Treatment of hepatic encephalopathy and liver cirrhosis
a technology for liver cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy, which is applied in the field of treatment or prevention of hepatic encephalopathy and liver cirrhosis, can solve the problems of increased risk of infection, poor long-term outcome, and potentially life-threatening, and achieves the effects of improving the overall cognitive function of the treated subject, shortening the length of the hepatic encephalopathy episode, and reducing the severity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Experimental Hepatic Encephalopathy is Accompanied by Activation of AMPK by Cannabinoids
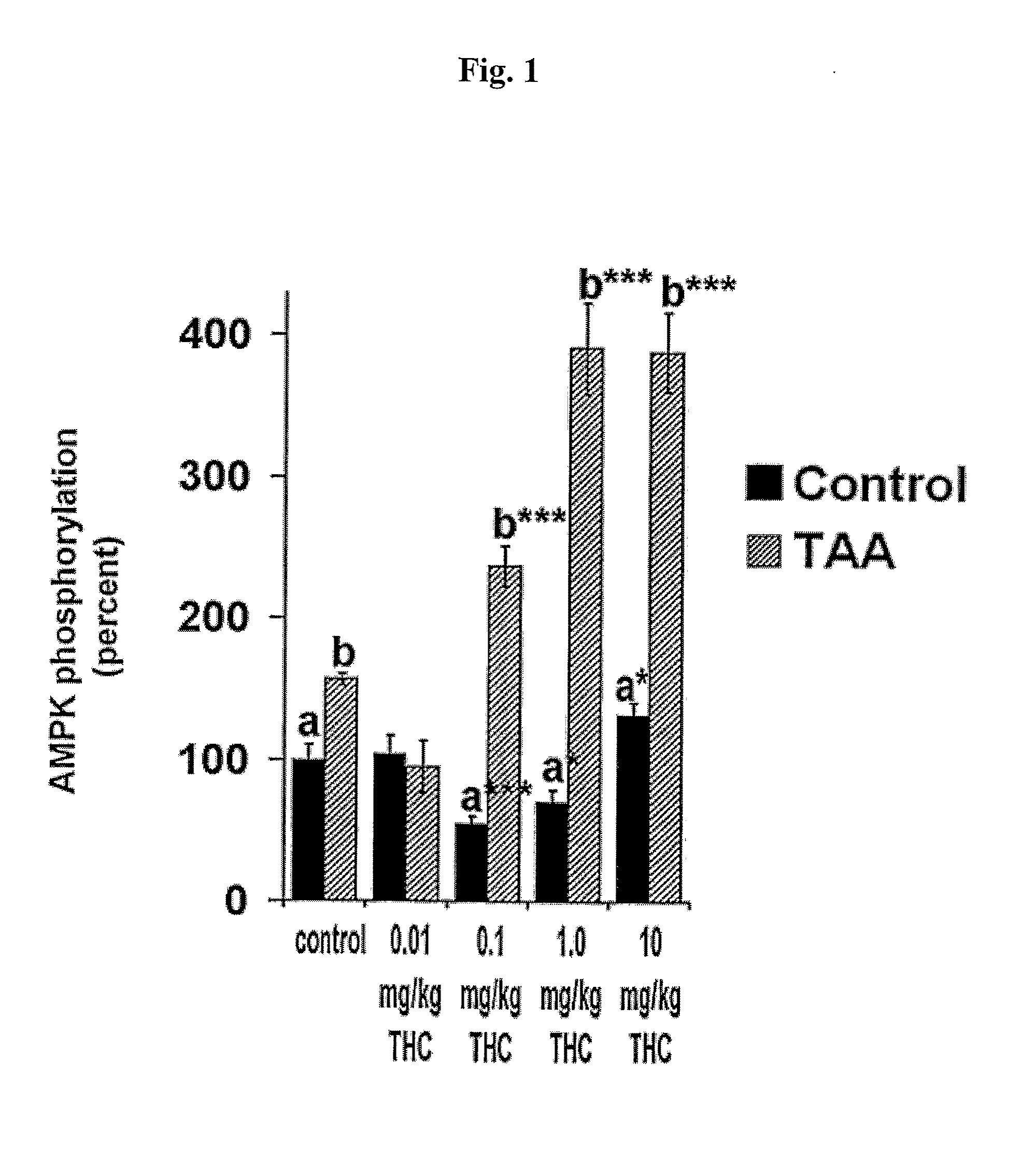
[0078]To consider their role in AMPK stimulation, we studied the effects of giving exogenous cannabinoids to activate AMPK. In the first step, control mice were administrated with 0.01 to 10 mg / kg THC and hippocampal AMPK phosphorylation was analyzed. THC treatment showed a biphasic effect (Sulcova et al., 1998). While low levels of THC (less than 0.1 mg / kg) reduced the level of activated AMPK, higher concentrations exhibited a dose dependent elevation in activated enzyme, reaching a significant activation of AMPK (FIG. 1). In the next step, the effect of THC was tested in TAA treated mice. In this instance THC also demonstrated a biphasic effect. However, an inactivating effect was already observed in 0.01 mg / kg and AMPK activation was achieved by 0.1 mg / kg. Elevation of the cerebral responsiveness to THC suggested that low doses of THC, which do not activate the AMPK in the healthy animals, cou...
