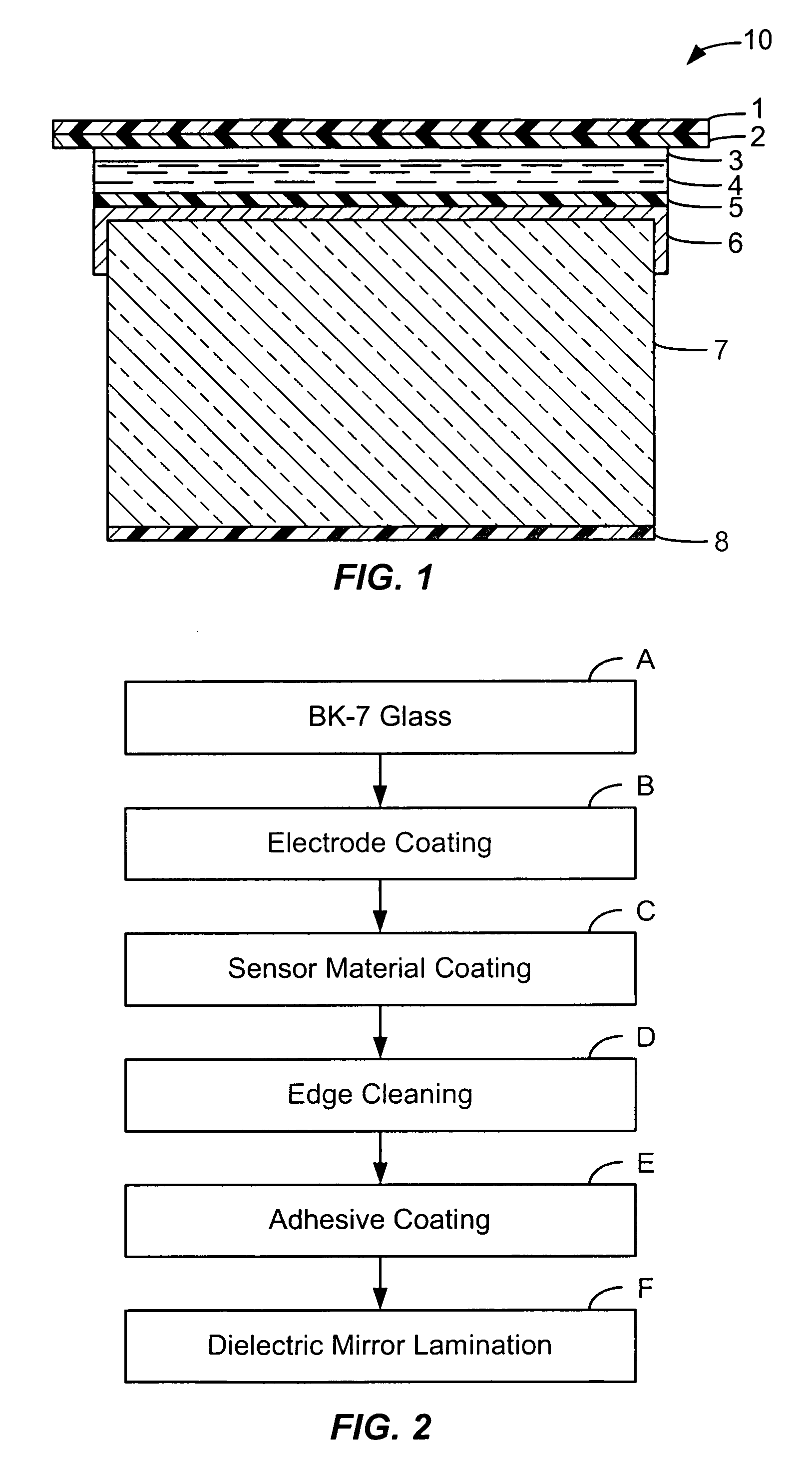
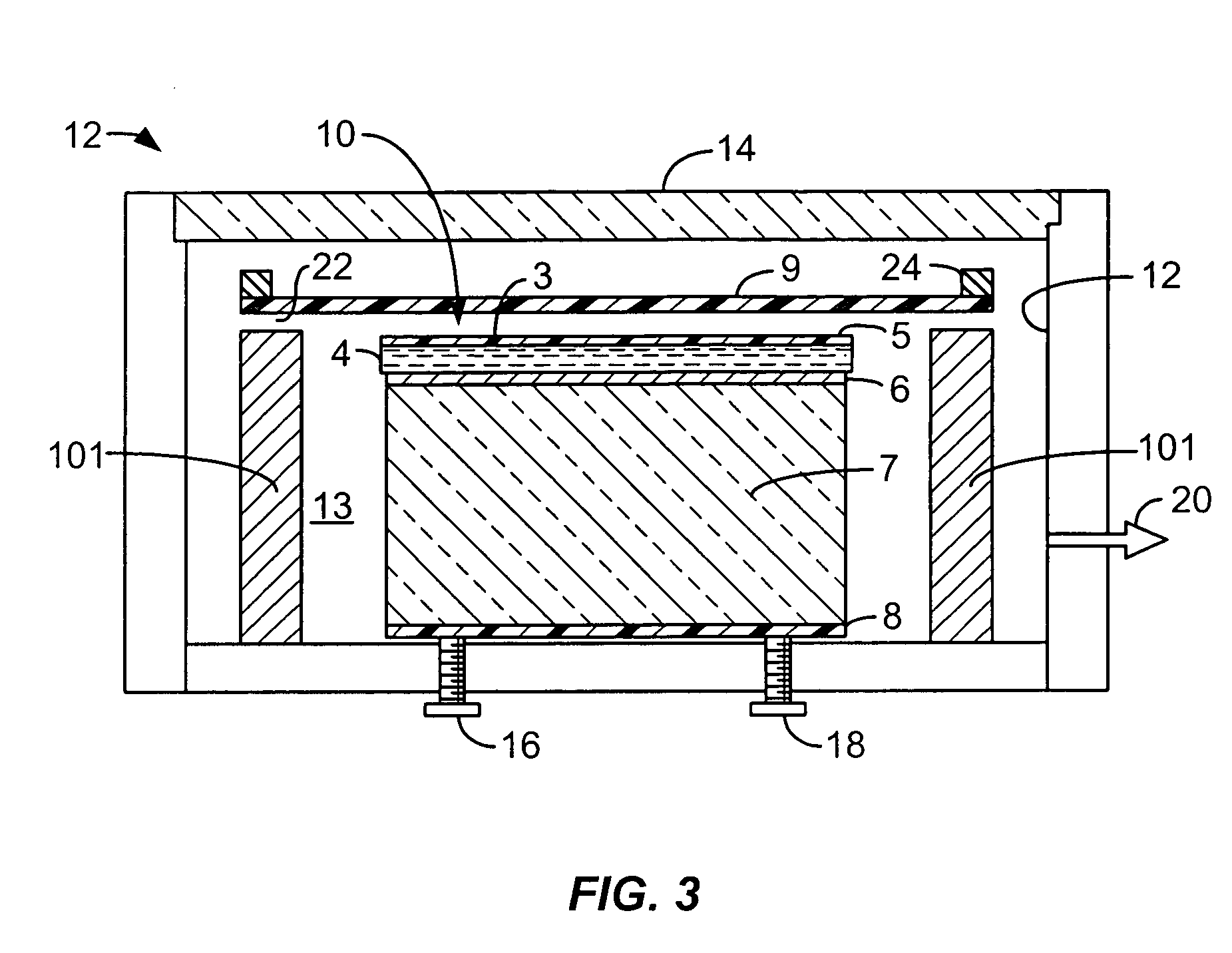
InactiveUS20050077005A1Improve mechanical stabilityImprove surface flatnessLayered product treatmentHollow inflatable ballsPolyesterAdhesive
In an electro-optic light modulator requiring an electro-optical sensor material such as polymer dispersed liquid crystal, or PDLC is directly coated on an optical glass substrate with a transparent electrode, such as indium tin oxide (ITO) and an optional layer of passivation coating such as silicon dioxide (SiO2) on its surface. A thin layer of polymeric adhesive is coated on top of PDLC layer and then this two-layer coating is laminated with a dielectric mirror on a polyester film (Mylar™) preferably with the assistance of a vacuum.
