Steel for low-temperature service having excellent surface processing quality
a low-temperature service, high-quality technology, applied in the direction of heat treatment equipment, manufacturing tools, furnaces, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the design thickness of the structure, increasing the cost of aluminum alloys, and low degree of weldability of aluminum alloys, so as to achieve a high degree of surface processing quality and increase the sfe of steel. , the effect of high degree of quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059]Hereinafter, the present disclosure will be described more specifically according to examples. However, the following examples should be considered in a descriptive sense only and not for purpose of limitation.
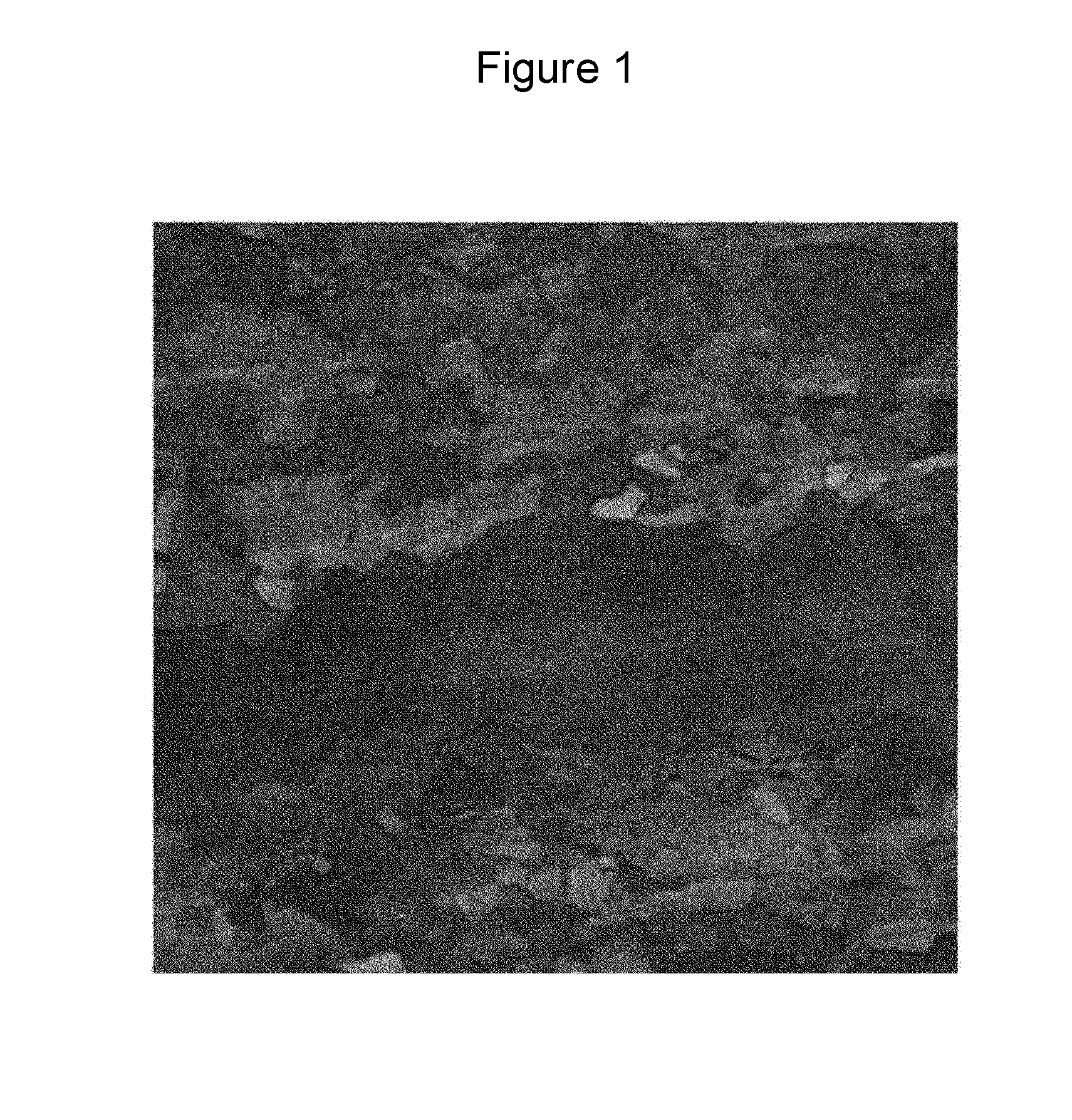
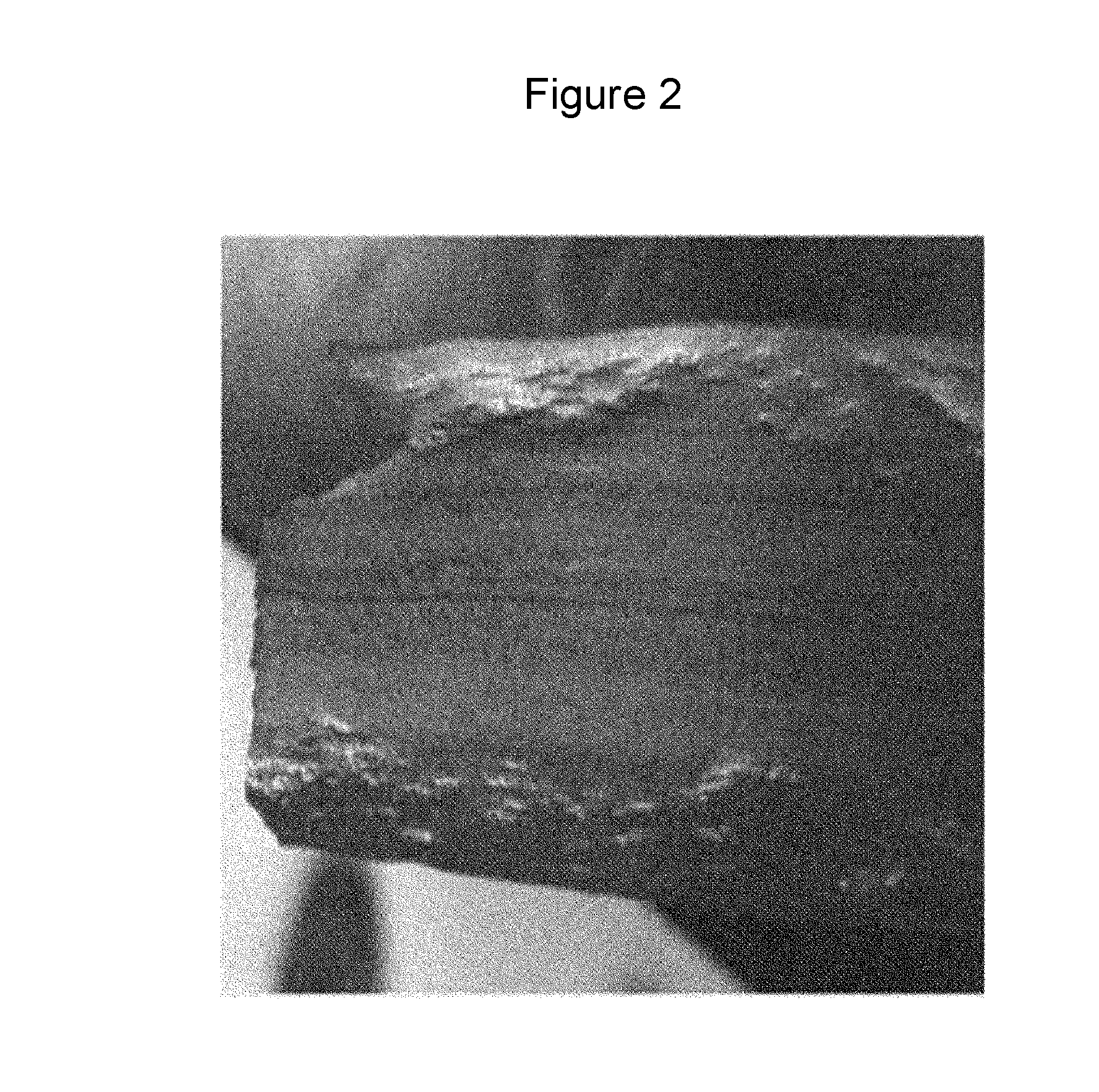
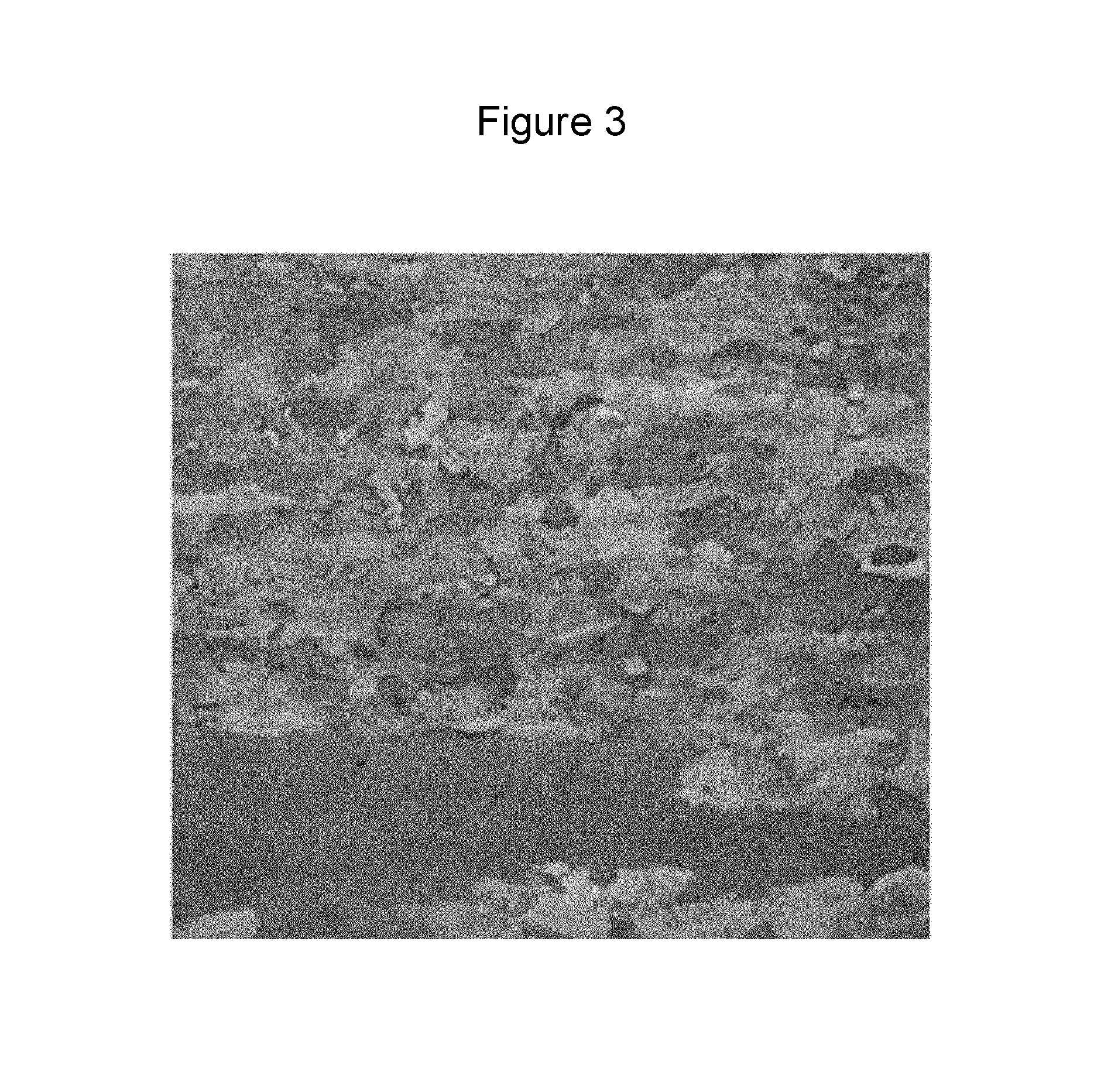
[0060]Slabs having compositions as illustrated in Table 1 below were processed under the conditions illustrated in Table 2 below so as to manufacture steel materials. Thereafter, the stacking fault energy (SFE), microstructures, yield strength, and carbide fractions of the steel materials were measured. In addition, physical properties of the steel materials such as elongation and Charpy impact toughness were measured as illustrated in Table 3. Referring to Table 3, the column “surface non-uniformity” shows evaluation results obtained by observing the steel materials by the naked eye.
TABLE 1No.CMnCuCrNiMoSiAlNCE10.6218.120.120.20.012CE20.3725.41.123.850.018CE30.6118.131.51.250.012CE40.2617.030.009CE51.3618.250.011CE60.4210.510.009CE70.9414.60.012CE80.3824.60.83.40.015IE1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strain | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| stacking fault energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com