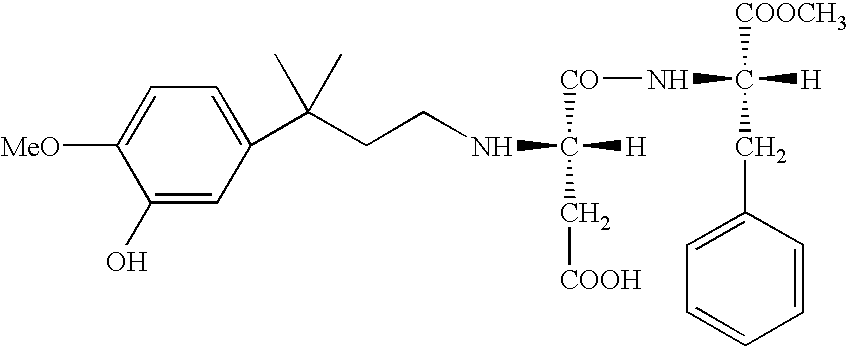
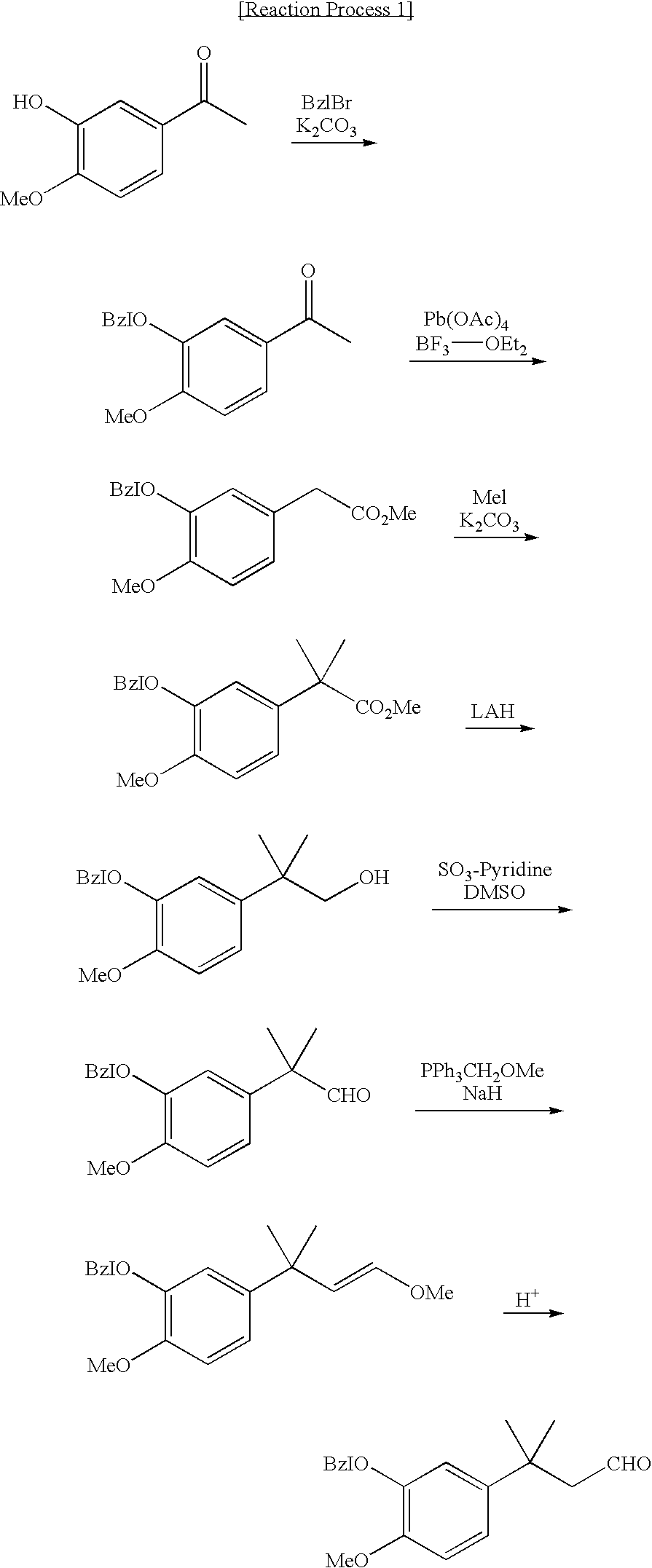
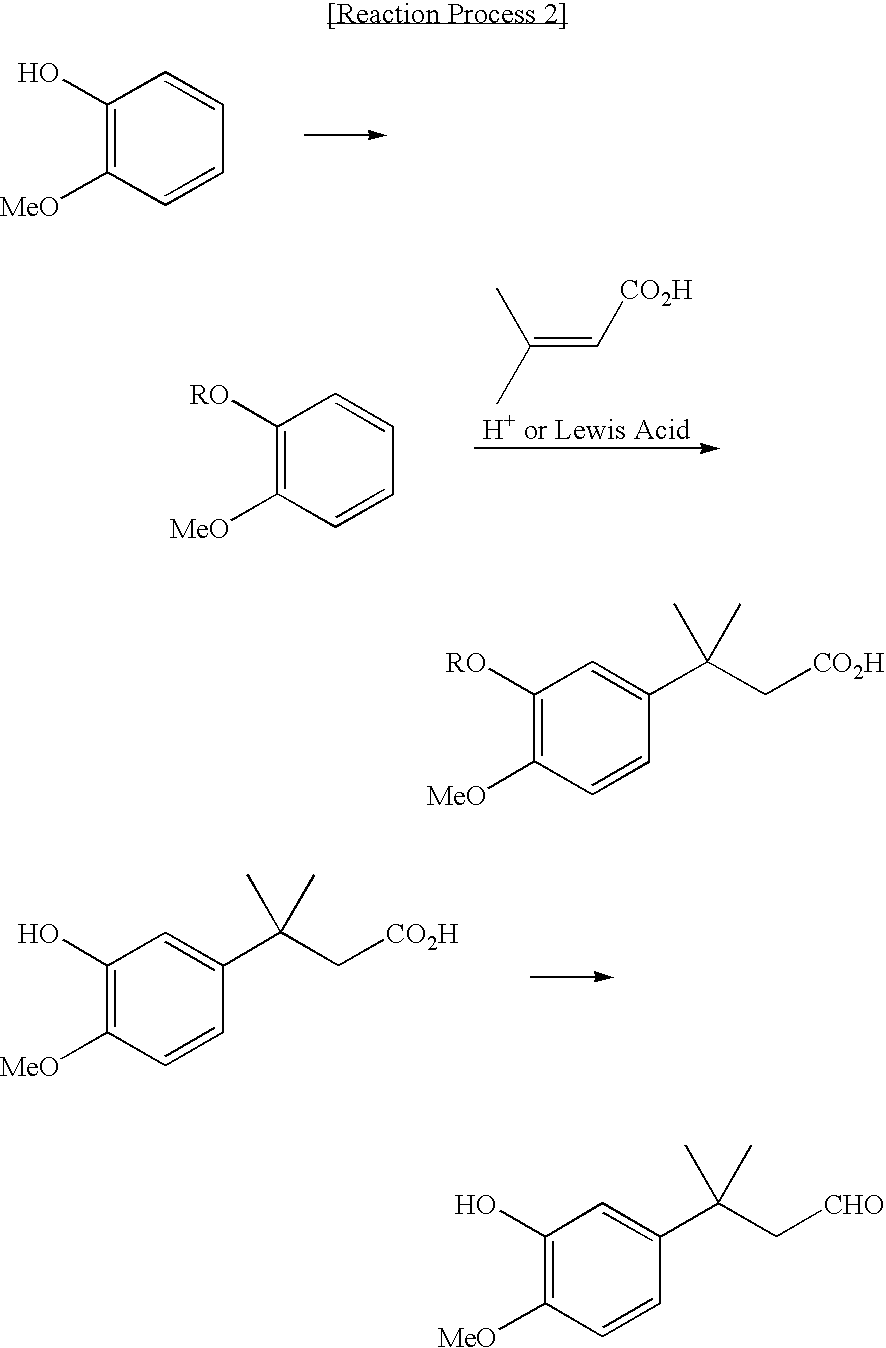
Novel intermediate for sweetener with high sweetness and process for producing the same
a sweetener and high sweetness technology, applied in the field of 3substitutedphenyl3merthylbutyric acid and 3substitutedphenyl3methylaldehyde derivatives, can solve the problems of unstable aspartame and unsatisfactory reaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of 3-(3-methanesulfonyloxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methylbutyric acid
To sodium hydroxide in the pellet form (70.8 g), toluene (200 ml) and distilled water (350 ml) were added to dissolve completely the solid material. Subsequently, 2-methoxy phenol (200 g) was added dropwise thereto over a period of 30 minutes, and then methanesulfonyl chloride (184.4 g) was added dropwise thereto at room temperature over a period of 1 hour, and thus obtained mixture as it is, was stirred for 10 hours. Subsequently, the organic layer was separated, and the obtained solution as it is, was subjected to a step for removal of the solvent by distillation under reduced pressure. Thus obtained residue was subjected a step for distillation under reduced pressure of 1.1 to 1.4 mmHg (146.7 to 186.7 Pa), to obtain unreacted 2-methoxy phenol (64 g) and 2-methanesulfonyloxy anisole (223.6 g, yield: 68%).
A mixture of 2-methanesulfonyloxy anisole (4.0 g) and 3-methylcrotonic acid (1.0 g) was stirred, and ...
example 2
Synthesis of 3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methylbutyric acid