Owner:PHOTON DYNAMICS
Modified polyolefins paper without plant fibre
InactiveCN101462387AImprove folding resistanceImprove rigiditySynthetic resin layered productsPolyolefinOrganic chloride compound
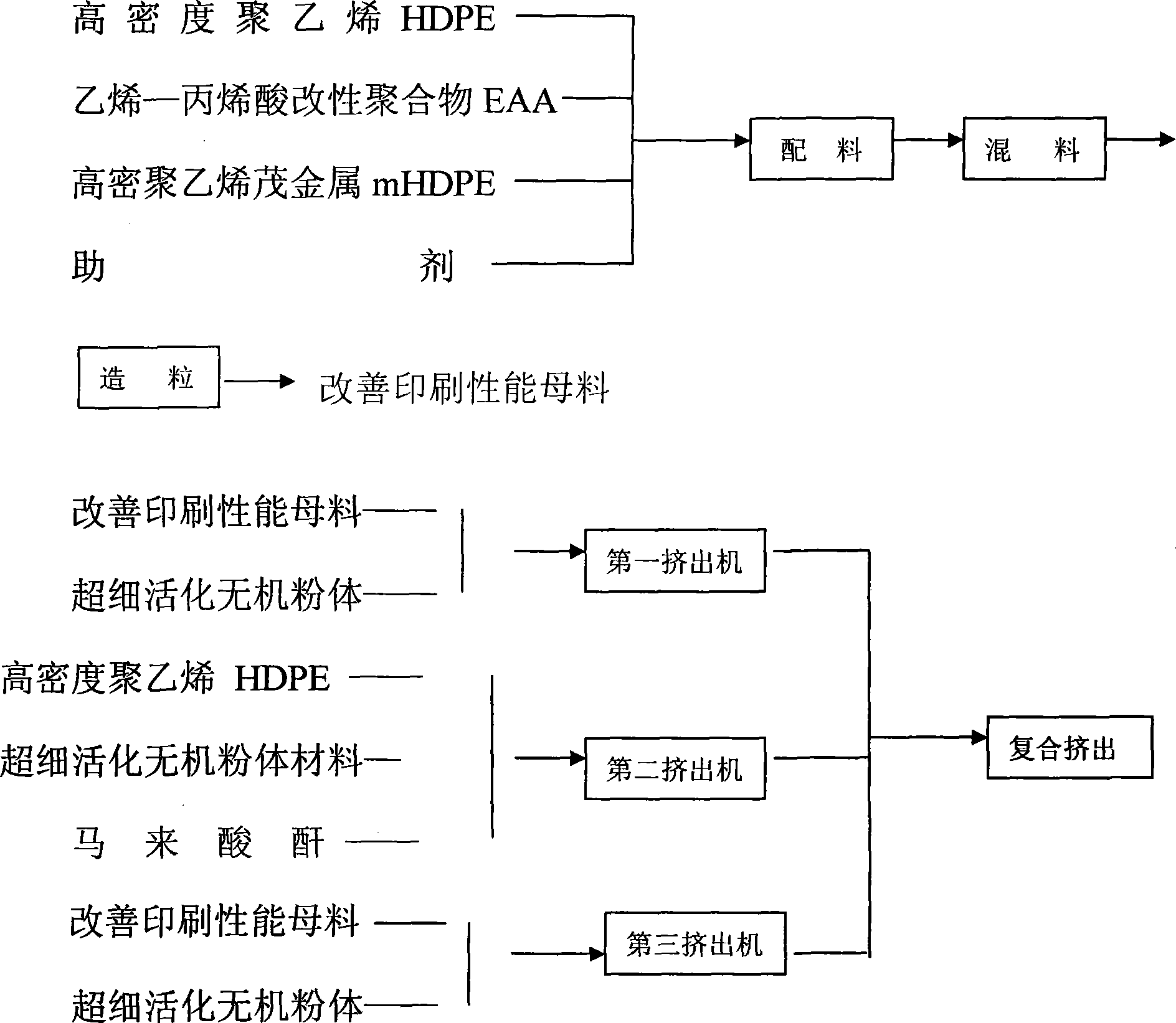
The invention discloses modified polyolefin paper without plant fiber. The modified polyolefin paper is formed by a matrix layer 1 without the plant fiber, a matrix layer 2 without the plant fiber and a matrix layer 3 without the plant fiber which are compounded into a whole, wherein the matrix layer 1 and the matrix layer 3 are prepared by 20 to 30 percent of ethylene-acrylic acid modified copolymer EAA, 45 to 60 percent of metallocene high-density polyethylene mHDPE, and 20 to 25 percent of activated ultrafine inorganic powder respectively, and the matrix layer 2 is prepared by 60 to 90 percent of activated ultrafine inorganic powder, 2 to 5 percent of maleic anhydride and 8 to 35 percent of high-density polyethylene. The modified polyolefin paper has the advantages of good ink receptivity and softness. Therefore, the modified polyolefin paper can be used as industrial paper, packing paper and household paper, can also be used as cultural paper, and enlarges the use range. The modified polyolefin paper has higher foldability and rigidity, has the longitudinal and transverse tearing strength which are superior to those of plant fiber paper, has good surface flattening, good handwriting, and clear printing performance, saves printing ink, has simple production technology, protects forest resources, saves energy sources and water, reduces the discharge of organic chlorides and harmful gas, has no waste, and protects the environment.
Owner:宋旭
Control technological method for planeness of surface of LTCC substrate
ActiveCN102724822AImprove surface flatnessLow costMultilayer circuit manufactureCo-fired ceramicFiller metal
The invention discloses a control technological method for the planeness of the surface of an LTCC (low temperature co-fired ceramic) substrate. Specific steps are as follows: preparing raw ceramic sheets for the preparation of an LTCC substrate, and punching circuit through holes with a punch press; tearing off a Mylar film; filling LTCC technological hole metal slurry on the raw ceramic sheets, using a roller to roll the holes so as to evenly press flat the protrusions of the holes filled with the metal slurry, and printing LTCC technological metal conductor slurry on the raw ceramic sheets so as to form a circuit figure; aligning and stacking all the raw ceramic sheets layer by layer, and laminating so as to obtain a large bulk of LTCC raw ceramic blank; and after cutting the large bulk of LTCC raw ceramic blank into circuits in the shape of small blocks, sintering so as to obtain the compact and flat LTCC circuit substrate. Therefore, the technological process of planeness control for the surface of the LTCC substrate is achieved. The method, which is low in cost, simple and effective, is suitable for the development and production of substrates with a complex cavity structure of an embedded chip requiring a lot for surface planeness, and substrates automatically micropackaged in a batch manner.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二十三所
