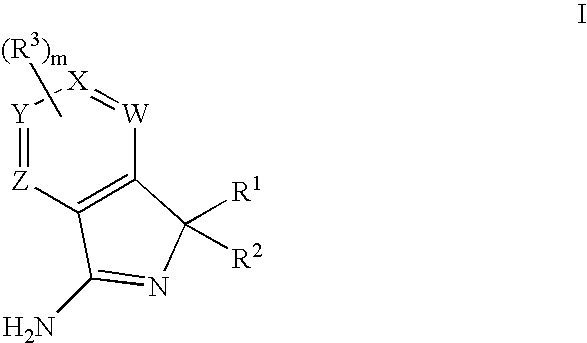
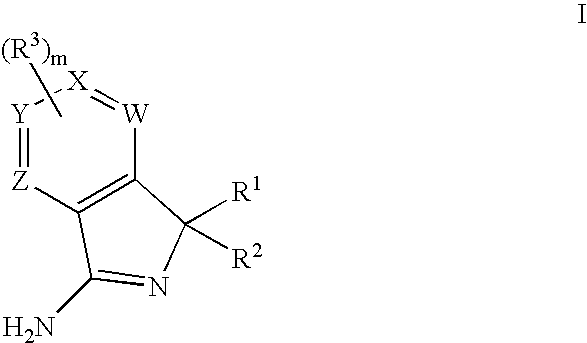
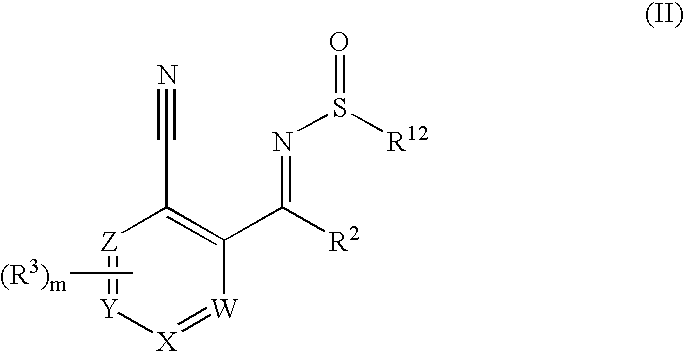
New compounds 834
a new type of compound and compound technology, applied in the field of new compounds 834, can solve the problems of increasing the prevalence of alzheimer's disease in this population, increasing the difficulty of drug preparation, etc., and achieve the effect of improving potency and beneficial properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
3-(3-Bromobenzoyl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile
[0245]
[0246]A suspension of highly active zinc (Rieke zinc) in THF (100 mg / mL, 12.7 mL, 19.4 mmol) was added via a syringe to a solution of 3-bromo-2-cyanopyridine (1.189 g, 6.497 mmol) in anhydrous THF (20 mL) under an atmosphere of argon. The mixture was stirred for four h at room temperature and then at 50° C. for 15 min. The remaining zinc powder was allowed to settle at the bottom of the flask overnight at −20° C. The top solution was transferred to another flask and cooled to −20° C. To this was added a 1 M solution of copper cyanide di(lithium bromide) complex in THF (6.82 mL) and the resulting mixture was stirred for 5 min at −20° C. and for 35 min at 0° C. and then cooled to −30° C. prior to the addition of 3-bromobenzoyl chloride (1.78 g, 8.12 mmol). The mixture was stirred for 6 h during which time the temperature went from −30° C. to 0° C. The reaction was quenched by the addition of saturated ammonium chloride solution and ethyl ...
example 2
N-[(1E)-(3-Bromophenyl)(2-cyanopyridin-3-yl)methylenel-2-methylpropane-2-sulfinamide
[0247]
[0248]Titanium(IV)ethoxide (1 M solution in THF, 18.7 mL) was added to a solution of 3-(3-bromobenzoyl)pyridine-2-carbonitrile (2.680 g, 9.334 mmol) and tert-butylsulfinamide (1.244 g, 10.27 mmol) in anhydrous THF (10mL) under an atmosphere of argon. The mixture was heated at 50° C. for 70 h. After cooling to room temperature the mixture was diluted with methanol (20 mL) and 100 drops of water was added. The resulting mixture was allowed to stand for about 1 h and then filtered through a pad of sodium sulfate. The filter cake was taken up in saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and dichloromethane. The mixture was stirred over night, the phases were separated and the aqueous phase was extracted with dichloromethane. The extracts were combined with the filtrate from above, dried over sodium sulfate and evaporated. Purification by column chromatography using a gradient of increasi...
example 3
5-(3-Bromophenyl)-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-blpyridin-7-amine
[0249]
[0250]Butyllithium (2.5 M in hexanes, 0.947 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of 4-bromoanisole (483 mg, 2.58 mmol) in anhydrous THF at −78° C. under an atmosphere of argon. The mixture was stirred at that temperature for 30 min and then a solution of N-[(1E)-(3-bromophenyl)(2-cyanopyridin-3-yl)methylene]-2-methypropane-2-sulfinamide (Example 2, 840 mg, 2.15 mmol) in THF (10 mL) was added dropwise. Stirring was continued for 3 h at −78° C., and then for 1 h at −25° C. The reaction was quenched by the addition of water, the mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with water, dried over magnesium sulfate and concentrated. The residue was dissolved in methanol (20 mL) and to this was added 2 M hydrochloric acid in diethyl ether (2.5 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 22 h and then concentrated. The residue was partitioned between dichloromethane and saturated aqueous sodium hydrog...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com