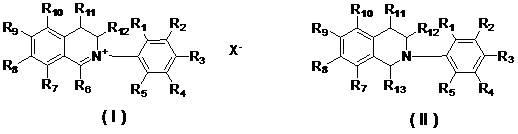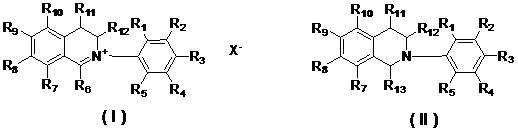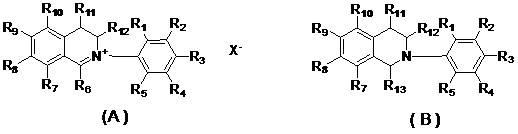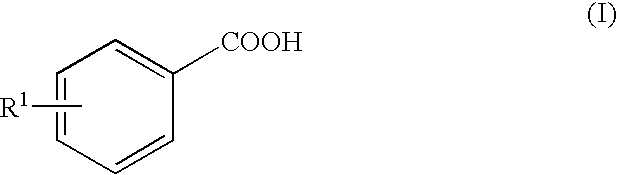Patents
Literature
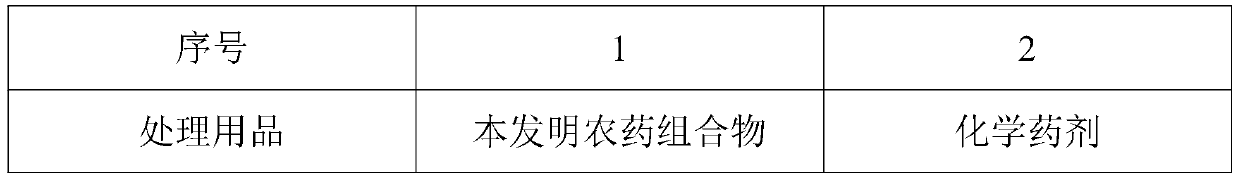
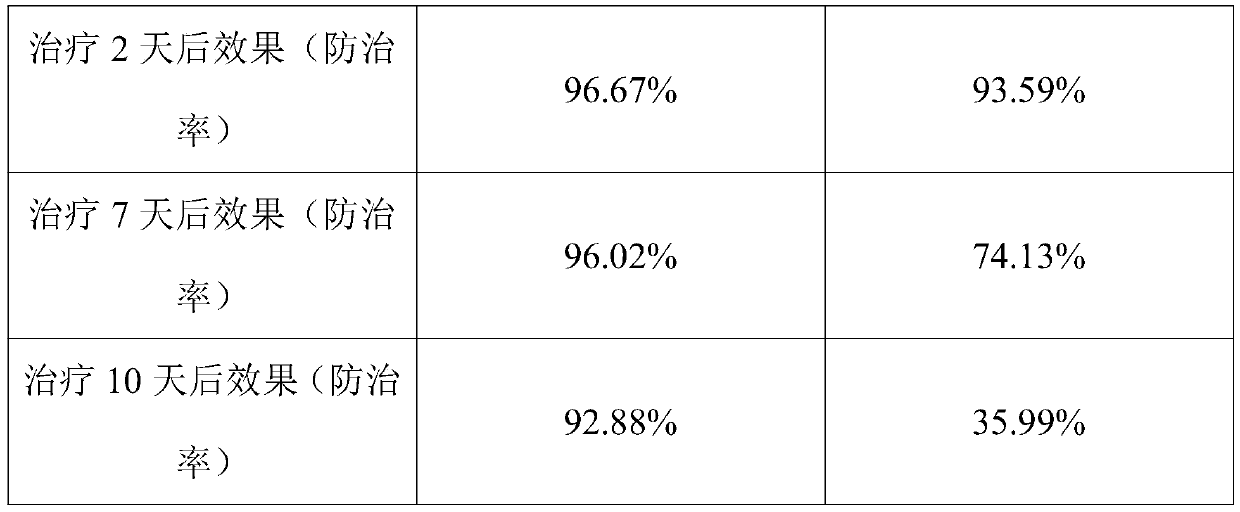
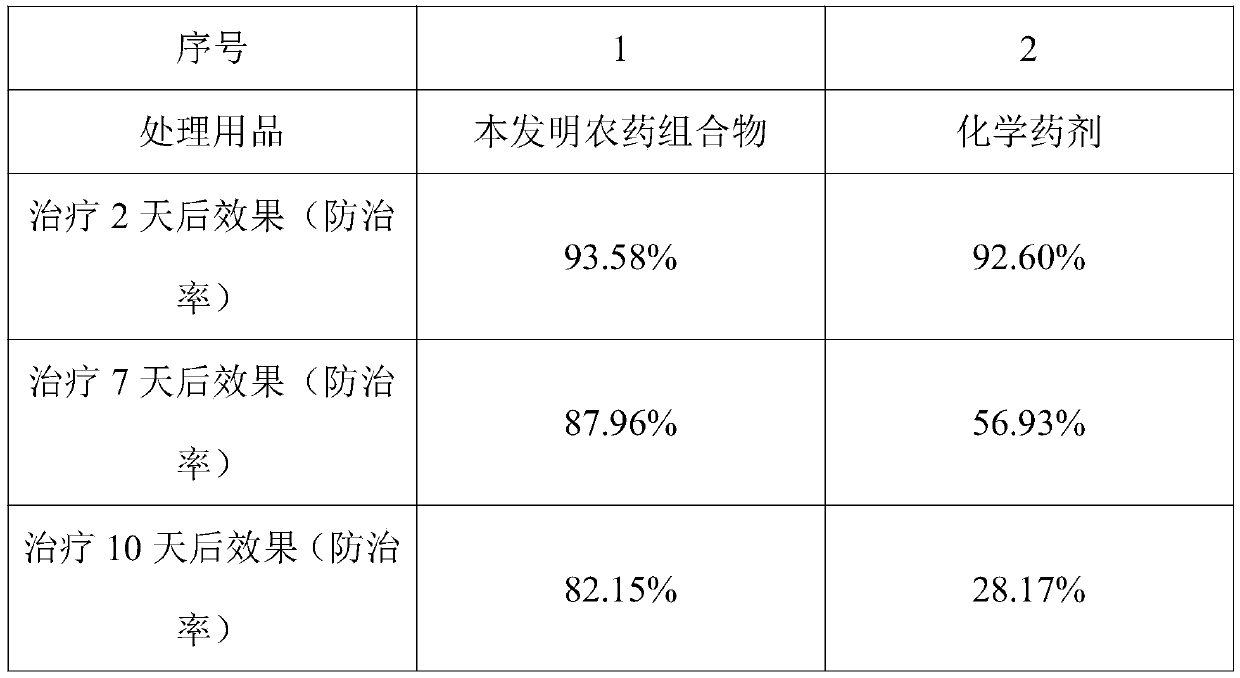
36 results about "Growth suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Growth suppression: The suppression of the growth of an individual. See detailed information below for a list of 4 causes of Growth suppression, Symptom Checker, including diseases and drug side effect causes.
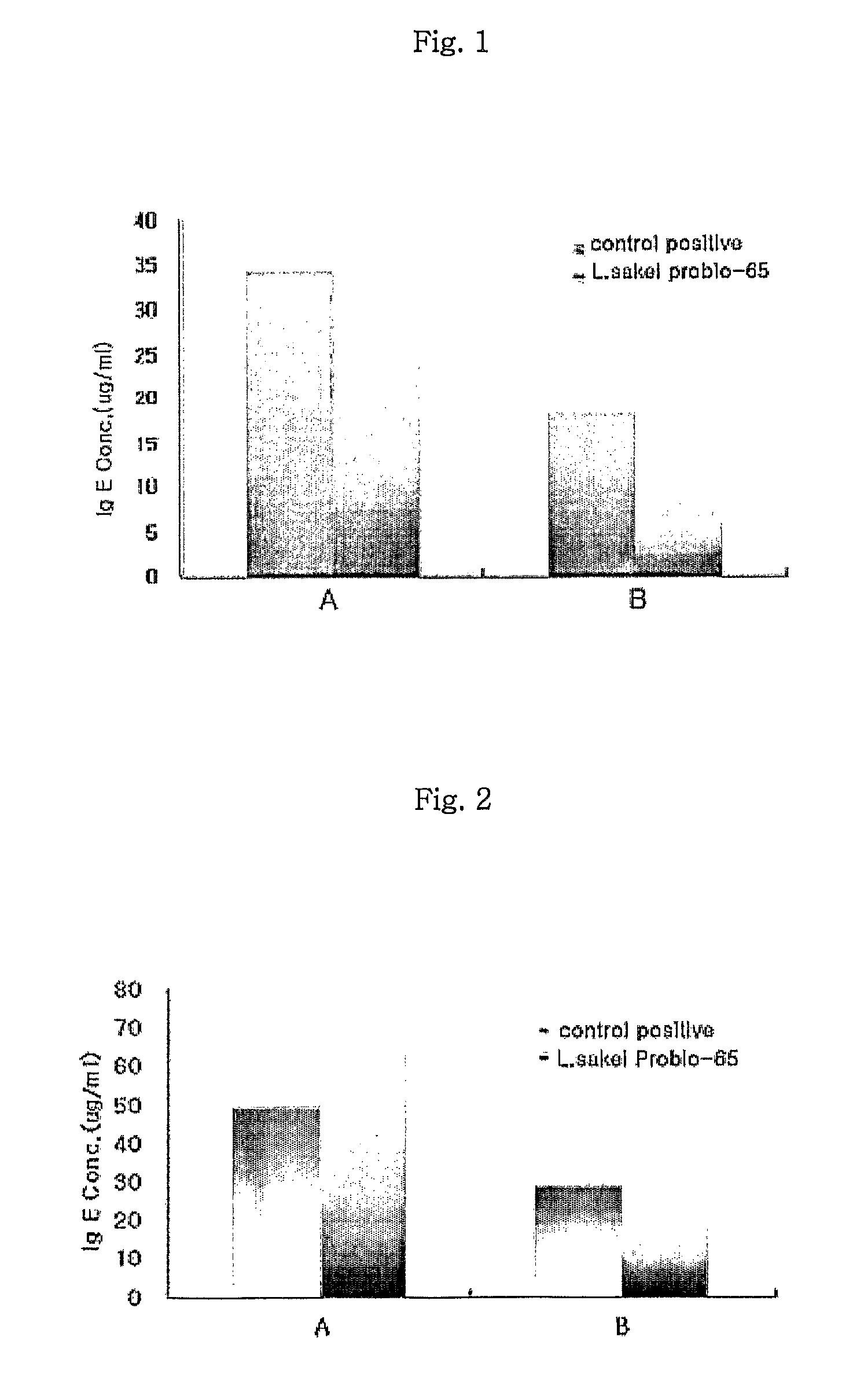
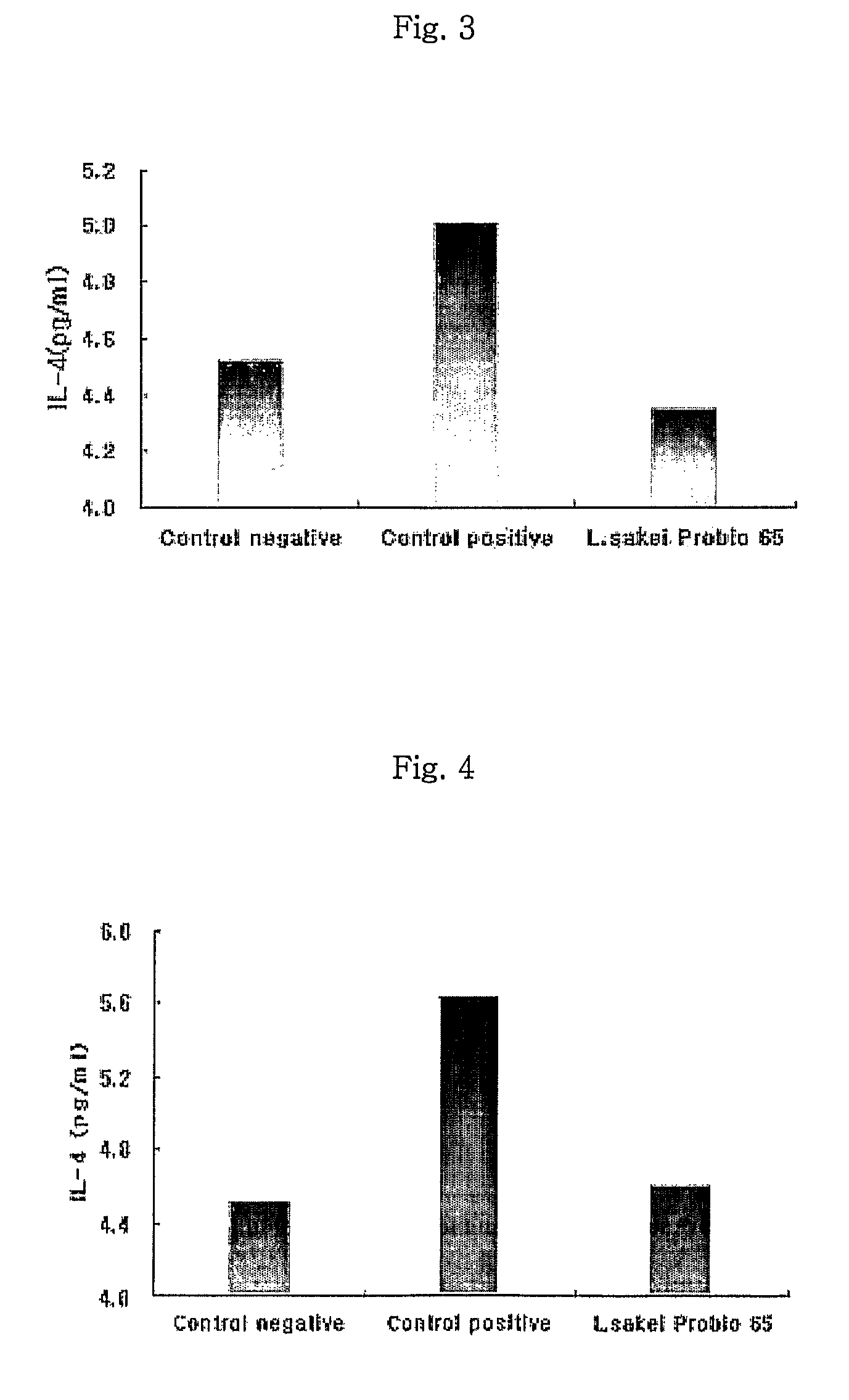
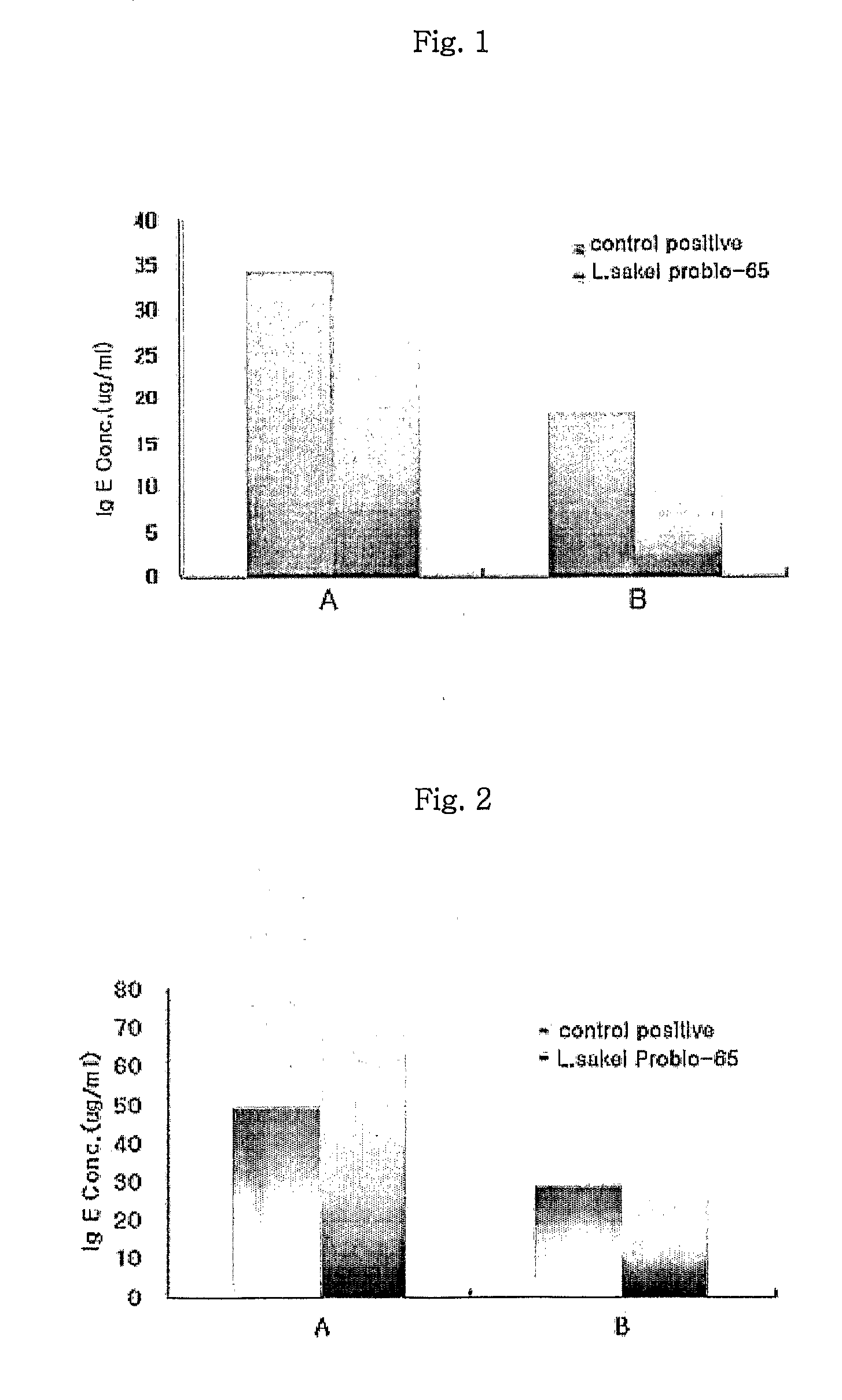
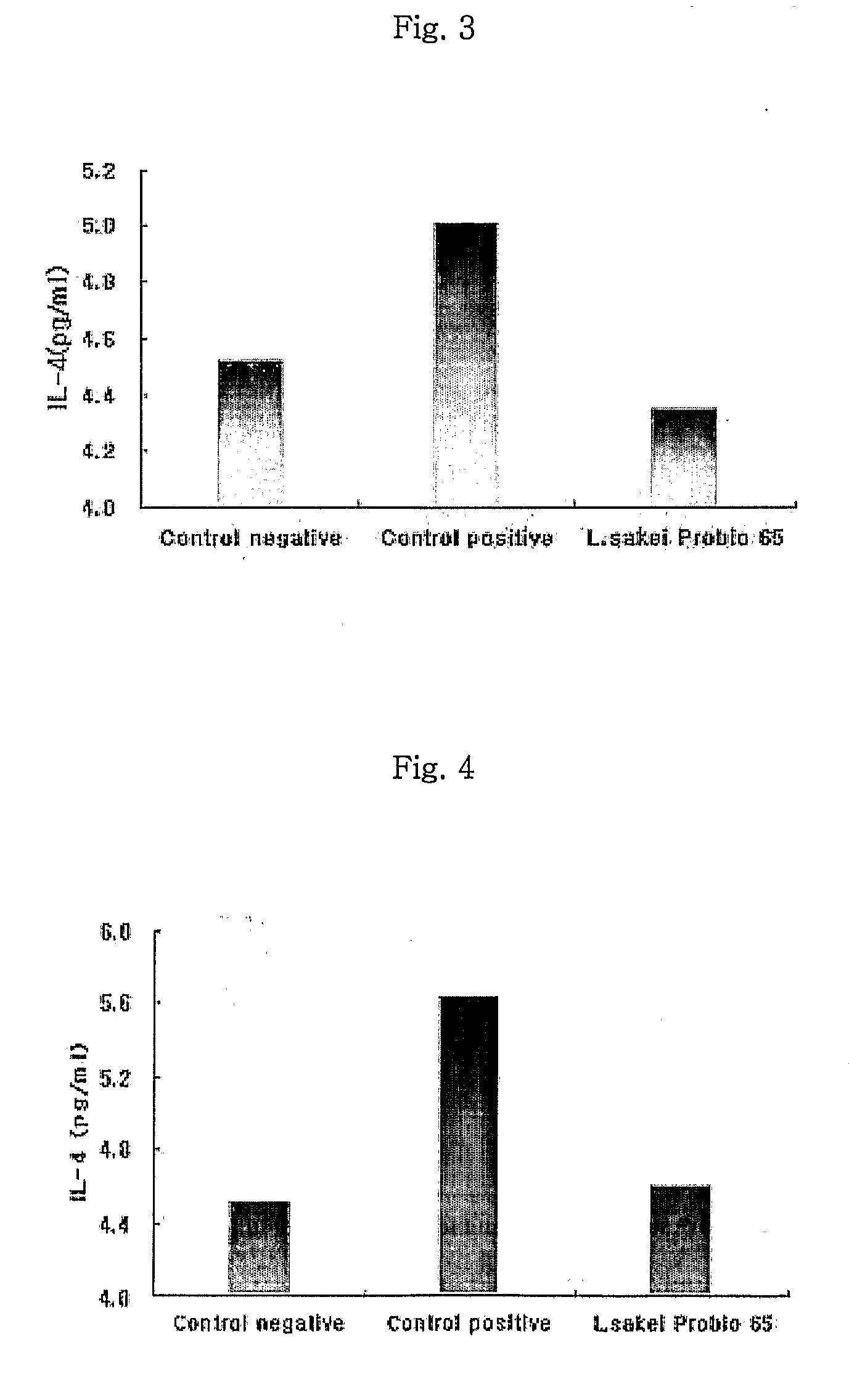
Acid tolerant Lactobacillus sakei probio-65 with the ability of growth suppression of pathogenic microorganisms and the anti-allergic effect
ActiveUS8034606B2Growth inhibitionEffectively inhibit harmful microorganismsBiocideCosmetic preparationsAcid-fastDisease
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
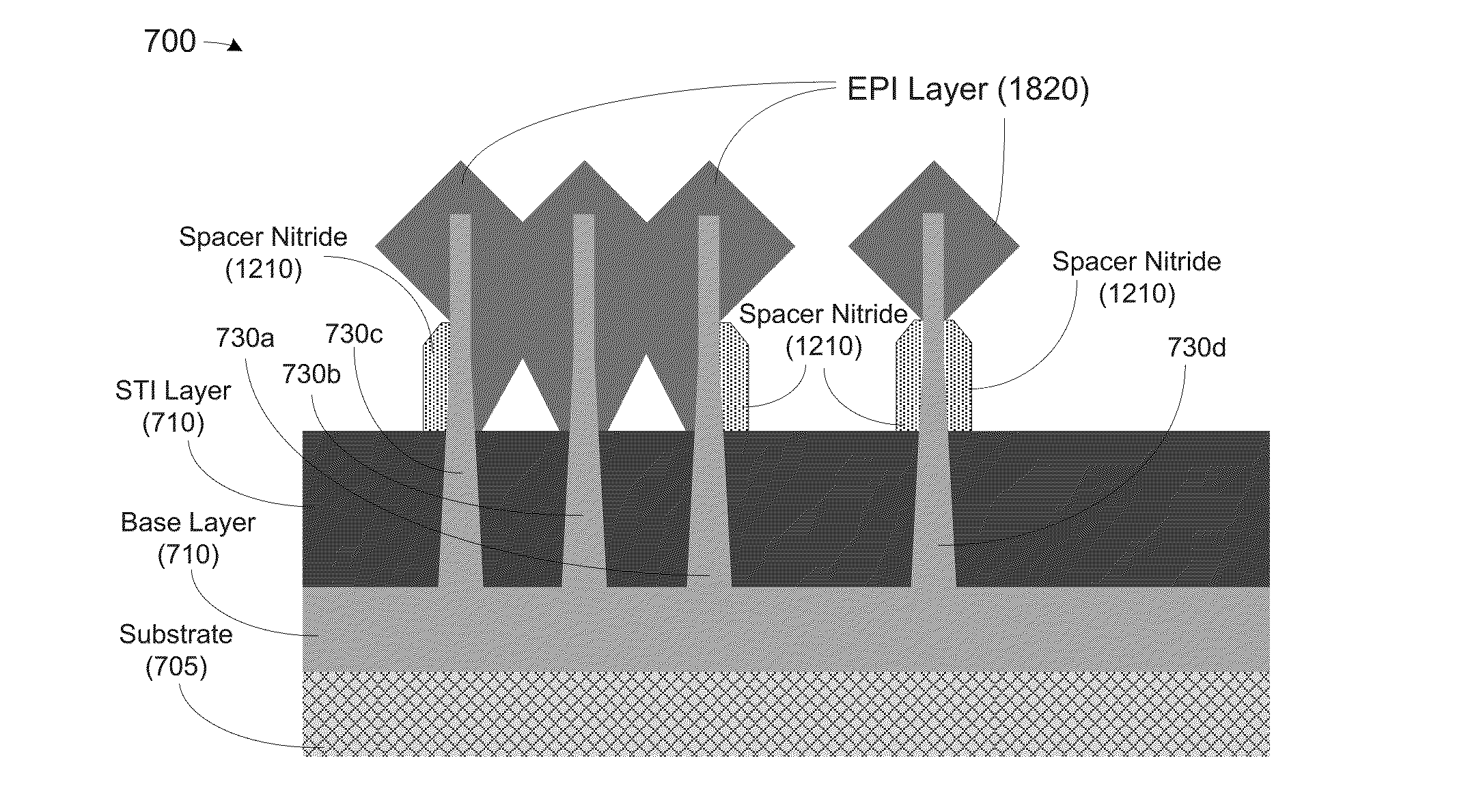
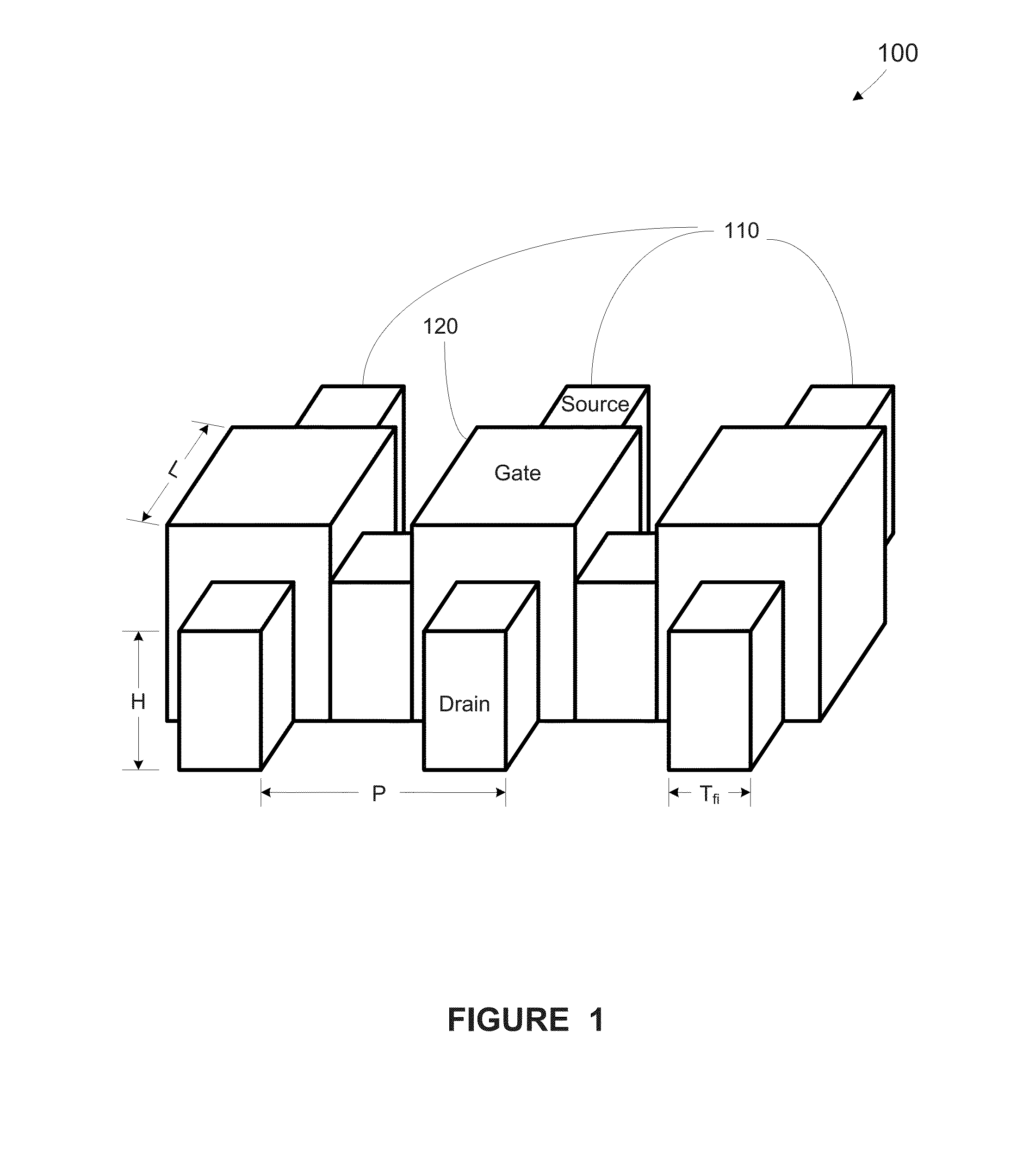
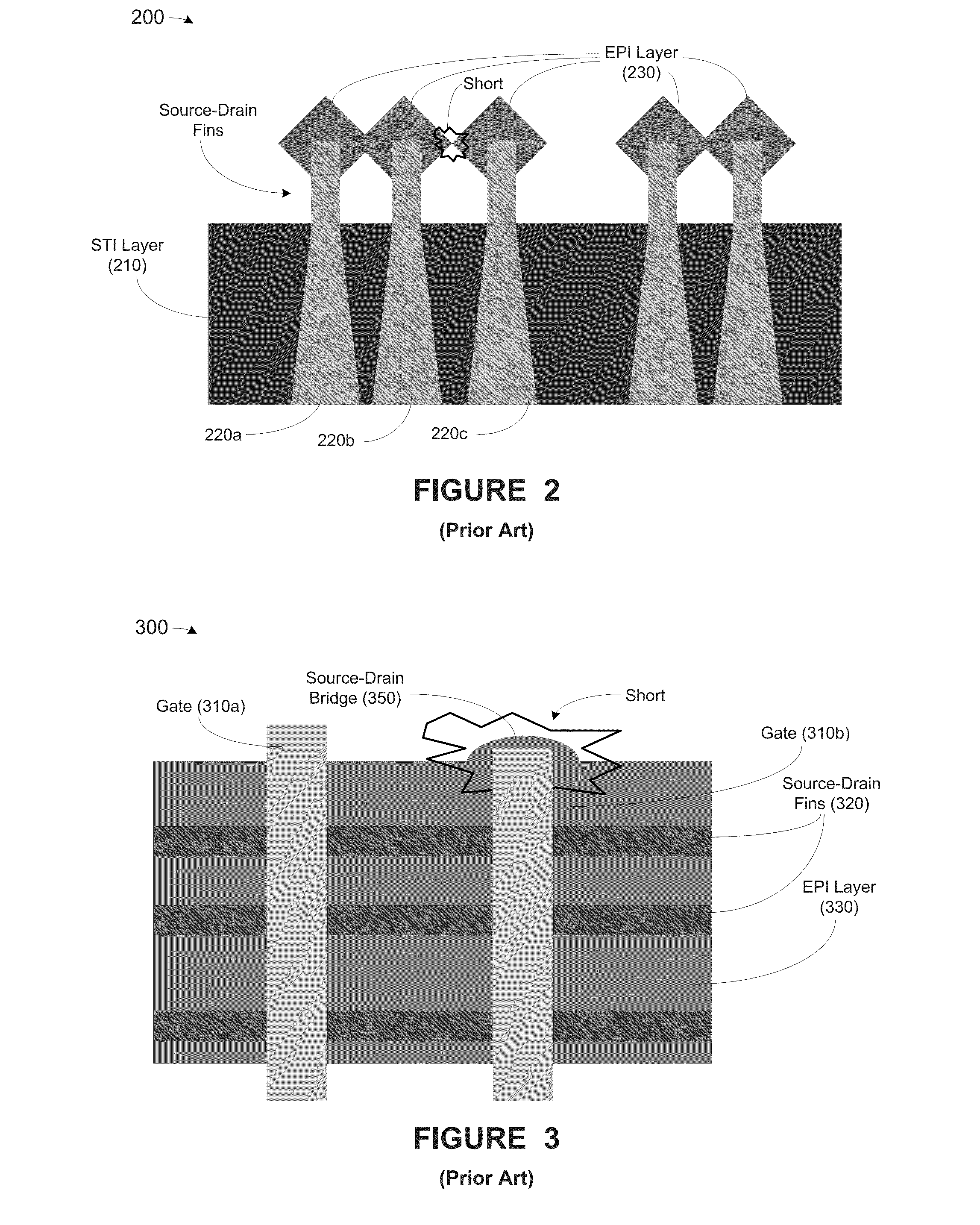
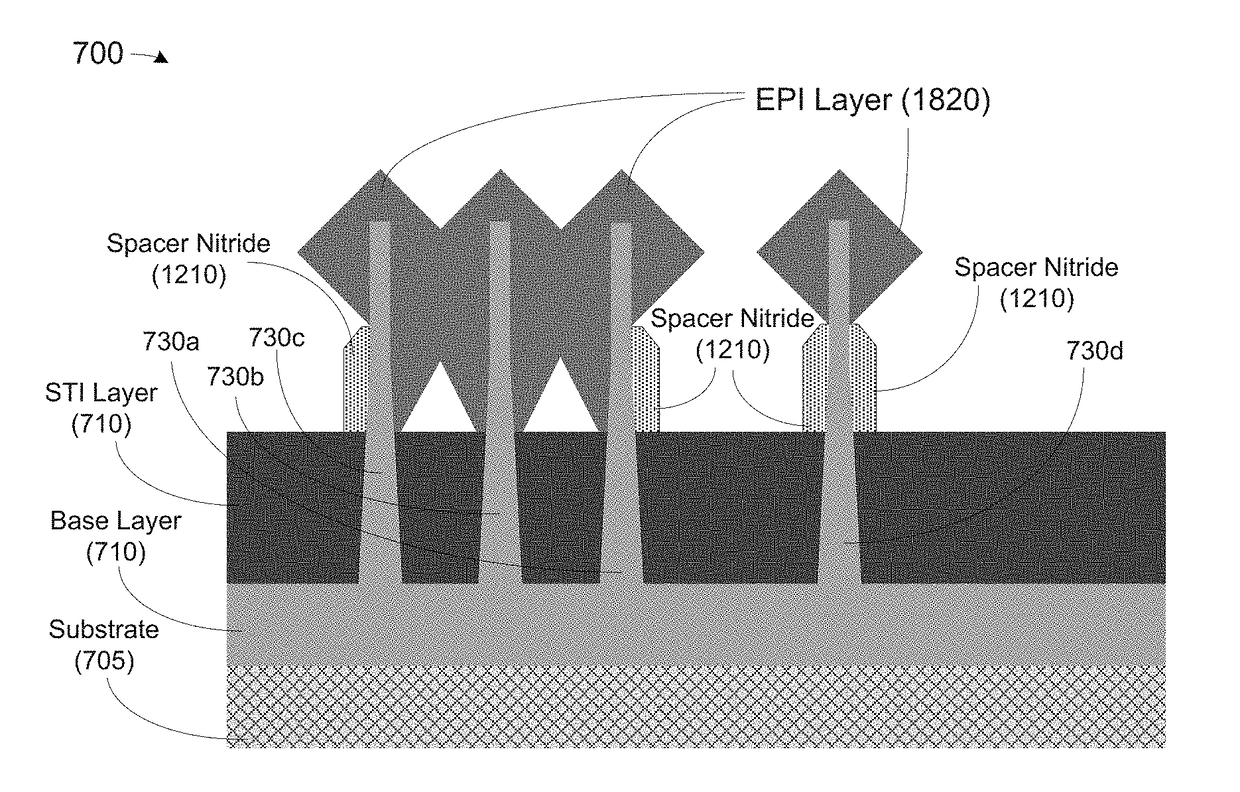
