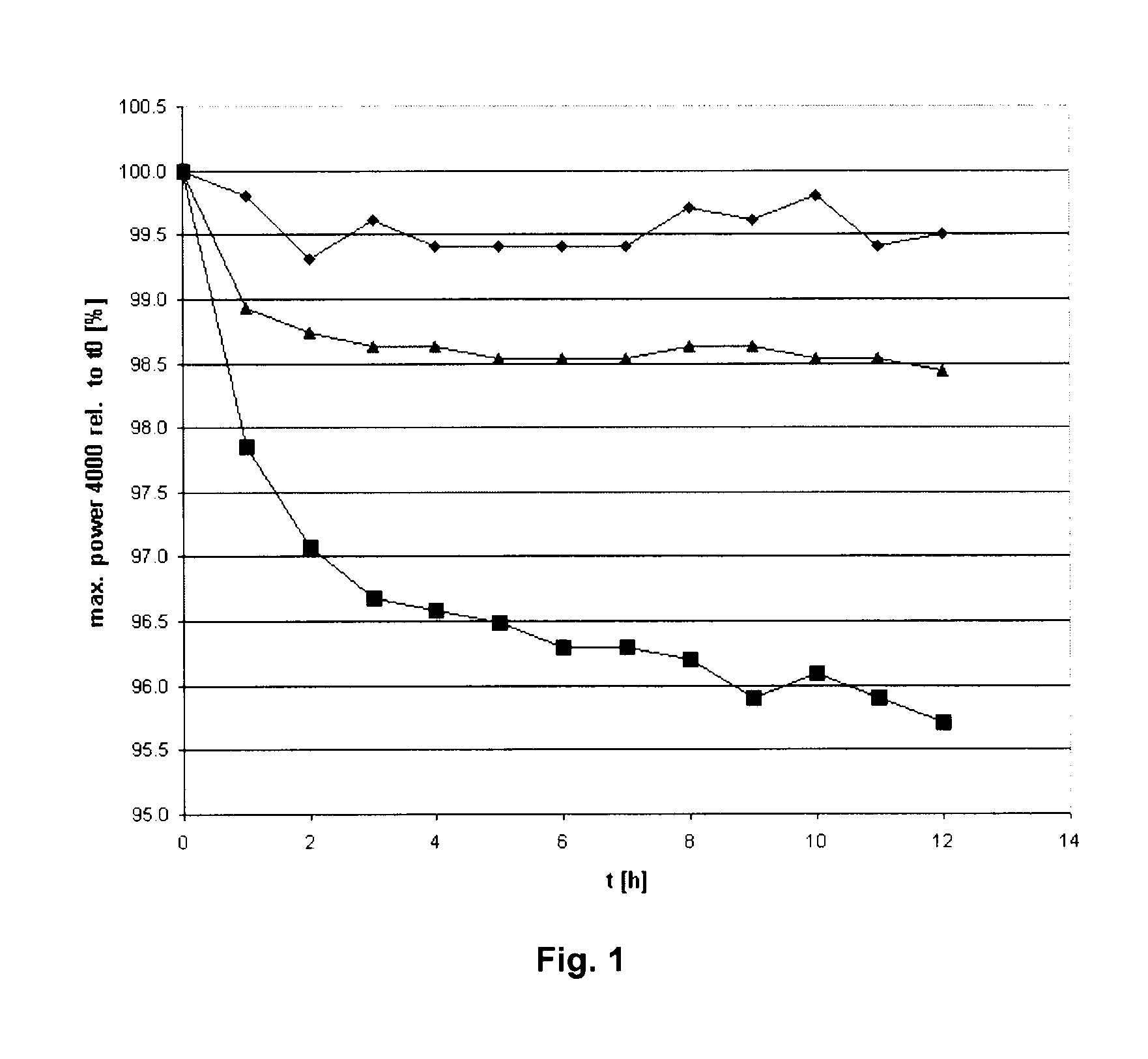
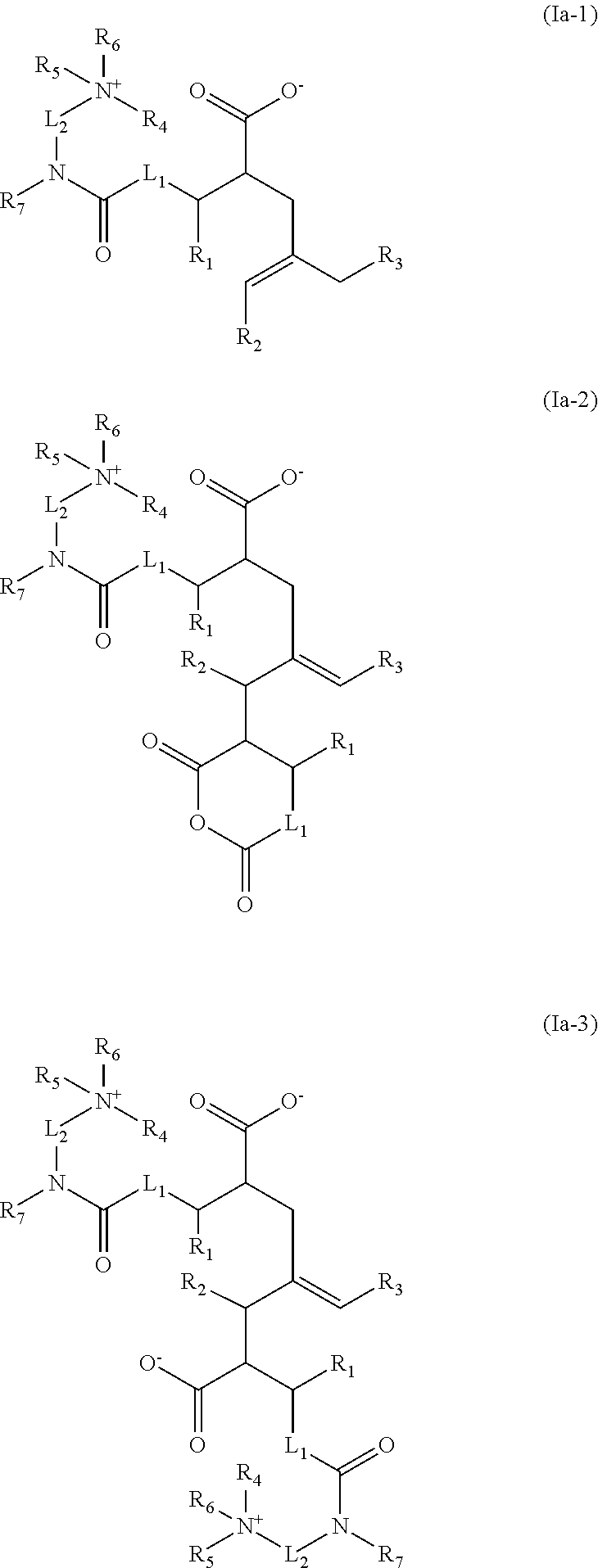
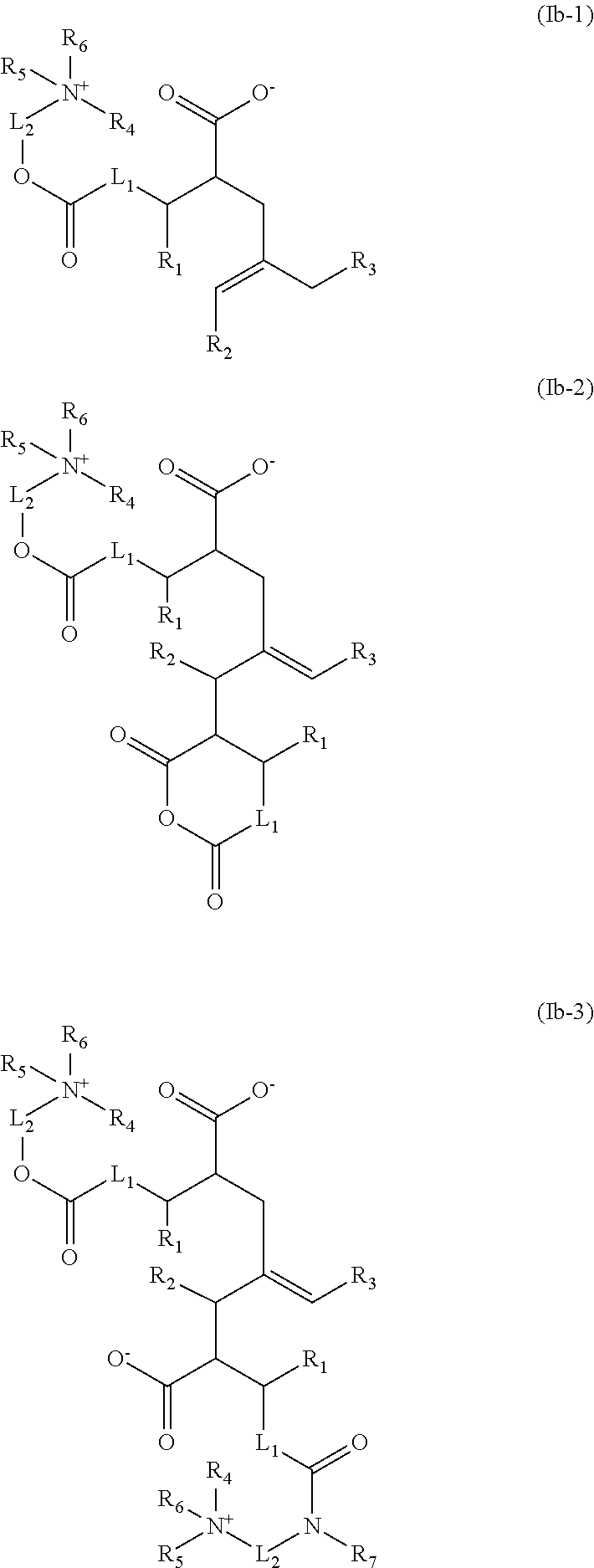
Acid-free quaternized nitrogen compounds and use thereof as additives in fuels and lubricants
a technology of quaternized nitrogen and additives, which is applied in the preparation of carboxylic acid amides, fuels, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of engine performance deterioration, engine performance deterioration, and engine performance deterioration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
Synthesis of an Inventive Acid-Free Quaternized Succinamide (PIBSA / DMAPA / Styrene Oxide; Amidation at 40° C.)
[0311]
[0312]386.8 g (0.35 mol) of polyisobutenesuccinic anhydride (PIBSA 1000) are dissolved in 176 g of Solvesso 150 in a 2-liter four-necked flask at room temperature under a gentle N2 stream. After the addition of 29.9 g (0.29 mol) of 3-dimethylamino-1-propylamine (DMAPA), the reaction temperature rises to 40° C. The solution is stirred at 40° C. for 10 minutes. Subsequently, 