A mixture of 2-methanesulfonyloxy anisole (240 g) and 3-methylcrotonic acid (39 g) was stirred, and to the thus mixed solution, aluminum chloride (104 g) was added, and the mixture was stirred for 5 hours at 70° C., and then further stirred for 2 hours at 100° C. The obtained solution was cooled to about room temperature, and then 6N hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution (390 ml) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred for 3 hours vigorously. The solution obtained was extracted with the use of methylene chloride (300 ml), and the organic layer separated was further extracted with the use of two normal (2N) sodium hydroxide (NaOH) aqueous solution (400 ml). Subsequently, 6N hydrochloric acid (HCl) solution was further added to the aqueous layer separated, to acidify the solution. The obtained aqueous solution was extracted with methylene chloride (300 ml) twice, and thereafter, thus obtained organic layer was concentr...
example 3
Synthesis of 3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methylbutyl aldehyde
Into a chemical reactor for hydrogen addition (hydrogenation) under elevated pressure, 3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methylbutyric acid (13.6 g), pivalic acid anhydride (22.8 g) and acetone (100 ml) were filled, and thereafter the mixture was bubbled with nitrogen gas for 30 minutes to substitute nitrogen gas completely for the gas in the system of reaction, whereby the system was filled with nitrogen gas. Palladium acetate (137 mg) and tetrahydrofuran solution (5 ml) of tri(p-tolyl) phosphine (930 mg) prepared previously, were added thereto, and then the mixture was stirred under hydrogen pressure of 5 MPa at 80° C. for 24 hours. From the obtained reaction solution, acetone was removed by vaporization. The remaining residue was subjected to a purification process with the use of a column chromatography to obtain 3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methylbutyl aldehyde (10.2 g, yield: 80%).
1H NMR (CDCl3):
δ:1.41 (s, 6...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com