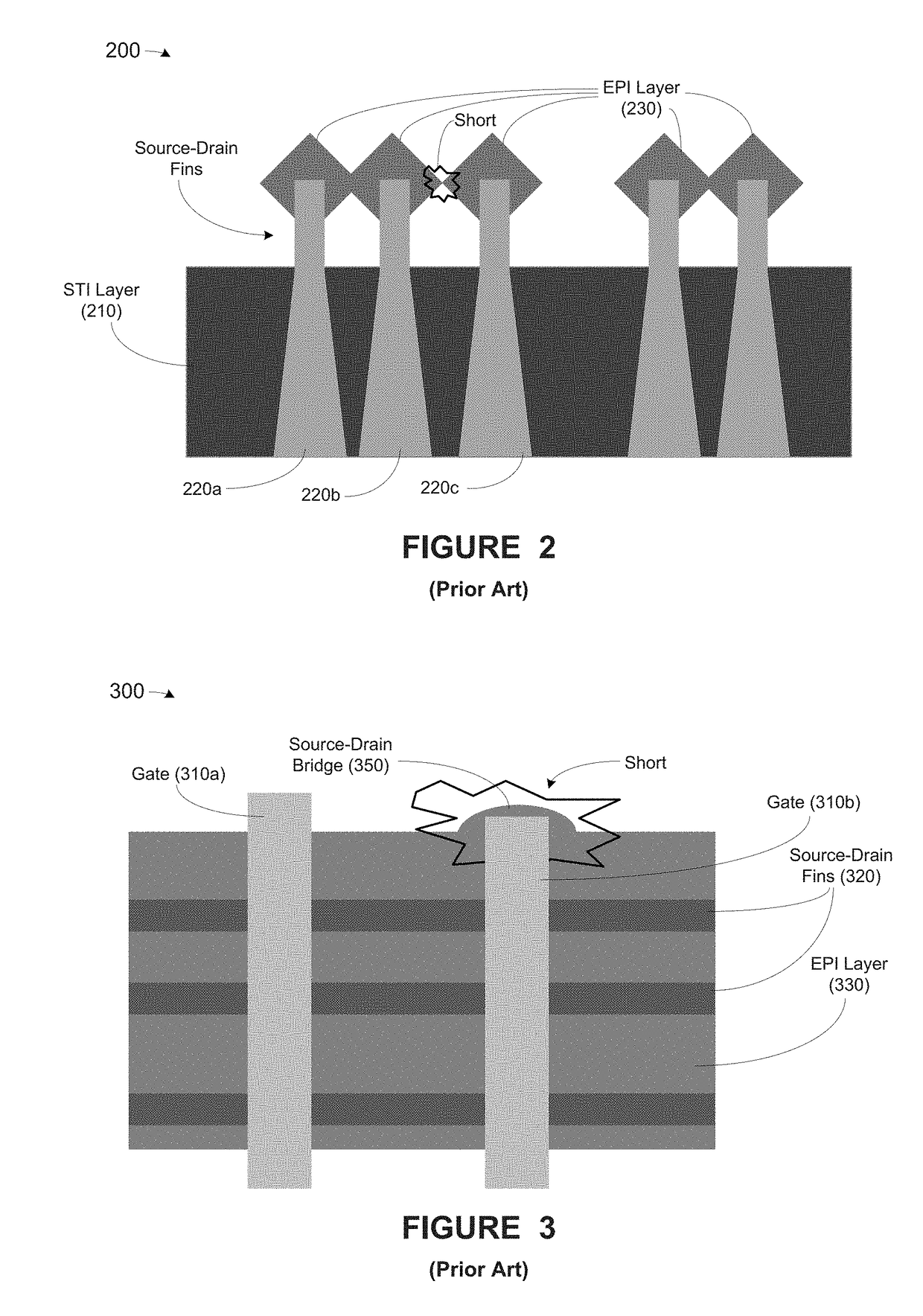
Methods, apparatus and system for providing source-drain epitaxy layer with lateral over-growth suppression
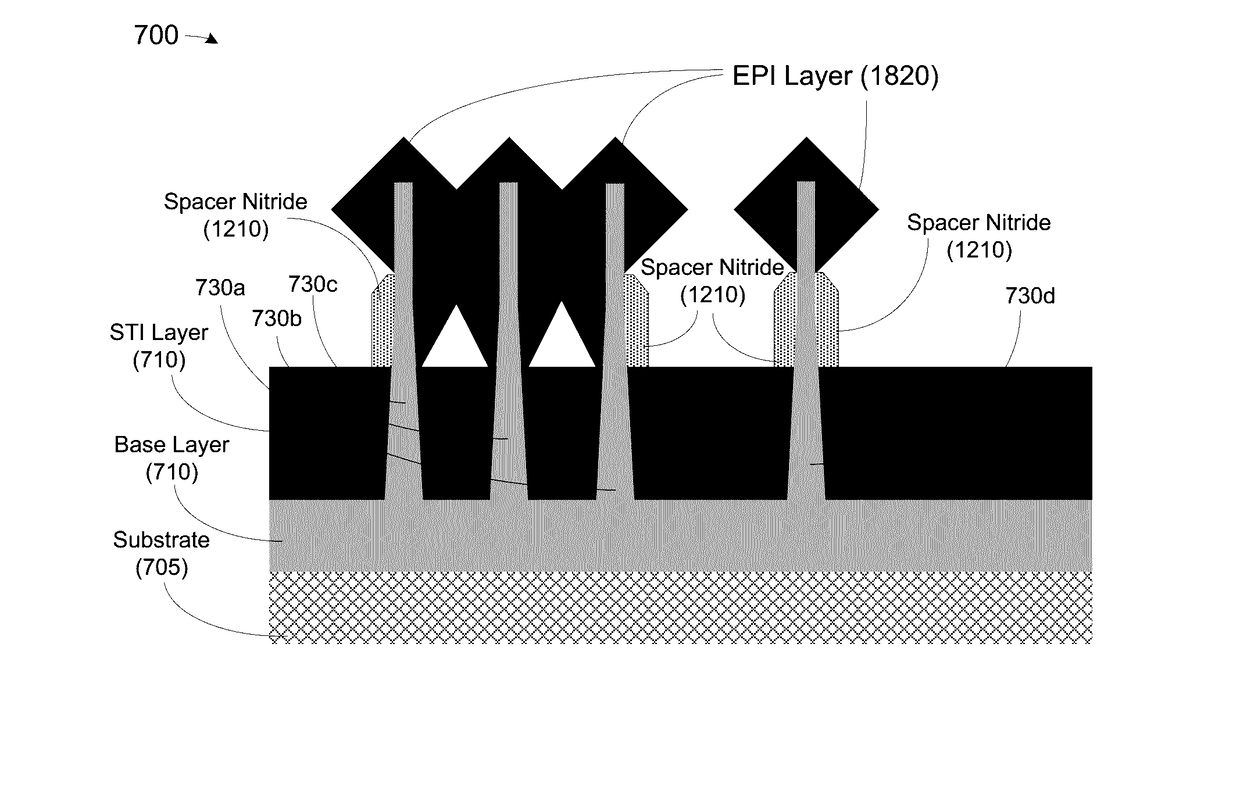
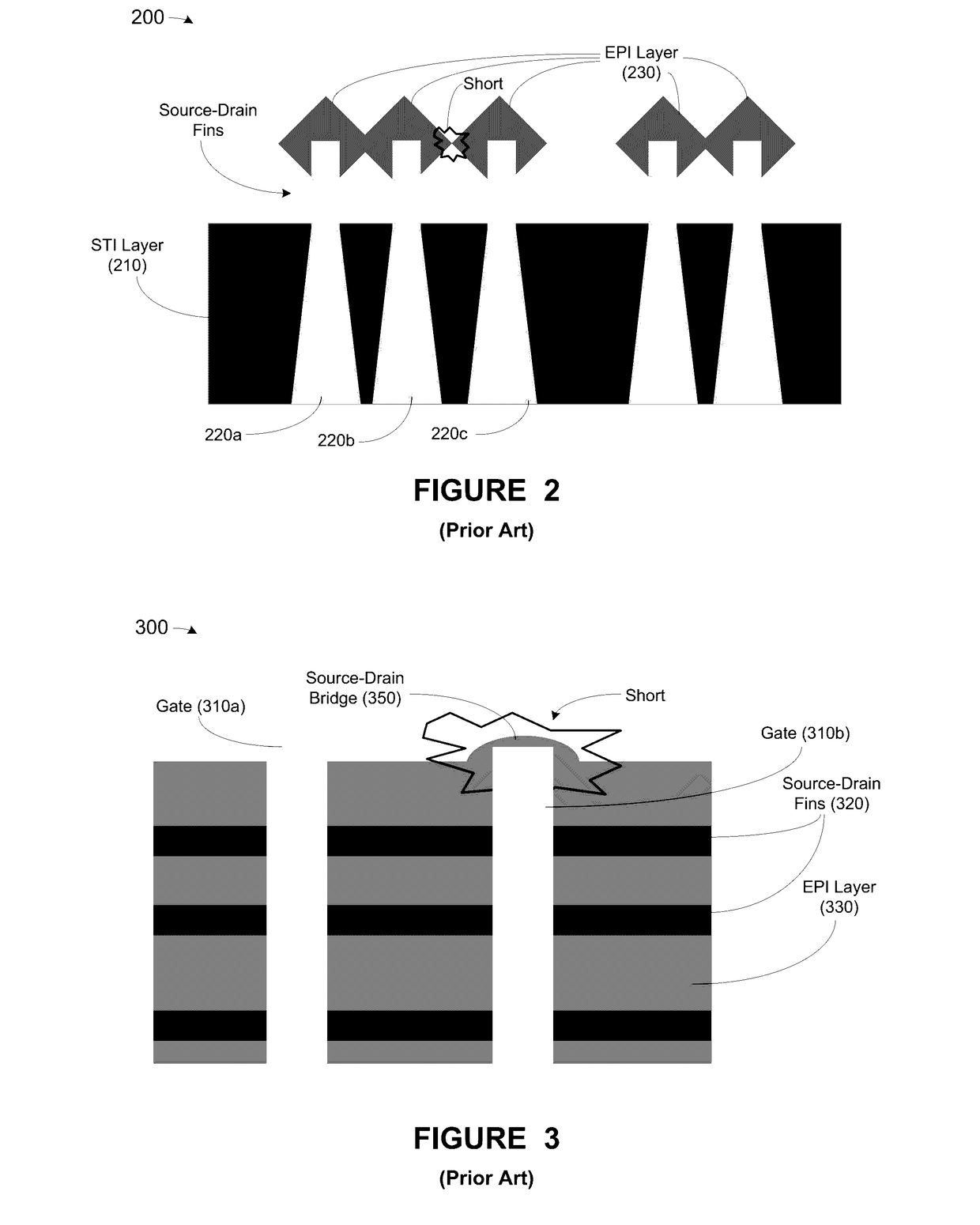
At least one method, apparatus and system disclosed herein for suppressing over-growth of epitaxial layer formed on fins of fin field effect transistor (finFET) to prevent shorts between fins of separate finFET devices. A set of fins of a first transistor is formed. The set of fins comprises a first outer fin, an inner fin, and a second outer fin. An oxide deposition process is performed for depositing an oxide material upon the set of fins. A first recess process is performed for removing a portion of oxide material. This leaves a portion of the oxide material remaining on the inside walls of the first and second outer fins. A spacer nitride deposition process is performed. A spacer nitride removal process is performed, leaving spacer nitride material at the outer walls of the first and second outer fins. A second recess process is performed for removing the oxide material from the inside walls of the first and second outer fins. An epitaxial layer