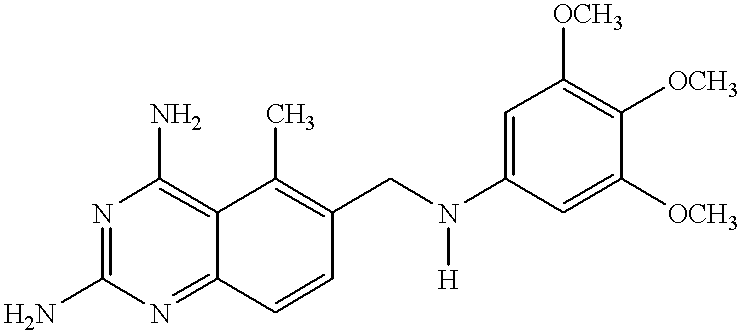
Compositions comprising trimetrexate and methods of their synthesis and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Trimetrexate Ascorbate
Trimetrexate ascorbate may be prepared from trimetrexate free base, an adduct of trimetrexate such as the DMF adduct, or a trimetrexate salt such as trimetrexate hydrochloride or trimetrexate trifluoroacetate. As described above, the synthesis of these forms of trimetrexate is well known. A preferred method of preparing trimetrexate ascorbate from trimetrexate hydrate follows.
A. Trimetrexate Trifluoroacetate
To a suspension of 5 g of trimetrexate hydrate in 30 ml of 2-propanol and 15 ml of water was added 2.10 g of trifluoroacetic acid (approximately a 40% excess). The solid partly dissolved, but new crystals came out before it was completely gone. The mixture was heated to near reflux to give a clear dark yellow-green solution. To this was added 100 ml of 2-propanol. The product crystallized rapidly, and was collected after ice-cooling for 1 hour, washed with ice-cold 2-propanol and dried in air at 50% relative humidity to give 5.95 g of greenish-y...
example 2
Stability Measurement Protocol
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to determine the purity and decomposition of trimetrexate in the compositions of the invention.
The HPLC mobile phase is prepared by first dissolving 5 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate (Aldrich 86,201-0 or equivalent) in 1100 ml water and adjusting the pH to 3.0 with glacial acetic acid (about 5 ml). 825 ml of HPLC grade acetonitrile is then added, and the solution is mixed thoroughly while avoiding excessive foaming. The unfiltered solution is then degassed by sonicating for 5 minutes. The solution is degassed immediately before use and at the beginning of each day.
Duplicate standard solutions are prepared with a trimetrexate ("TMTX") reference compound at a concentration of 0.2 mg / ml in the mobile phase solution ("STD-1" and "STD-2"). The standard solutions are stored under refrigeration when not in use, and fresh solutions are prepared daily. The system is checked before testing the sample solutions by...
example 3
Preparation of Liquid Dosage Form
Liquid dosage forms comprising trimetrexate and ascorbic acid, and liquid dosage forms comprising trimetrexate, ascorbic acid, and monothioglycerol, are made according to the procedures outlined below.
Liquid Dosage Form A (Trimetrexate and Ascorbic Acid).
A sufficient quantity of purified water is added to 12.5 grams of trimetrexate free base and 20 grams ascorbic acid to provide a mixture with a volume of 1000 ml. The mixture is stirred.
Liquid Dosage Form B (Trimetrexate, Ascorbic Acid, and 0.25% Monothioglycerol).
A sufficient quantity of purified water is added to 12.5 grams of trimetrexate free base, 20 grams ascorbic acid, and 2.5 grams monothioglycerol to provide a mixture with a volume of 1000 ml. The mixture is stirred.
Liquid Dosage Form C (Trimetrexate, Ascorbic Acid, and 0.50% Monothioglycerol).
A sufficient quantity of purified water is added to 12.5 grams of trimetrexate free base, 20 grams ascorbic acid, and 5 grams monothioglycerol to prov...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Linear density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com