Method for producing group III nitride semiconductor and template substrate
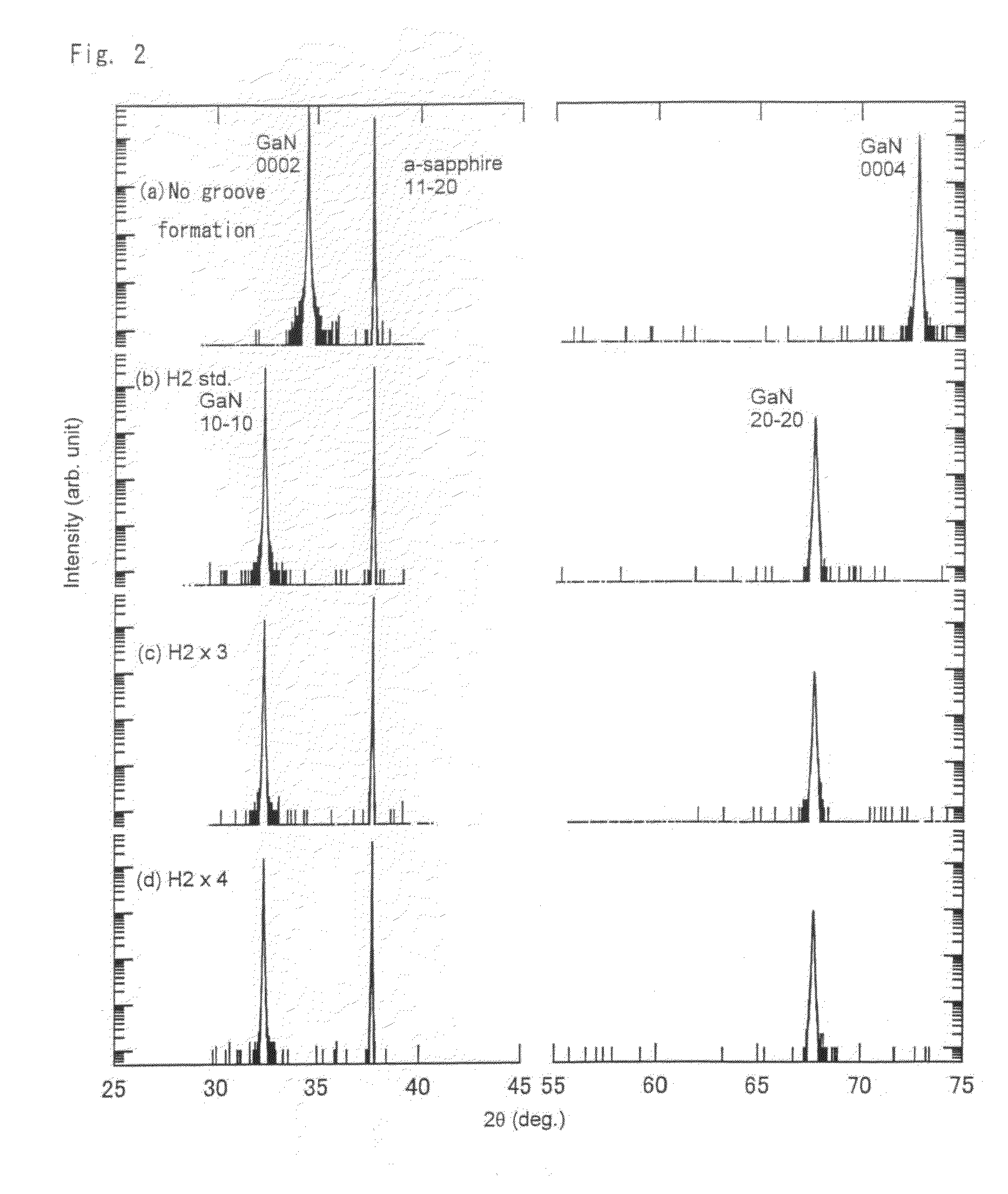
ActiveUS20100102360A1High crystallinityImprove surface flatnessSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSputteringHydrogen
The present invention provides a method for producing a Group III nitride semiconductor. The method includes forming a groove in a surface of a growth substrate through etching; forming a buffer film on the groove-formed surface of the growth substrate through sputtering; heating, in an atmosphere containing hydrogen and ammonia, the substrate to a temperature at which a Group III nitride semiconductor of interest is grown; and epitaxially growing the Group III nitride semiconductor on side surfaces of the groove at the growth temperature. The thickness of the buffer film or the growth temperature is regulated so that the Group III nitride semiconductor is grown primarily on the side surfaces of the groove in a direction parallel to the main surface of the growth substrate. The thickness of the buffer film is regulated to be smaller than that of a buffer film which is employed for epitaxially growing the Group III nitride semiconductor on a planar growth substrate uniformly in a direction perpendicular to the growth substrate. The growth temperature is regulated to be lower than a temperature at which the Group III nitride semiconductor is epitaxially grown on a planar growth substrate uniformly in a direction perpendicular to the growth substrate. The growth temperature is preferably 1,020 to 1,100° C. The buffer film employed is an AlN film having a thickness of 150 Å or less.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Slurry compositions for selectively polishing silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, methods of polishing a silicon nitride layer and methods of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the same
InactiveUS8043970B2Reduce rateSuppress and reduce damagePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesDevice materialSlurry
Slurry compositions for selectively polishing silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide, methods of polishing a silicon nitride layer and methods of manufacturing a semiconductor device using the same are provided. The slurry compositions include a first agent for reducing an oxide polishing rate, an abrasive particle and water, and the first agent includes poly(acrylic acid). The slurry composition may have a high polishing selectivity of silicon nitride relative to silicon oxide to be employed in selectively polishing a silicon nitride layer in a semiconductor manufacturing process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing functional film and method for manufacturing thin film transistor
InactiveUS20060068091A1High densityImprove surface flatnessSolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesTransistorMetal salts
