Cellulose acetate films prepared by coating methods
a technology of cellulose acetate and coating, which is applied in the direction of polarising elements, synthetic resin layered products, record information storage, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the cost of resin film manufacturing, etc., to achieve the effect of low in-plane birefringen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
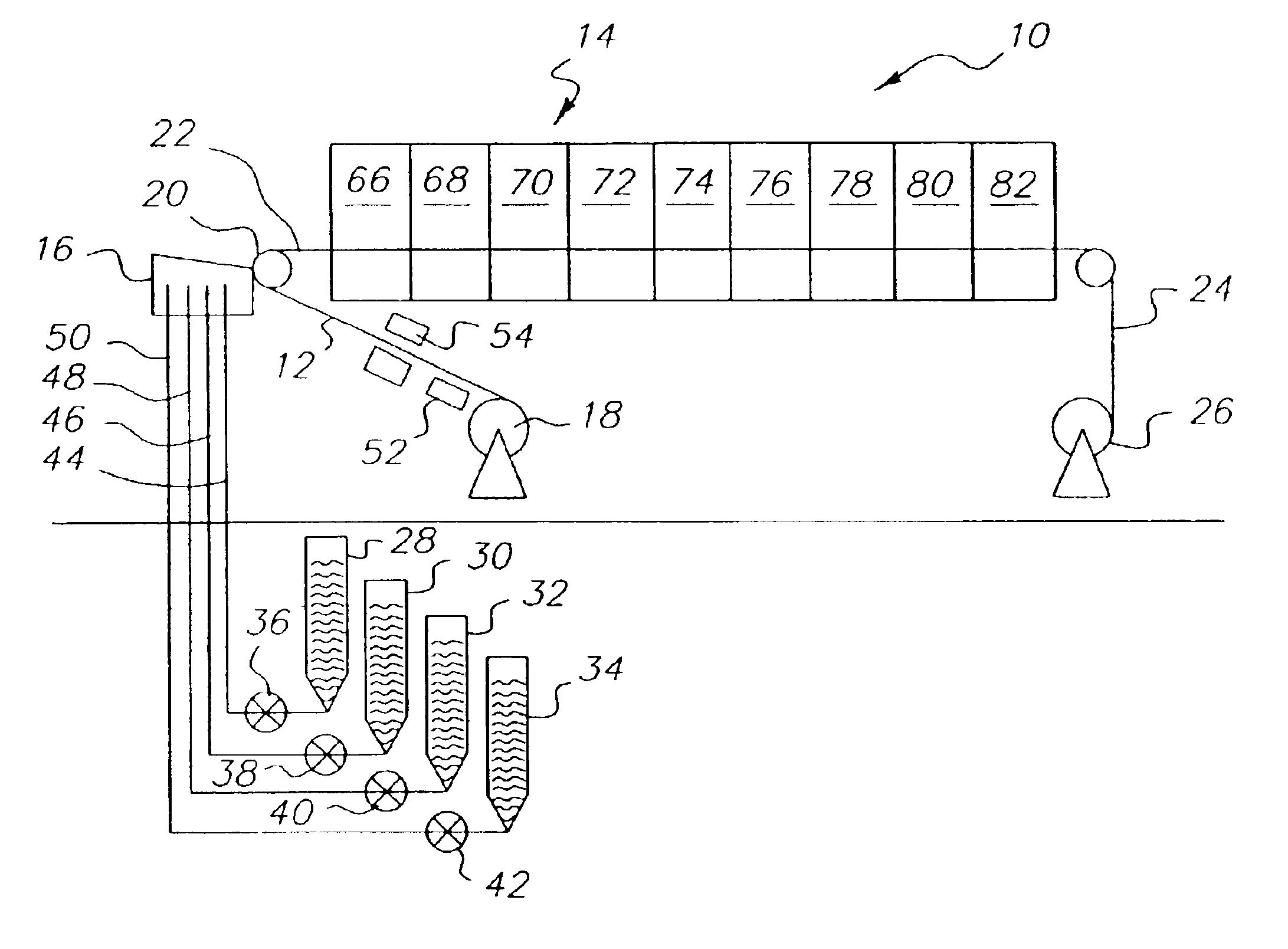
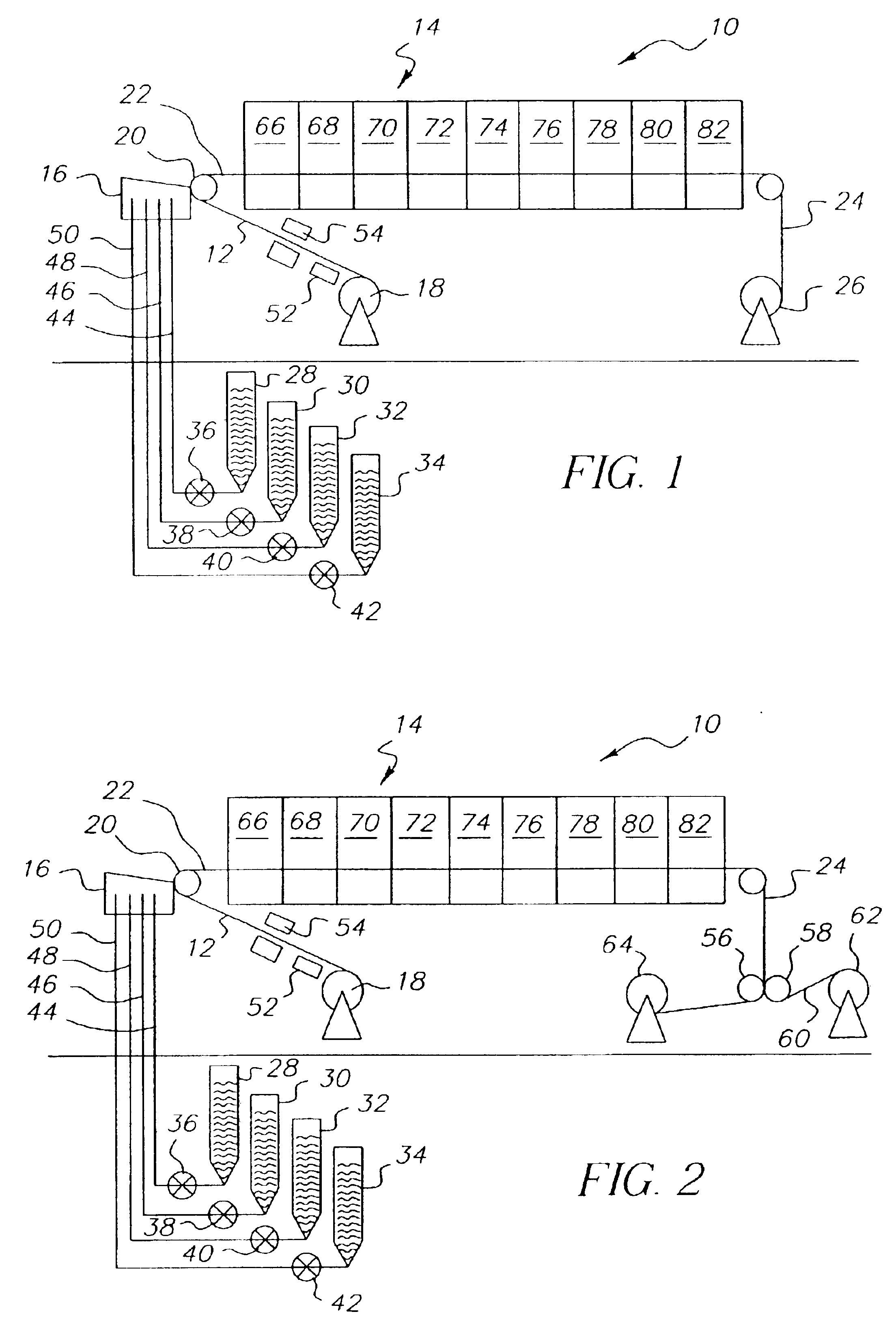
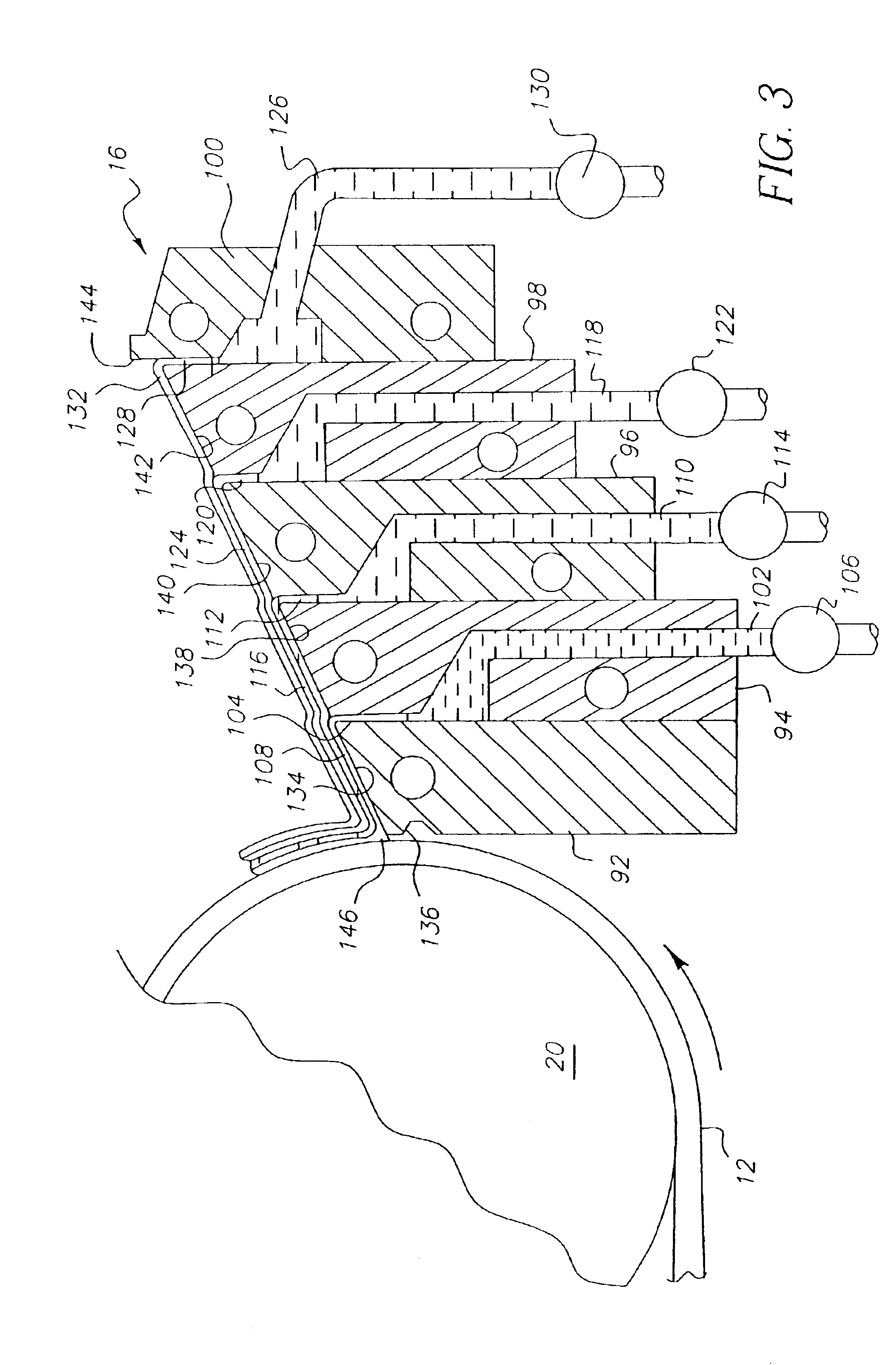
[0056]This example describes the single pass formation of an ultra thin cellulose acetate film. The coating apparatus 16 illustrated in FIG. 1 was used to apply four liquid layers to a moving substrate 12, 170 of untreated polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to form a single layer film as illustrated earlier in FIG. 6. The substrate speed was 25 cm / s. All coating fluids were comprised of CTA dissolved in a blend of two