Method of controlling a drug release rate
a drug release rate and release rate technology, applied in the field of drug delivery systems, can solve the problems of serious complications associated with the use of coronary stents, the benefits of their use remain controversial, and the non-uniform thickness of the patient's skin is reduced, and the quality of life of patients is improved. , the effect of reducing complications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
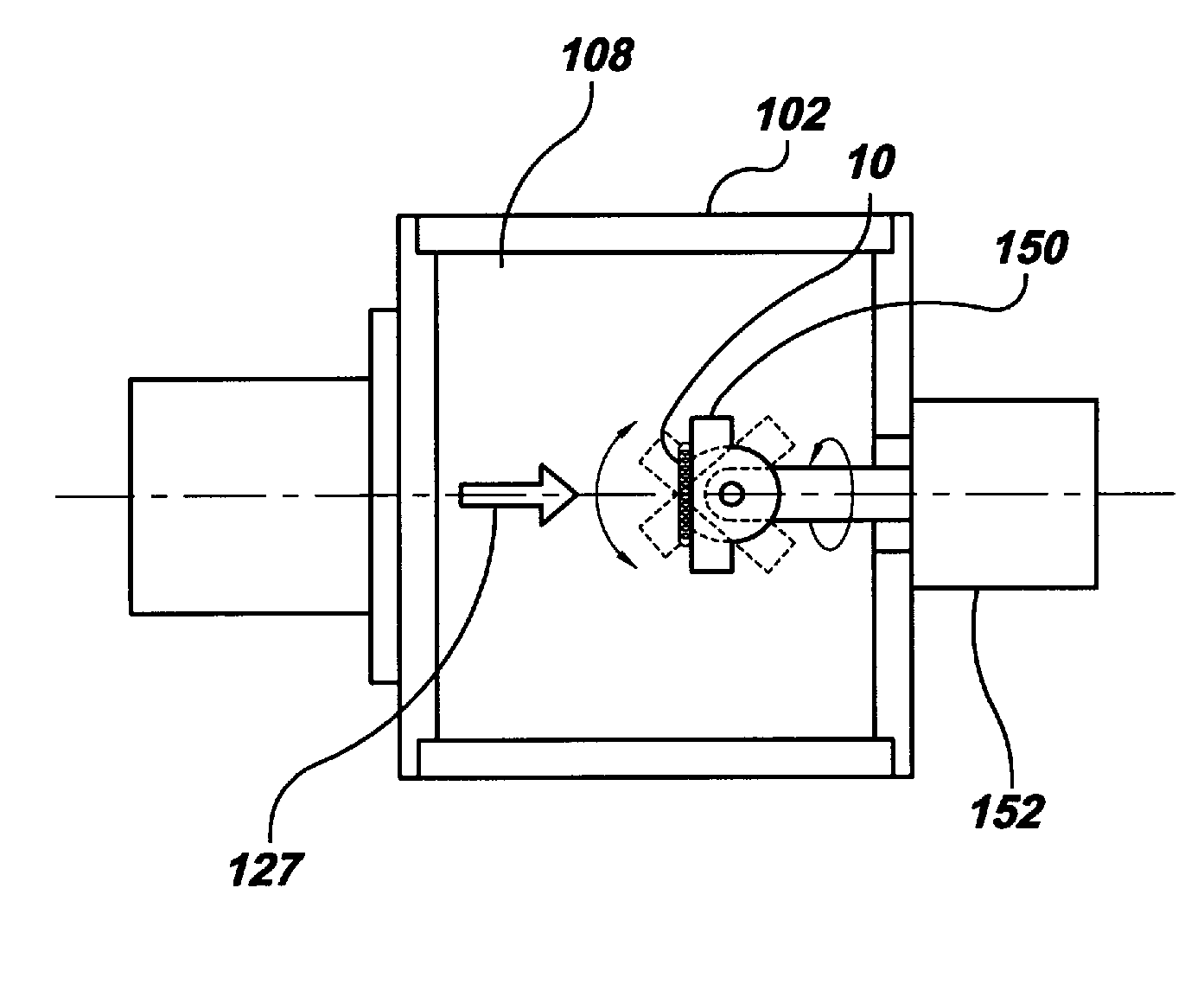
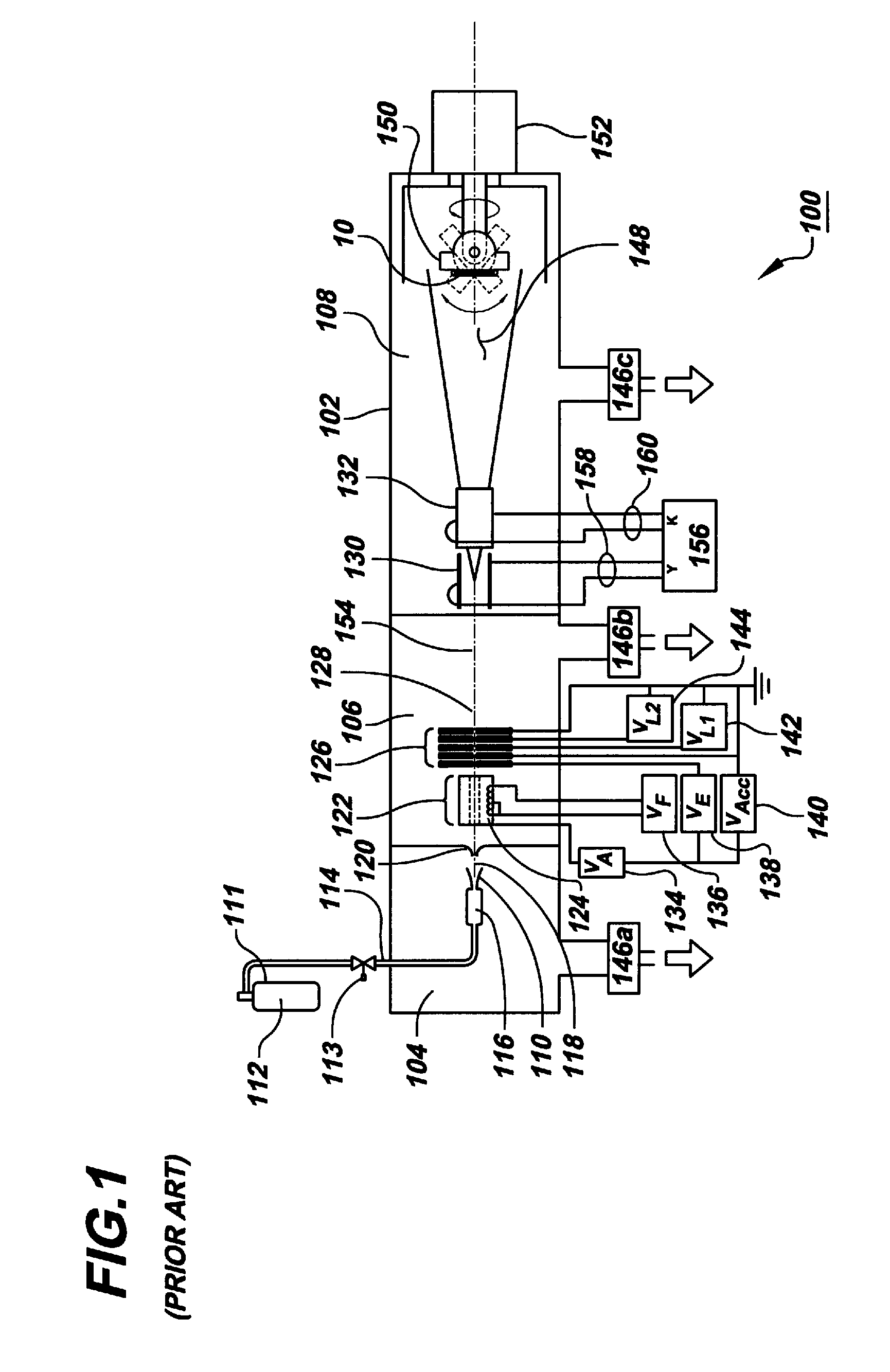