example 2
THC Activates AMPK and Improves Impaired Brain Function in Experimental Hepatic Encephalopathy
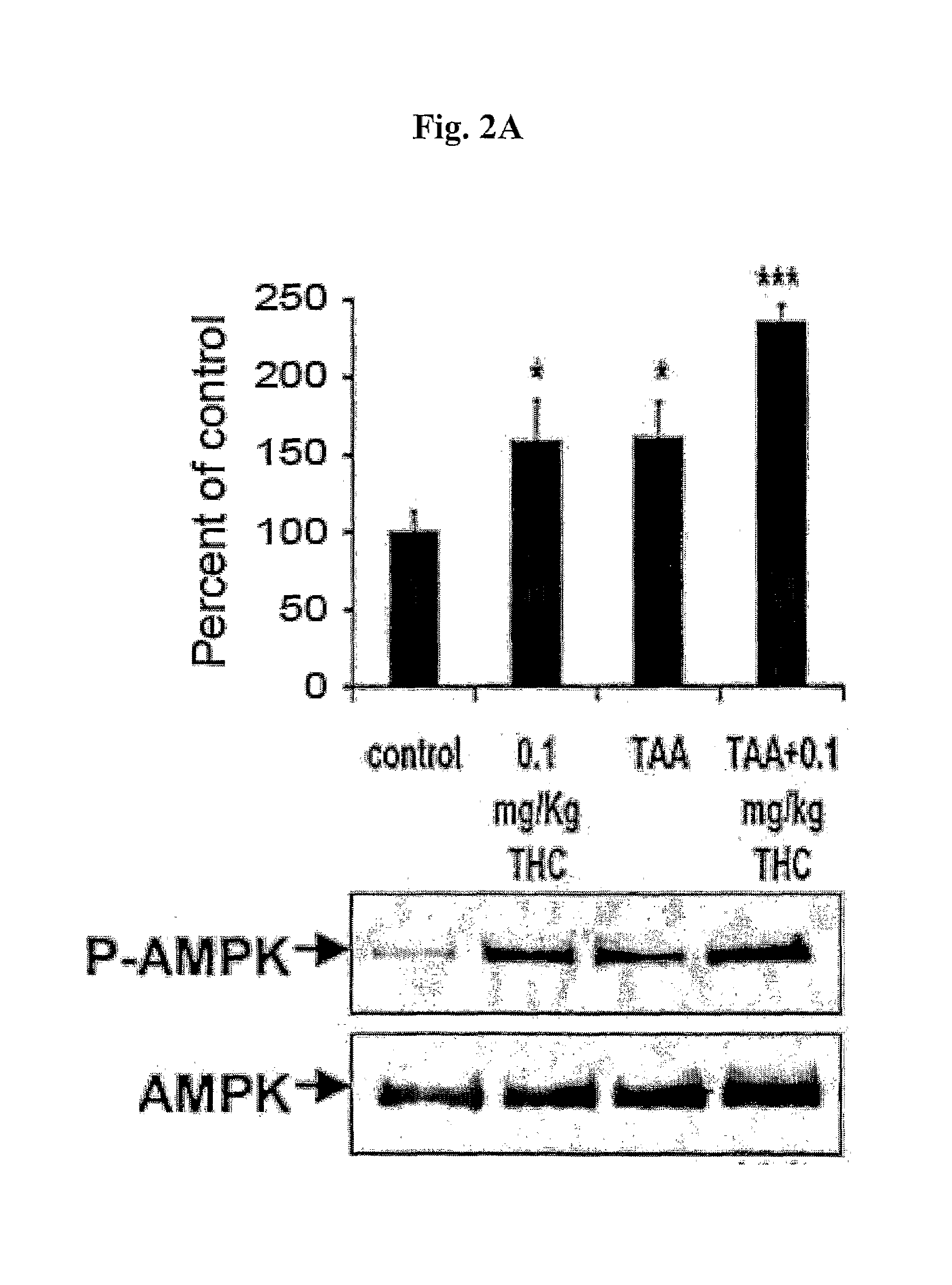
[0079]Since treatment of 0.1 mg / kg THC augmented AMPK activation in a similar manner to AICAR treatment, we chose this dose to test THC's physiological effects on the experimental hepatic encephalopathy. TAA treated mice were administrated daily with 0.1 mg / kg THC for 5 days. Amplification of AMPK activation in response to THC administration was confirmed in the brains of the experimental animals at the end of the behavioral studies (FIG. 2A).