solvents (a 1:1 ratio of 1,3-dioxolane: acetone where the ratio is by weight). The lowermost layer 162 had a viscosity of 60 cp. and a wet thickness of 11 μm on the moving substrate 170. The second 164 and third 166 layers each had a viscosity of 860 cp. and had a combined final wet thickness of 69 μm on the moving substrate 170. The second 164 and third 166 layers also each contained plasticizers (diethyl phthalate) at a concentration of 15% by weight relative to the amount of CTA polymer. In addition, the third layer 166 also contained a fluorinated surfactant (Surflon...
example 2
[0057]This example describes the single pass formation of a very thin cellulose acetate film. The conditions were identical to those described in Example 1 except that the combined wet thickness of the second and third layers 164 and 166 was increased to 154 μm. The composite of CTA film and PET substrate was wound into rolls. When peeled from the subbed PET substrate, the final dry film had a thickness of 10 μm. The peeled CTA film had a good appearance, was smooth, was free from wrinkles and cockle artifacts, and had an in-plane retardation of less than 1.0 nm. Properties of this cellulose acetate film are summarized in Table I.
example 3
[0058]This example describes the single pass formation of a thin cellulose acetate film. The conditions were identical to those described in Example 1 except that the combined wet thickness of the second and third layers 164 and 166 was increased to 324 μm. The composite of CTA film and PET subtrate was wound into rolls. When peeled from the subbed PET substrate, the final dry film had a thickness of 20 μm. The CTA film had a good appearance, was smooth, was free from wrinkles and cockle artifacts, and had an in-plane retardation of less than 1.0 nm. Properties of this cellulose acetate film are summarized in Table I.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adhesive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com