Reagents and methods for detecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae
a technology of neisseria gonorrhoeae and reagents, applied in the field of molecular biology and nucleic acid chemistry, can solve the problems of sterility among other conditions, low detection efficiency, and low sensitivity of culture-based methods, so as to minimize the number of diagnostic procedures and minimize the overall cost of diagnosis. , the effect of rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Detection of N. Gonorrhoeae Via Nesseria Gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 9
Selection and synthesis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 9 specific Oligonucleotide Primers for PCR Analysis
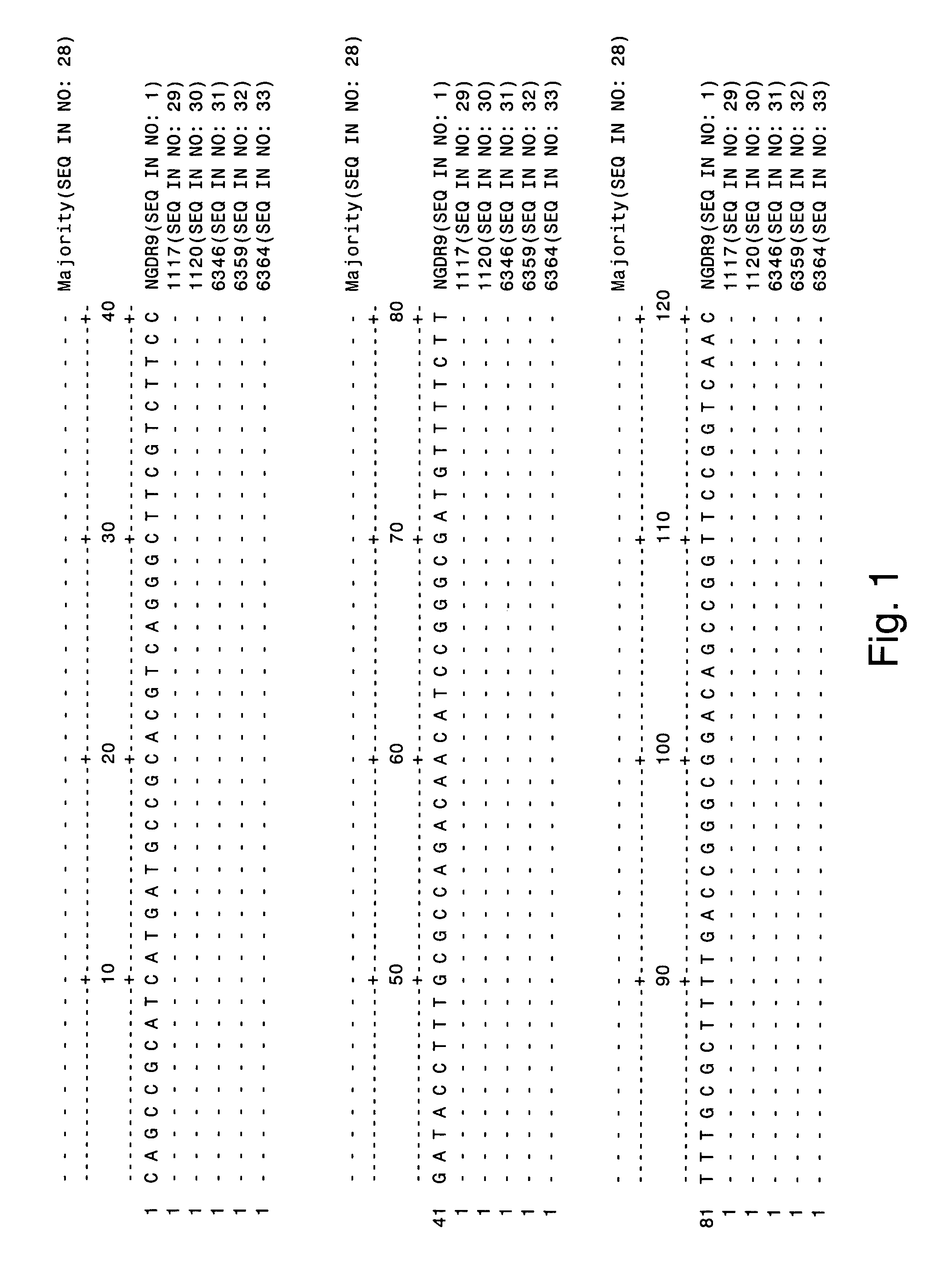
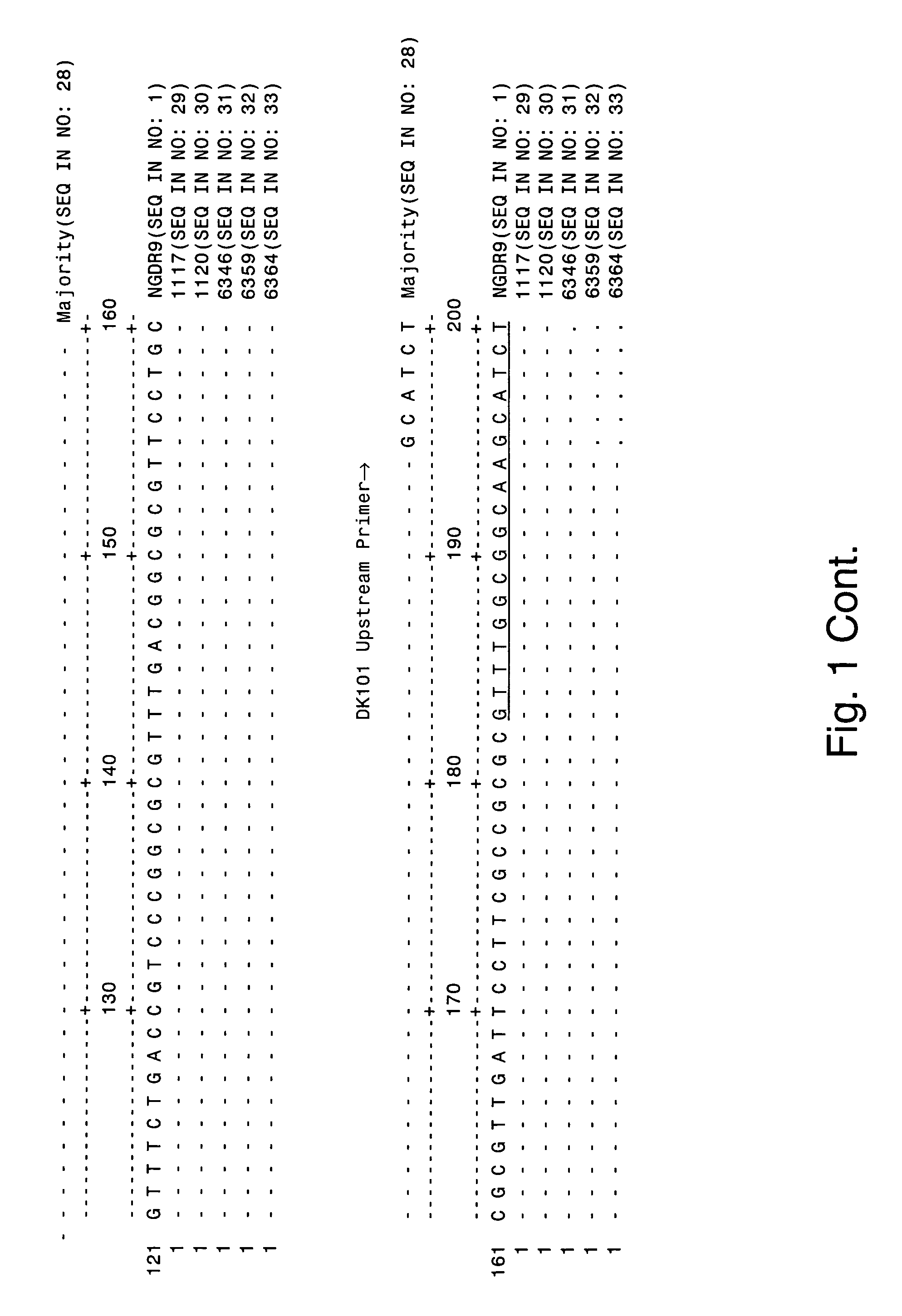
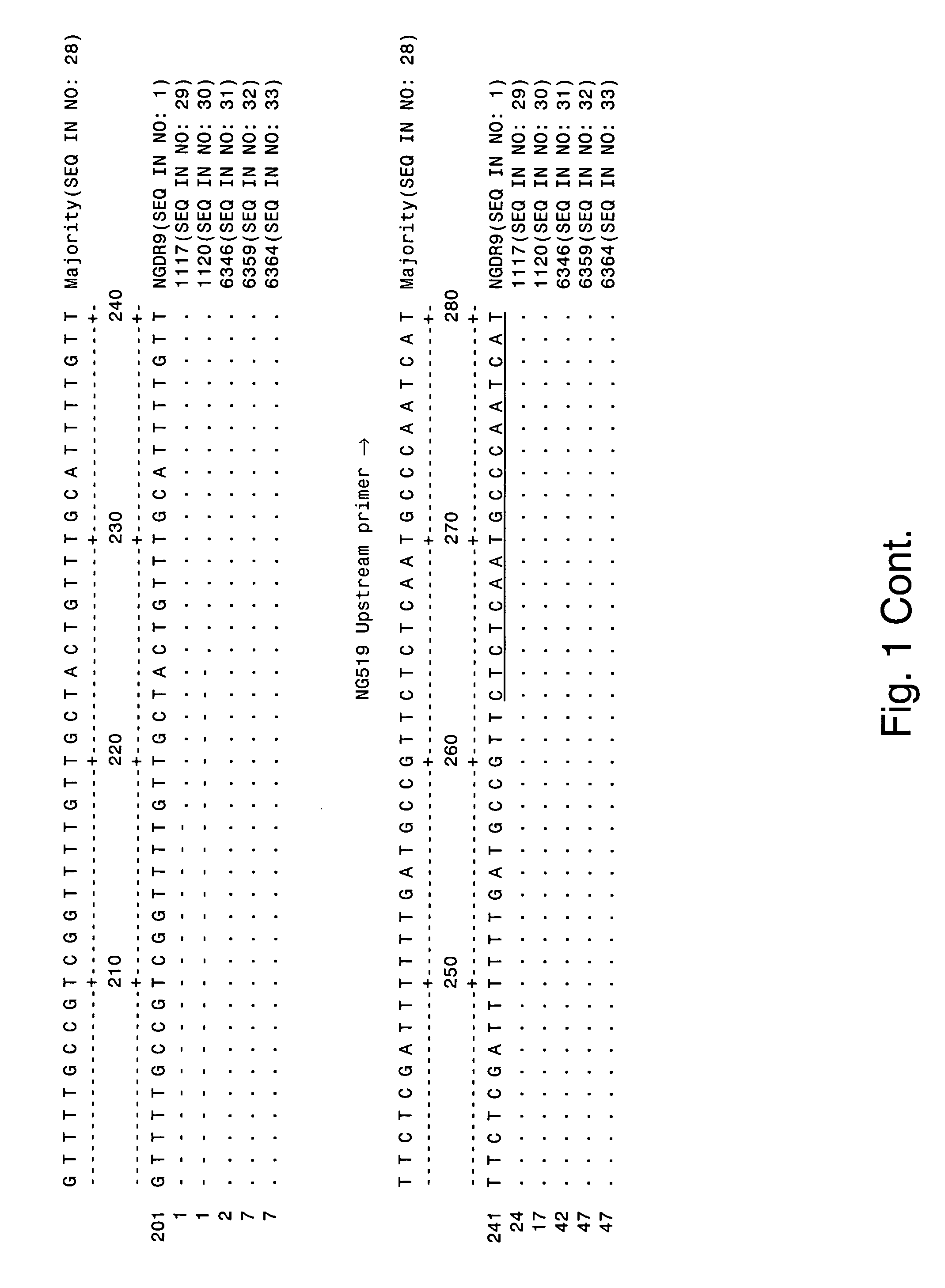
[0195] The Neisseria gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 9 (NGDR9) previously was identified as a two-copy DNA sequence in the Neisseria gonorrhoeae genome. The sequence of NGDR9 was obtained from the Los Alamos National Laboratory Sexually Transmitted Diseases database via the world wide web at stdgen.lanl.gov / stdgen / bacteria / ngon / as of Mar. 12, 2004. The entire 806 base pair NGDR9 sequence lacks substantial identity