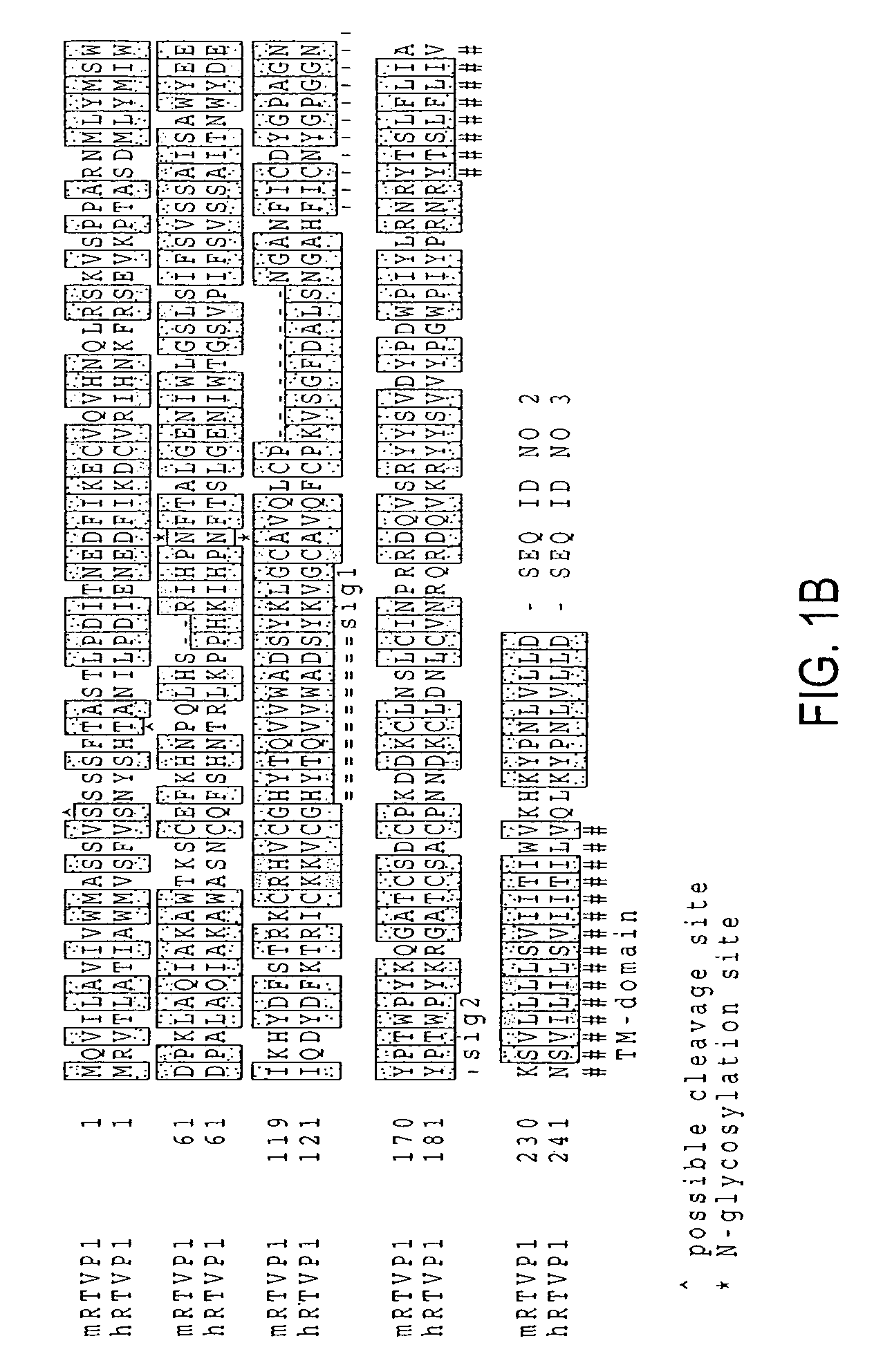
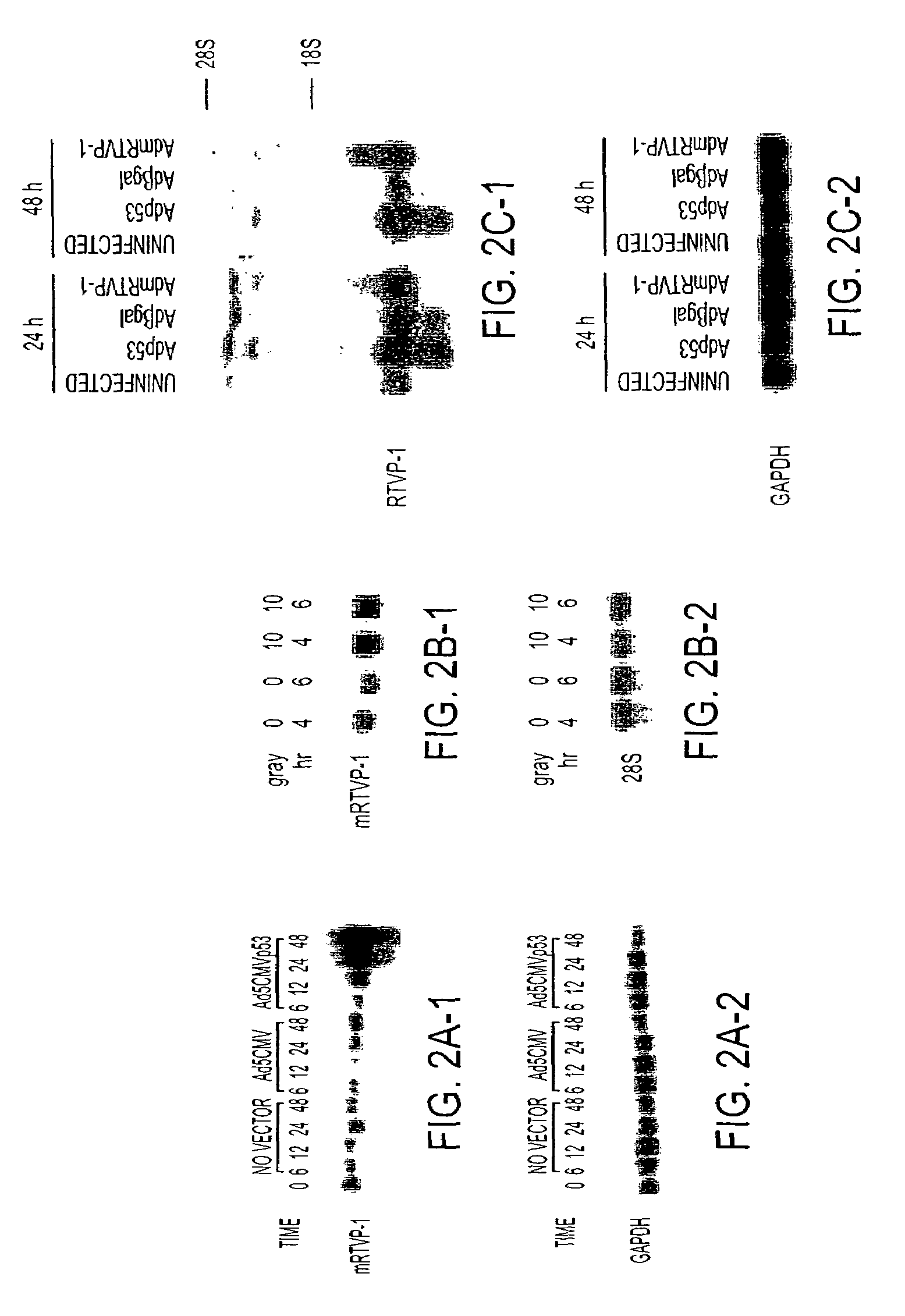
RTVP based compositions and methods for the treatment of prostate cancer
a composition and prostate cancer technology, applied in the field of rtvp genes and associated sequences, can solve the problems of poor survival rate of late-stage carcinoma patients, and achieve the effect of reducing or shutting down rtvp expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Identification of mRTVP-1 as a p53 Target Gene
[0065]Over the last decade, numerous studies have established p53 mutations as being paramount to the development and progression of various malignancies. The p53 tumor suppressor protein has been associated with various antitumor activities that include growth suppression, apoptosis, and anti-angiogenic activities. The majority of human tumor mutations decrease the sequence-specific DNA binding and transcriptional activity of the p53 protein 26. Today the large and expanding list of genes under the transcriptional control of p53 have been reported and it has been estimated that 200-300 genes are under the transcriptional regulation of p53 27. To date, the number of reported p53-regulated genes is approximately 80 28.
[0066]To identify prostate cancer-related genes under the transcriptional regulation of p53, a model system was established using adenoviral vector delivery of wild-type p53 compared to β-gal or an empty cassette together wi...
example 2
RTVP-1 mRNA Levels are Down-Regulated in Prostate Cancer Metastases
[0068]Having demonstrated that mRTVP-1 is induced by p53; it was next determined the mRNA expression profile of RTVP-1 in mouse and human prostate cancer tissue specimens by in situ hybridization (FIG. 3). Briefly, normal mouse prostate or prostate cancer developed in the