34.2 g (0.29 mol) of (1,2-epoxyethyl)benzene are added, which is followed by a further reaction time of 7 hours at 70° C. under N2. The solution is finally adjusted to an active ingredient content of 50% with 274.9 g of Solvesso 150.
[0313]By IR analysis, it was possible to detect the formation of the inventive amide addition product (A).
[0314]By means of ESI-LC / MS and MALDI-TOF-MS, the betaine structure of (A) was determined experimentally.
preparation example 2
(Comparison): Synthesis of an Acid-Containing Quaternized Succinimide (PIBSA / DMAPA / Styrene Oxide / Acetic Acid) Analogously to WO 2006 / 135881
[0315]
[0316]The overall experiment is performed under a gentle N2 stream. The initial charge of PIBSA 1000 (481.61 g) and Pilot 900 oil (84.99 g) is stirred at 110° C. Then DMAPA (37.28 g) is metered in at 110-115° C. within 42 minutes. A slightly exothermic reaction is observed. Subsequently, the mixture is heated to 150° C. and stirred at 150° C. for 3 h to remove water of reaction. The mixture is then cooled to room temperature, and successively admixed with MeOH (152 g), acetic acid (21.91 g) and styrene oxide (43.84 g). The mixture is then stirred at reflux (67-69° C.) for 5 h. After standing at 30-35° C. overnight, the mixture is concentrated by distillation (1 h / 6 mbar / 36° C. oil bath). The final weight of 661.1 g is adjusted to an active ingredient content of 50% with Pilot 900 oil (493.07 g).
[0317]By IR analysis, it was possible to detec...
use examples
C. USE EXAMPLES
[0319]In the use examples which follow, the additives are used either as a pure substance (as synthesized in the above preparation examples) or in the form of an additive package. The following packages were used:
[0320]M2450: Inventive Additive Package
AdditiveProportion (%)Product according48.06to Prep. Ex. 1Dehazer0.92Antifoam1.11Solvesso 15025.88Pilot 90024.03Sum100
[0321]M2452: Comparative Additive Package
AdditiveProportion (%)Product according48.06to Prep. Ex. 2Dehazer0.92Antifoam1.11Solvesso 15049.91Sum100
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com