deposition processed upon the set of fins. A portion of the lateral over-growth of epitaxial layer on the outer walls of the first and second outer fins is suppressed by the spacer nitride material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
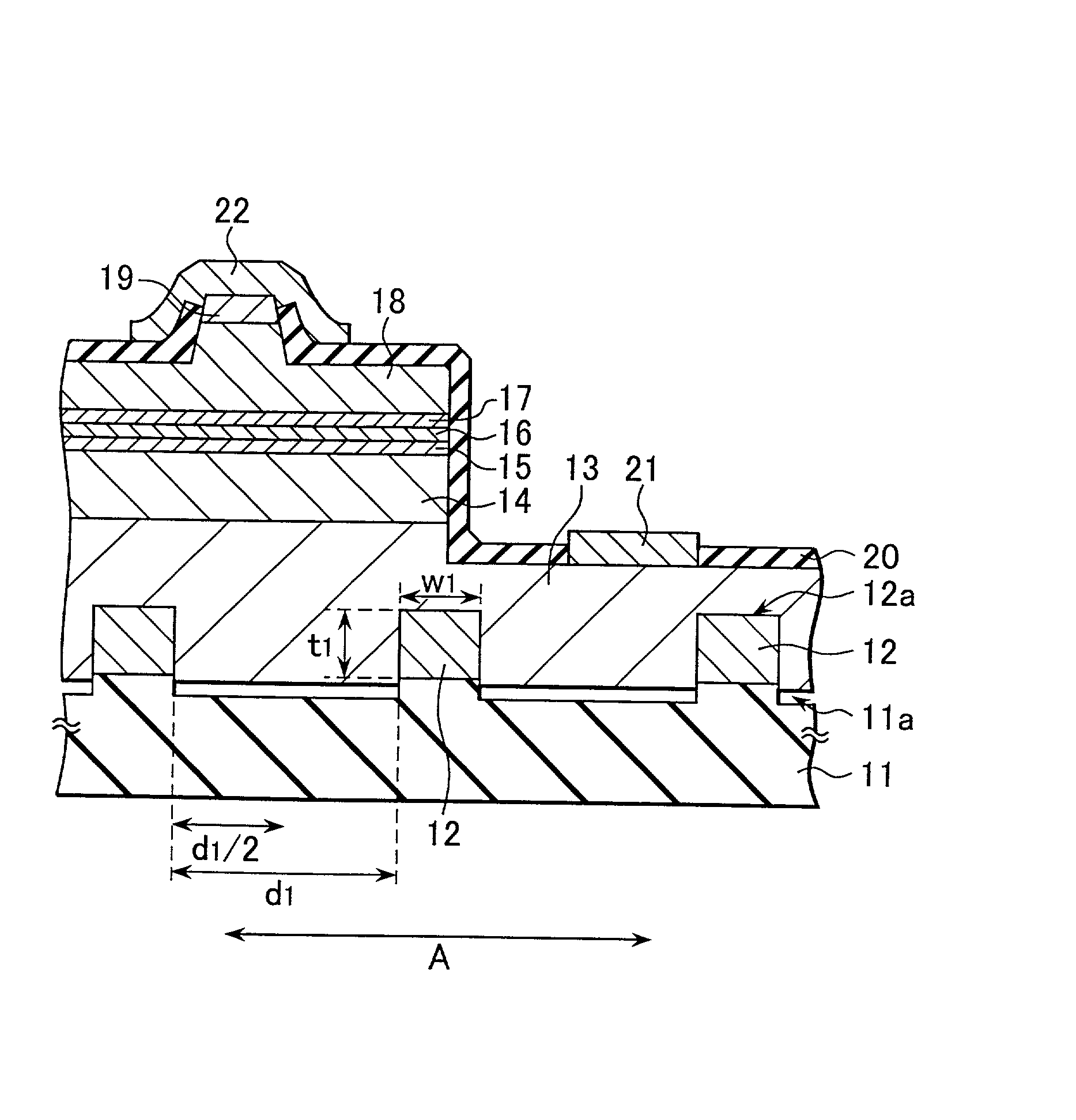
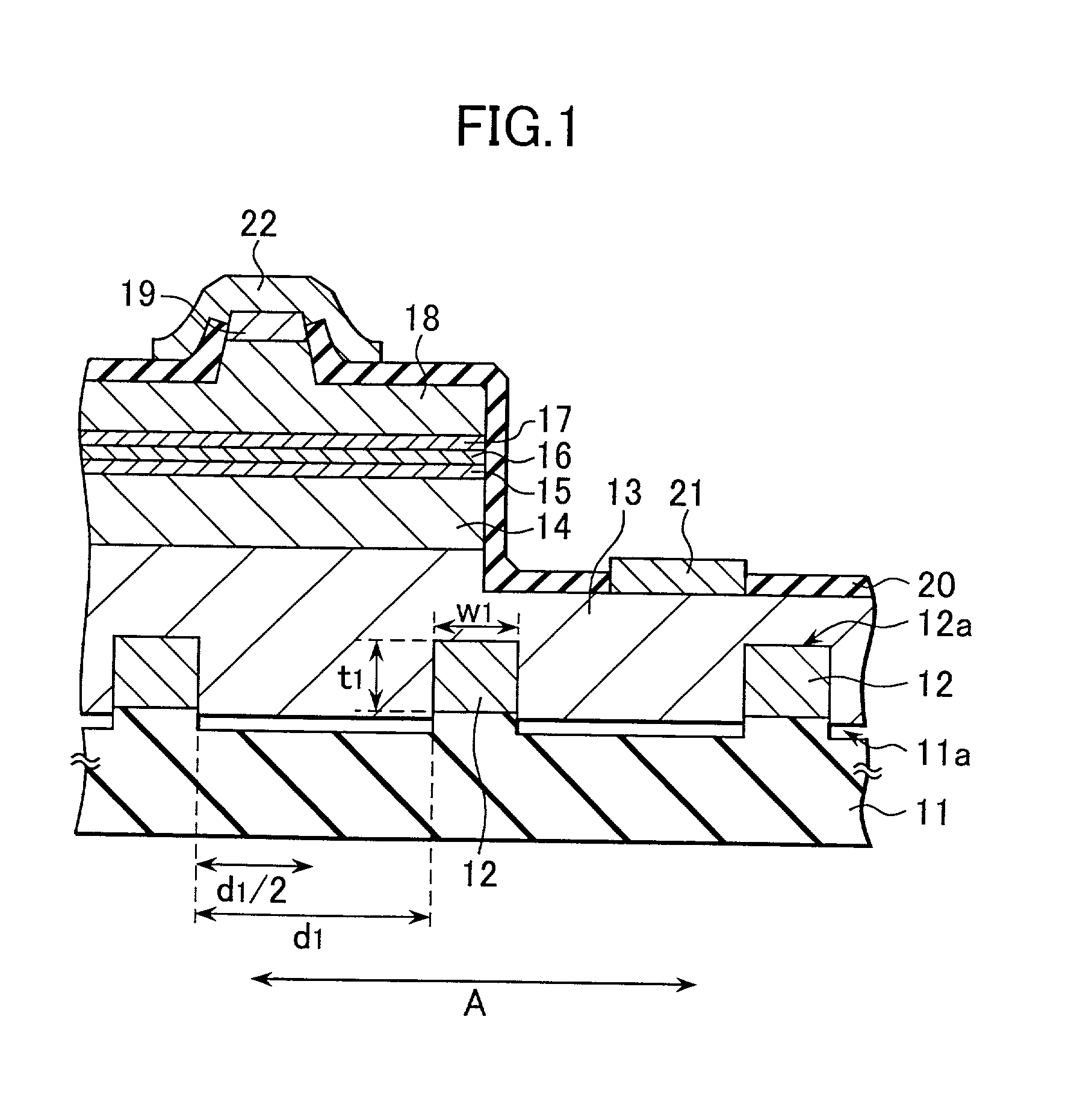
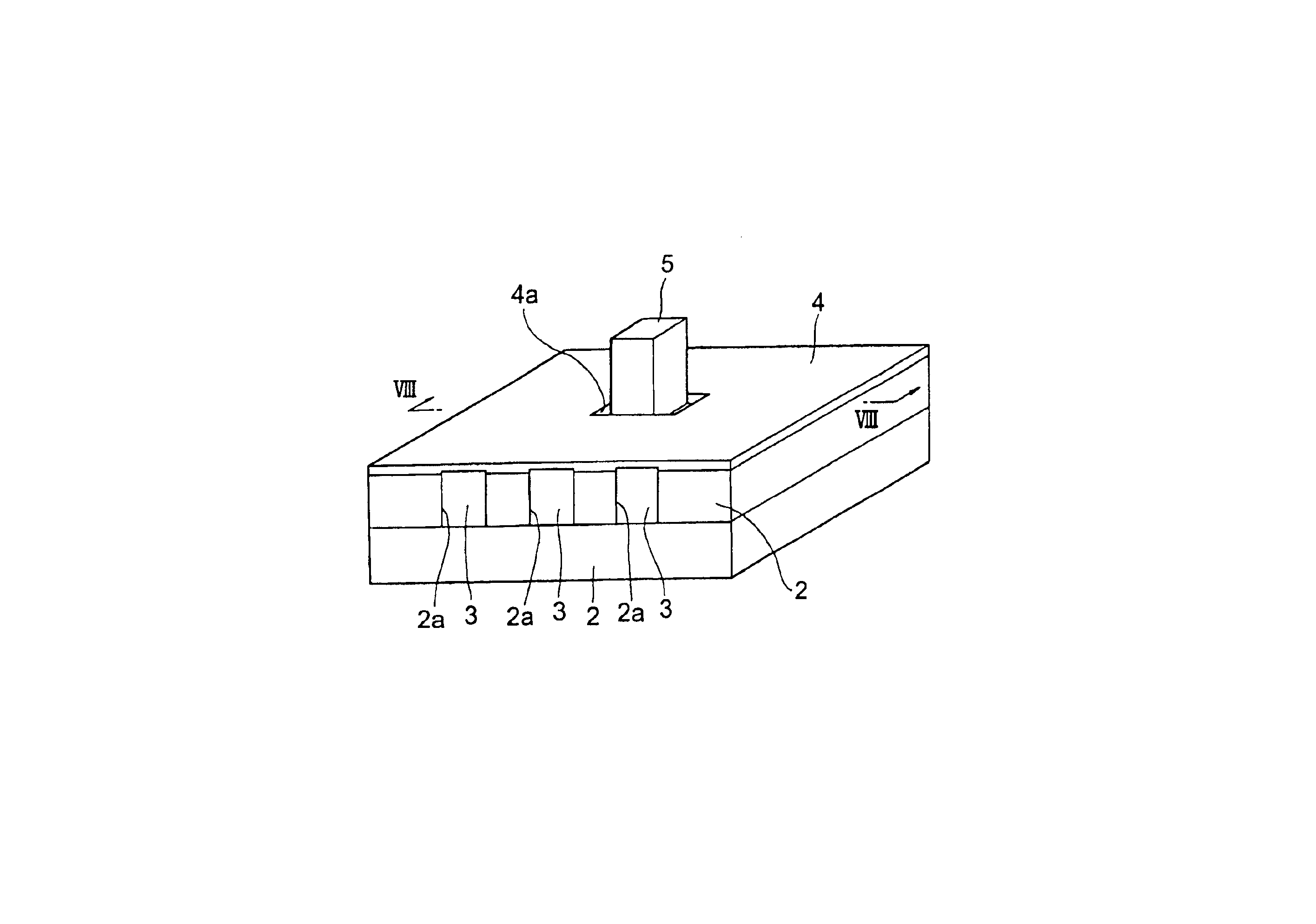
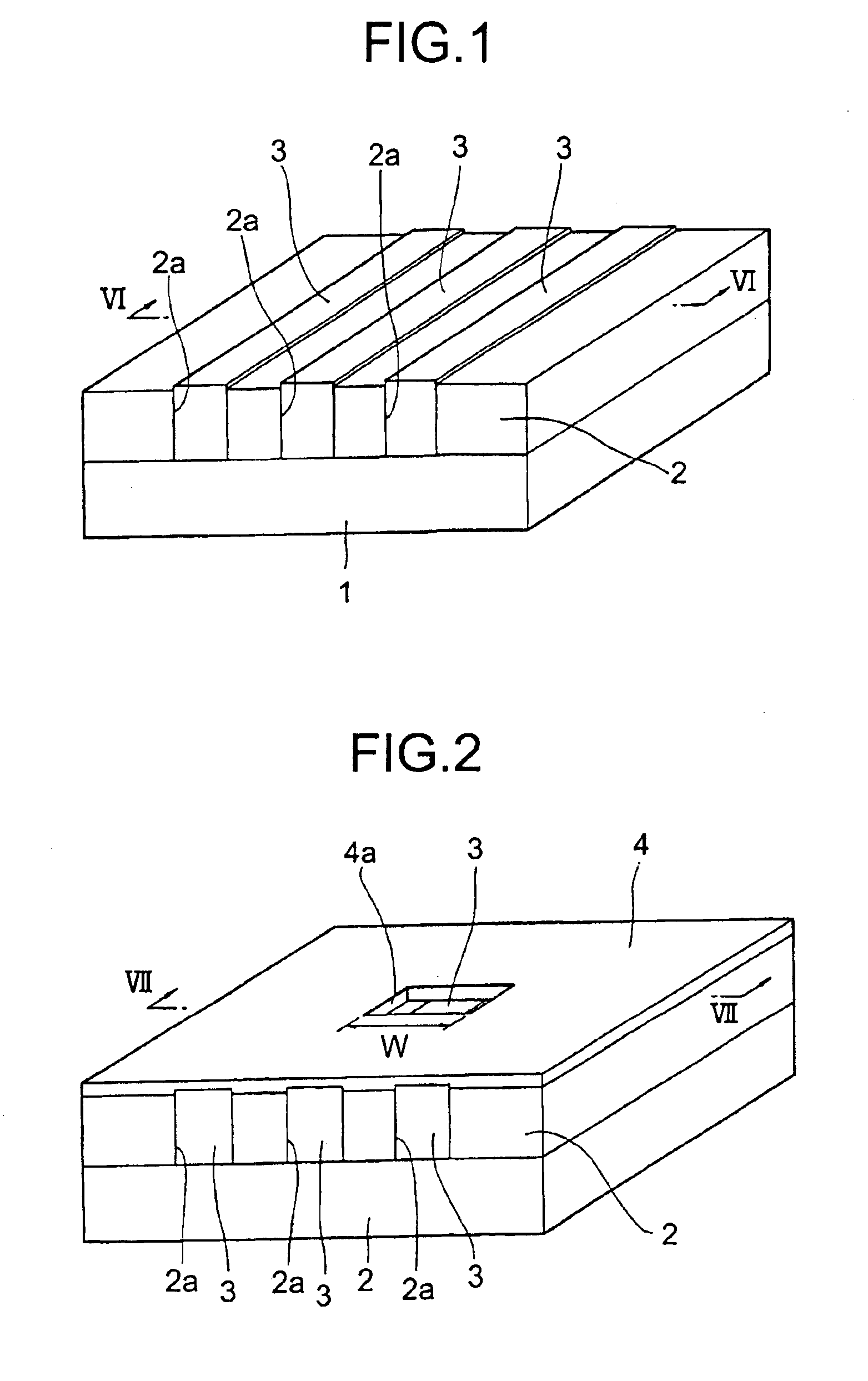
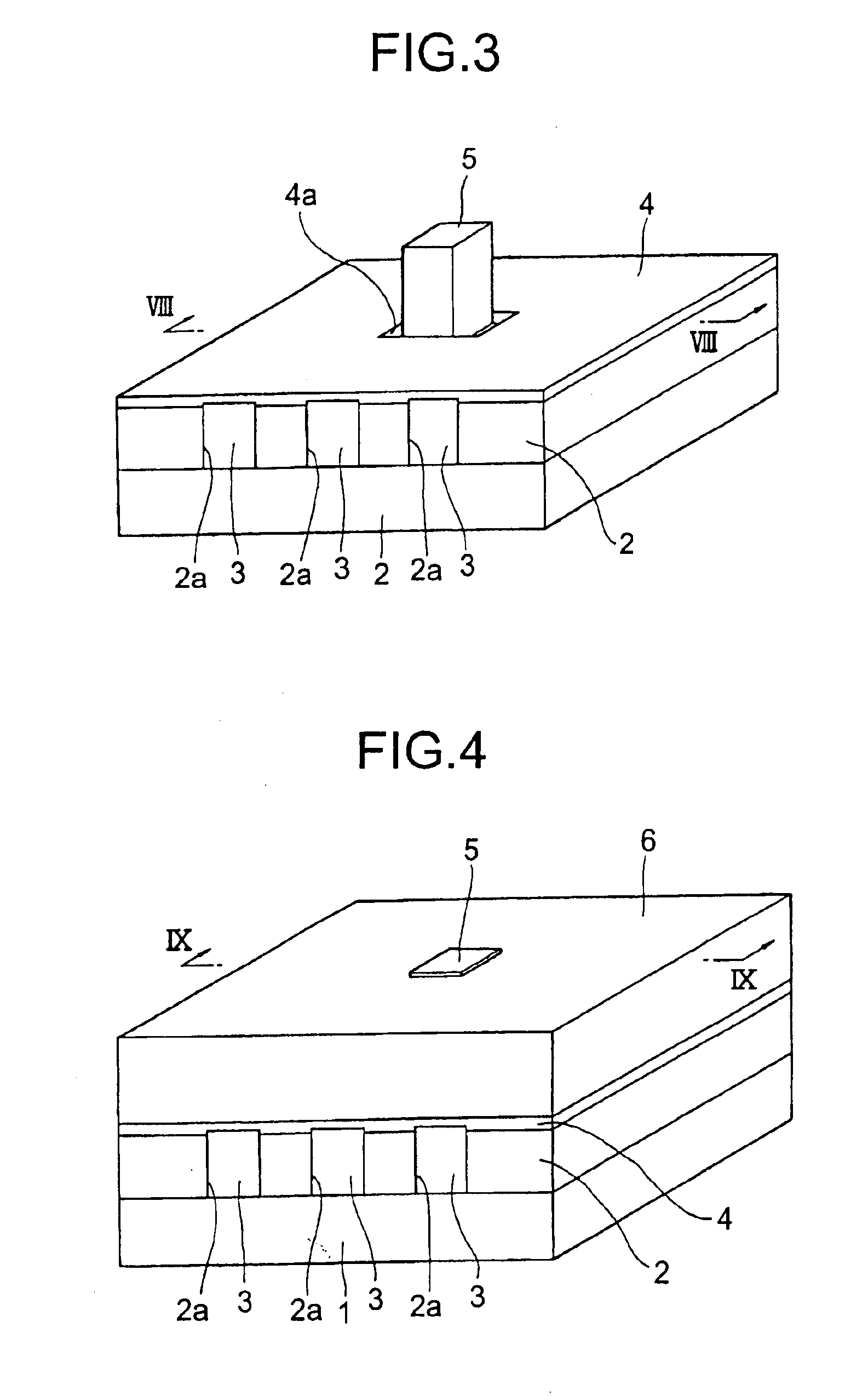
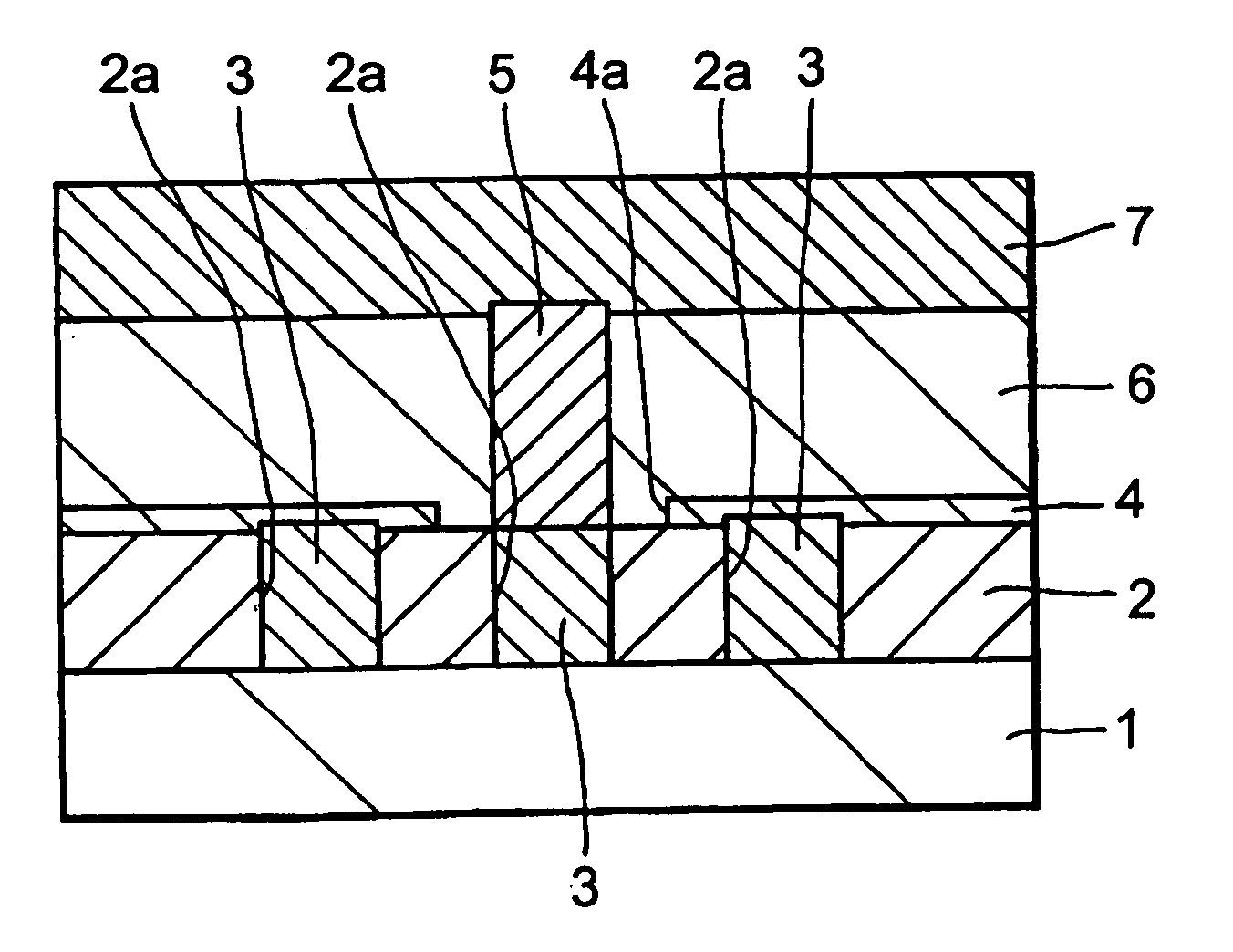
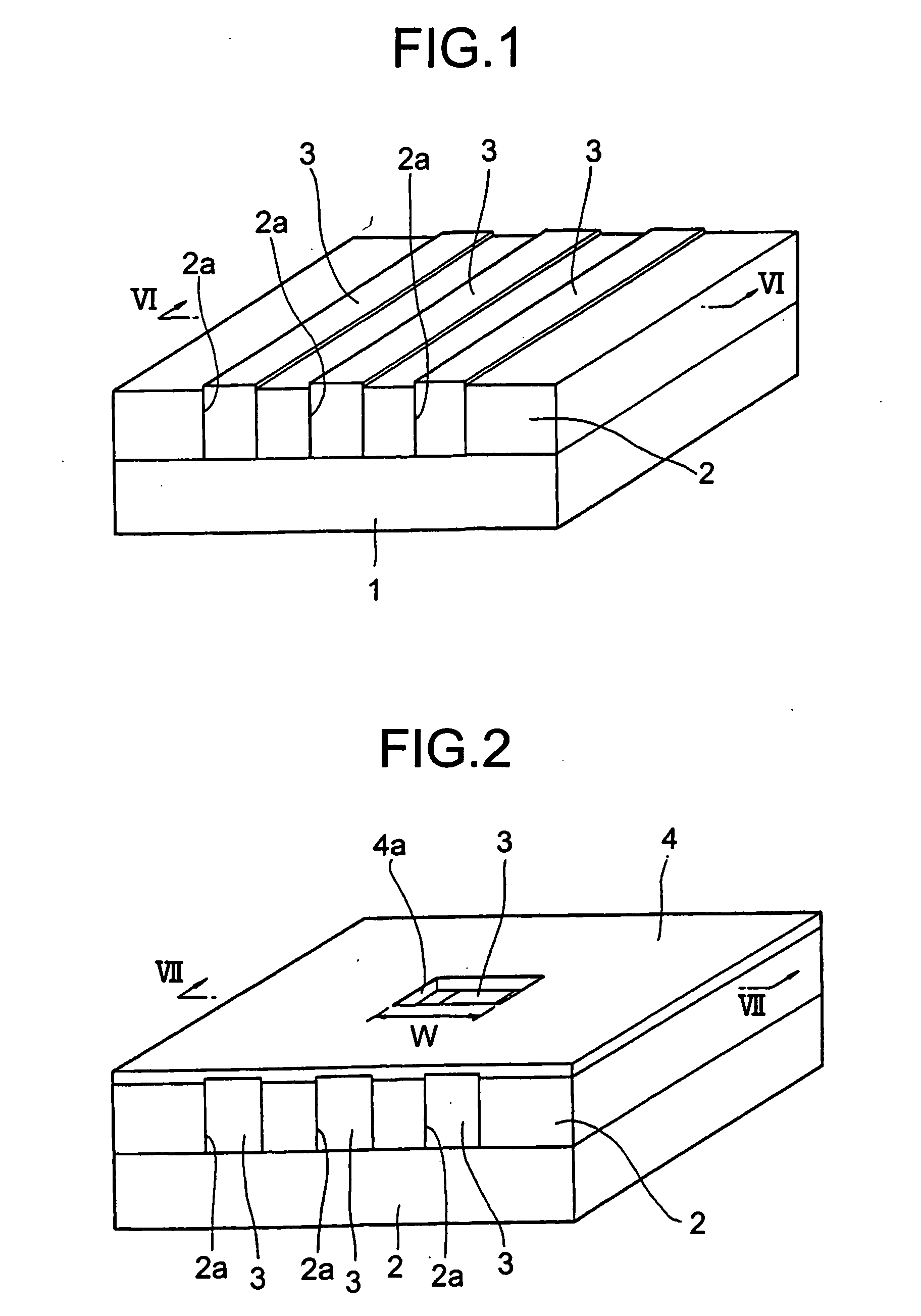
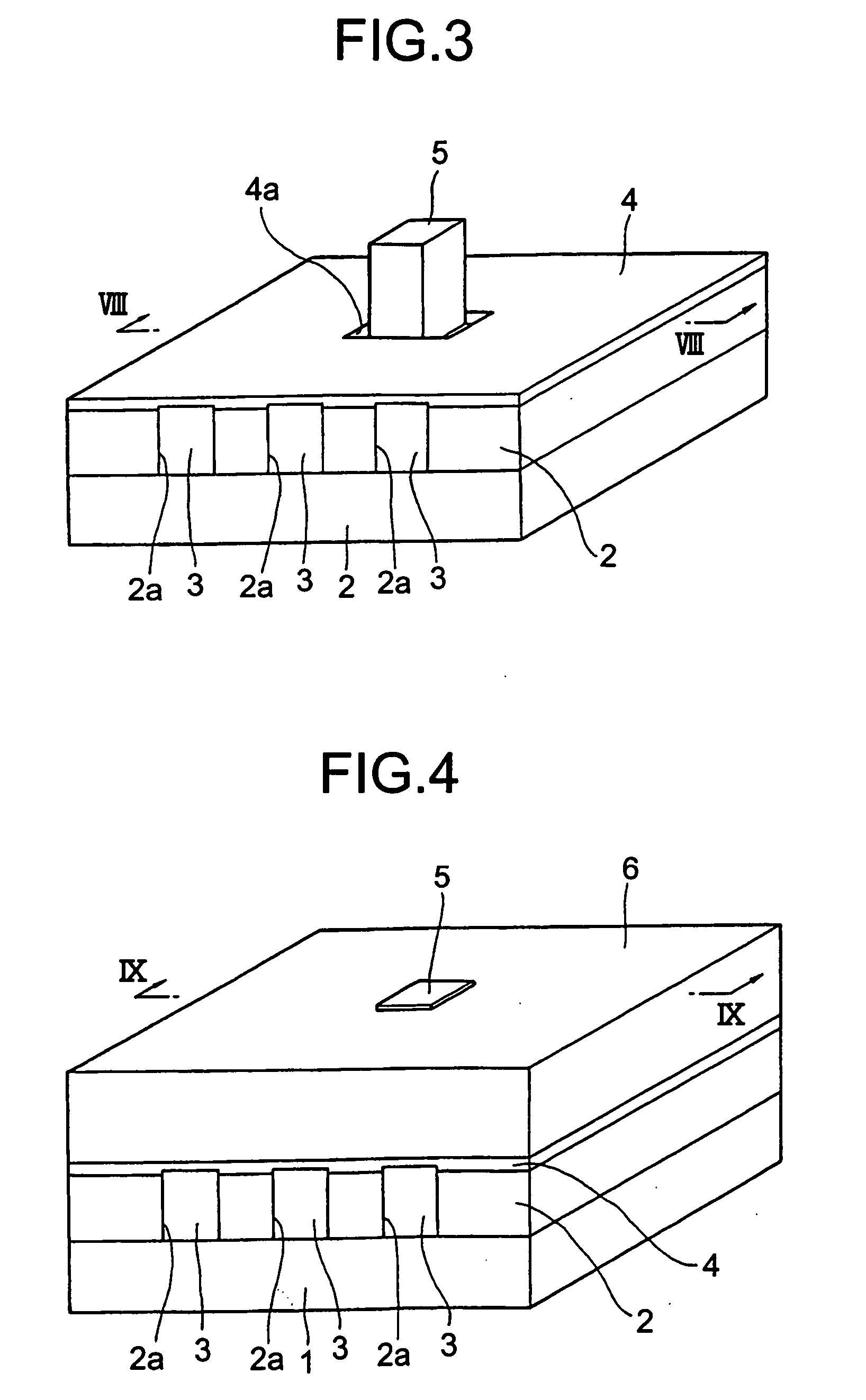
Semiconductor laser, semiconductor device and nitride series III-V group compound substrate, as well as manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20020064195A1Enhance layeringReduce volatilityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSemiconductor packageContact layer
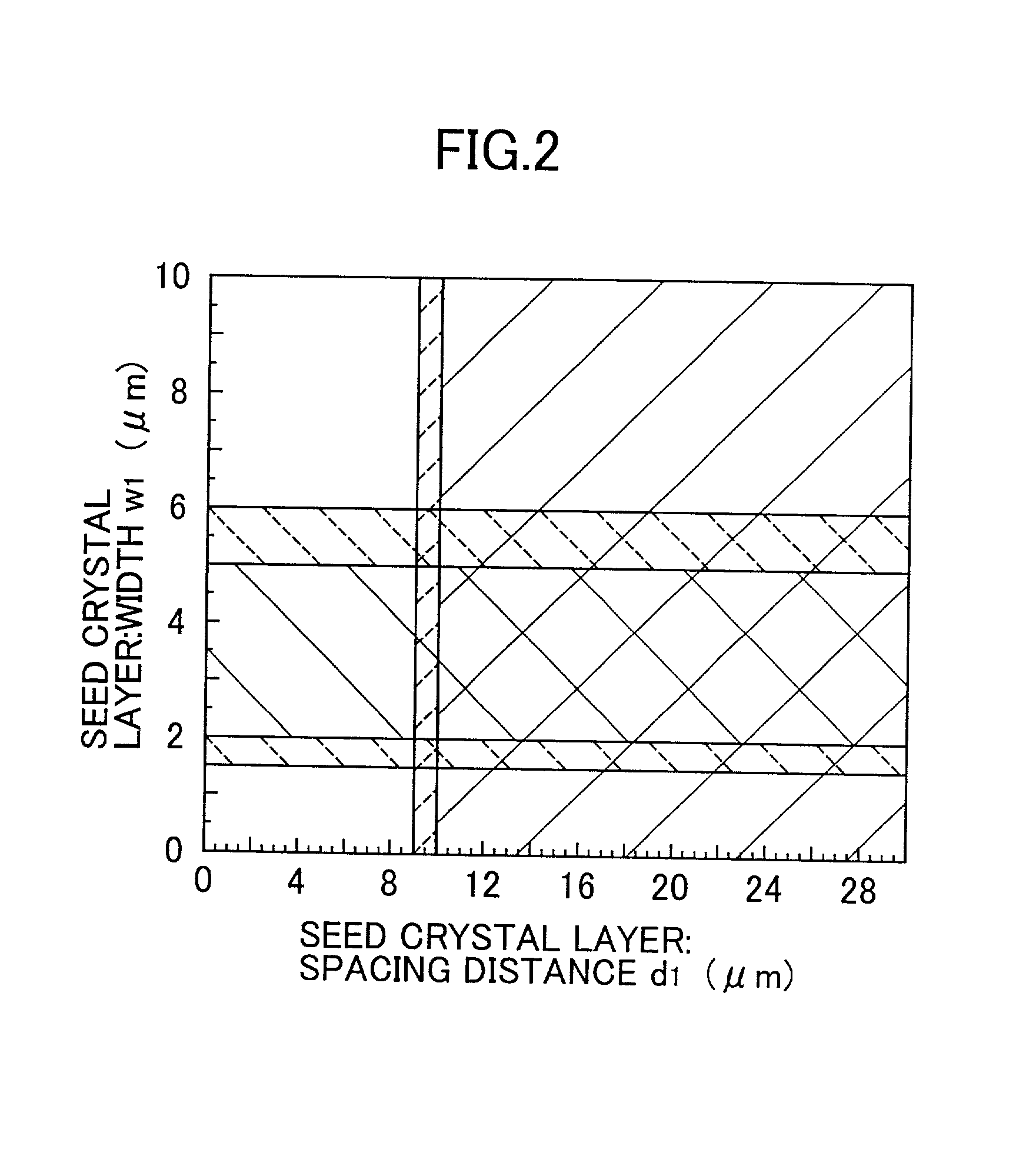
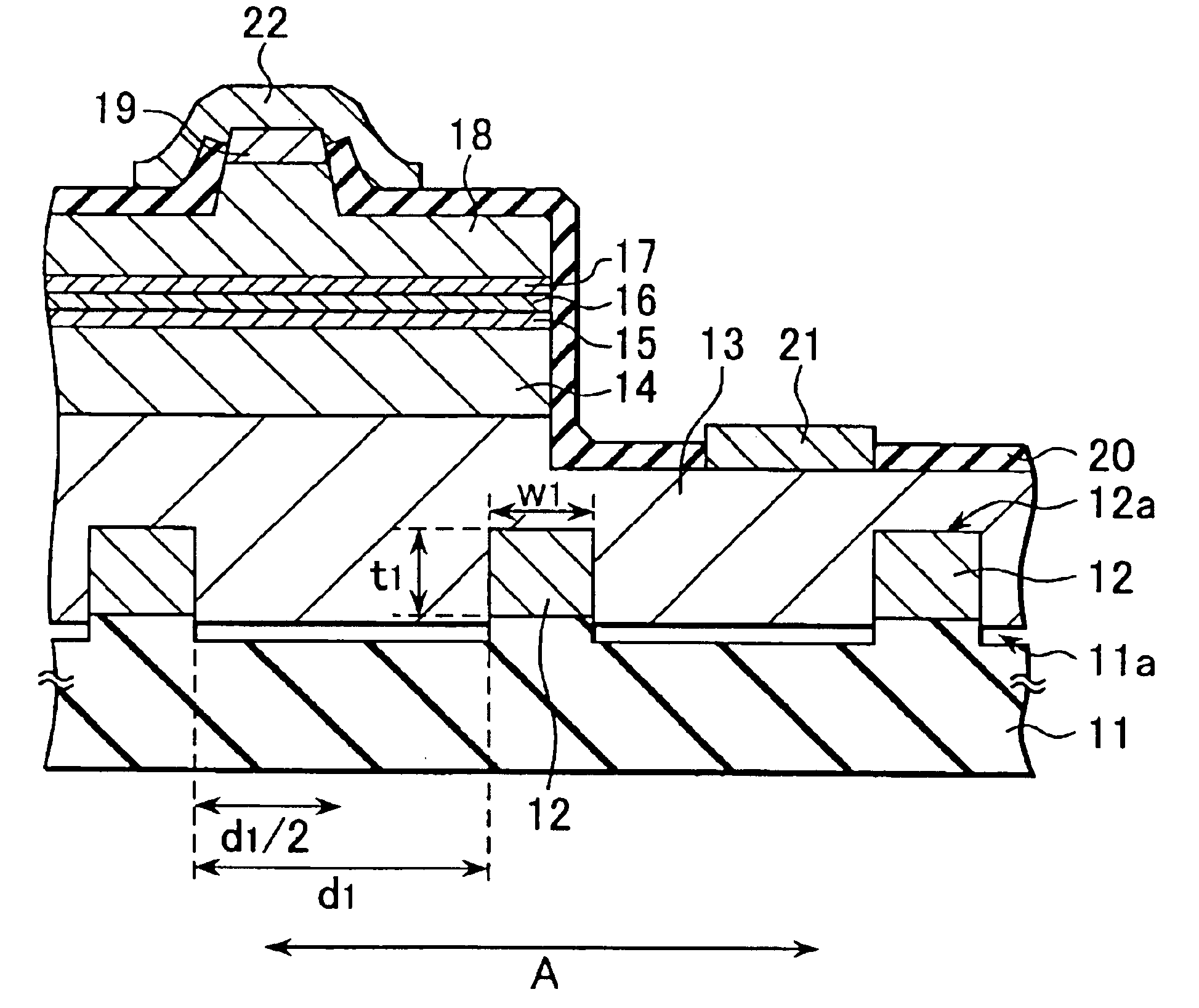
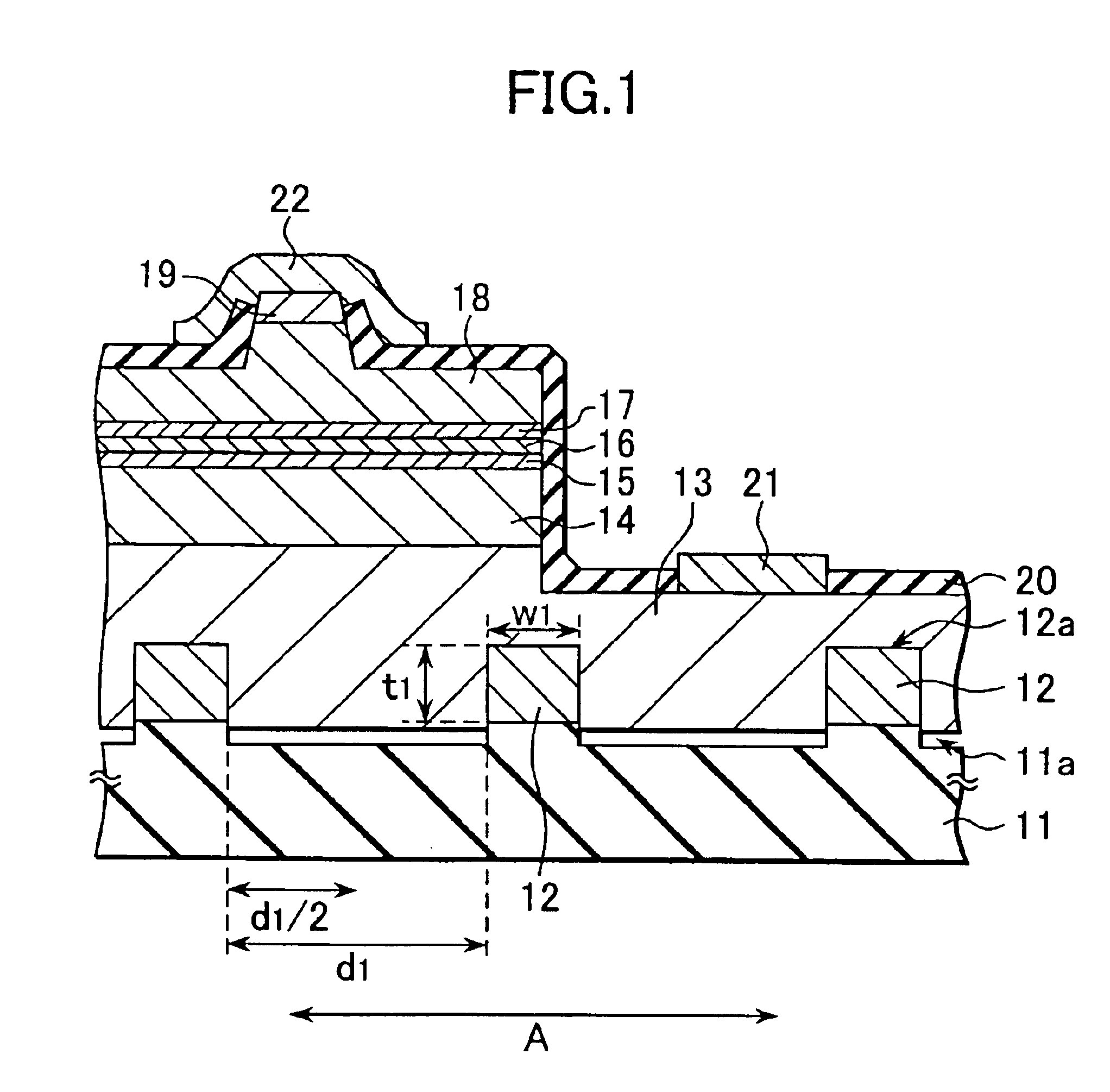
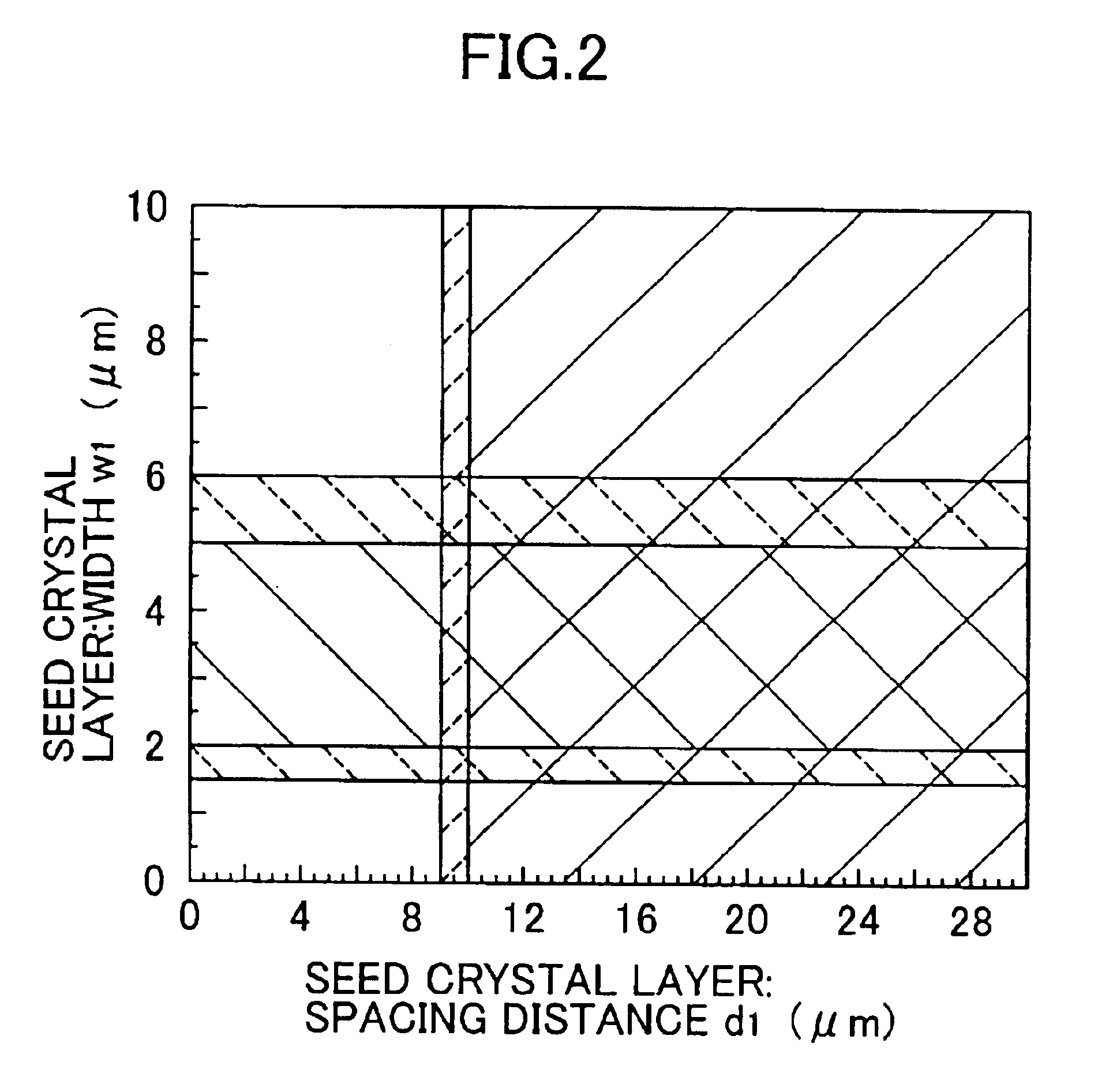
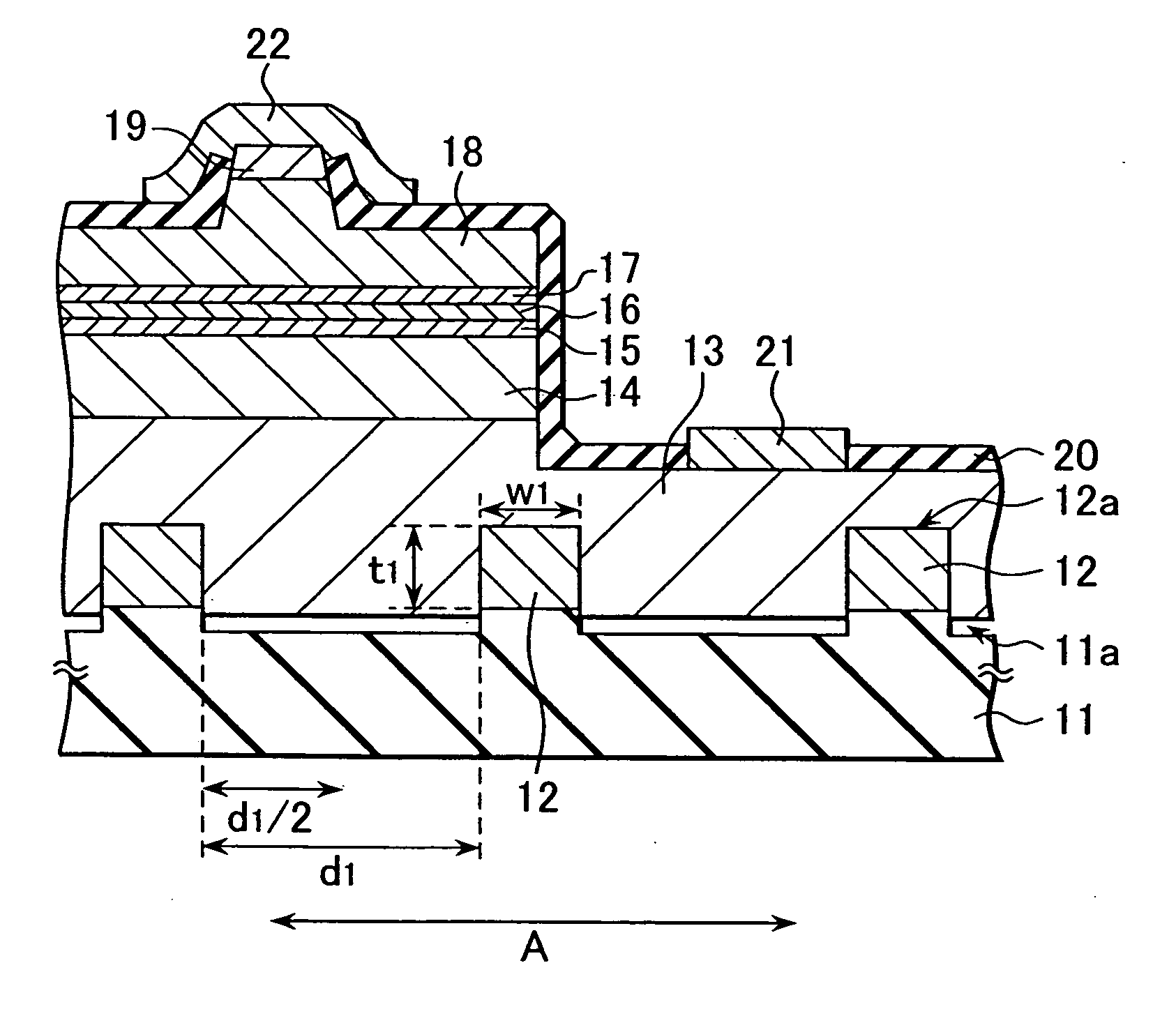
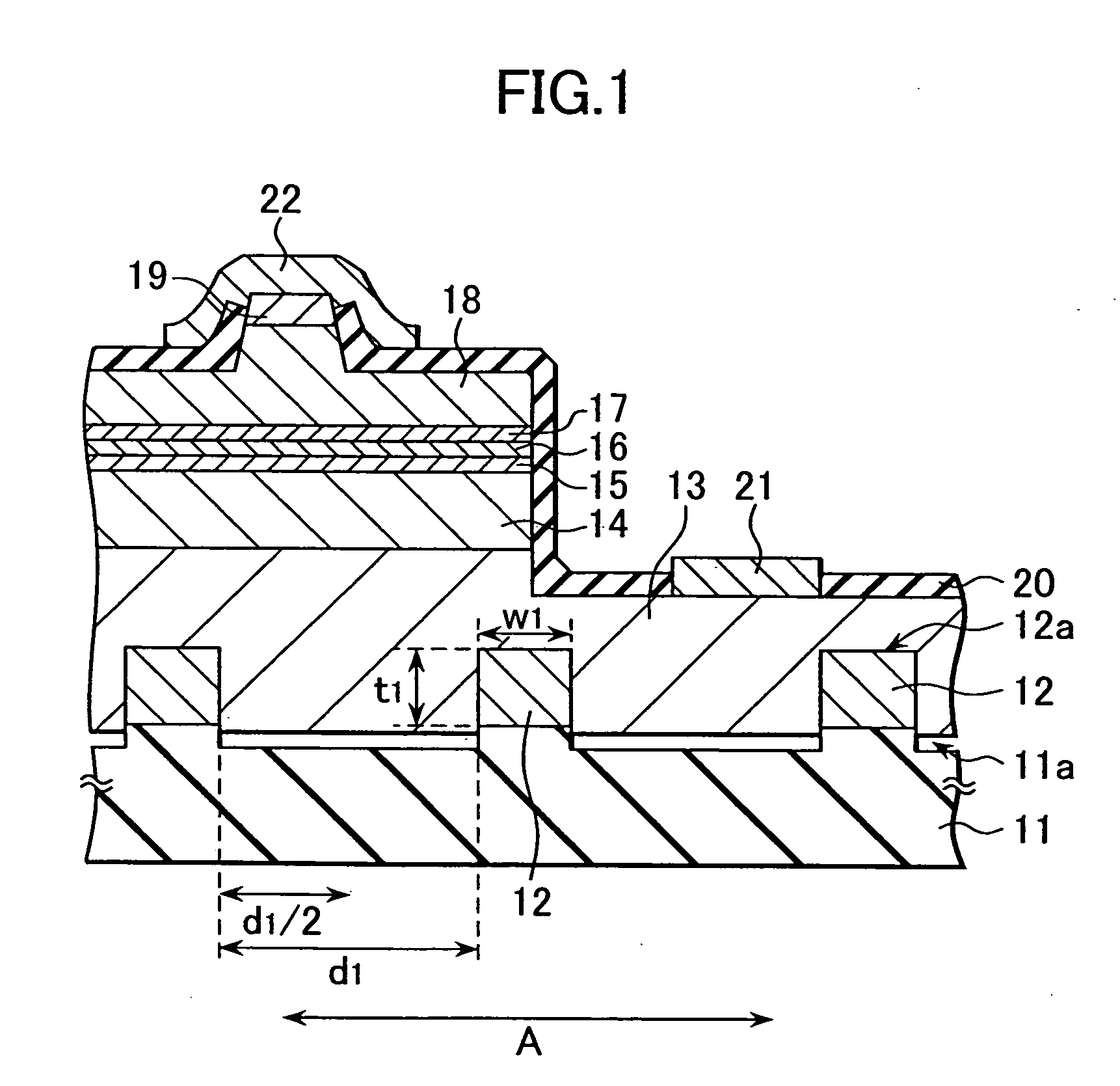
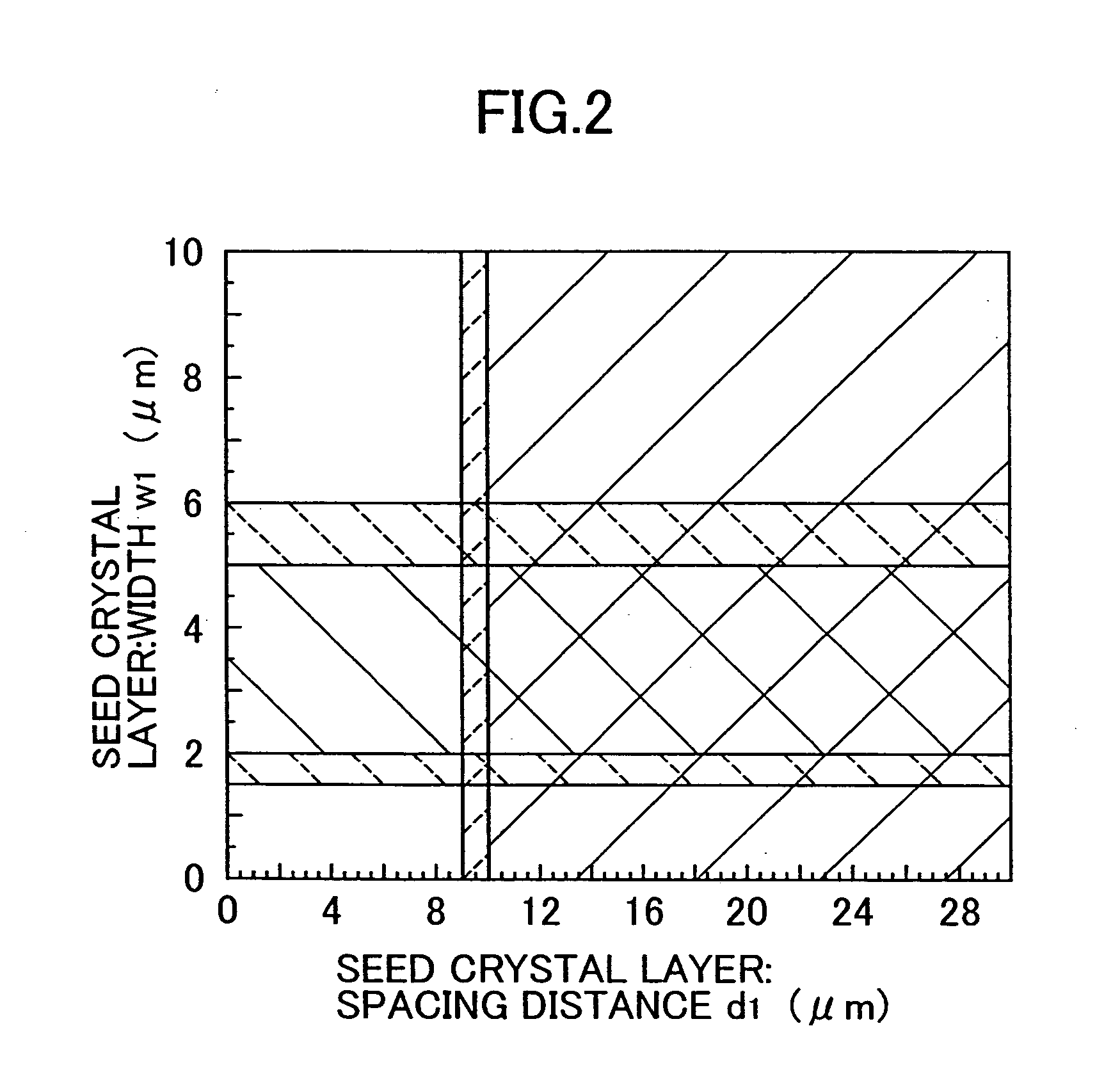
A semiconductor laser, a semiconductor device and a nitride series III-V group compound substrate capable of obtaining a crystal growth layer with less fluctuation of the crystallographic axes and capable of improving the device characteristics, as well as a manufacturing method therefor are provided. The semiconductor laser comprises, on one surface of a substrate used for growing, a plurality of spaced apart seed crystal layers and an n-side contact layer having a lateral growing region which is grown on the basis of the plurality of seed crystal layers. The seed crystal layer is formed in that a product of width w1 (unit: mum) at the boundary thereof relative to the n-side contact layer along the arranging direction A and a thickness t1 (unit: mum) along the direction of laminating the n-side contact layer is 15 or less. A semiconductor layer comprising a nitride series III-V group compound semiconductor is laminated on a substrate 11 comprising an n-type GaN. Protruded seed crystal portions are formed and a growth suppression layer having an opening corresponding to the seed crystal portion is disposed to the substrate. The semiconductor layer grows on the basis of the seed crystal portion and has a lateral growing region of low dislocation density.
