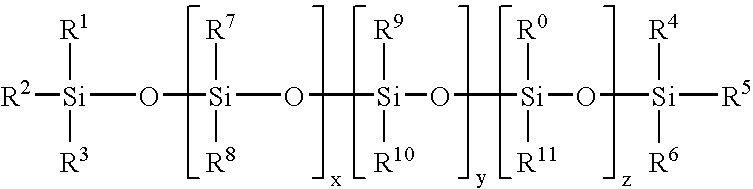Tissue products containing deliquescent materials and non-ionic surfactants
a technology of deliquescent materials and surfactants, which is applied in the directions of non-fibrous pulp addition, application, biocide, etc., to achieve the effects of improving handfeel, reducing the surface tension of solution, and optimizing the tactile sheet properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0029] This example demonstrates the reduction in the Single Water Drop Test values by incorporating small amounts of a non-ionic surfactant into the surfactant / deliquescent salt solution. Specifically, an aqueous solution of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) was prepared by dissolving 2.95 parts of MgCl2.6H20 in 1 part of distilled water at room temperature. This ratio gave a deliquescent salt solution having 35 percent by weight MgCl2. The solution had a Single Water Drop Test value of 41 seconds when placed on a 3-ply creped, untreated, facial tissue basesheet.
[0030] For comparison, 20×10−3 ml of an non-ionic surfactant was added to 100 parts of the concentrated magnesium chloride solution. The non-ionic surfactant was, 2,4,7,9-tetramethyl-5-decene-4,7-diol ethoxylate (1.75 EO / OH) obtained from Aldrich Chemical Co., Milwaukee, Wis. After mixing, when placed on the same 3-ply creped, untreated facial tissue basesheet, the resulting surfactant / deliquescent salt solution was found to have...
examples 2 and 3
[0031] These comparative examples demonstrate the impact that the addition of a small amount of non-ionic surfactant can have on speed and absorption of the deliquescent salt solution into a tissue product run on commercial manufacturing equipment. For both Examples 2 and 3, a two-ply creped tissue sheet having a finished basis weight of 15.0 pounds per 2880 square feet and a furnish consisting of 65 percent hardwood and 35 percent softwood fibers was used. Each ply was made from a stratified fiber furnish including two outer layers and a middle layer. The deliquescent salt solution was printed on both outer sides of the 2-ply tissue product via a simultaneous offset rotogravure printing process. The salt solutions were delivered as aqueous solutions having approximately 42 percent solids. The gravure rolls were electronically engraved, chrome-over-copper rolls supplied by Southern Graphics Systems, located at Louisville, Ky. The rolls had a line screen of 360 cells per lineal inch ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com