A method for manufacturing a functional film, including disposing a first ink on a substrate and disposing a second ink on the first ink that has been disposed, the first ink containing at least one of a metal and a metal oxide as a solute, the metal and the metal oxide having a melting point of 900 degrees and above in bulk, upon making the metal and the metal oxide to a particle of having a diameter of from 30 to 150 nm, the particle having a melting point of 255 degrees centigrade and above, and the second ink containing an organic metal salt as a solute.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
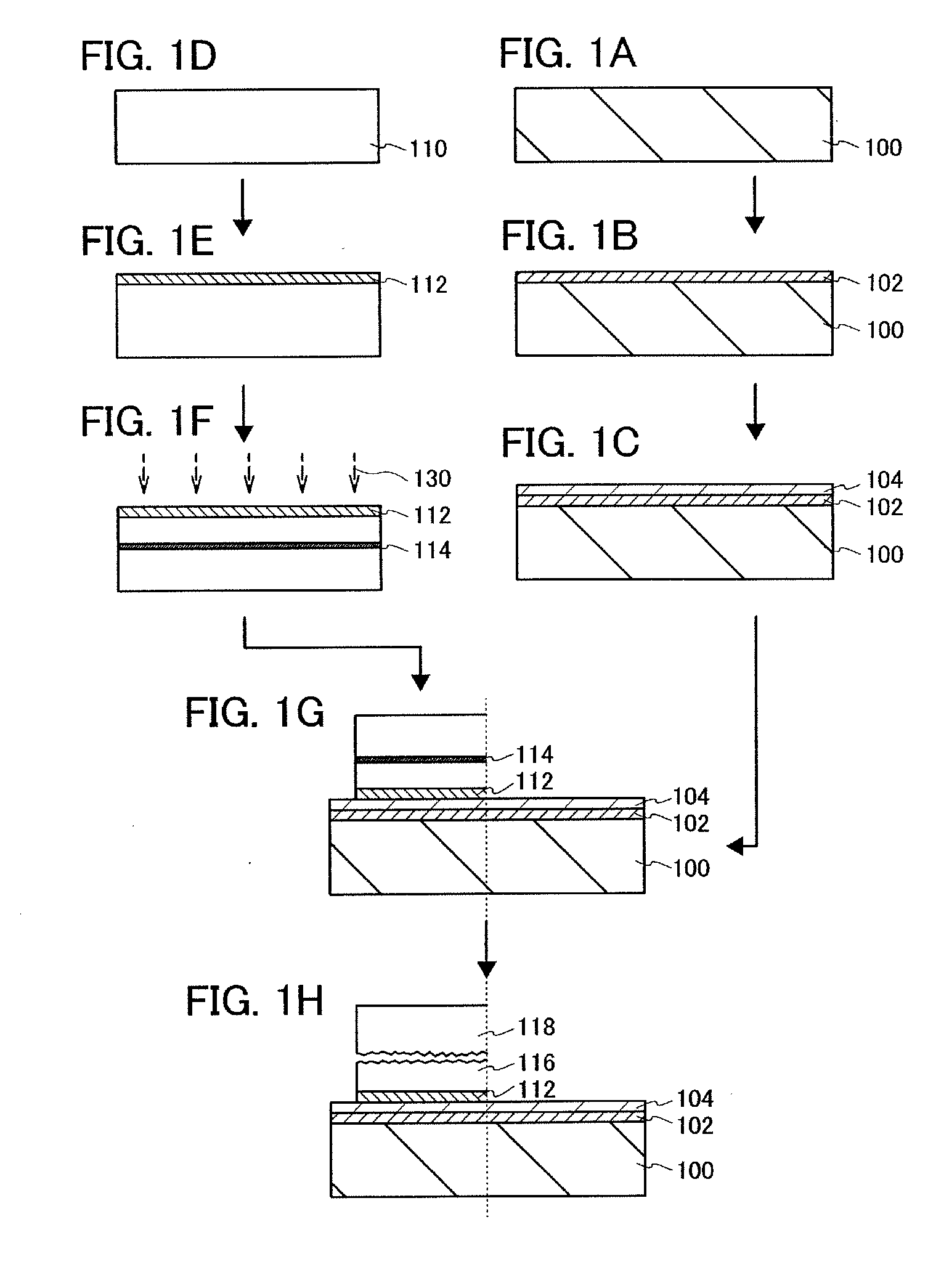
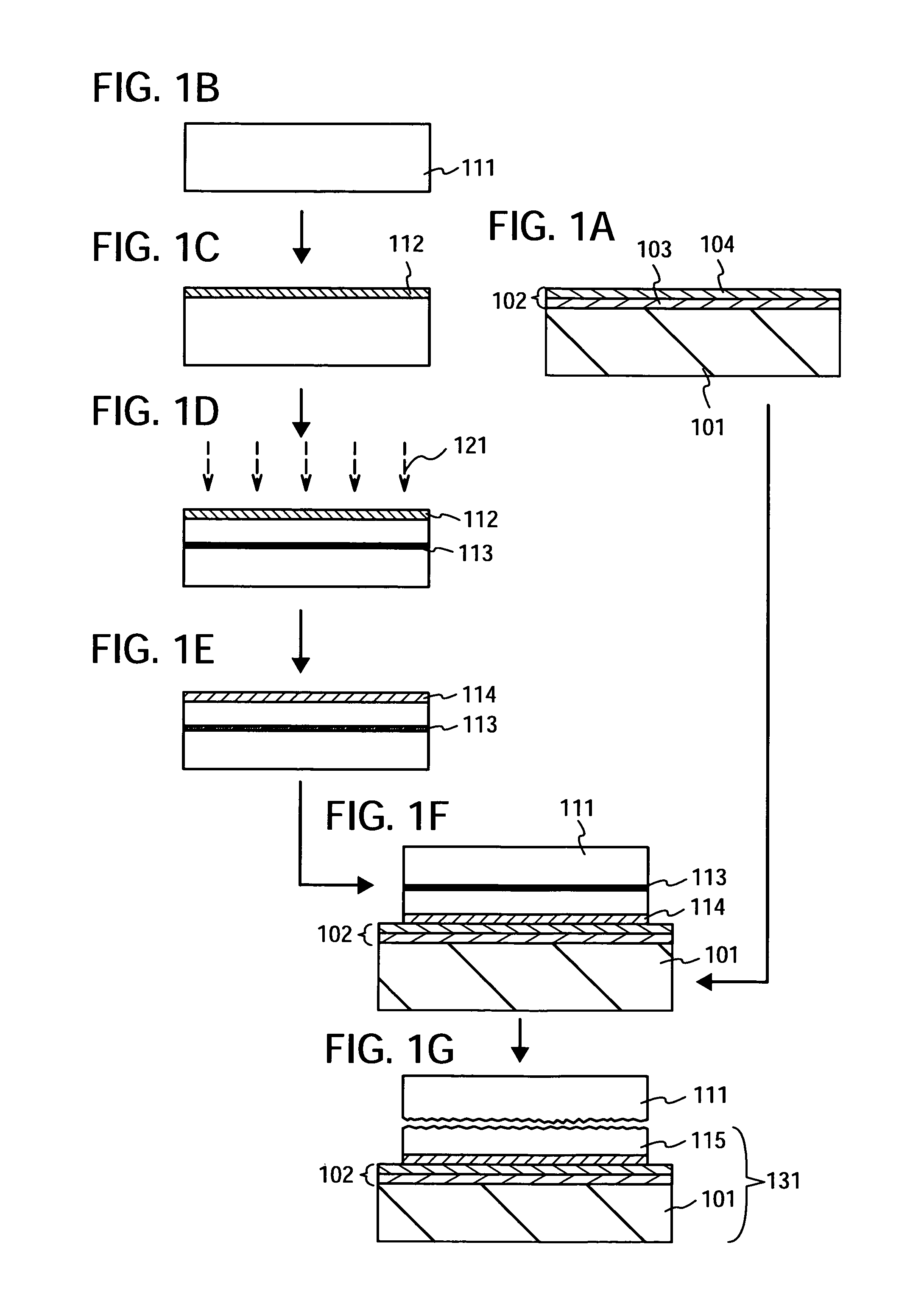
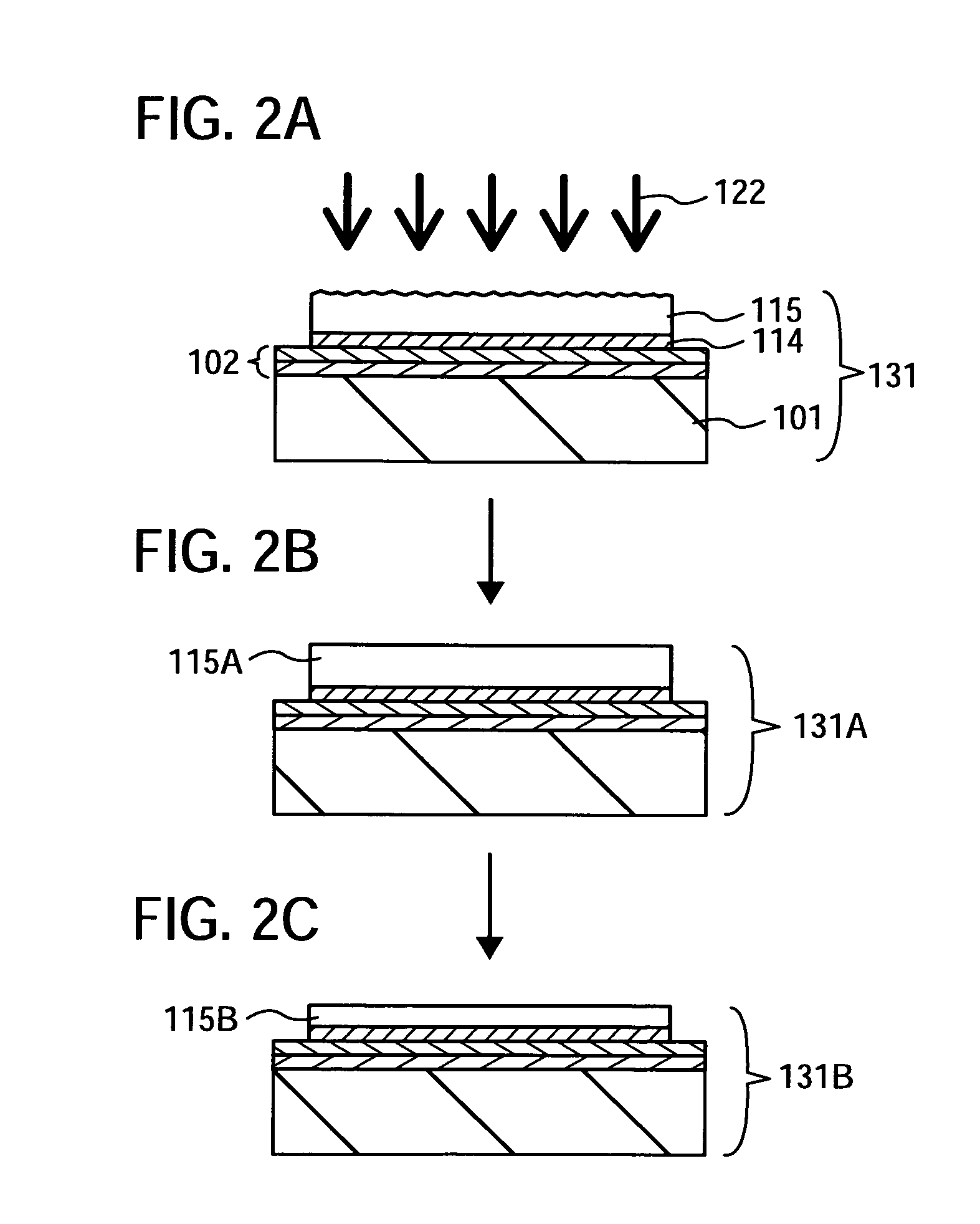
Manufacturing method of SOI substrate and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7820524B2Improve performanceImprove flatnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenHeat resistance
A manufacturing method of an SOI substrate which possesses a base substrate having low heat resistance and a very thin semiconductor layer having high planarity is demonstrated. The method includes: implanting hydrogen ions into a semiconductor substrate to form an ion implantation layer; bonding the semiconductor substrate and a base substrate such as a glass substrate, placing a bonding layer therebetween; heating the substrates bonded to each other to separate the semiconductor substrate from the base substrate, leaving a thin semiconductor layer over the base substrate; irradiating the surface of the thin semiconductor layer with laser light to improve the planarity and recover the crystallinity of the thin semiconductor layer; and thinning the thin semiconductor layer. This method allows the formation of an SOI substrate which has a single-crystalline semiconductor layer with a thickness of 100 nm or less over a base substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Forming method of high-precision thin-wall ceramic tube
InactiveCN102431086AImprove plasticityImprove liquidityCeramic shaping apparatusClaywaresHigh densityMethylcellulose Powder
The invention discloses a forming method of high-precision thin-wall ceramic tube which can produce high-precision thin-wall ceramic tube with high density, accurate physical dimension of tube inside and external wall, and internal wall smooth as mirror. The forming method of thin-wall ceramic tube comprises steps as follows: (1) adding water to the formula material, ball milling to obtain mud material; (2) adding 1-3% methylcellulose powder into the mud material and smelting into mud bars; (3) extruding the mud bar into thin-wall ceramic tube blank and directly applying to a metal internal die tube, and drying to be pressed; (4) sleeving flexible oilproof rubber external die on external wall of the thin-wall ceramic tube blank and sealing the metal internal die tube and the rubber sleeve at two ends of the ceramic tube blank by oilproof rubber; (5) putting the ceramic tube assembly into a high pressure container, and forming by bidirectional isostatic pressing, removing the internal and external dies to obtain the high-precision thin-wall ceramic tube; (6) hoisting and sintering the high-precision thin-wall ceramic tube by conventional sintering method.
