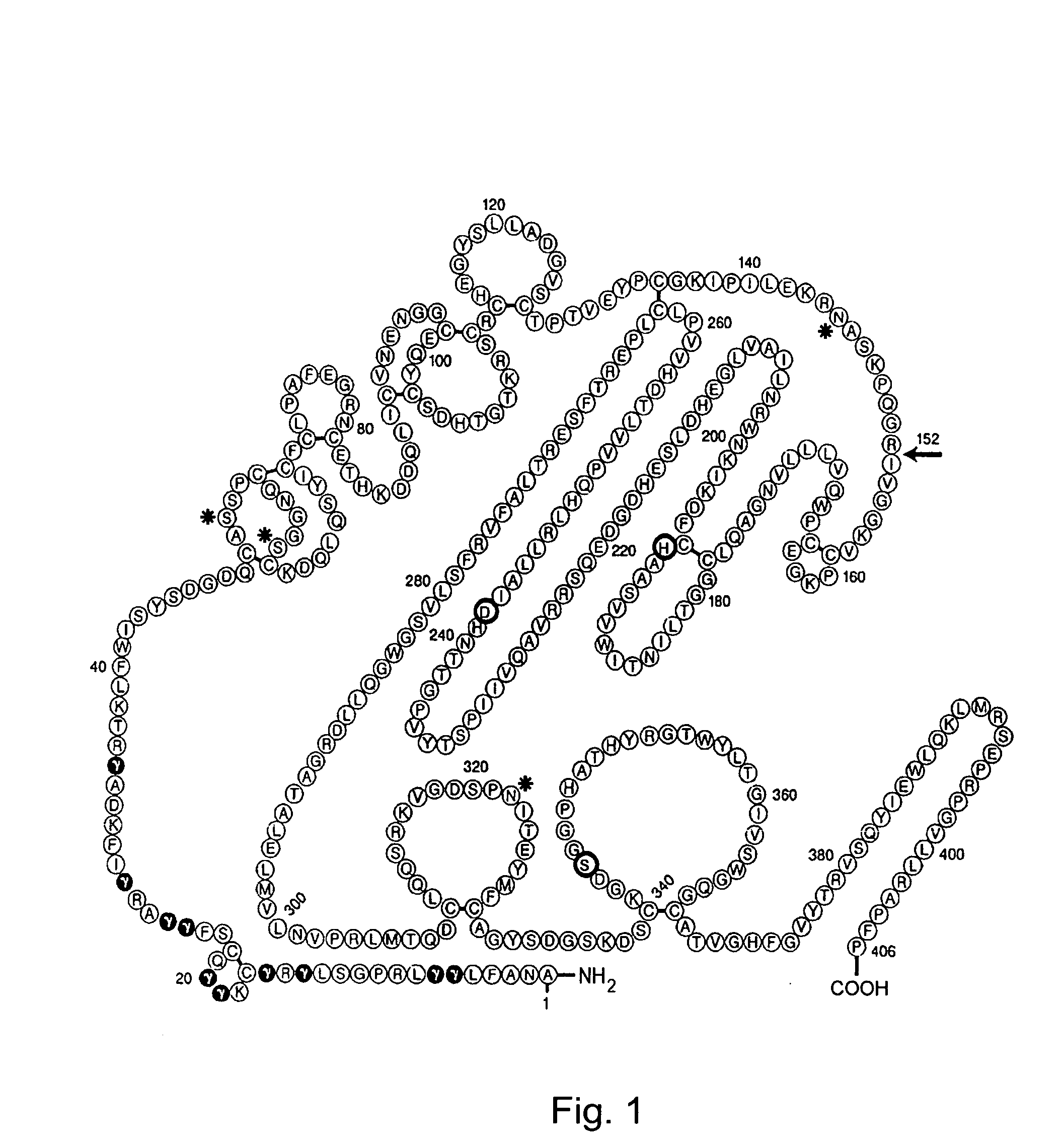
Coagulation Factor VII polypeptides
a technology of coagulation factor and polypeptide, which is applied in the field of human coagulation factor vii polypeptides, can solve the problems of fibrin clot formation and bleeding, and achieve the effect of increasing tf independent activity and increasing activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0396] Construction of DNA Encoding FVII-(S43N), FVII-(K62E), FVII-(Q64E), FVII-(I69F), FVII-(K62E / I69A), FVII-(Q64E / I69A), FVII-(Q62E / Q64E / I69A), FVII-(K62E / I69F), FVII-(Q64E / I69F), FVII-(K62E / Q64E / I69F), FVII-(S43C), FVII-(I69C), FVII-(Q64C), FVII-(M306C), FVII-(R277C), FVII-(I69N / F71T), FVII-(F71N / L73T), FVII-(R277N), and FVII-(D309N / L311T):
[0397] DNA constructs encoding FVII-(S43N), FVII-(K62E), FVII-(Q64E), FVII-(I69F), FVII-(K62E / I69A), FVII-(Q64E / I69A), FVII-(Q62E / Q64E / I69A), FVII-(K62E / I69F), FVII-(Q64E / I69F), FVII-(K62E / Q64E / I69F), FVII-(S43C), FVII-(I69C), FVII-(Q64C), FVII-(M306C), FVII-(R277C), FVII-(I69N / F71T), FVII-(F71N / L73T), FVII-(R277N), and FVII-(D309N / L311T) were prepared by site-directed mutagenesis using a supercoiled, double stranded DNA vector with insert of human FVII and two synthetic primers containing the desired mutation. The following primers were used:
For FVII-(S43N):5′-GGACGAAGCTGTTCTGGATTAACTACAGTGATGGGGACCAG-3′(SEQ ID NO:2)5′-CTGGTCCCCATCACTGTAGTTA...
example 2
[0400] Preparation of FVII-(S43N), FVII-(K62E), FVII-(Q64E), FVII-(I69F), FVII-(K62E / I69A), FVII-(Q64E / I69A), FVII-(Q62E / Q64E / I69A), FVII-(K62E / I69F), FVII-(Q64E / I69F), FVII-(K62E / Q64E / I69F), FVII-(S43C), FVII-(I69C), FVII-(Q64C), FVII-(M306C), FVII-(R277C), FVII-(I69N / F71T), FVII-(F71N / L73T), FVII-(R277N), and FVII-(D309N / L311T).