Owner:SONY CORP
Novel Acid Tolerant Lactobacillus Sakei Probio-65 with the Ability of Growth Suppression of Pathogenic Microorganisms and the Anti-Allergic Effect
ActiveUS20090214497A1Prevent proliferationGrowth inhibitionBiocideCosmetic preparationsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Disclosed are a novel tactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65, and the use thereof. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain has acid tolerance, bile acid tolerance and antibiotic resistance, inhibits the growth of harmful pathogenic microorganisms in the body and the intestine of animals, and has immunuenhancing activity. In particular, the novel strain inhibits the growth of Staphylocccus aureus, which is known to be a factor aggravating atopic dermatitis. Thus, the novel strain is useful for preventing or treating atopic dermatitis and allergy-related disorders. Also, the novel strain stabilizes intestinal microflors by inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the intestine. The L. sakei Probio-65 strain or a culture thereof is useful in pharmaceutical, feed, food, and cosmetic compositions.
Owner:PROBIONIC CO LTD
Semiconductor laser, semiconductor device and nitride series III-V group compound substrate, as well as manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6836498B2Enhance layeringReduce volatilityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSemiconductor packageContact layer
A semiconductor laser, a semiconductor device and a nitride series III-V group compound substrate capable of obtaining a crystal growth layer with less fluctuation of the crystallographic axes and capable of improving the device characteristics, as well as a manufacturing method therefor are provided. The semiconductor laser comprises, on one surface of a substrate used for growing, a plurality of spaced apart seed crystal layers and an n-side contact layer having a lateral growing region which is grown on the basis of the plurality of seed crystal layers. The seed crystal layer is formed in that a product of width w1 (unit: mum) at the boundary thereof relative to the n-side contact layer along the arranging direction A and a thickness t1 (unit: mum) along the direction of laminating the n-side contact layer is 15 or less.A semiconductor layer comprising a nitride series III-V group compound semiconductor is laminated on a substrate 11 comprising an n-type GaN. Protruded seed crystal portions are formed and a growth suppression layer having an opening corresponding to the seed crystal portion is disposed to the substrate. The semiconductor layer grows on the basis of the seed crystal portion and has a lateral growing region of low dislocation density.
Owner:SONY CORP
Two types of isoquinoline compounds and application thereof to preparing anti-cancer medicaments
InactiveCN102627604AEnhanced inhibitory effectExtensive pharmacological activity studiesBoron compound active ingredientsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsMeth-Boronic acid
The invention relates to two types of isoquinoline compounds and application thereof to preparing anti-cancer medicaments. The compounds have obvious growth suppression and activity killing effects on various human cancer cells. The two types of isoquinoline compounds have the molecular structural characteristics shown in the specification respectively, wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11 and R12 are same or different hydrogen, alkyl group, naphthenic group, alkenyl group, alkine group, unsaturated monocyclic alkyl group, alkoxy group, halogen, hydroxyl group, nitryl group, cyano group, trifluoromethyl group, heterocyclic substituent, carboxyl group, ester group, amido group, acryl group or aldehyde group; R6 is an aliphatic hydrocarbon group or aryl group; R13 is cyano (-CH) or alkoxy (RO-); and X- is sulfate radical, halogen anion, carbonate, bicarbonate radical, phosphate radical, hydrogen phosphate radical, fatty acid radical, sulfonic acid radical or tetraphenyl borate radical.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Semiconductor laser, semiconductor device and nitride series III-V group compound substrate, as well as manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20050000407A1Less fluctuationImprove featuresLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialContact layer
A semiconductor laser, a semiconductor device and a nitride series III-V group compound substrate capable of obtaining a crystal growth layer with less fluctuation of the crystallographic axes and capable of improving the device characteristics, as well as a manufacturing method therefor are provided. The semiconductor laser comprises, on one surface of a substrate used for growing, a plurality of spaced apart seed crystal layers and an n-side contact layer having a lateral growing region which is grown on the basis of the plurality of seed crystal layers. The seed crystal layer is formed in that a product of width w1 (unit: μm) at the boundary thereof relative to the n-side contact layer along the arranging direction A and a thickness t1 (unit: μm) along the direction of laminating the n-side contact layer is 15 or less. This can decrease the fluctuation of the crystallographic axes in the n-side contact layer. Accordingly, crystallinity of the semiconductor layer including from n-type clad layer to a p-side contact layer laminated on the n-side contact layer is improved. A semiconductor laser and a semiconductor device capable of decreasing dislocation density and improving device characteristics, as well as a manufacturing method therefor are provided. A semiconductor layer comprising a nitride series III-V group compound semiconductor is laminated on a substrate 11 comprising an n-type GaN. Protruded seed crystal portions are formed and a growth suppression layer having an opening corresponding to the seed crystal portion is disposed to the substrate. The semiconductor layer grows on the basis of the seed crystal portion and has a lateral growing region of low dislocation density. When a current injection region is disposed corresponding to the lateral growing region, the light emission efficiency can be improved. Further, when the growth suppression layer is provided with a function of reflecting or absorbing light generated in the semiconductor layer, it is possible to prevent leakage of light or intrusion of stray light from the substrate to suppress generation of noises.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