Owner:何剑明
Glass/resin laminate, and electronic device using same
ActiveCN102481764AWarpage suppressionEasy to operateElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectronAcid anhydride
Disclosed is a glass / resin laminate comprising a glass substrate and a resin layer, wherein the resin layer contains a polyimide that is obtained by polycondensing an aromatic diamine having a benzoxazole structure and an aromatic tetracarboxylic acid anhydride, the difference between the average linear expansion coefficient of the glass substrate and the average linear expansion coefficient of the resin layer for the range of 25-300 DEG C is from -100 10-7 / DEG C to +100 10-7 / DEG C, and the glass substrate forms at least one outermost layer of the laminate.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD +1
Polycrystalline silicon film, preparation method thereof, array substrate and display device
ActiveCN102856173ALarge grainUniform grain sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrierDisplay device
The invention discloses a polycrystalline silicon film and a preparation method thereof, an array substrate and a display device, belonging to the technical field of semiconductors. The preparation method of the polycrystalline silicon film comprises the following steps of: (1) forming a graphene layer and a noncrystalline silicon layer which are adjacent; and (2) enabling noncrystalline silicon to crystallize and form polycrystalline silicon and obtaining the polycrystalline silicon film. The polycrystalline silicon in the polycrystalline silicon film has the advantages of no pollution and low defect density, the crystal grain size of the polycrystalline silicon is uniform in size, the arrangement is ordered, the crystal grain is larger, and further the surface flatness is better. The speed rate of current carriers in the polycrystalline silicon film prepared by the method is increased, and the element performance of a polycrystalline silicon film transistor is improved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Spectroscopic sensor and angle limiting filter
ActiveUS20120236313A1Improve surface flatnessSmall sizeSpectrum investigationOptical filtersEngineeringOptical filter
An angle limiting filter includes: a first light-shielding layer containing a first light-shielding material and provided with a first opening; a second light-shielding layer containing a second light-shielding material and located in a region which surrounds at least one portion of the first light-shielding layer; a third light-shielding layer containing the first light-shielding material, provided with a second opening at least one portion of which overlaps the first opening, and located above the first light-shielding layer; and a fourth light-shielding layer containing the second light-shielding material and located above the second light-shielding layer in a region which surrounds at least one portion of the third light-shielding layer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of producing a device with a movable portion
ActiveUS7396740B2Improve propertiesLow production costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrostructural device manufactureEngineeringCommon method
A method of producing a device with a movable portion spaced apart from a support wafer comprises a step of providing the support wafer having a structured surface and a further step of providing a device wafer with a backing layer and a device layer disposed thereon. Further, the method comprises the step of generating a first planarization layer from a first starting material on the support wafer with a first method to fill in the structures of the structured surface of the support wafer, whereby a surface with a first degree of planarization is obtained. Further, the method comprises a step of generating a second planarization layer from a second starting material on the planarized surface of the support wafer with a second method to obtain a surface with a second degree of planarization, which is higher than the first degree of planarization, wherein the first and second planarization layers can be removed together. Additionally, the support wafer is connected to the device wafer such that the device layer and the planarized surface of the support wafer are connected. Then, removing the backing layer of the device wafer is performed, followed by structuring the resulting structure and removing the first and second planarization layers via a common method to generate the moveable portion of the device.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Paper, image-recording material support, and image-recording material