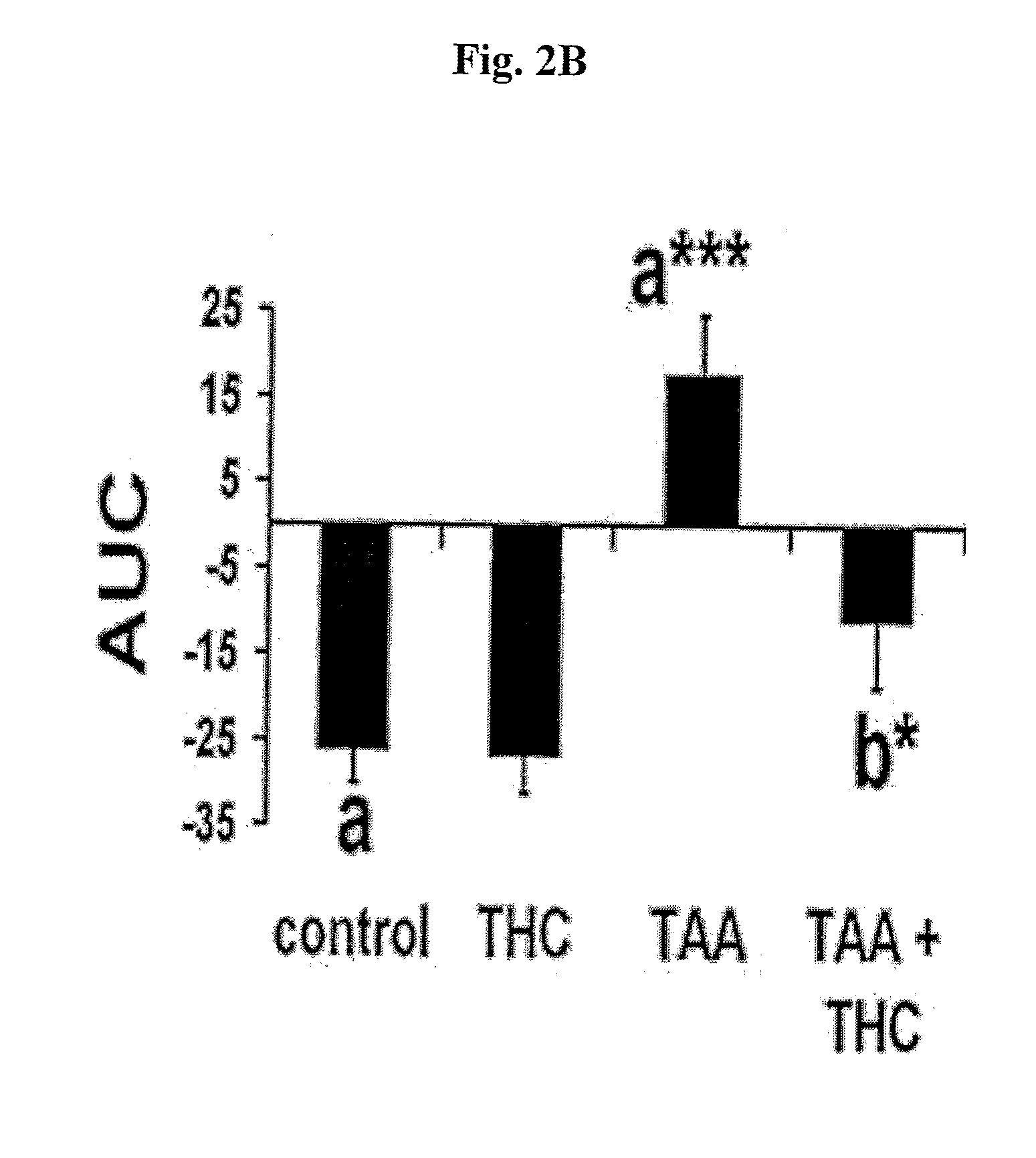
[0080]Next, we investigated the outcome of AMPK activation increase on brain function. Following the treatment, TAA-induced impaired cognitive function was improved significantly (FIG. 2B), poor activity performances were restored (FIG. 2C) and the reduced neurological score was improved (FIG. 2D). To reveal the mechanism by which THC could improve brain function, we studied the catecholaminergic response to THC treatment. Brain tissue in animals with ...
example 3
AICAR and THC Treatment do not Improve Markers of Hepatic Function
[0081]To investigate the possibility that the neural benefits of AICAR and THC might also result from peripheral effects (i.e. improvement of liver function) rather than cerebral function, we studied their effects on liver function. Animals treated with TAA exhibited hyperammonemia as a result of the liver dysfunction; AICAR and THC treatment had no effect on the ammonia level (FIG. 3A). Bilirubin levels and liver enzymes activity are the most commonly used laboratory markers of liver function. TAA treated mice demonstrated increased levels of bilirubin (FIG. 3B), alanine transaminase (ALT) (FIG. 3C), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (FIG. 3D) and gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) (FIG. 3E). Neither AICAR nor THC ameliorated these markers indicating lack of direct action on liver recovery. Glucose analysis revealed a systemic hypoglycemia following TAA treatment (FIG. 3F) providing additional evidence for the metabolic ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com