with any sequence in the Neisseria meningitidis genome, but has 36.85% identity with gaps (44.4% identity without gaps) to Brucella suis 1330 chromosome I section 155 (GenBank® accession number AE014469). FIG. 4 depicts a Clustal W alignment of the NGDR9 sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) with a portion of this Brucella sequence (SEQ ID NO: 34). The NGDR9 sequence was scanned for regions of minimal sequenc...
example ii
Assays Illustrating the Selective Detection of N. Gonorrhoeae
[0202] This example provides lists of organisms that were analyzed in assays that included the use of primer nucleic acids NG519 (having a sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 5) and NG514R (having a sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 24) and a 5′-nuclease probe (having a sequence corresponding to SEQ ID NO: 18) alone or in combination with C. trachomatis primers. In particular, the inclusivity (i.e., a measure of the ability to detect the target organism, N. gonorrhoeae in samples) of these assays is illustrated in Table IX.
TABLE IXGenusSpeciesNumberPrimersResultsNeisseriagonorrhoeae108CT / NGAll Positive
[0203] The exclusivity (i.e., a measure of the ability to exclude false positives when neisserial organisms of species other than gonorrhoeae are present in samples) of these assays is illustrated in Table X.
TABLE XGenusSpeciesNumberPrimersResultsNeisseriaanimalis3CT / NGAll NegativeNeisseriacaviae2″″Neisseriacinerea6...
example iii
Detection of N. Gonorrhoeae Via Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 33
Selection and Synthesis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 33 Specific Oligonucleotide Primers for PCR Analysis
[0205] The Neisseria gonorrhoeae Direct Repeat 33 (NGDR33) was previously identified as a two-copy DNA sequence in the Neisseria gonorrhoeae genome. The sequence of NGDR33 was obtained from the Los Alamos National Laboratory Sexually Transmitted Diseases database via the world wide web at stdgen.lanl.gov / stdgen / bacteria / ngon / as of Mar. 12, 2004. A blast homology search of NGDR33 revealed numerous significant hits with Neisseria meningitidis and the entire 1142 base pair NGDR33 sequence has 38.09% identity with gaps (50.44% identity without gaps) to N. meningitidis serogroup B strain MC58 section 77 (GenBank® accession number AE002435). FIG. 8 depicts a Clustal W alignment of the NGDR33 sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2) with a portion of this N. meningitidis sequence (SEQ ID NO: 35). The NGDR33 sequence was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com