[0401] BHK cells were transfected essentially as previously described (Thim et al. (1988) Biochemistry 27, 7785-7793; Persson and Nielsen (1996) FEBS Lett. 385, 241-243) to obtain expression of the variant FVII polypeptide. The Factor VII polypeptide was purified as follows:
[0402] Conditioned medium was loaded onto a 50-ml column of Q Sepharose Fast Flow (Pharmacia Biotech) after addition of 5 mM EDTA, and 10 mM Tris, adjustment of pH to 8.0 and adjustment of the conductivity to 10-11 mS / cm by adding water. Elution of the protein was accomplished by a gradient from 10 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, pH 8.0 to 10 mM Tris, 50 mM NaCl, 25 mM CaCl2, pH 8.0. The fraction...
example 3
[0403] In Vitro Hydrolysis Assay
[0404] Native (wild-type) Factor VIIa and Factor VIIa variant (both hereafter referred to as “Factor VIIa”) are assayed in parallel to directly compare their specific activities. The assay is carried out in a microtiter plate (MaxiSorp, Nunc, Denmark). The chromogenic substrate D-Ile-Pro-Arg-p-nitroanilide (S-2288, Chromogenix, Sweden), final concentration 1 mM, is added to Factor VIIa (final concentration 100 nM) in 50 mM Hepes, pH 7.4, containing 0.1 M NaCl, 5 mM CaCl2 and 1 mg / ml bovine serum albumin. The absorbance at 405 nm is measured continuously in a SpectraMax™ 340 plate reader (Molecular Devices, USA). The absorbance developed during a 20-minute incubation, after subtraction of the absorbance in a blank well containing no enzyme, is used to calculate the ratio between the activities of variant and wild-type Factor VIIa:
Ratio=(A405 nm Factor VIIa variant) / (A405 nm nm Factor VIIa wild-type).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| dissociation constant Kd | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant Kd | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dissociation constant Kd | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com