InactiveUS20050020448A1Improve surface flatnessHigh glossPhotosensitive materialsPaper coatingImage recordingSurface roughness
Paper and an image-recording material support which have high surface planarity and excellent gloss are disclosed. Moreover, an image-recording material is disclosed which uses the image-recording material support and is capable of obtaining high quality image. The paper includes raw paper. The paper satisfies at least one of the following conditions (i) and (ii): (i) the paper has an inner bonding strength of 160 mJ or more specified in Japan Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry No. 54, and an average center surface roughness (SRa) on at least one face of the paper is 0.9 μm or less at a cutoff wavelength of 0.3 mm to 0.4 mm, and (ii) an Oken type smoothness S (second) on the at least one face of the paper, and a density ρ (g / cm3) of the paper satisfy an expression S1 / 2 / ρ3≧15.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method for producing a group iii nitride semiconductor
ActiveCN103700579AImprove surface flatnessHigh crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenNitrogen
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Polishing method for lithium tantalate substrate
The invention discloses a polishing method for a lithium tantalate substrate. The method includes the steps of 1, grinding a cut tantalate lithium wafer with an abrasive material with the particle size of 5-20 microns, and obtaining a lithium tantalate grinding sheet with the surface of a rough structure; 2, directly conducting chemical corrosion on the lithium tantalate grinding sheet in a sealed container filled with the mixed acid of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid, wherein the roughness of the tantalate lithium wafer is smaller than 200 nm, and the flatness is smaller than 5 microns; obtaining a lithium tantalate corrosion sheet with the surface of a random disordered pit structure; 3, conducting single-side polishing on the lithium tantalate corrosion sheet with a single-polishing machine and a polishing liquid, wherein the polishing pressure is 0.005-1 MPa, the roughness of the tantalate lithium wafer is smaller than 0.5 nm, and the flatness is smaller than 3 microns; obtaining a lithium tantalite polishing sheet. The polishing method has the advantages of one-time polishing, batch production and high polishing efficiency, and the produced lithium tantalate substrate has high surface flatness which determines that the lithium tantalate substrate is not easily broken in the application of devices; the material utilization is high, and the processing yield is high.
Owner:TDG HLDG CO LTD
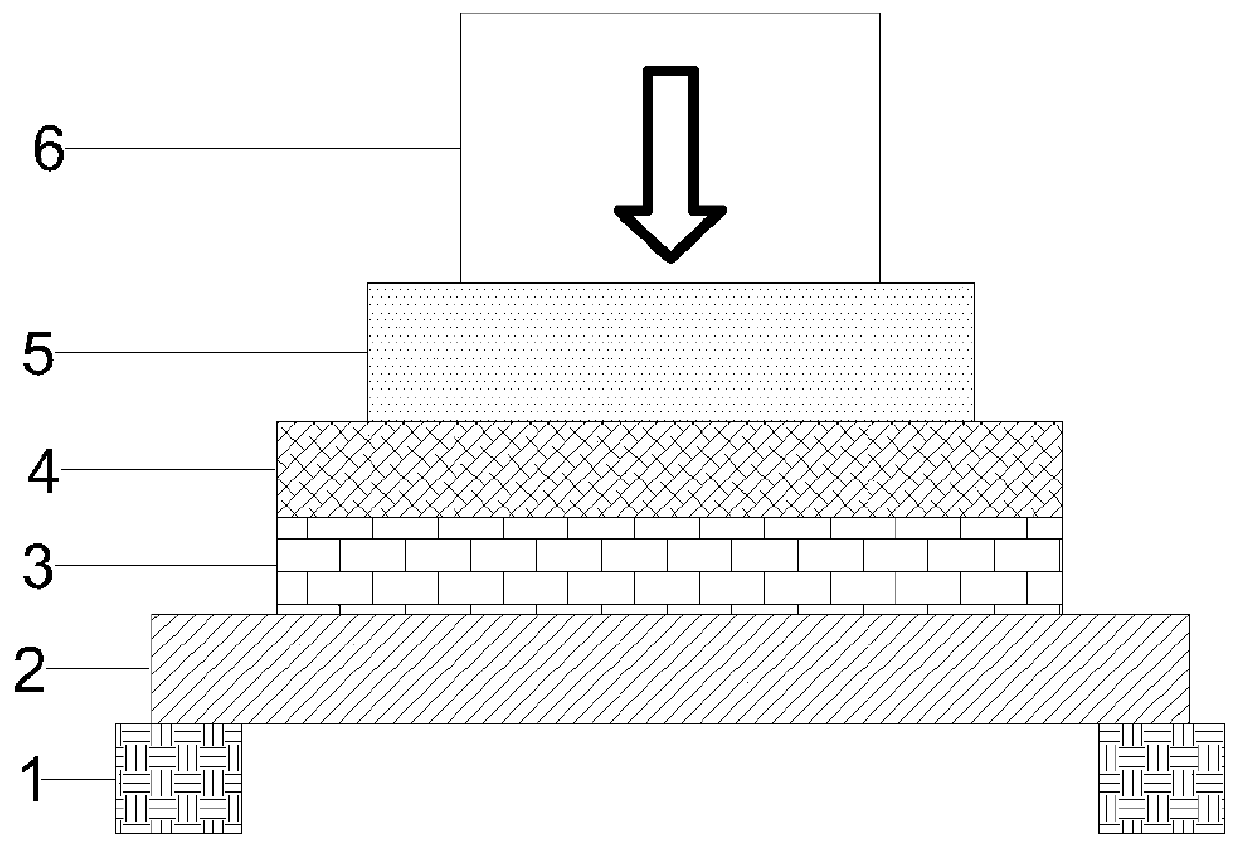
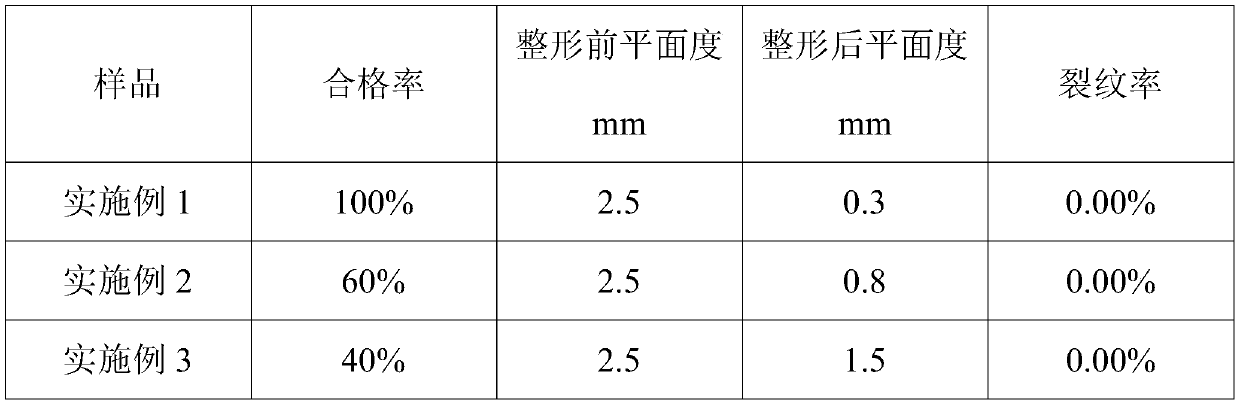
Post-welding shaping method and welding method for metal target material
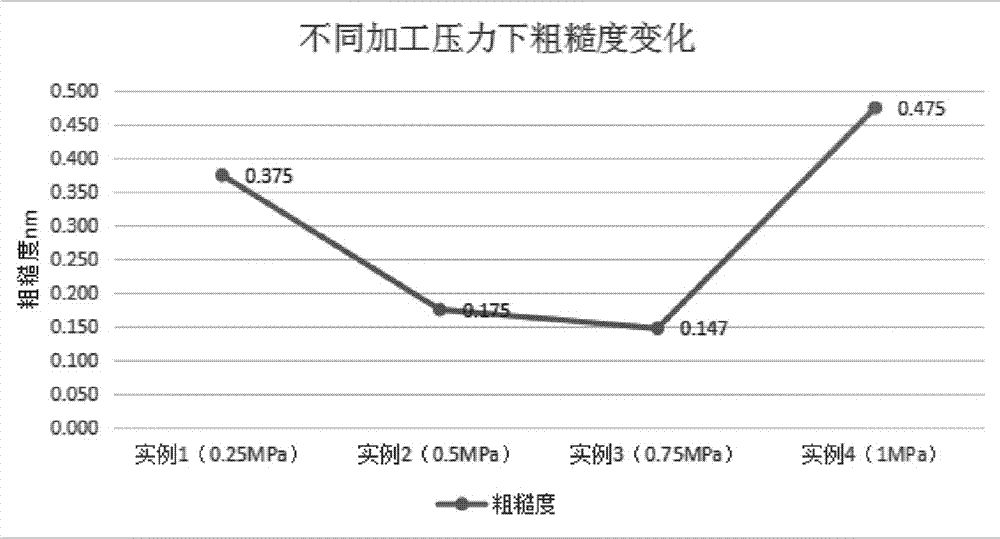
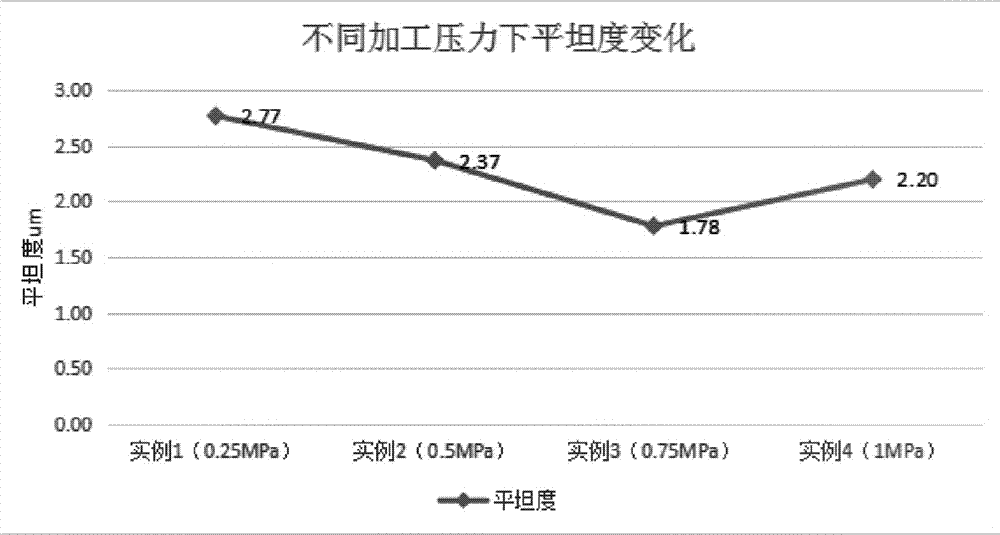
The invention provides a post-welding shaping method for a metal target material. According to the method, a buffer cushion and a cushion block are sequentially arranged above the target material of atarget material assembly, and then pressing shaping is carried out, wherein the hardness of the buffer cushion is 30-60HA, the tensile strength is 50-100kg / cm<2>, the problem that penetrating cracksand a cracking phenomenon easily occur due to a great pressure instantaneously born by the surface of the target material in a shaping process is alleviated well, good protection and buffer effects are acted on the target material, and the yield of the target material is increased; and the target material is heated before shaping and a washer is arranged below a back plate of the target material assembly, so that the shaping efficiency of a shaping machine for the target material is increased and the planeness of the target material after shaping is improved, and a high industrial applicationvalue is achieved.