Methods, apparatus and system for providing source-drain epitaxy layer with lateral over-growth suppression
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6876079B2Improve coupling strengthHigh mechanical strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
The present invention is to improve yield and reliability in a wiring step of a semiconductor device. When an Al wiring on an upper layer is connected through an connection pillar onto an Al wiring on a lower layer embedded in a groove formed on an interlayer insulation film, a growth suppression film having an opening whose width is wider than that of the Al wiring is formed on the interlayer insulation film and the Al wiring. In this condition, Al and the like are grown by a selective CVD method and the like. Accordingly, the connection pillar is formed on the Al wiring within the opening, in a self-matching manner with respect to the Al wiring.
Owner:SONY CORP
Preparation method for supermolecule hydrogel containing silver nanoparticles
ActiveCN109079153AEvenly dispersedStrong growth inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusStaphylococcus aureusSupermolecule
The invention discloses a preparation method for supermolecule hydrogel containing silver nanoparticles, and belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials. The preparation method for supermolecule hydrogel containing silver nanoparticles comprises the following steps that: dissolving a D type Fmoc-Phe gel factor in buffer solution of which the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value is 7.4, and guaranteeing that the concentration of the D type Fmoc-Phe gel factor in first mixed solution is 6-20mg / mL; shocking the first mixed solution for 30s, and then, heating and dissolving at the temperature of 80-100DEG C to obtain even solution; adding silver nitrate solution into the even solution to obtain hot solution; weighing ascorbic acid, and adopting ultrapure water to dissolve to obtain ascorbic acid solution; and adding the ascorbic acid solution into the hot solution to form even and transparent grayish hydrogel. By use of the preparation method for the supermolecule hydrogel containingsilver nanoparticles, the silver nanoparticle can be subjected to in-situ preparation in the hydrogel, and silver nanoparticles are evenly dispersed, and perform a good growth suppression effect on gram positive bacteria which take staphylococcus aureus as a representative.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
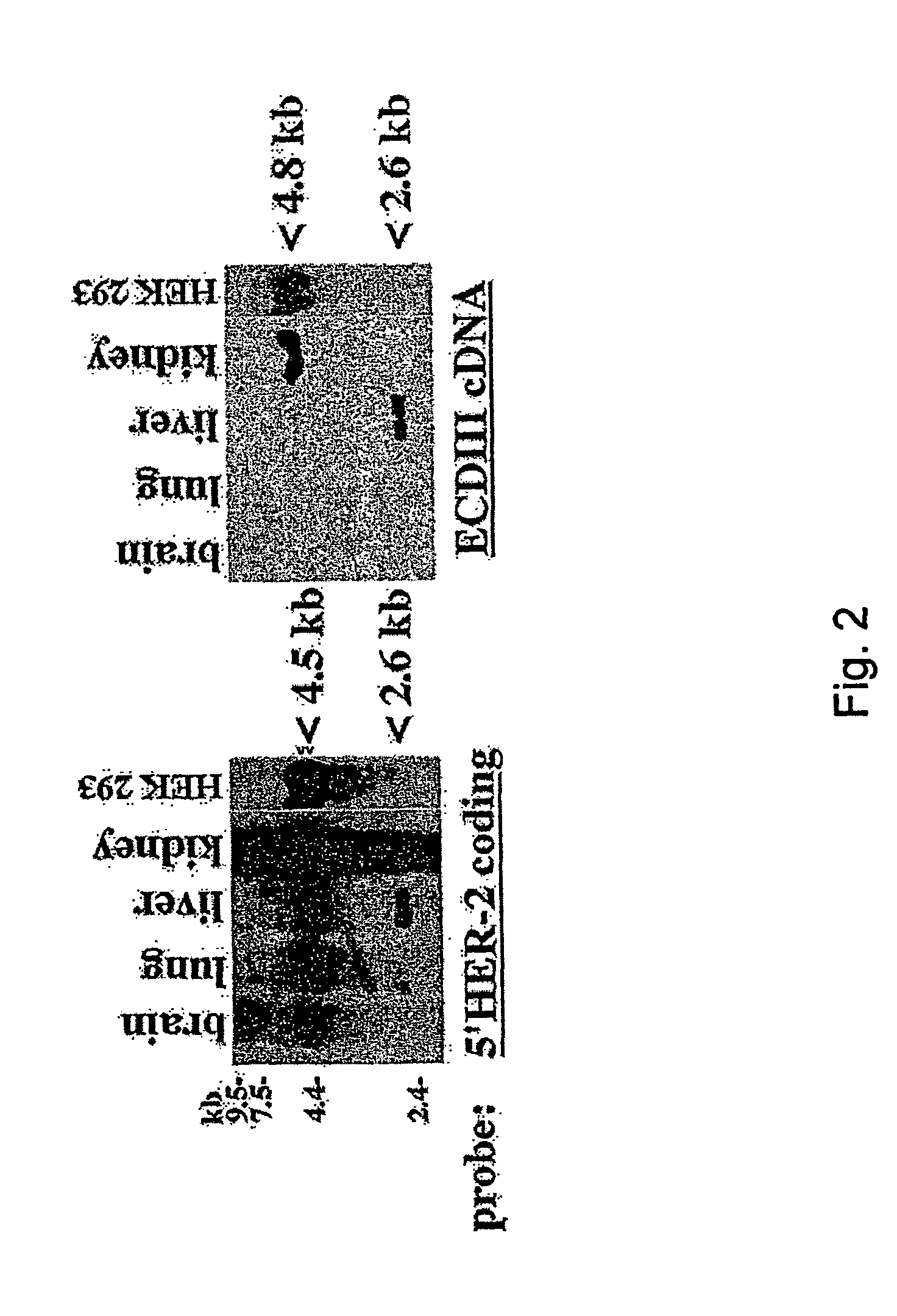
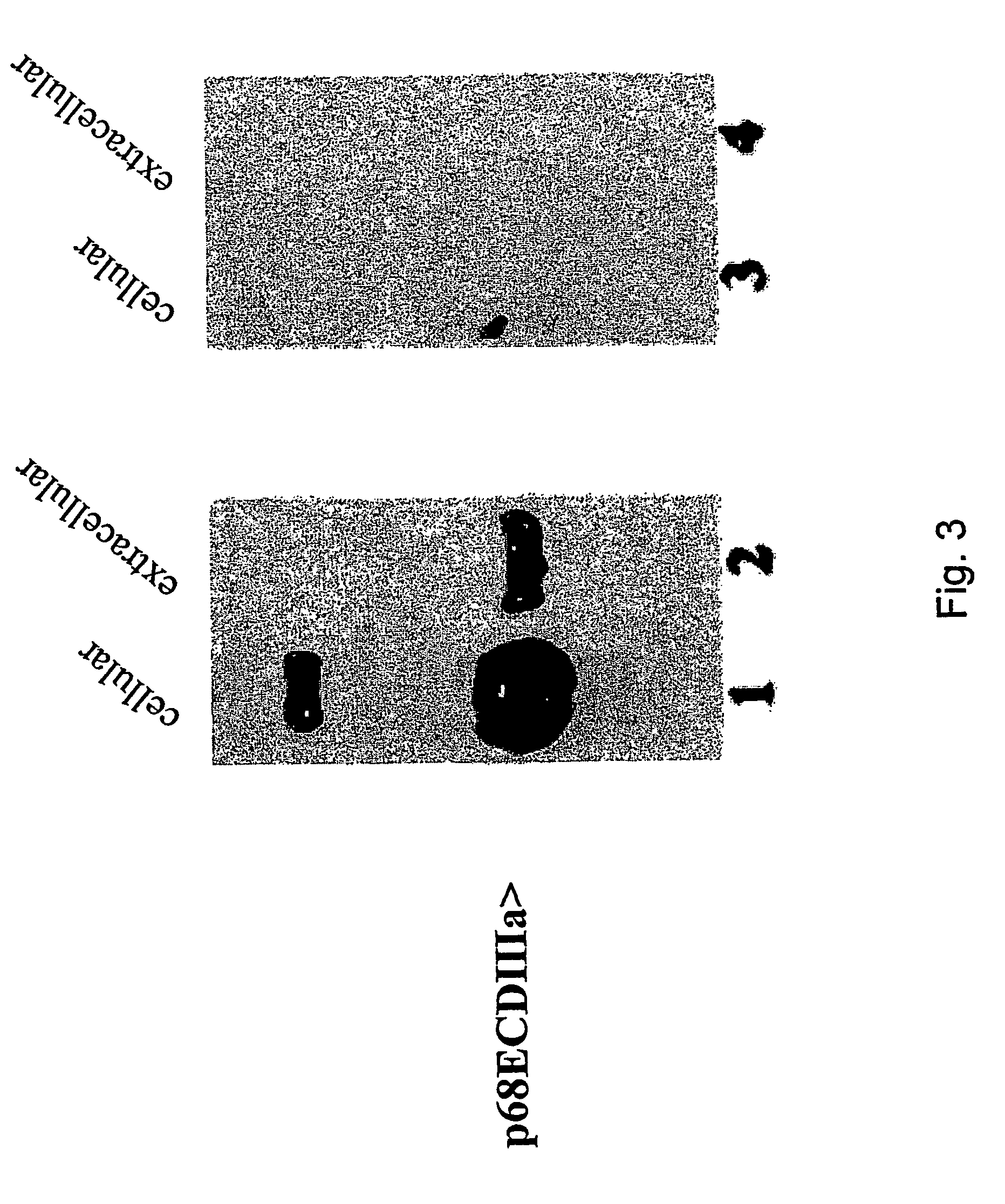
Compositions and methods for treating cancer by modulating HER-2 and EGF receptors
InactiveUS7396810B1Improved prognosisGrowth inhibitionSaccharide peptide ingredientsDisease diagnosisEctopic expressionOncology
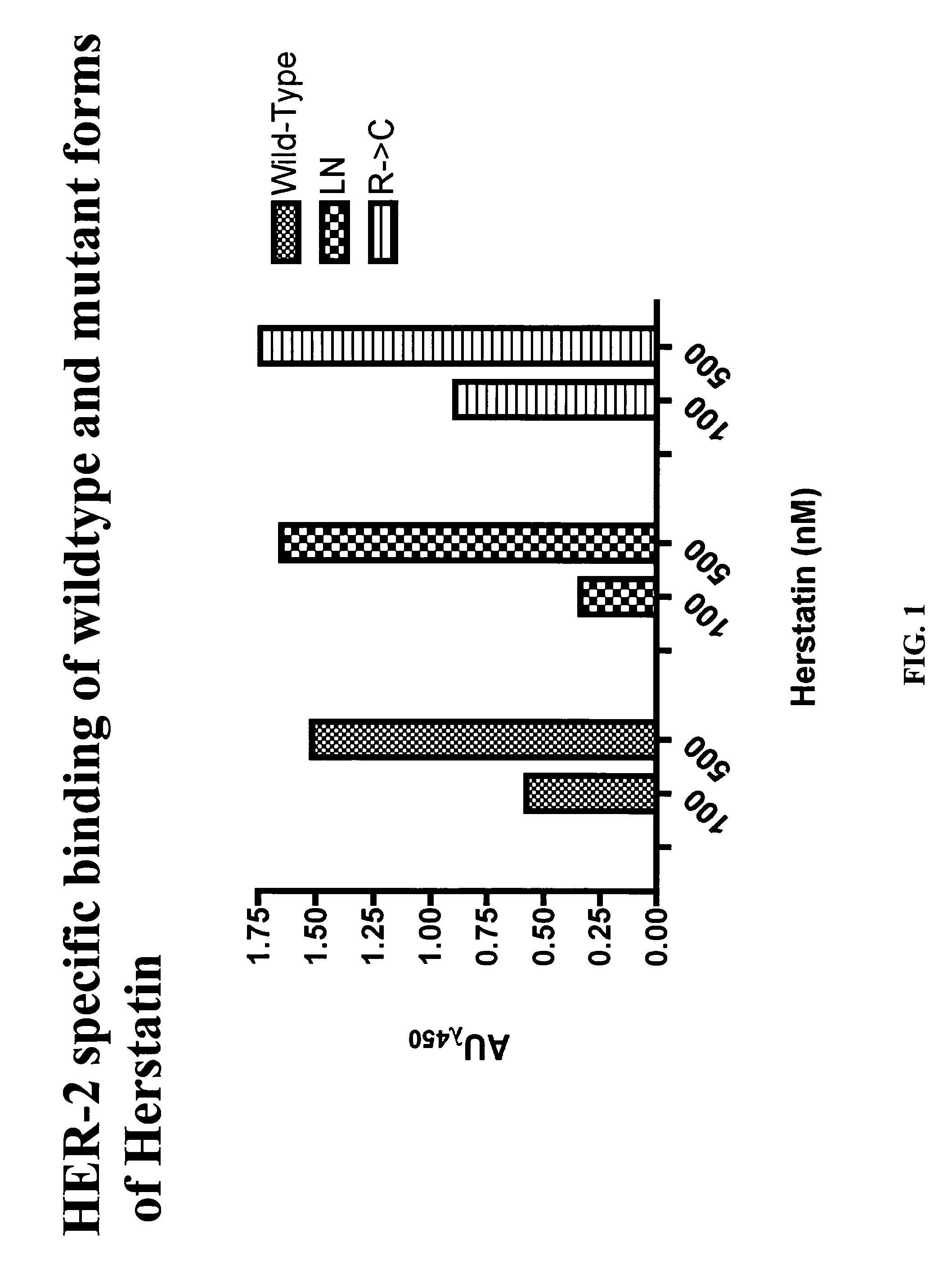
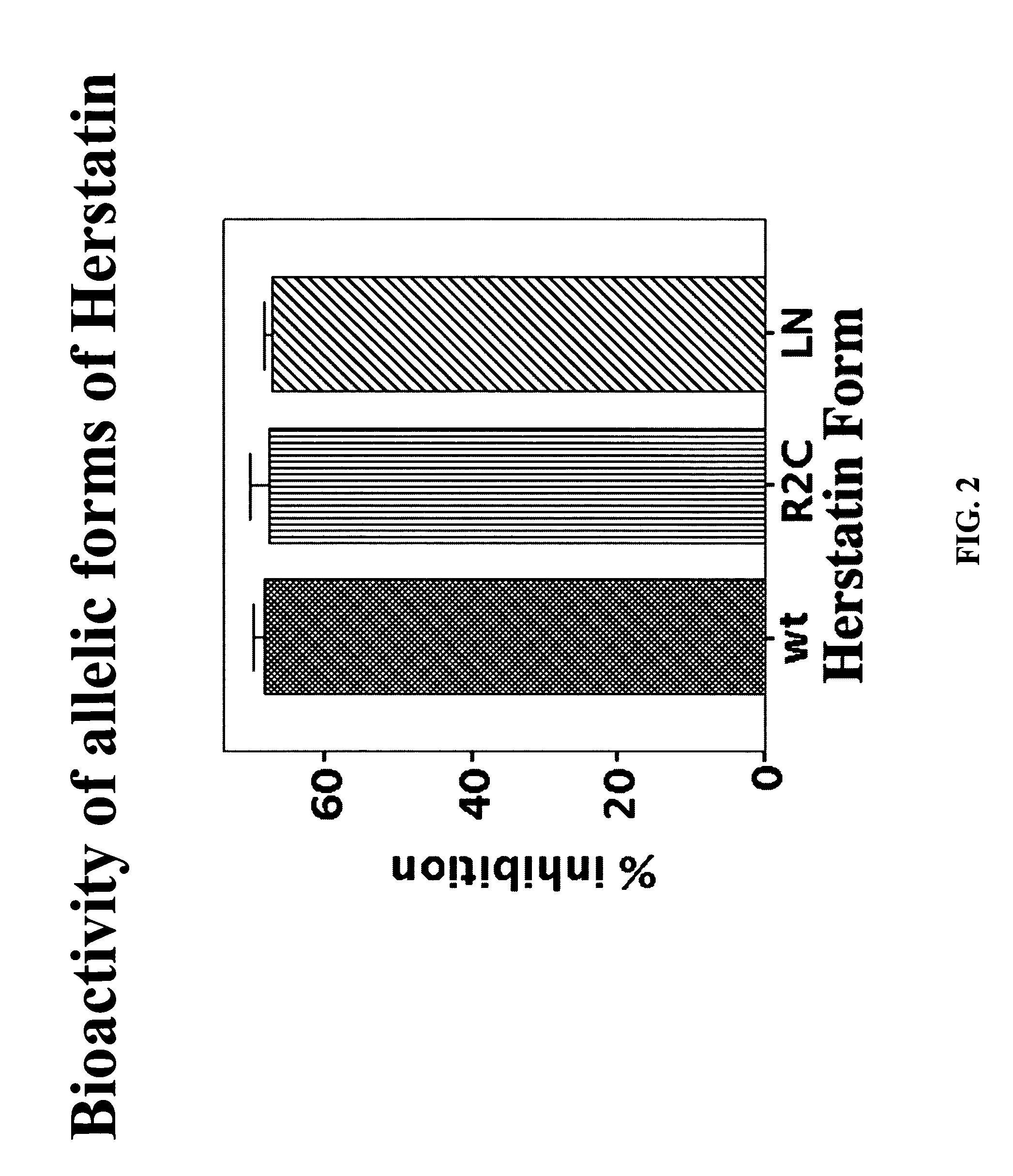
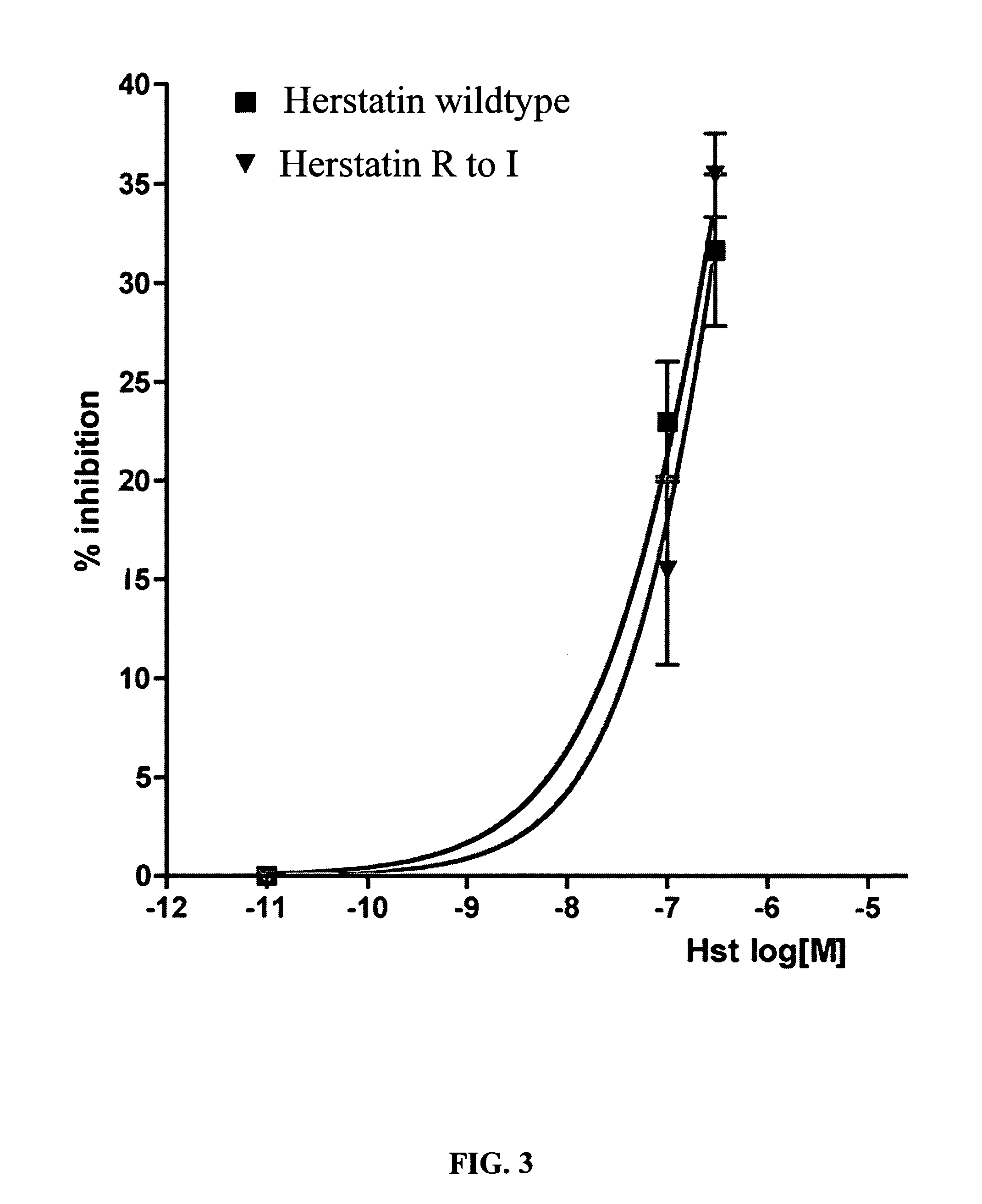
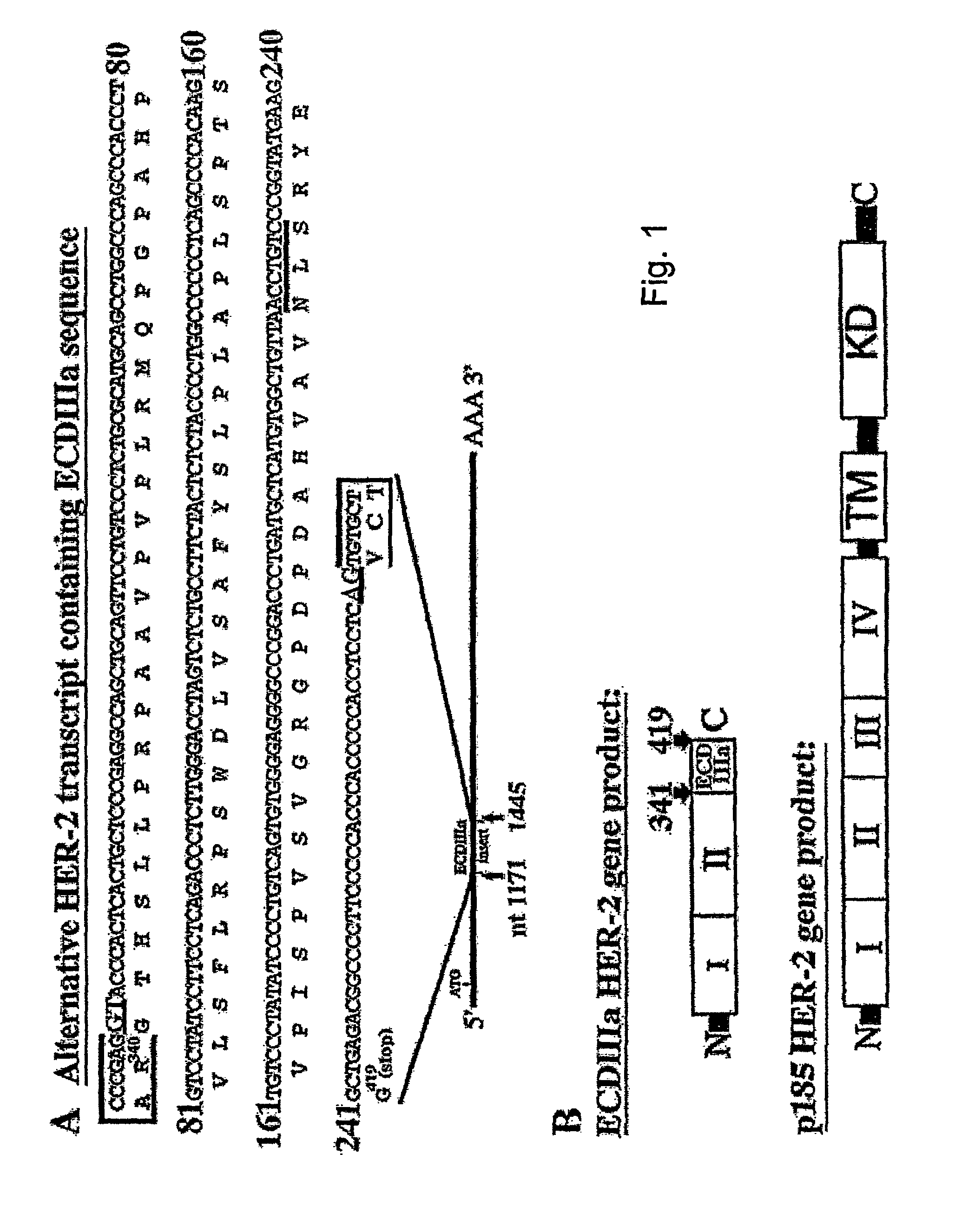
An alternative HER-2 / neu product, herstatin, consists of subdomains I and II from the ectodomain of p185HER-2 and a unique 79 amino acid C-terminus encoded by intron 8. Recombinant herstatin added to cells was found to bind to and inhibit p185HER-2. The effects of ectopic expression of herstatin in combination with either p185HER-2 or with its homolog, the EGF receptor, in several cell lines was studied. Cotransfection of herstatin with HER-2 inhibited p185HER-2 levels and caused an approximate 8 fold reduction in p185 tyrosine phosphorylation. Inhibition of p185HER-2 tyrosine phosphorylation corresponded to a dramatic decline in colony formation by cells that coexpressed p185HER-2 and herstatin. Herstatin also interfered with EGF activation of the EGF receptor in cotransfected cells demonstrated by impaired receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, reduced receptor down-regulation, and growth suppression. For both p185HER-2 and the EGF receptor, the extent of inhibition was affected by the expression levels of herstatin relative to the receptor. Herstatin is an autoinhibitor of p185HER-2 and expands its inhibitory activity to another member of the group I family of receptor tyrosine kinases, the EGF receptor.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
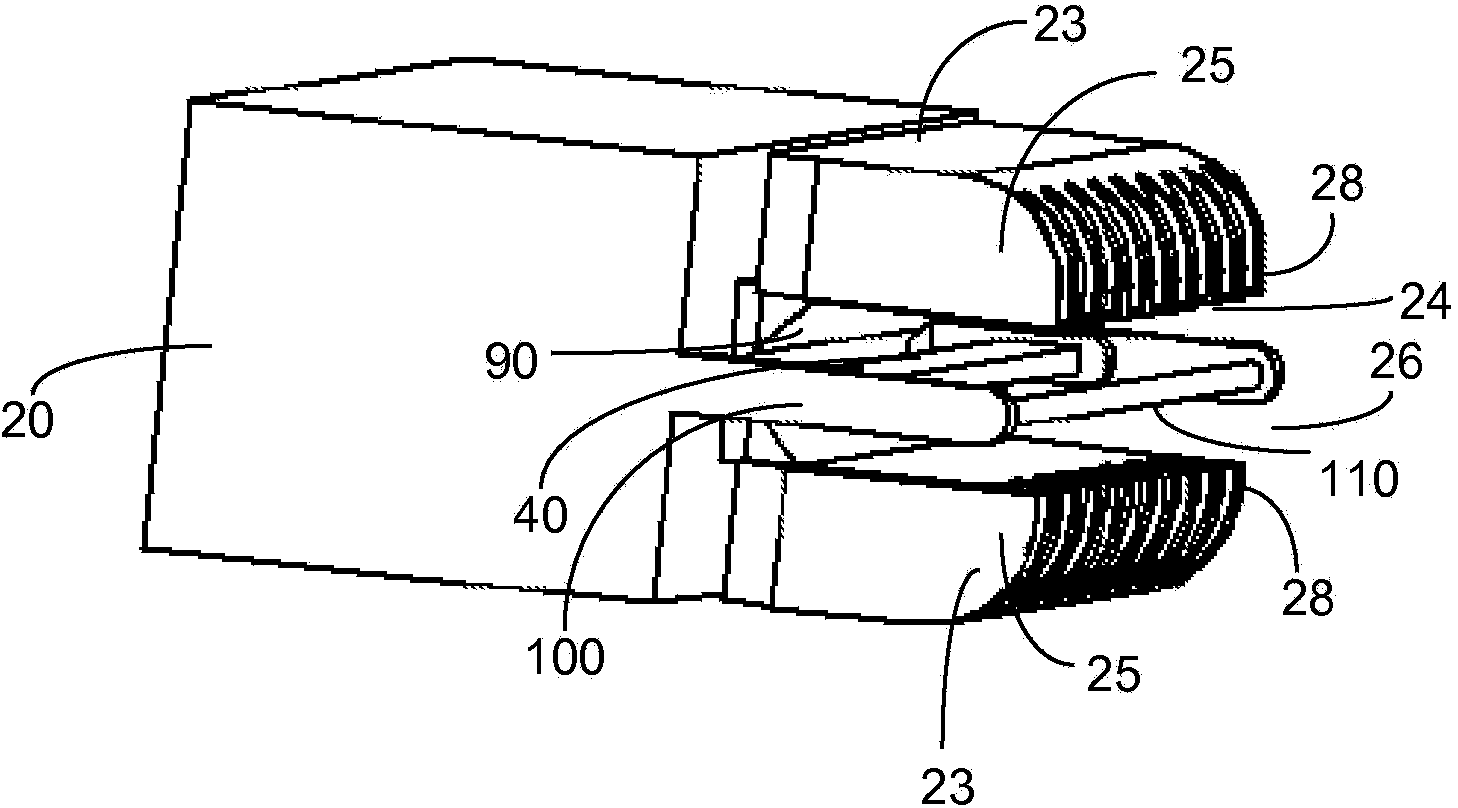
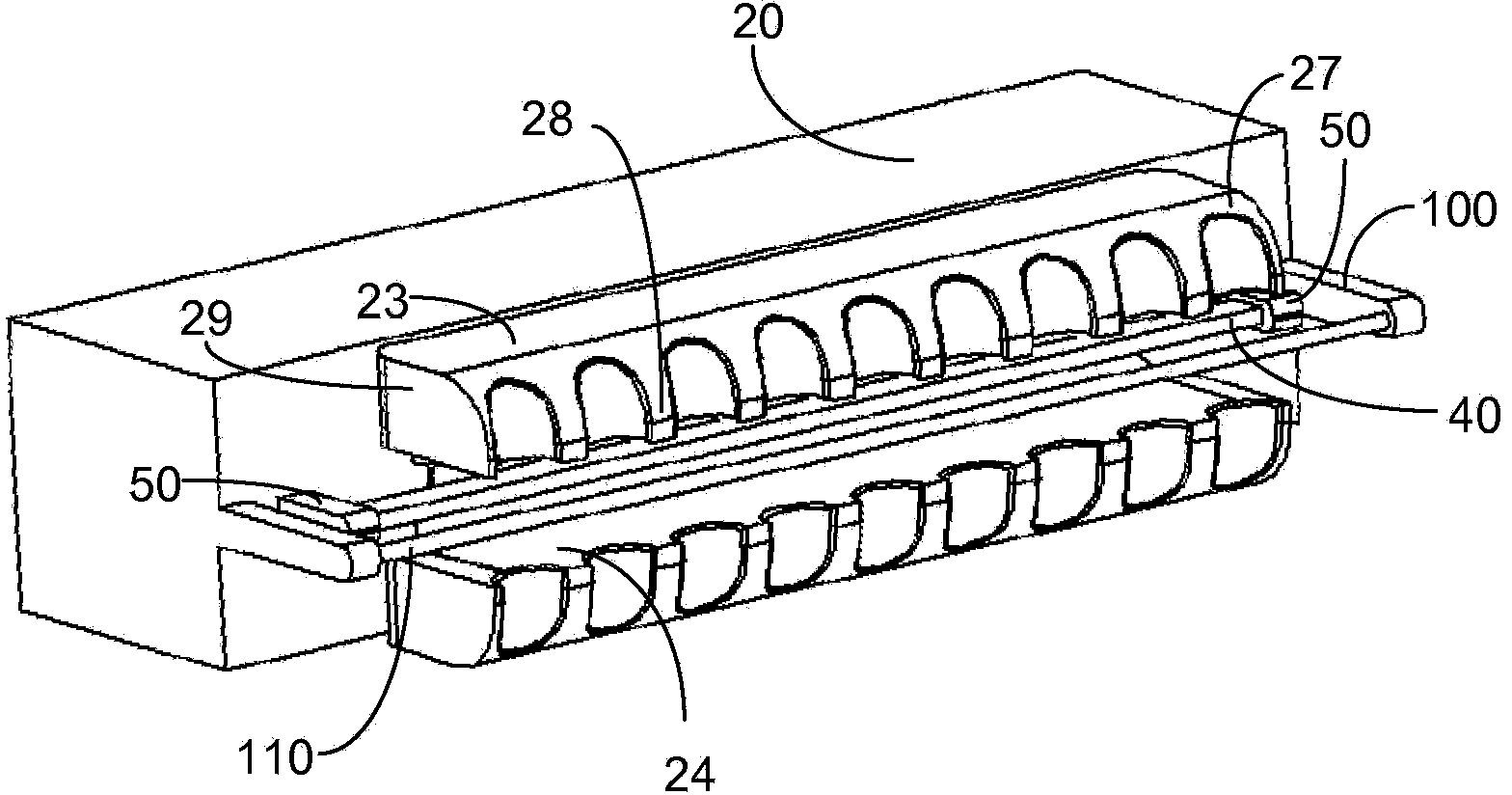
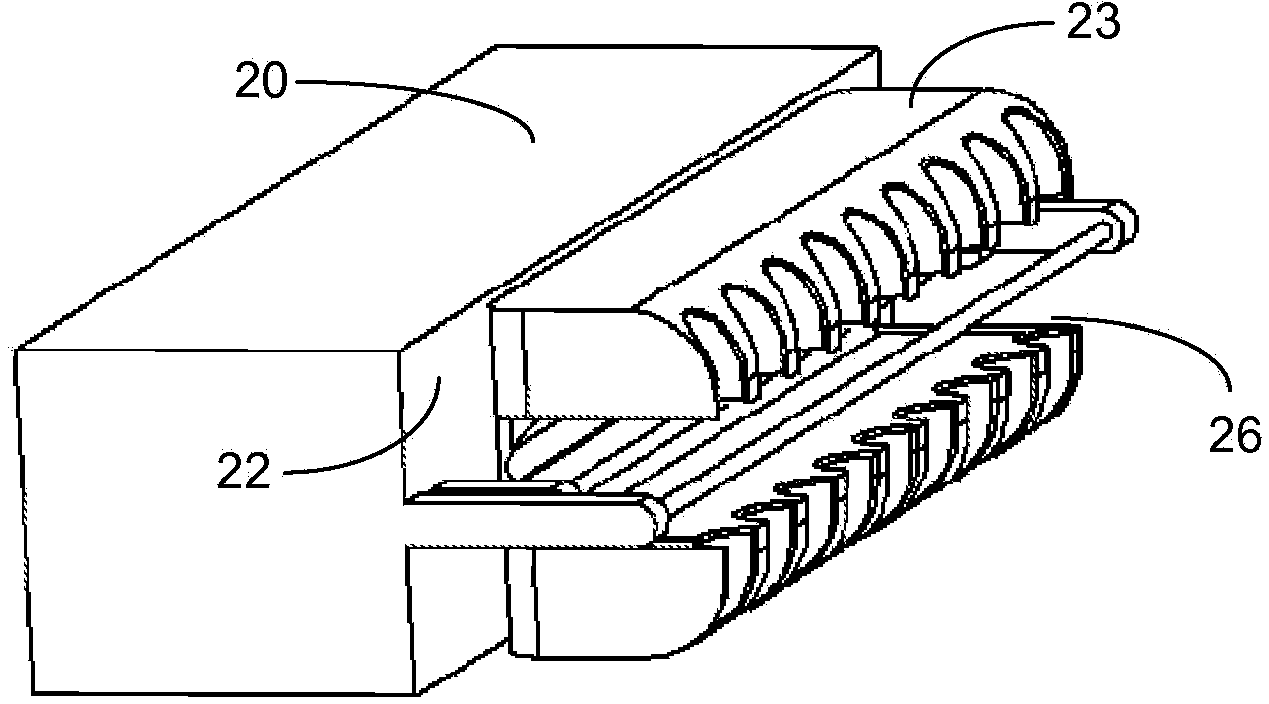
Hair removal and re-growth suppression apparatus
A hair removal and re-growth suppression apparatus (10) is constituted by: a control circuitry (70); a removal and suppression head (20); an extender assembly (23) coupled to the head (20) and extending away from a wall of the head (20) towards an end thereof, the extender assembly defining an opening (17) at an end thereof removed from the wall of the head (20); an irradiating element (40) secured to the head (20) responsive to the control circuitry (70); a reflector (90) disposed on the head (20) between the irradiating element (40) and the head (20); and a cutting element (110) secured to the head (20) and arranged to cut hair when the opening (17) is juxtaposed with a skin portion (140) having a hair (150) extending outward there from, wherein the reflector (90) is arranged to substantially reflect the out not put electromagnetic radiation toward the opening (17). Optionally, the irradiating element (40) is regularly translated between a first and a second position to heat and cut the hair without damaging the skin.
