Methods for altering acetic acid production and enhancing cell death in bacteria
a technology of acetic acid and cell death, which is applied in the direction of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and processes, oxidoreductases, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the growth yield of the industry, cell death, and cost of removal of acetate from the medium, so as to increase growth, increase longevity in culture, and enhance survival
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
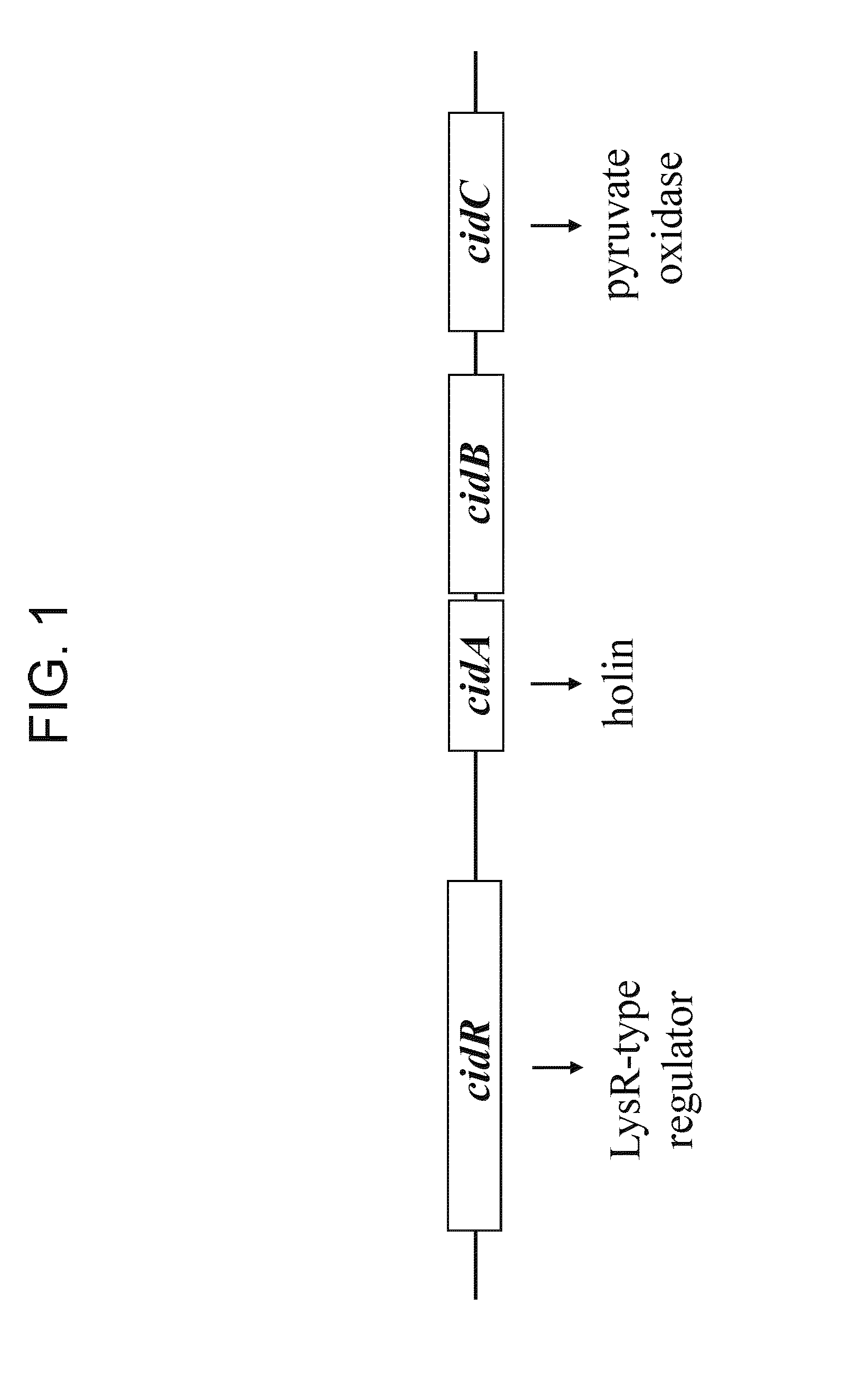
Acetic Acid Induces Expression of the Staphylococcus aureus cidABC and lrgAB Murein Hydrolase Regulator Operons
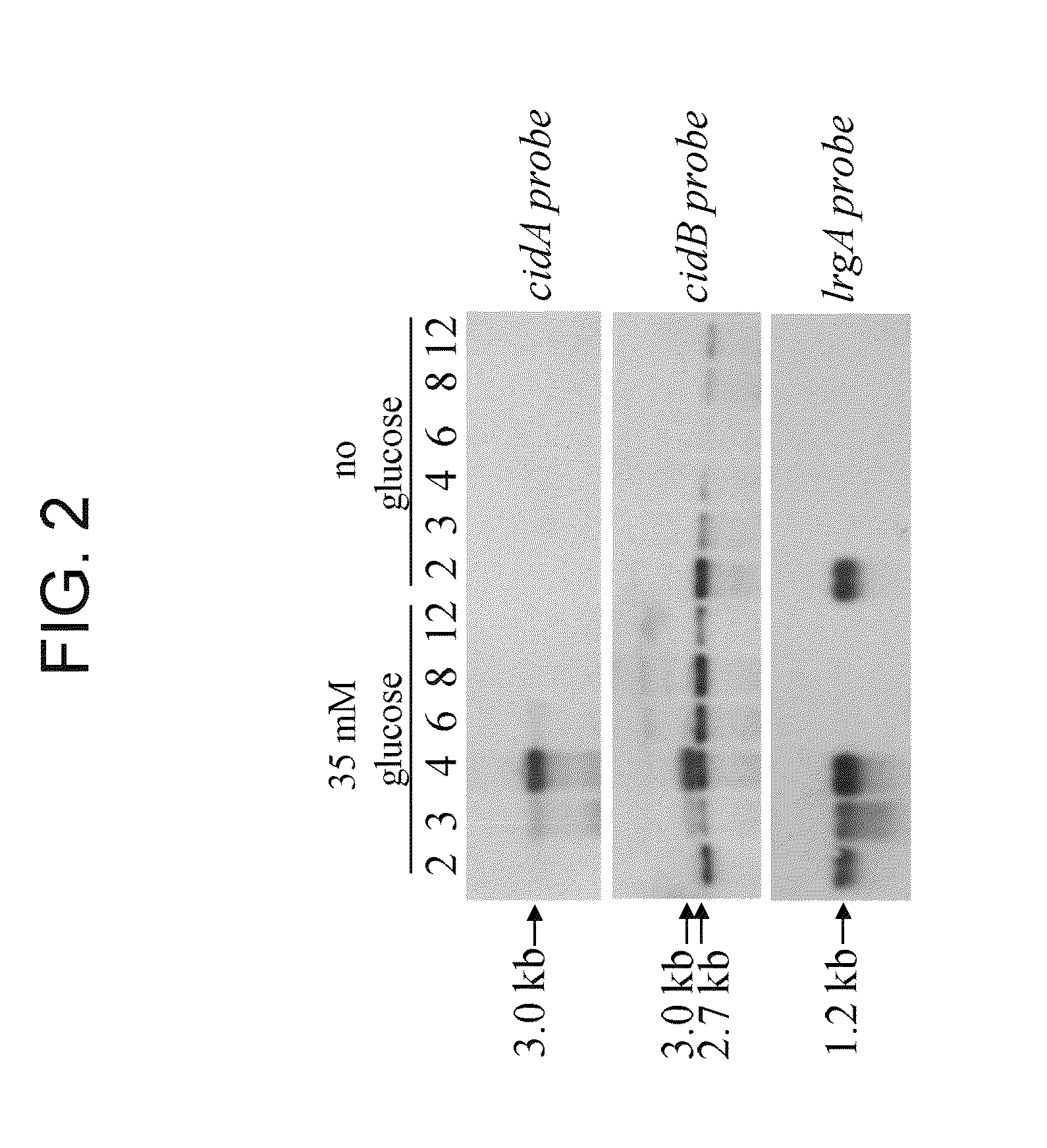
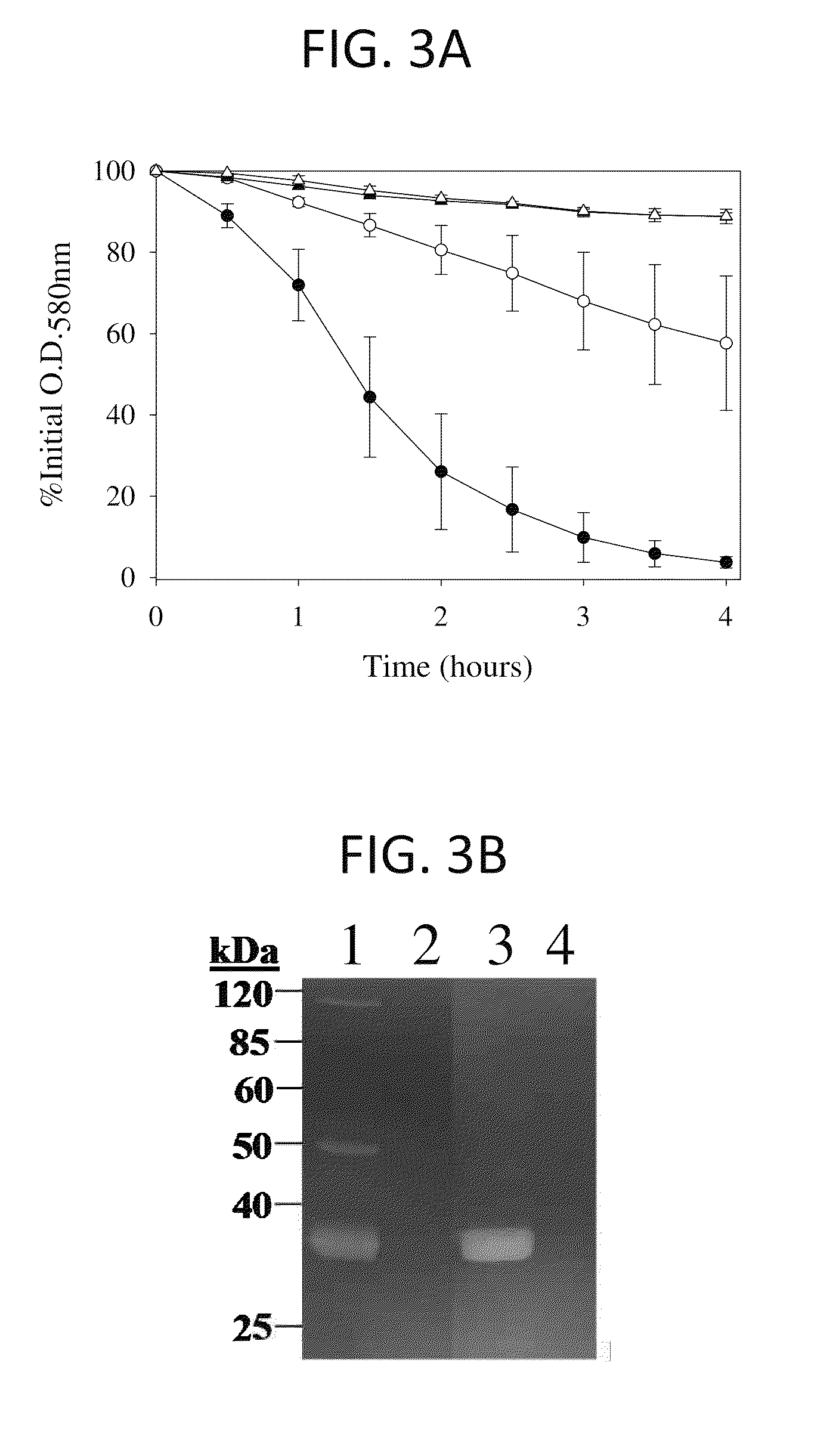
[0231]Responsiveness of cidABC and lrgAB to growth in glucose was evaluated by northern blot analysis and biochemical assays. Expression of both cidABC and lrgAB was stimulated by growth in the presence of 35 mM glucose. This effect was found to be dependent on the accumulation of acetic acid in the culture supernatant, a consequence of glucose metabolism. Furthermore, extracellular murein hydrolase activity and rifampin sensitivity of UAMS-1 (a previously-characterized low-passage