Owner:KONFOONG MATERIALS INTERNATIONAL CO LTD
Low-loss oriented cutting method of large-size sapphire crystal blanks
InactiveCN102152420AImprove processing efficiencyReduce processing stepsFine working devicesSheet steelCrystal orientation
The invention provides a low-loss directional cutting method of large-size sapphire crystal blanks. The large sapphire crystal blanks are fed in a rotation manner in the method, and the processing efficiency of the method is improved by one time than that of a traditional band-saw cutting method. Before cutting, the end faces of the large-size sapphire crystal blanks are oriented, steel plates in corresponding angles are selected according to the crystal orientation deviation of the end faces for bonding, thereby the accurate orientation is finished in a cutting procedure. The method is greatly improved on the basis of the traditional band-saw cutting method, has the advantages of higher cutting efficiency, better cutting surface quality, high surface flatness, shorter follow-up processing time, lower unit production cost and the like, and can be used for correcting the crystal orientation of the end faces of the large sapphire crystal blanks.
Owner:HARBIN AURORA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
Soi substrate and method for manufacturing soi substrate
ActiveUS20100025804A1Suppression amountSuppress surface roughnessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBonding processOptoelectronics
On the side of a surface (the bonding surface side) of a single crystal Si substrate, a uniform ion implantation layer is formed at a prescribed depth (L) in the vicinity of the surface. The surface of the single crystal Si substrate and a surface of a transparent insulating substrate as bonding surfaces are brought into close contact with each other, and bonding is performed by heating the substrates in this state at a temperature of 350° C. or below. After this bonding process, an Si—Si bond in the ion implantation layer is broken by applying impact from the outside, and a single crystal silicon thin film is mechanically peeled along a crystal surface at a position equivalent to the prescribed depth (L) in the vicinity of the surface of the single crystal Si substrate.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Transparent conductive oxide thin film substrate, method of fabricating the same, and organic light-emitting device and photovoltaic cell having the same
InactiveUS20140026952A1Improve surface flatnessIncrease electrical reliability and chemical stabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectrically conductiveHigh concentration
A transparent conductive oxide thin film substrate that has a high level of surface flatness, a method of fabricating the same, and an OLED and photovoltaic cell having the same. The transparent conductive oxide thin film substrate that includes a base substrate, a first transparent conductive oxide thin film formed on the base substrate, the first transparent conductive oxide thin film being treated with a first dopant, and a second transparent conductive oxide thin film formed on the first transparent conductive oxide thin film. The second transparent conductive oxide thin film is treated with a second dopant at a higher concentration than the first dopant. The surface of the second transparent conductive oxide thin film is flatter than the surface of the first transparent conductive oxide thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG CORNING PRECISION MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing sic single-crystal substrate for epitaxial sic wafer, and sic single-crystal substrate for epitaxial sic wafer
InactiveCN104981892AImprove featuresImprove yieldPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystal substrateSingle crystal