mouse prostate reconstitution model with strain 129 / SV wild type, heterozygous or homozygous for p53 knockout 6 were used for in situ hybridization. Human primary prostate cancers and lymph node metastatic deposits as well as histologically normal prostate were obtained at radical prostatectomy. The specimens were frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after surgical removal and 6-μm sections cut with a cryostat. Sections were air-dried and fixed in a solution containing 3 parts 4% paraformaldehyde, 4 parts ethanol and 3 parts glacial acetic acid for 20 min. Anti-sense cRNAs of mRTVP-1 (400 bases) and hRTVP-1 (256 bases) or corresponding sense RNA pr...
example 3
Pro-Apoptotic Activities of mRTVP-1 are Mediated Through the Mitochondrial Pathway
[0072]To analyze the biological activities of mRTVP-1, a series of human prostate cancer cell lines (Tsu-Prl, LNCaP, and PC3) and the human lung cancer cell line, H1299, were infected with AdmRTVP-1 or Adβgal. Western blotting analysis demonstrated high levels of intracellular mRTVP-1 protein by 48 hours after infection.
[0073]As shown in FIG. 4, mRTVP-1 induces apoptosis through mitochondrial death pathway. Apoptosis was determined by annexin V binding and flow cytometry on cells infected with Adβgal (open boxes) or AdmRTVP-1 (closed boxes) at an MOI of 100 as described 38 (FIG. 4a). Protein levels of mRTVP-1 in Tsu-Prl cells were determined by western blotting. Western blotting for bcl family member proteins and cytosolic cytochrome c in LNCaP lysates following transfection with control plasmid pcDNA or pmRTVP-1 (FIG. 4b). Relative caspase activity was determined by densitometric analysis of western b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Immunogenicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com