clinical isolate) was greatly enhanced when grown in the presence of 35 mM glucose. A variant of UAMS-1 with a mutation in the cidA gene displayed a complete loss of extracellular murein hydrolase activity as well as decreased sensitivity to rifampin, a phenotype very similar to the previously characterized cidA mutant of RN6390 (Rice et al., J. Bacteriol. 185: 2635-2643, 2003). However, unlike U...
example 2
The Staphylococcus aureus cidC Gene Encodes a Pyruvate Oxidase and Affects the Production of Acetic Acid in Stationary Phase
[0244]The cid operon expresses two overlapping transcripts. One transcript spans the cidB and cidC genes and is expressed in a sigma B-dependent manner. The other transcript spans all three genes and its expression is enhanced by growth in the presence of 35 mM glucose. Based on sequence comparison studies, the cidC gene encodes a pyruvate oxidase that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetate and CO2. The cidC gene product shares 33% identity with PoxB, the Escherichia coli pyruvate oxidase, and LpPOX, the Lactobacillus plantarum pyruvate oxidase (Rice et al., J. Bacteriol. 186(10):3029-3037, 2004). These two enzymes catalyze the decarboxylation of pyruvate although their end products are different (Russell & Gennis J Biol Chem 252:7877-7882, 1977; Tittmann et al., Biochemistry 39:10747-10754, 2000). The end products of the reaction cataly...
example 3
Induction of the cidABC Operon by CidR
[0266]The cidABC operon lies downstream from an open reading frame (ORF), designated cidR (GenBank accession no. AY581892). The gene product of the cidR gene is homologous to the LysR-type transcriptional regulator family of proteins (LTTR). The role of the cidR gene product in regulating expression of the cidABC operon was investigated in detail by creating an isogenic cidR mutant of the previously characterized S. aureus clinical isolate, UAMS-1. Northern blot analyses of the cidR mutant indicated that CidR enhances cidABC expression in the presence of acetic acid generated by the metabolism of excess glucose. These data also demonstrate that the cidR gene product affects the control of murein hydrolase activity by enhancing cidABC expression. Finally, the cidR mutation was also shown to affect both antibiotic tolerance and survival of S. aureus in stationary phase.
Materials and Methods:
[0267]Bacterial strains and growth conditions. The bacter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com