Provided is a method for manufacturing an SiC single-crystal substrate making it possible to obtain an epitaxial SiC wafer provided with a high-quality SiC single-crystal thin film devoid of surface defects, etc. Also provided is said SiC single-crystal substrate. A method for manufacturing an SiC single-crystal substrate for an epitaxial SiC wafer having a high-quality SiC single-crystal thin film devoid of surface defects, etc., wherein the surface of the SiC single-crystal substrate is polished using chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) at a speed of no more than 100 nm / hr to remove the surface in a thickness of 100 nm or greater, and produce no more than 1 substantially round pit per cm2, the pit having a diameter of 0.5-1.5 µm and a depth of 50-500 nm
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
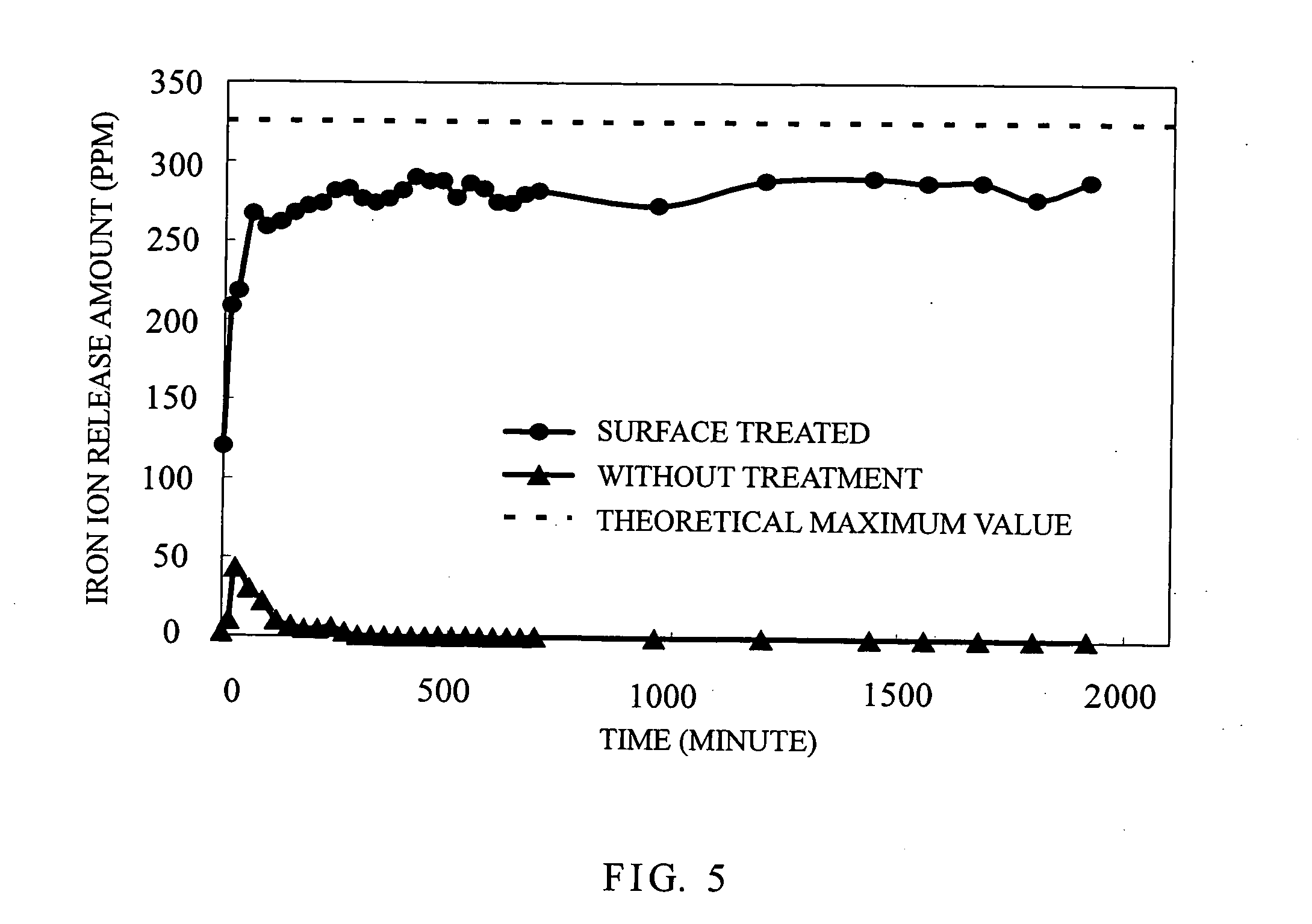
Surface treatment process for enhancing a release rate of metal ions from a sacrificial electrode and a related sacrificial electrode
ActiveUS20050126918A1Increase release rateReduce layeringWater/sewage treatmentLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingHigh densityWorking life
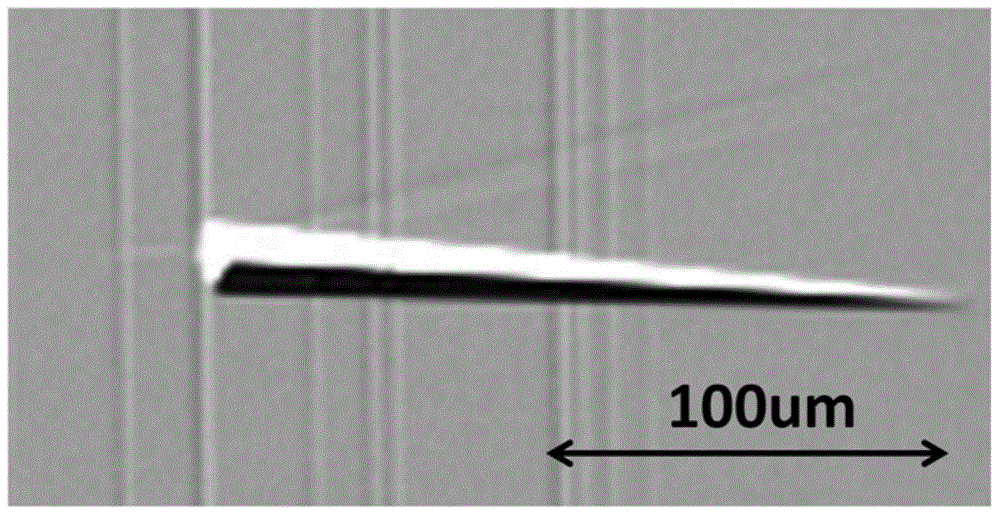
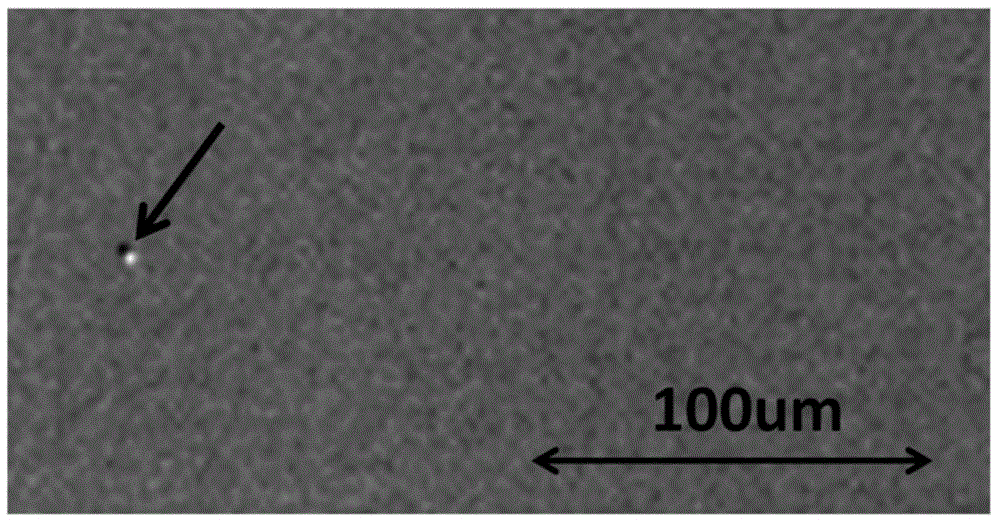
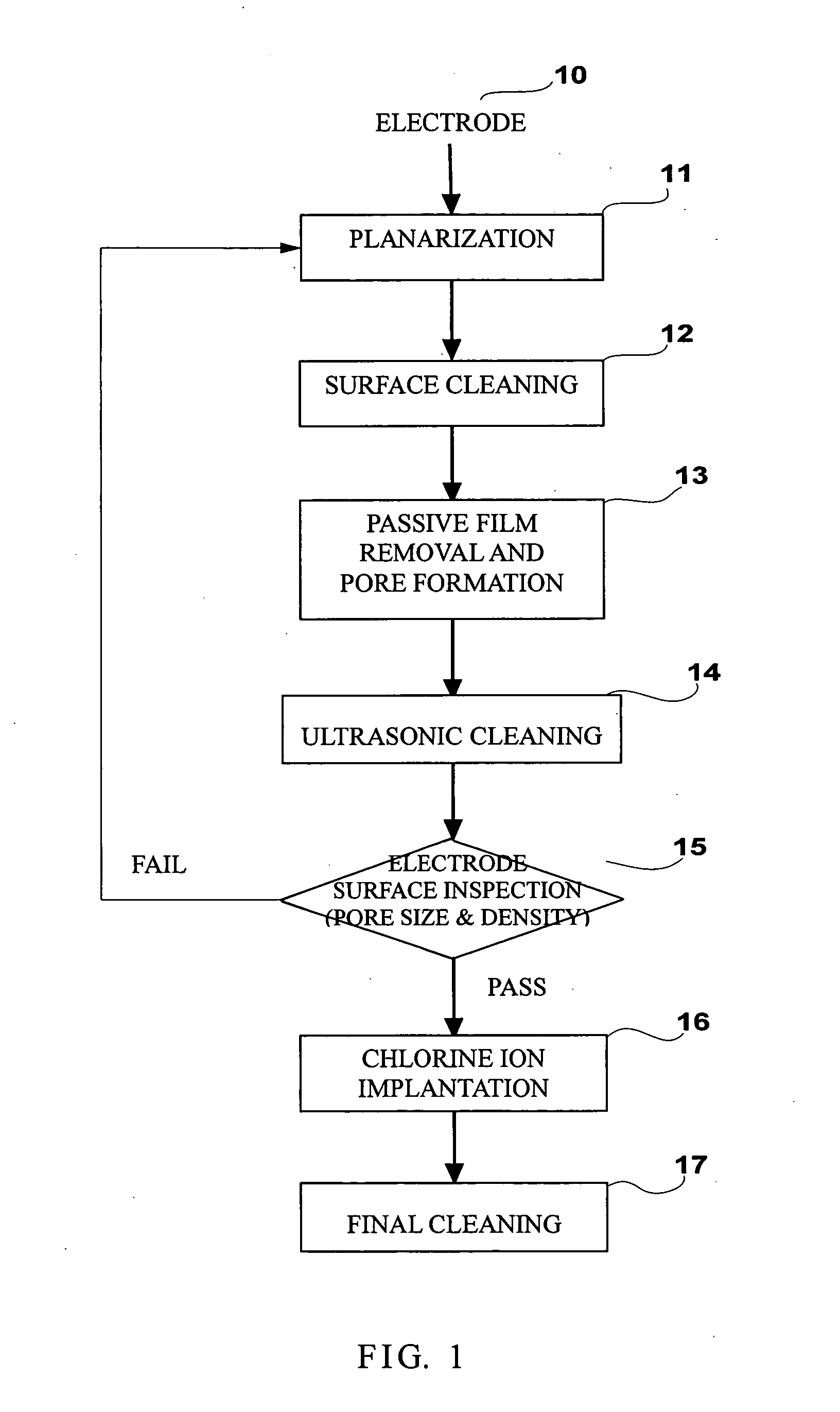
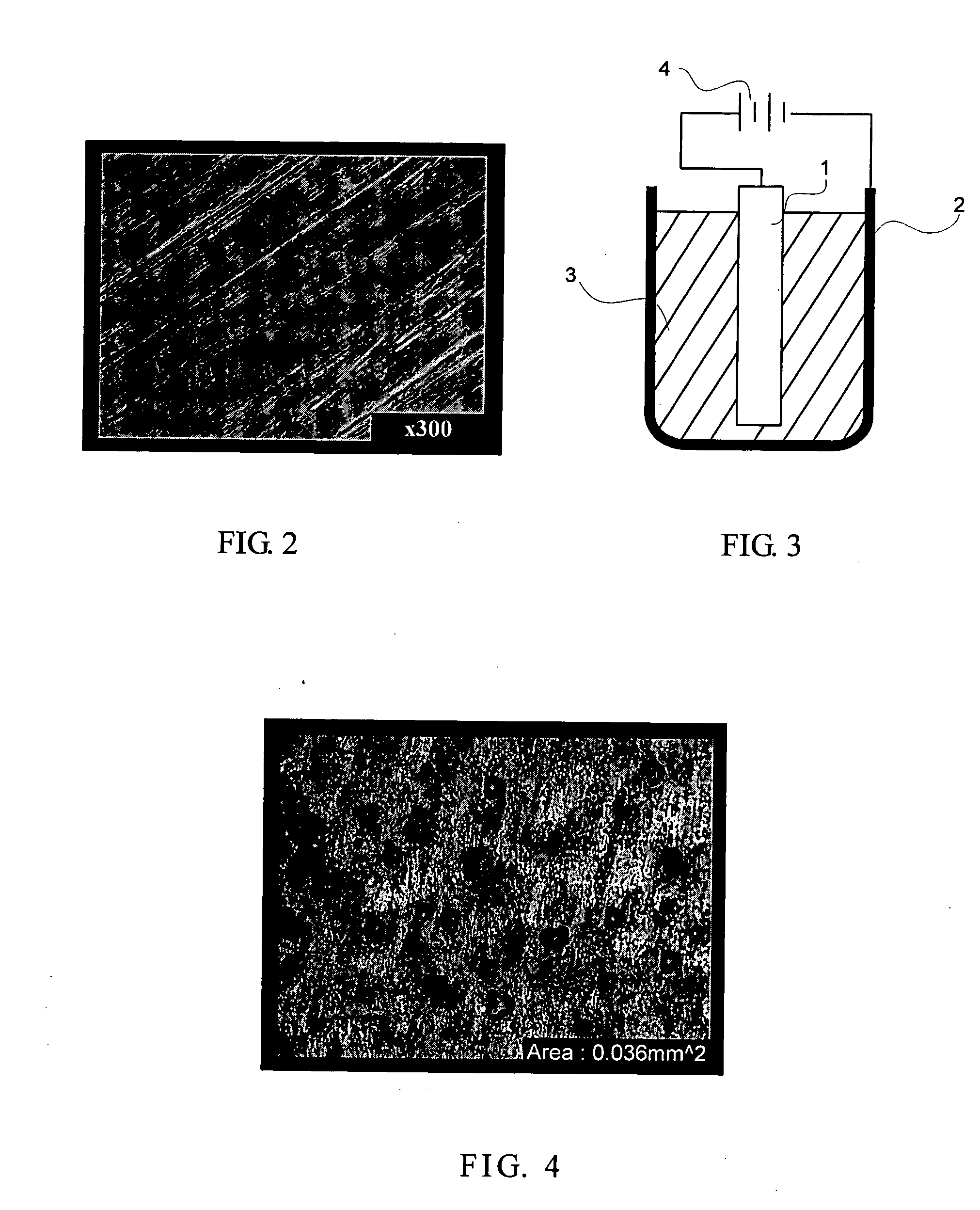
The present invention discloses a surface treatment process for enhancing both the release rate of metal ions from a sacrificial electrode, and the working life of the electrode. A high density of micro pores are formed on the surface of the sacrificial electrode. Chlorine ions are then implanted into the pores. The chlorine ions prevent a passive film from forming on the sacrificial electrode during use, in which an electric current flows through the sacrificial electrode.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Formed article, method of producing same, electronic device member, and electronic device
ActiveUS20120101221A1Excellent gas barrier capabilityExcellent bendabilityMolten spray coatingSynthetic resin layered productsOxygen atomElectric devices
A formed article comprising a gas barrier layer that is formed of a material including at least an oxygen atom, a carbon atom, and a silicon atom, the gas barrier layer including an area (A) where an oxygen atom content rate gradually decreases, and a carbon atom content rate gradually increases in a depth direction from a surface, the area (A) including a partial area (A1) and a partial area (A2), the (A1) having a specific oxygen, carbon and silicon content, and the (A2) having a specific oxygen, carbon and silicon content; a method of producing the same; an electronic device member; an electronic device. The formed article exhibits an excellent gas barrier capability, excellent bendability, excellent adhesion, and excellent surface flatness.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Method for producing color filter, color filter and liquid crystal display panel
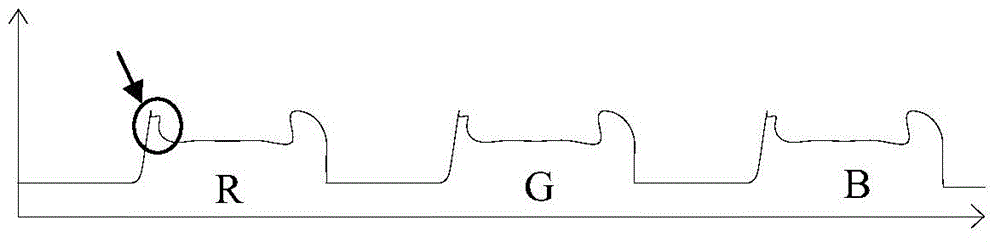
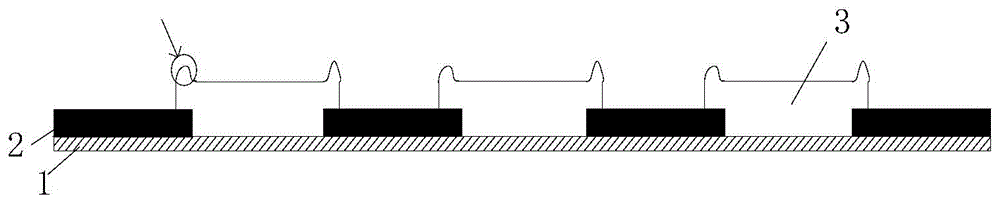
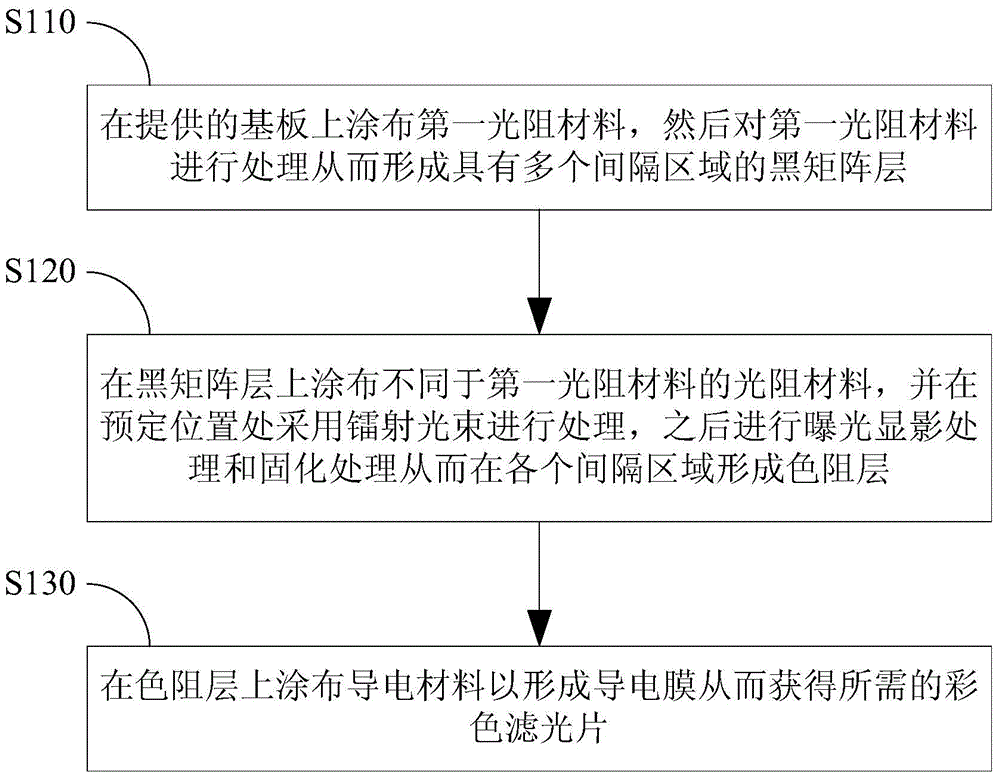
ActiveCN104391349AEliminate or reduce horn phenomenonImprove performanceOptical filtersPhotomechanical apparatusHeifer calfLight beam
The invention discloses a color filter, a liquid crystal display panel and a method for producing the color filter. The method for producing the color filter comprises steps of: coating a substrate with a first photoresist material and processing to form a black matrix layer with a plurality of spacer regions; coating the black matrix layer with a photoresist material different from the first photoresist material, processing by laser beam at a preset position, and then exposing developing and solidifying to form a color resistance layer in each spacer region; coating the color resistance layer with a conductive material to form a conductive film and consequently obtain the color filter. According to the color filter, the liquid crystal display panel and the method for producing the color filter, the ox horn phenomenon of the color resistance layer in the color filter can be eliminated or reduced, the surface plainness of the color resistance layer is improved, the situation that ITO conductive film is easy to fracture at the position where the cattle horn phenomenon occurs on the color resistance layer is improved, and thereby the performance of the color filter is improved.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com