Electronic device substrate and its fabrication method, and electronic device and its fabrication method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
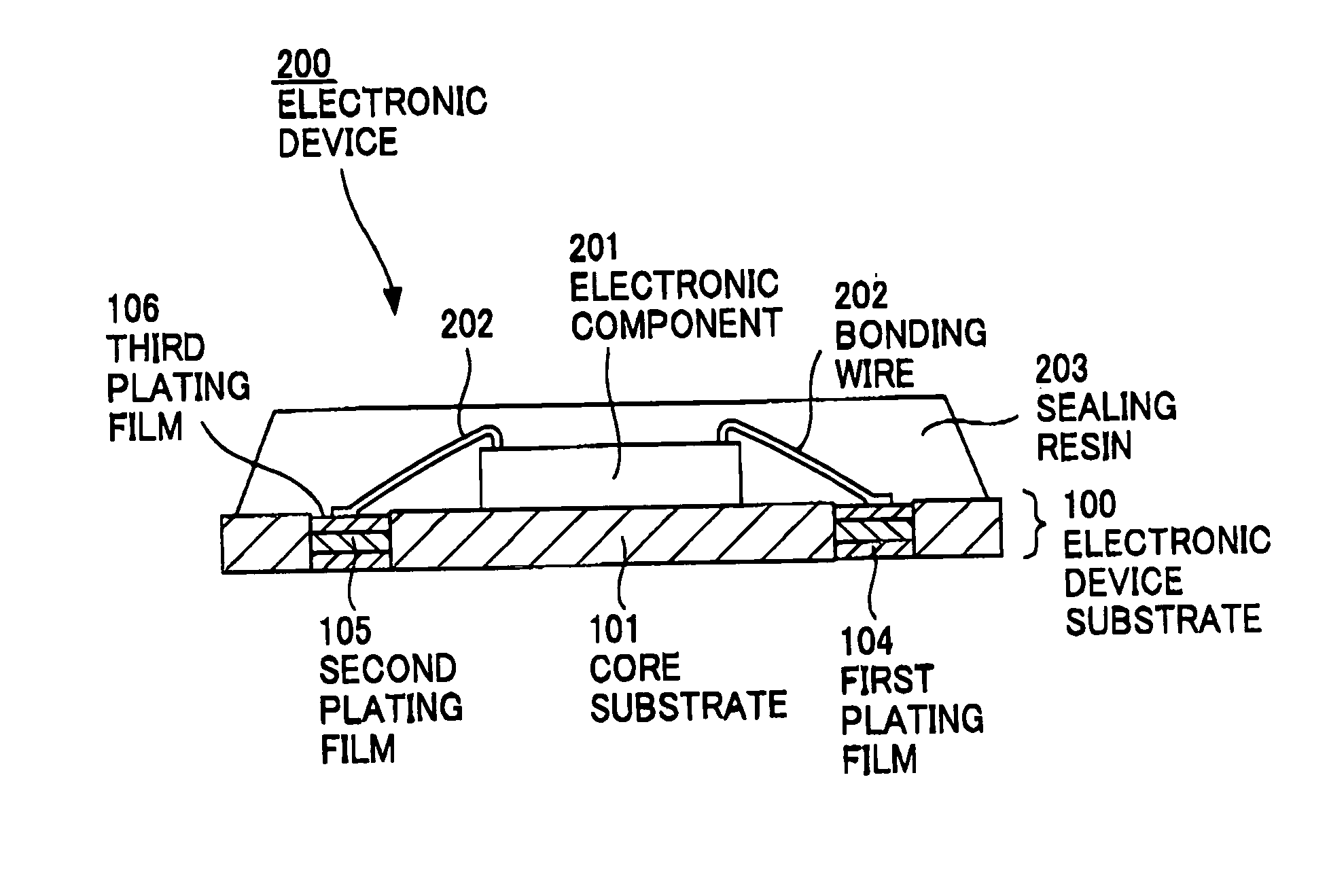
[0094]FIG. 5 shows an electronic device substrate according to the present invention. This electronic device substrate 100 comprises a core substrate 101 formed of copper foil as base material, a photo solder resist (hereinafter, “PSR”) film 102 as a first electrical insulation layer formed in a specified pattern on the core substrate 101, a first plating film 104 provided in an opening 103 formed in a specified position of the PSR film 102, a second plating film 105 provided on the first plating film 104, and a third plating film 106 provided on the second plating film 105.
[0095] From the points of view of availability, cost, high electrical conductivity, and removability in a final step, the core substrate 101 most preferably comprises copper foil, but may comprise stainless foil, aluminum or aluminum alloy foil, nickel or nickel alloy foil, tin or tin alloy foil.
[0096] The core substrate 101 needs to be 20 μm or more thick because mechanical durability is required in carrying an...
second embodiment
[0114] Next, there will be explained a fabrication method of the electronic device of FIG. 7 according to the FIGS. 8A-8E show a fabrication method of the electronic device of FIG. 7.
[0115] There is first prepared an electronic device substrate 100 as shown in FIG. 8A. Next, as shown in FIG. 8B, after an electronic component (IC chip) 201 having an aluminum electrode terminal not shown on a top surface is bonded with a die bonding paste to a coated surface of the PSR film 102 of the electronic device substrate 100, the aluminum electrode terminal of electronic component 201 and the third plating film 106 are electrically connected to each other with metallic bonding wires 202, as shown in FIG. 8C.
[0116] Next, this is followed by sealing resin 203 sealing for covering the electronic component 201, bonding wires 202, and third plating film 106 for protecting the electronic component 201 and bonded portions from external environment, as shown in FIG. 8D.
[0117] Next, a ferric chlorid...
third embodiment
[0128] Next, there will be explained a fabrication method of the electronic device substrate according to the FIGS. 10A-10G show a fabrication method of the electronic device substrate 100 of FIG. 9.
[0129] First, a carrier-laminated core substrate 120 (FIG. 10A) is coated with a 15 μm thick PSR film 102 by screen printing, as shown in FIG. 10B. Next, as shown in FIG. 10C, using a photomask 108, the PSR film 102 is irradiated with ultraviolet rays 107 via the photomask 108. As shown in FIG. 10D, this is followed by development and formation of openings 103 in a desired shape on the PSR film 102.
[0130] Next, as shown in FIG. 10E, the surface of the carrier layer 121 is protected with a plating-resistant chemical electrical insulation tape (masking tape) 109, followed by immersion in an electrical gold plating liquid for forming a first plating film 104 and, using the core substrate 120 as a cathode, a 0.5 μm thick gold plating film is applied to the opening as a first plating film 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com