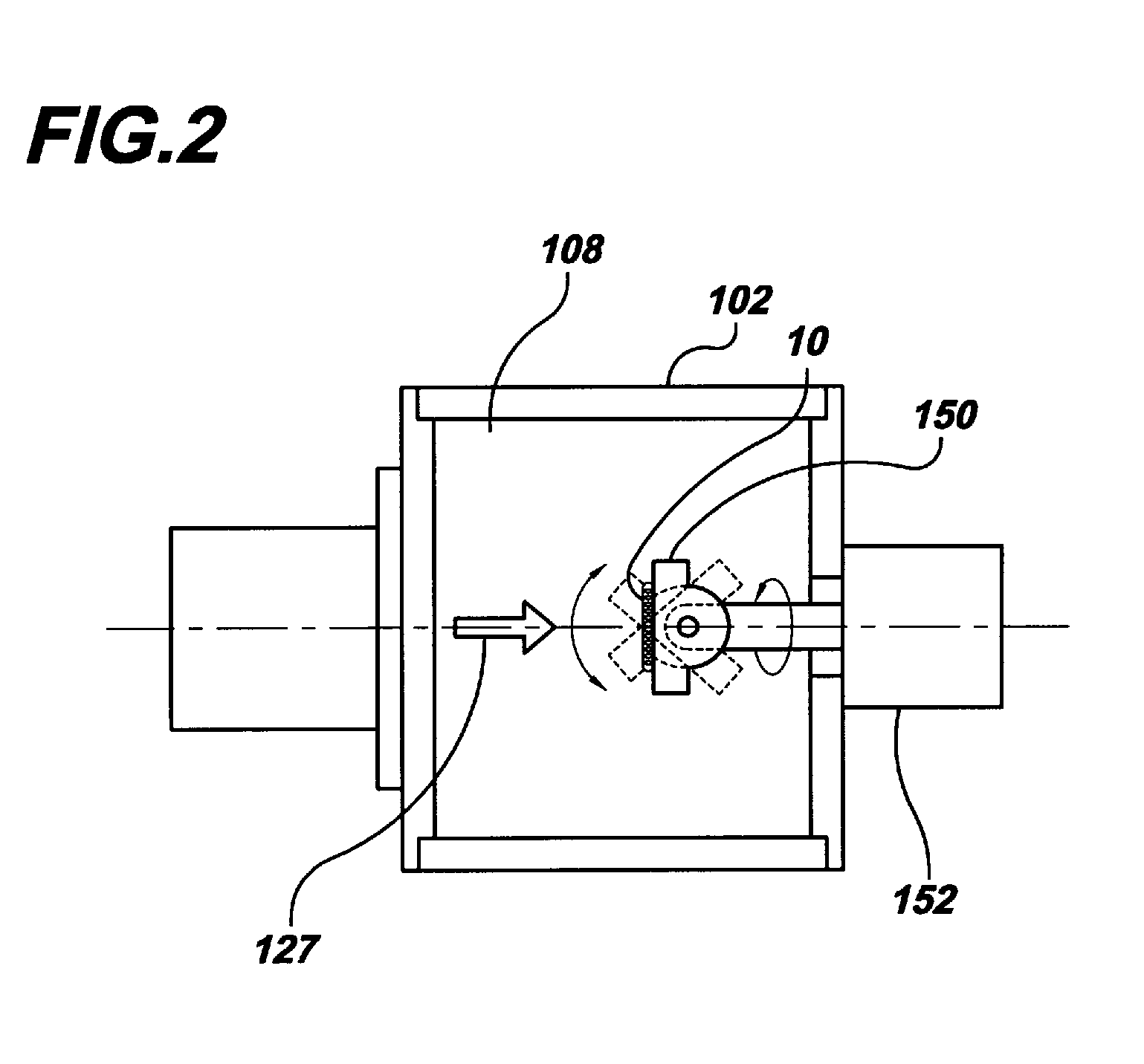
[0030]Beams of energetic ions, electrically charged atoms or molecules accelerated through high voltages under vacuum, are widely utilized to form semiconductor device junctions, to smooth surfaces by sputtering, and to enhance the properties of thin films. In the present invention, these same beams of energetic ions are utilized for the applying and adhering drugs to a surface of a medical device, such as a coronary stent, thereby converting the surface into a drug delivery system.
[0031]In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, gas cluster ion beam GCIB processing is utilized. Gas cluster ions are formed from large numbers of weakly bound atoms or molecules sharing common electrical charges and accelerated together through high voltages to have high total energies. Cluster ions disintegrate upon impact and the total energy of the cluster is shared among the constituent atoms. Because of this energy sharing, the atoms are individually much less energetic than the case of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com