Owner:RADIANCY
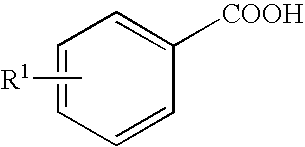
Phytotoxicity Controlling Agent for Upland Farming and Phytotoxicity Controlling Method Using the Same
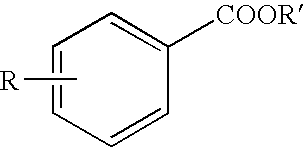
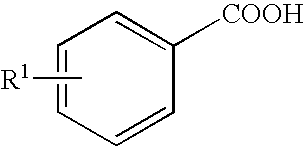
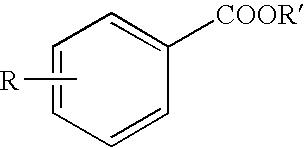
It is intended to provide a phytotoxicity controlling agent usable as a herbicide for upland farming, which exerts a sufficient herbicidal effect on weeds growing together with upland crops, for example, wheat, rye, barley, oat, corn, sorghum, cotton, soybean, adzuki bean, oilseed rape, beet, upland rice and so on but causes no phytotoxic phenomenon (for example, growth inhibition, growth suppression, tiller inhibition or yellowing) in cultivated plants, comprising a nuclear-substituted benzoic acid represented by the following general formula:wherein R1 represents linear or branched C4-15 alkyl; a salt thereof or an alkyl ester thereof.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
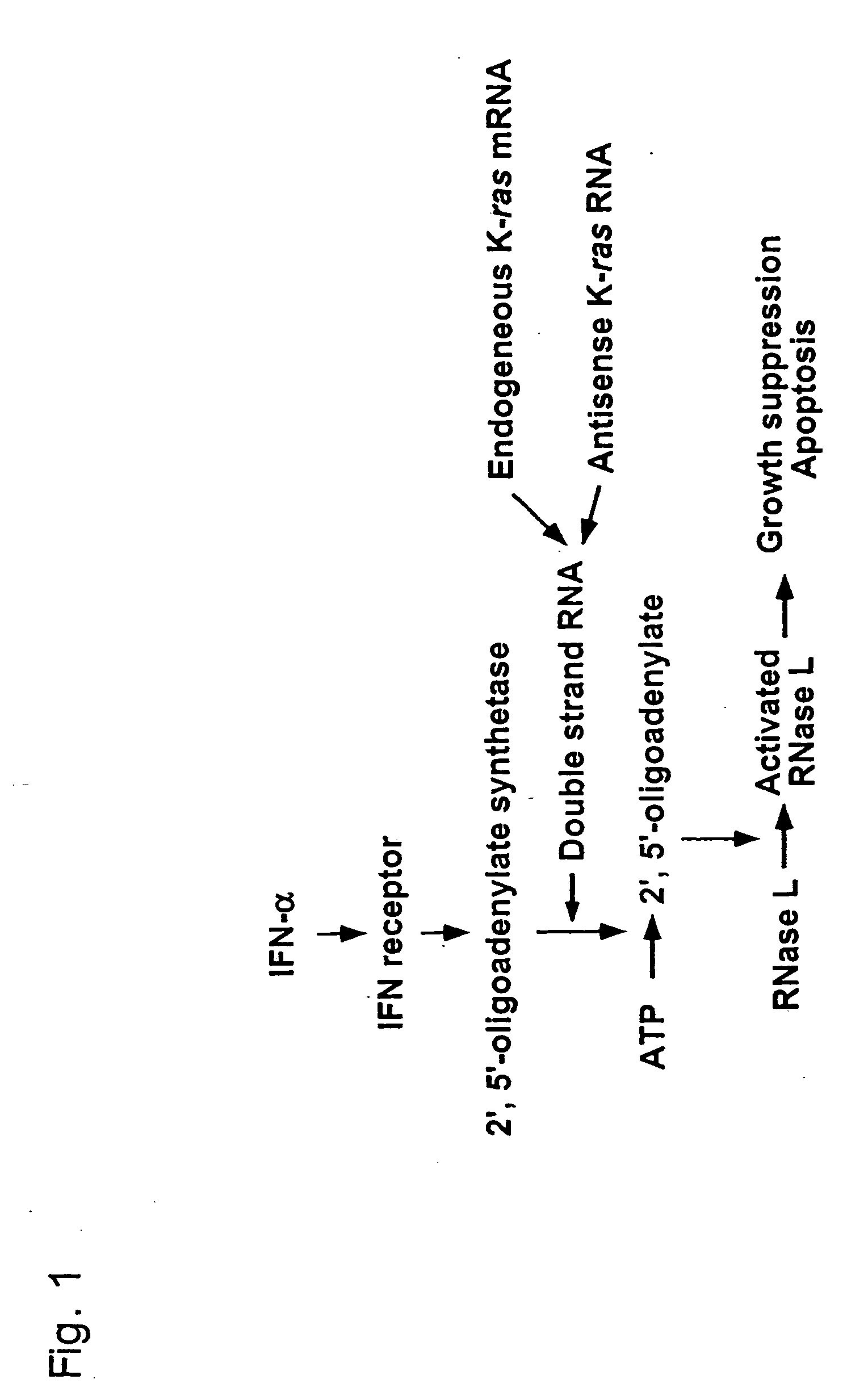
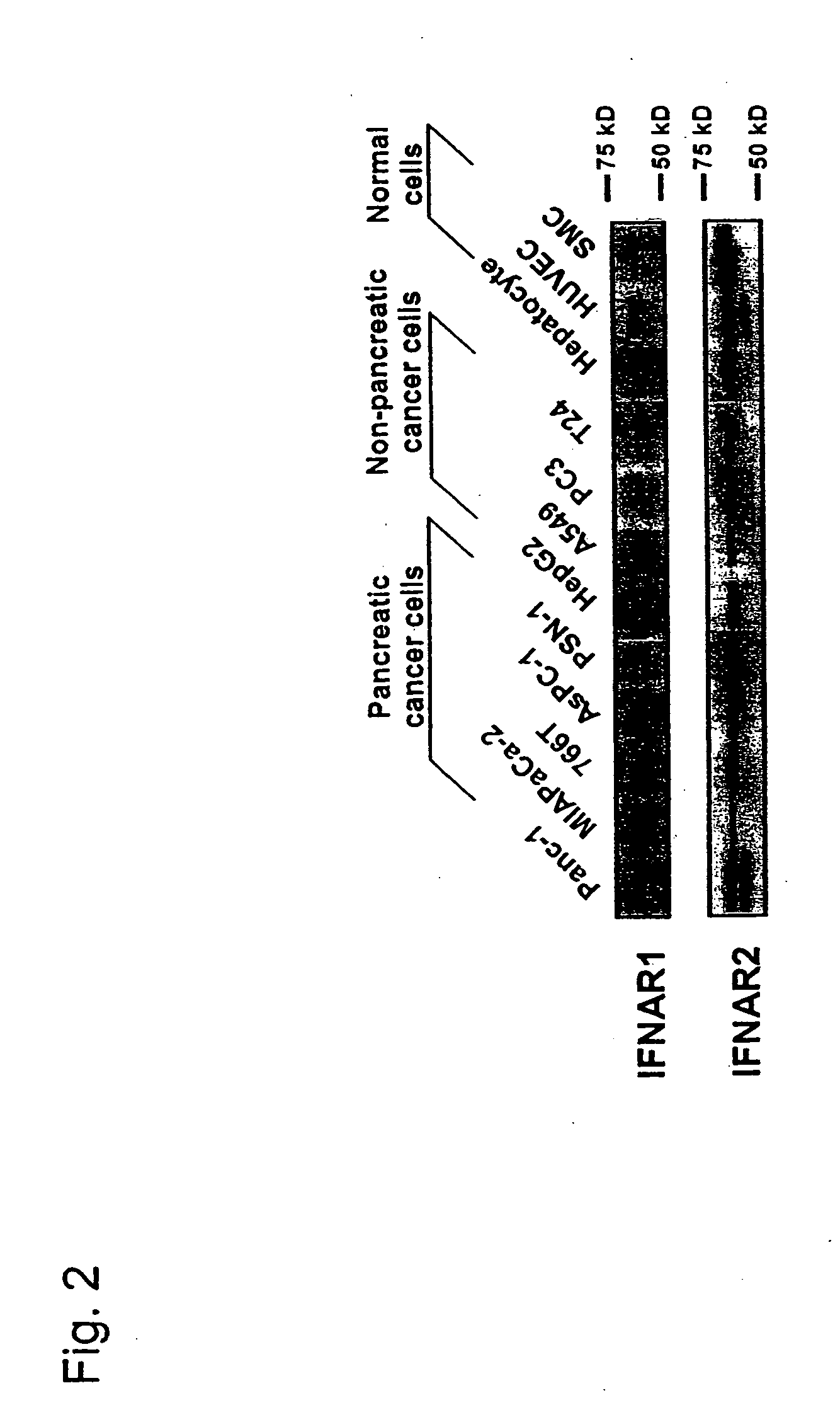
Interferon alpha and antisense K-ras RNA combination gene therapy
InactiveUS20050260167A1Increased cell deathEasy to solveBiocideSugar derivativesAbnormal tissue growthWhole body
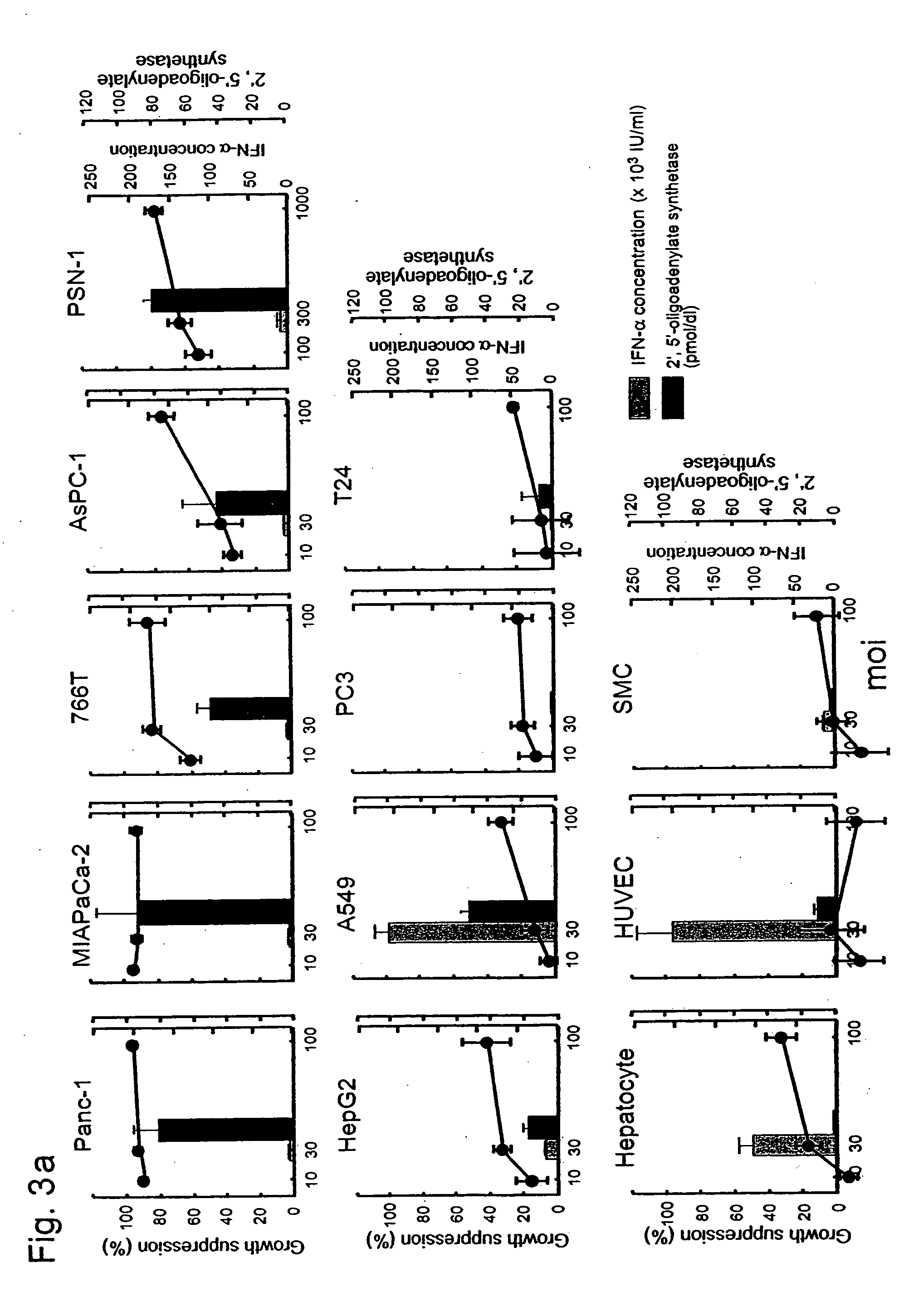
An antiproliferative effect of IFN-α gene transduction in pancreatic cancer cells. The invention relates to expression of IFN-α to effectively induce growth suppression and cell death in pancreatic cancer cells, an effect which appeared to be more prominent when compared with other types of cancers and normal cells. Another aspect of the invention relates to targeting the characteristic genetic aberration, K-ras point mutation, in pancreatic cancer, and that the expression of antisense K-ras RNA significantly suppresses the growth of pancreatic cancer cells. When these two gene therapy strategies are combined, the expression of antisense K-ras RNA significantly enhanced IFN-α-induced cell death (1.3-3.5 fold), and suppressed subcutaneous growth of pancreatic cancer cells in mice. The invention also relates to a method of suppressing pancreatic cancer cells using double strand RNA formed by antisense and endogeneous K-ras RNA in combination with the anti-tumor activity of IFN-α. The invention relates to the combination of IFN-α and antisense K-ras RNA as an effective gene therapy strategy against pancreatic cancer. The invention also relates to a method of treating pancreatic cancer cells disseminated throughout the body by administering the inventive combination to localized pancreatic cancer cell tumor. The invention also relates to inducing indirect immunological antitumor activity to provide systemic immunity against pancreatic cancer cells.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
Farm chemical composition containing thymol
InactiveCN111183991AGood killing effectStrong and effective protective barrierBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyFragaria
The invention discloses a farm chemical composition containing thymol. The effective components of the composition are thymol, carvacrol and menthol. The composition disclosed by the invention is a pure botanical natural farm chemical, has no harvesting interval when in use, and has no harm to human beings and pathogenic bacteria natural enemies; when diseases are treated, adverse reactions (suchas growth suppression, flower bud differentiation influence and the like) of plants cannot be caused; the composition has a strong killing effect on gray mold and powdery mildew of various crops, andalso has a very good treatment effect on some other crop diseases such as cowpea sooty mould, tomato leaf mold, tomato bacterial leaf spot, cucumber angular leaf spot, cucumber gummosis, watermelon shade skin disease, pepper stem rot, strawberry root rot and pineapple heart rot.
Owner:安徽金敦福农业科技有限公司
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050133925A1Improve coupling strengthHigh mechanical strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInter layerDevice material
Owner:SONY CORP
Heat treatment jig for silicon semiconductor substrate
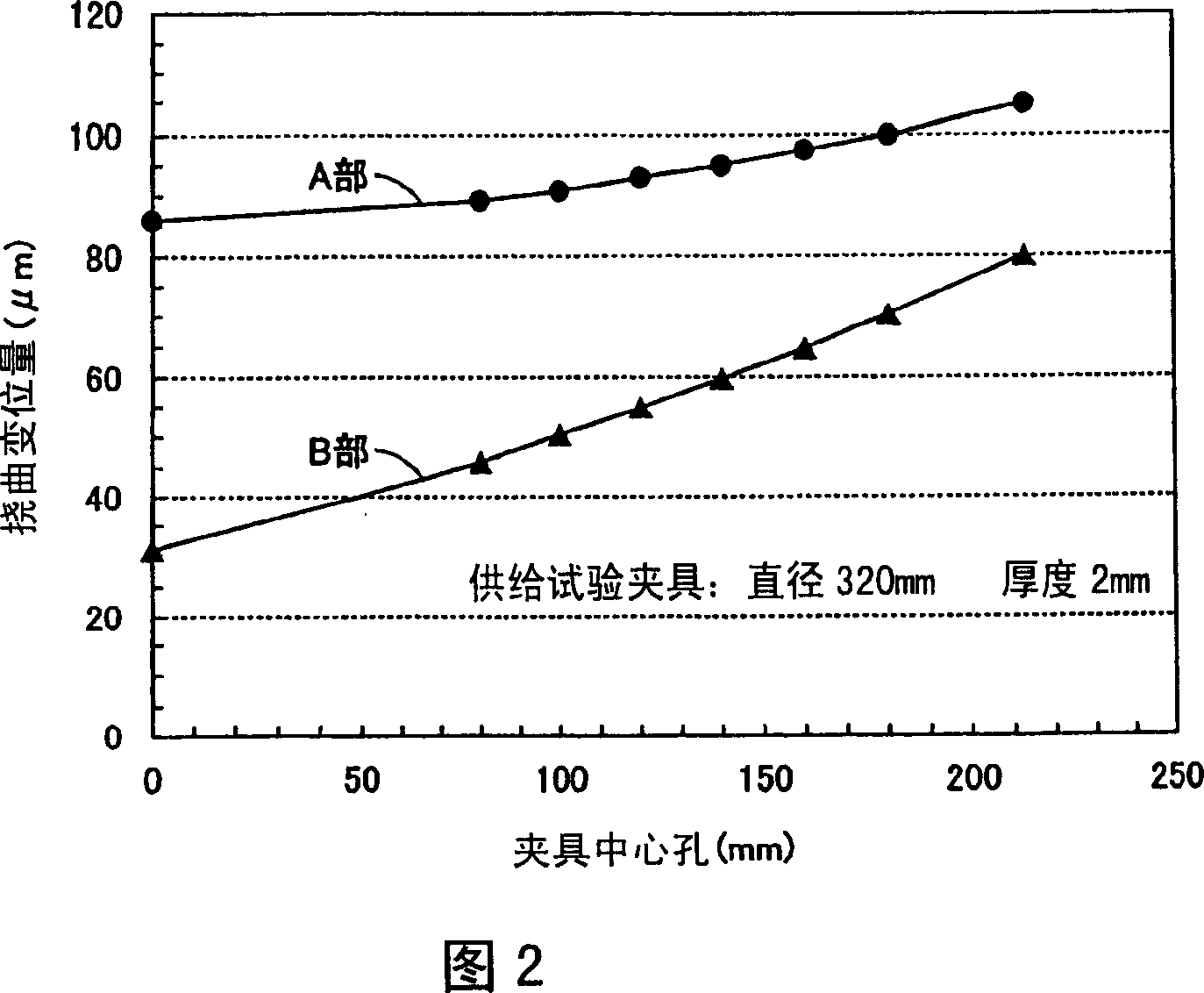
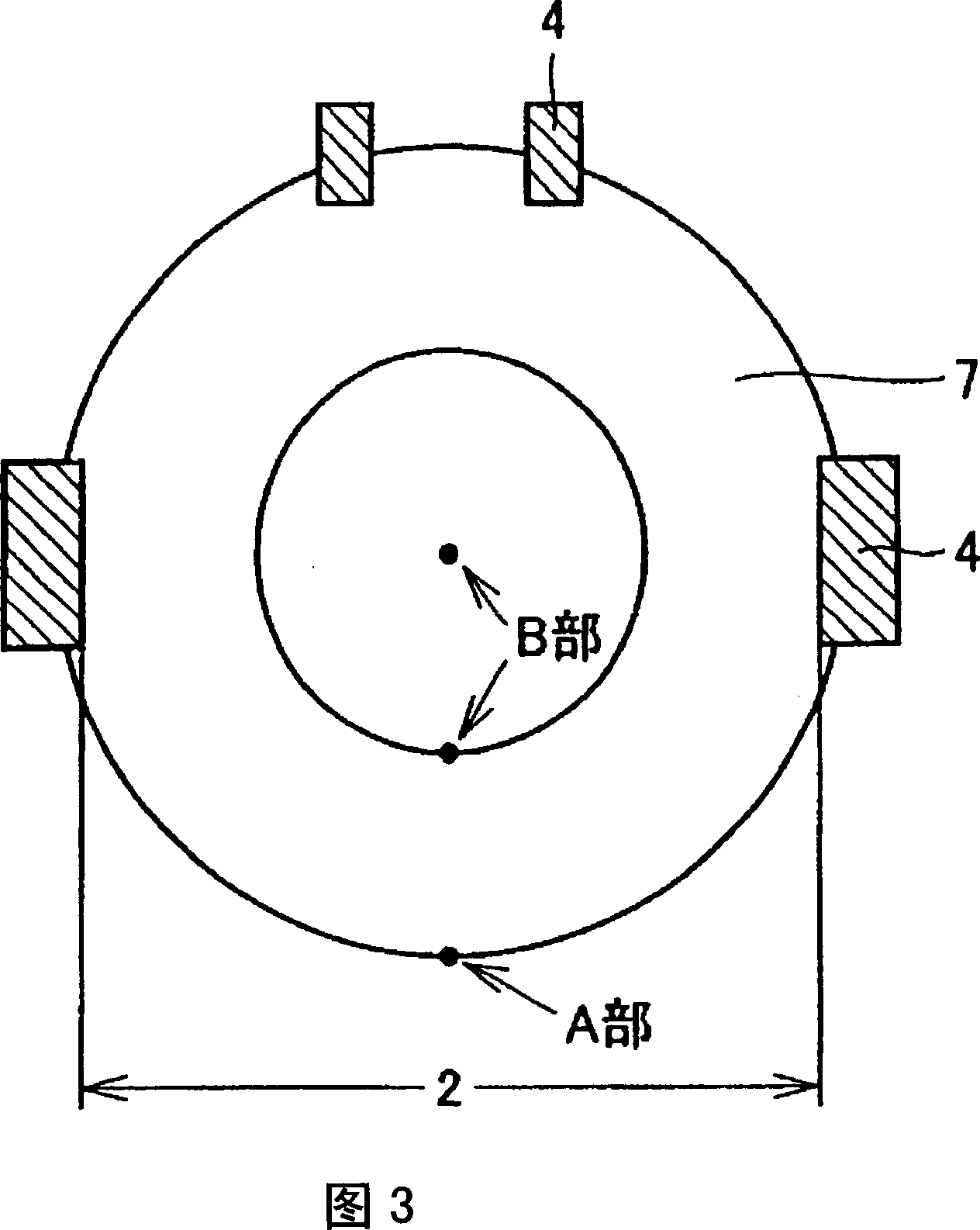
ActiveCN1969376AAvoid growth inhibitionReduce smooth cracksCharge supportsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessSilicon
A heat treatment jig for a semiconductor silicon substrate making contact with a semiconductor silicon substrate to hold the substrate is to be mounted on a heat treatment boat in a vertical heat treatment furnace. The jig has a ring structure or a disc structure, with a thickness of 1.5mm or more but not more than 6.0mm and a flexure displacement quantity of 100mum or less in an area making contact with the semiconductor silicon substrate when mounted on the heat treatment boat. An outer diameter of the jig making contact with the semiconductor silicon substrate to hold the substrate is 65% or more of a diameter of the semiconductor silicon substrate, a surface roughness (Ra value) of a plane making contact with the semiconductor silicon substrate is 1.0mum or more but not more than 100mum. The heat treatment jig effectively reduces slipping, and at the same time, prevents growth suppression of a thermally oxidized film on a substrate rear plane, and eliminates a front plane step, which causes defocusing in a photolithography process in device manufacture. Thus, a high quality of the semiconductor silicon substrate can be maintained and device yield can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
Perfusion medium
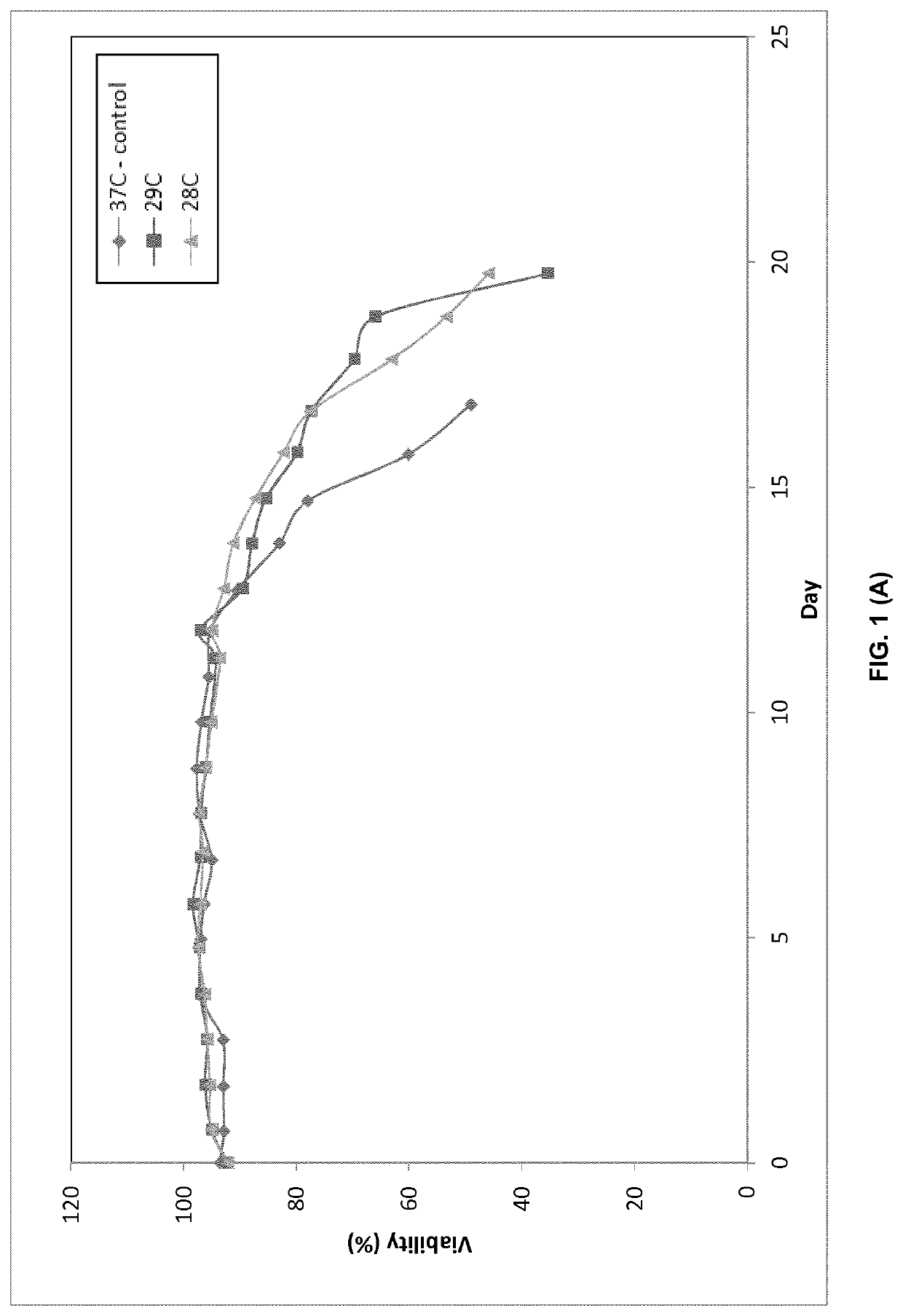
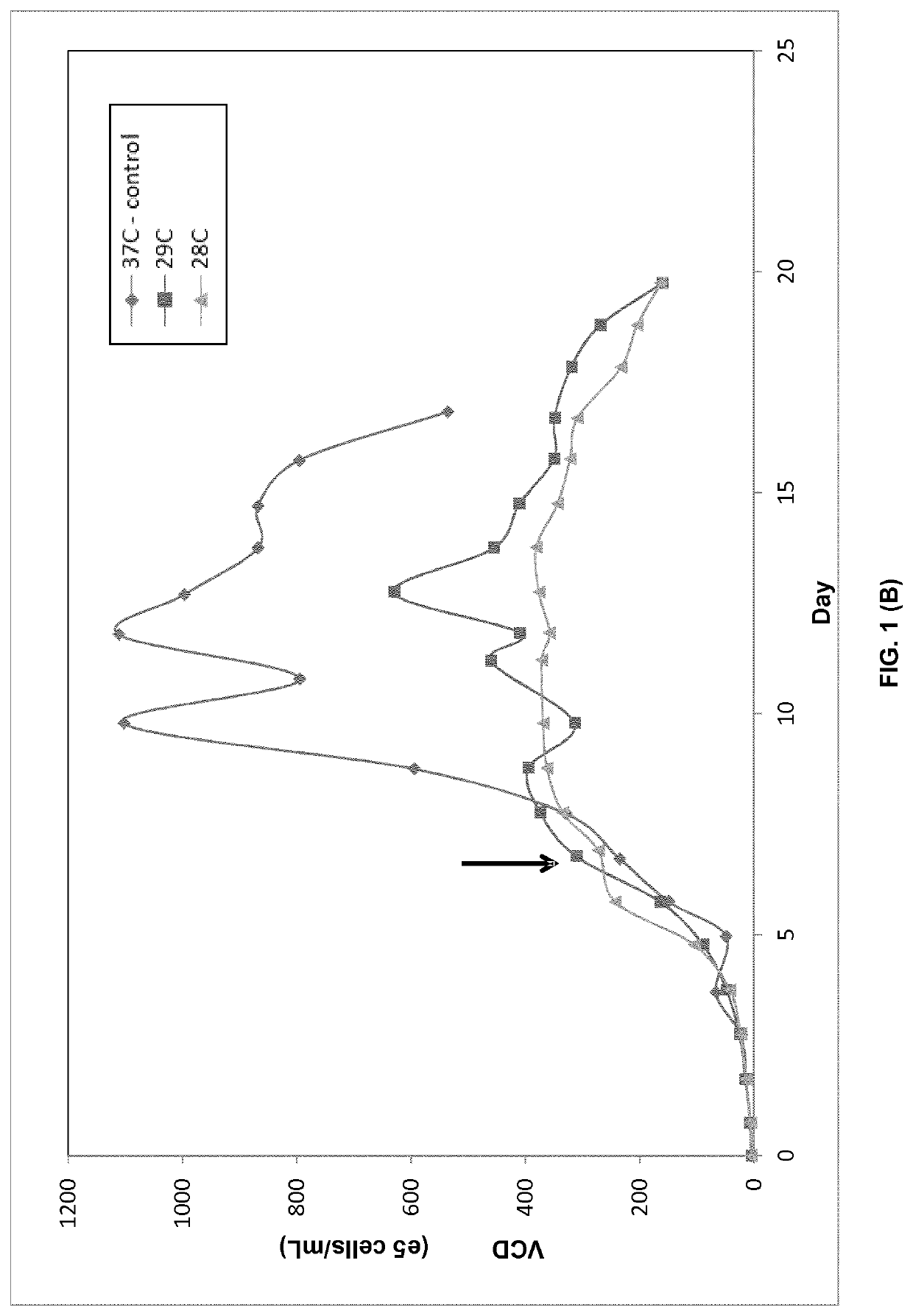
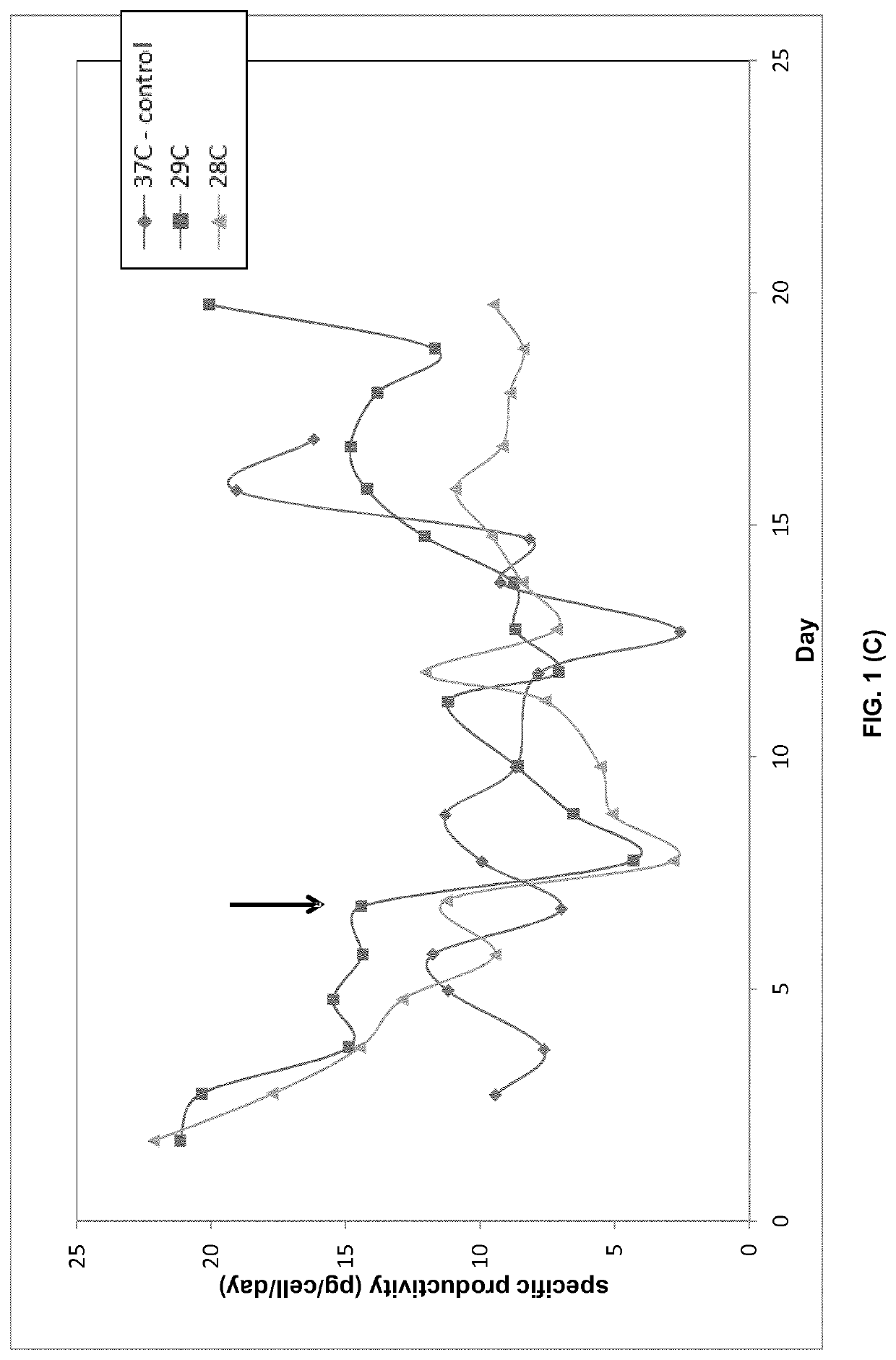
ActiveCN111201315ARaise specific productivityCulture processCell culture mediaPerfusion CultureHeterologous
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
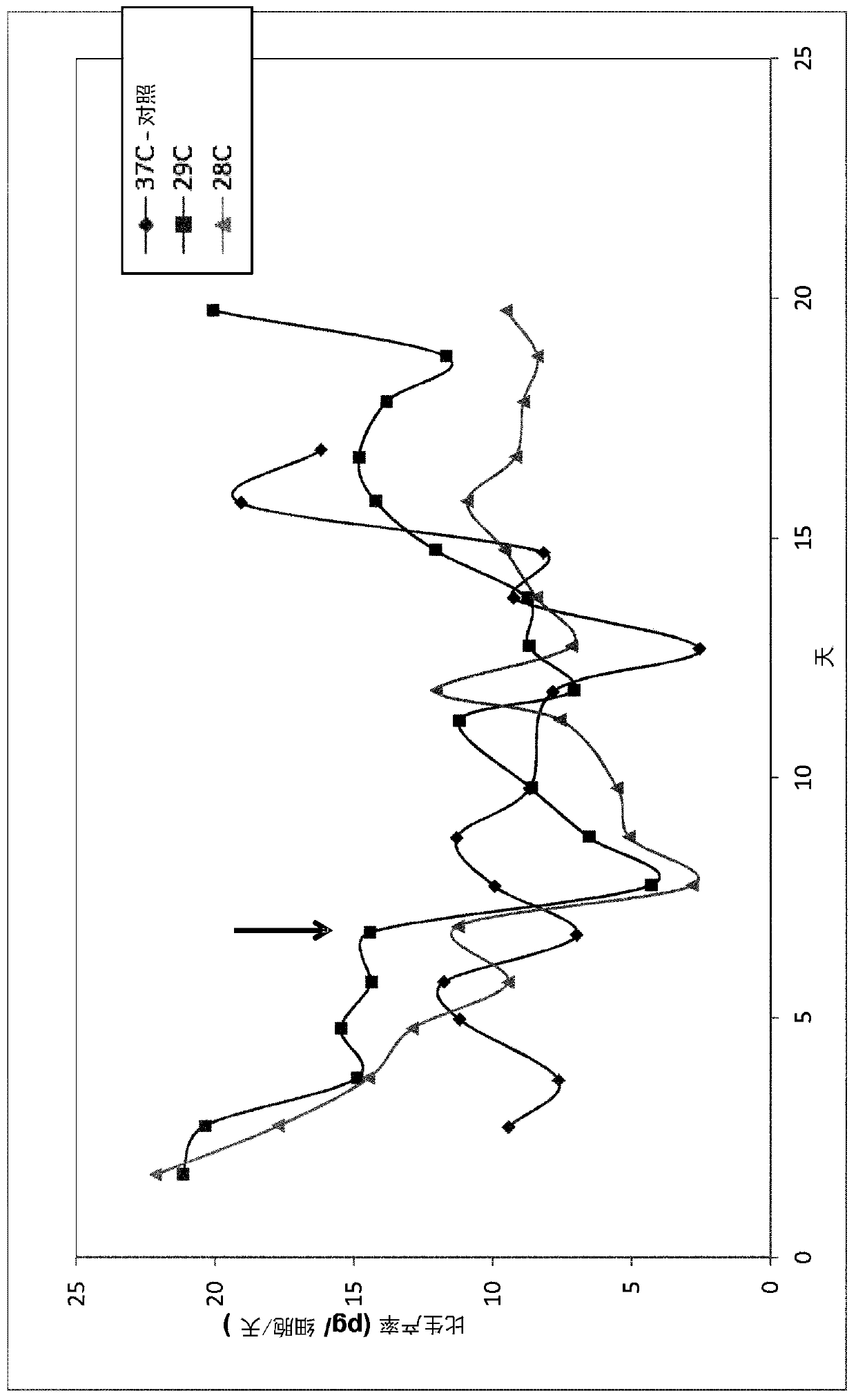
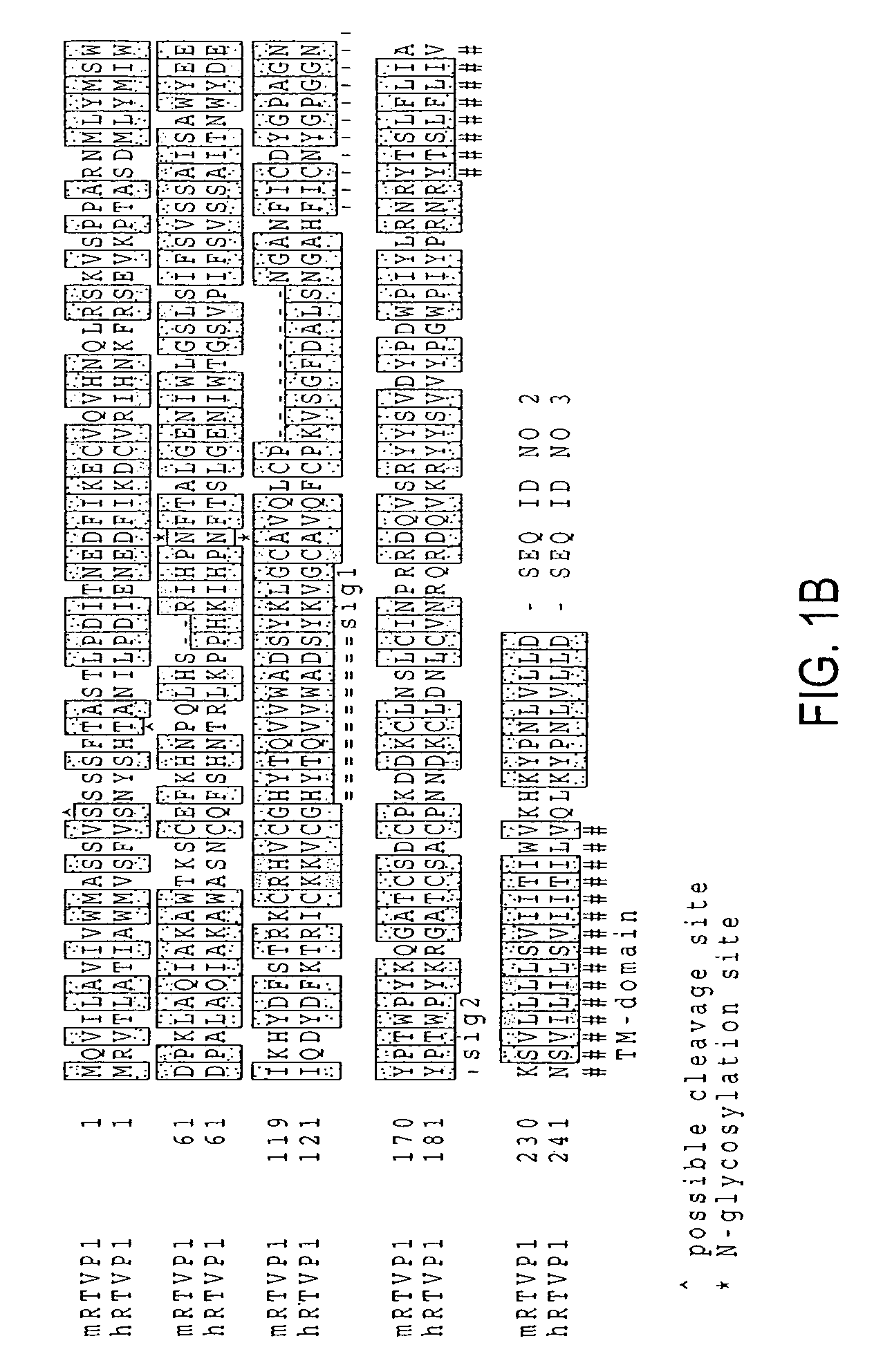
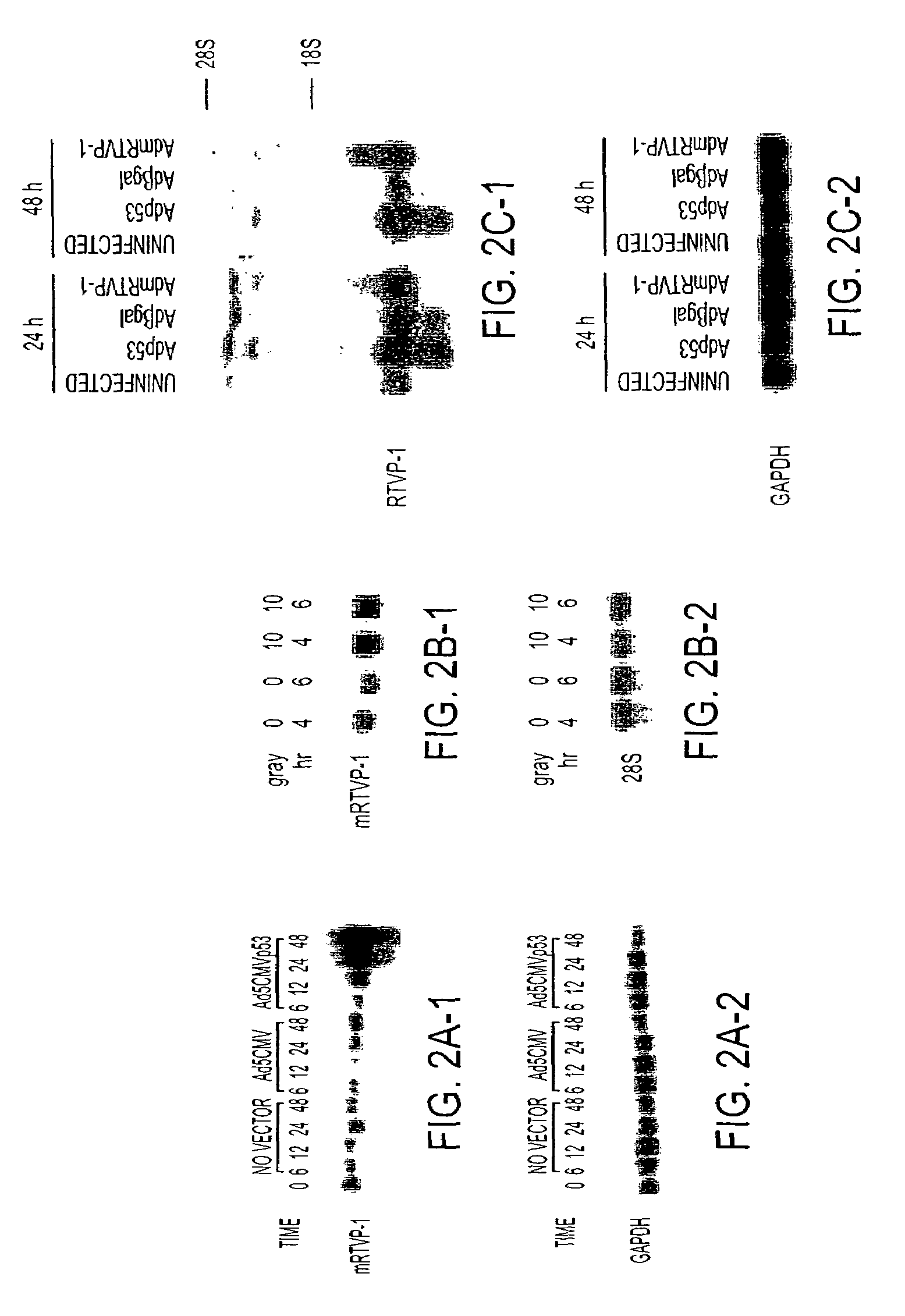
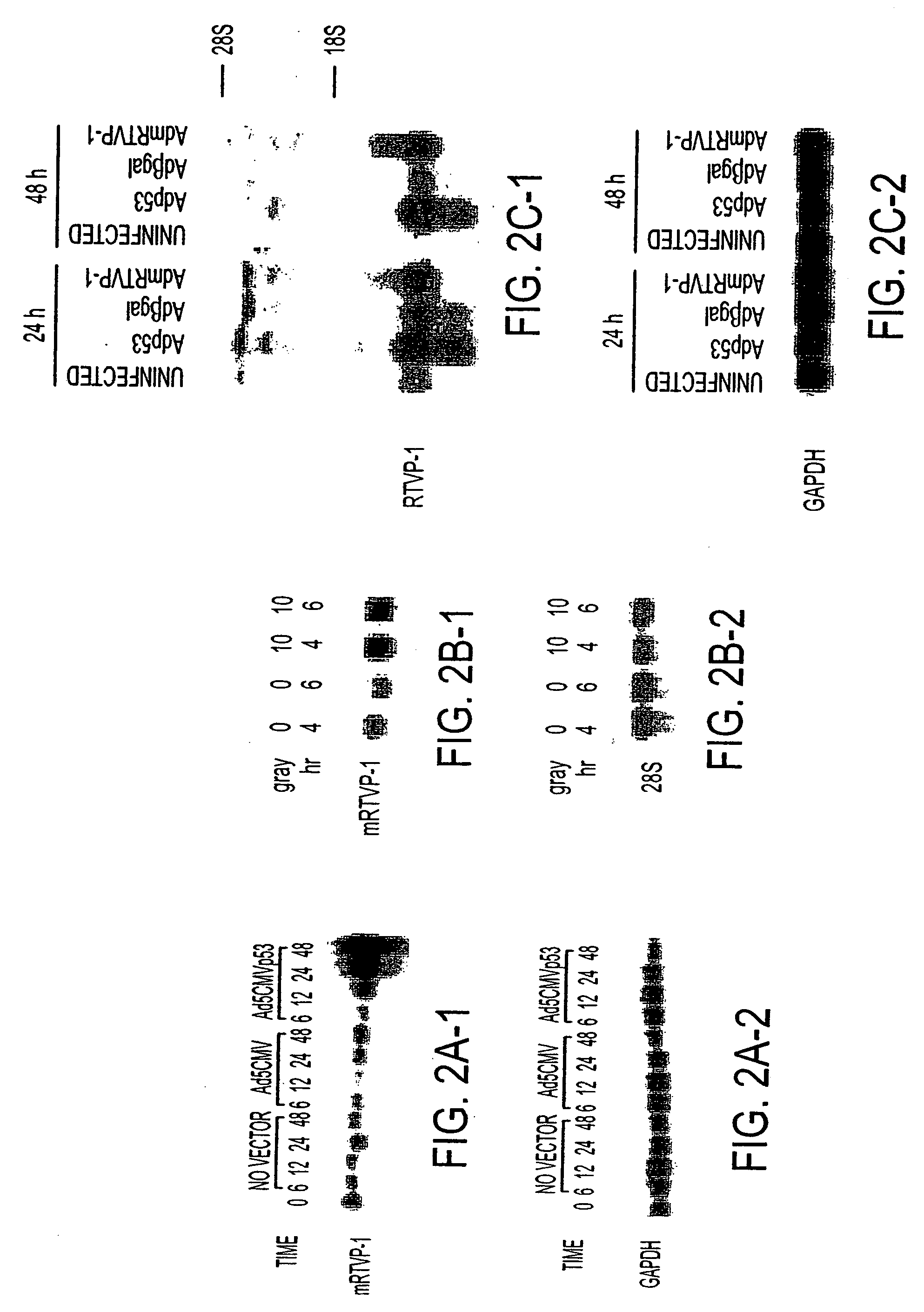
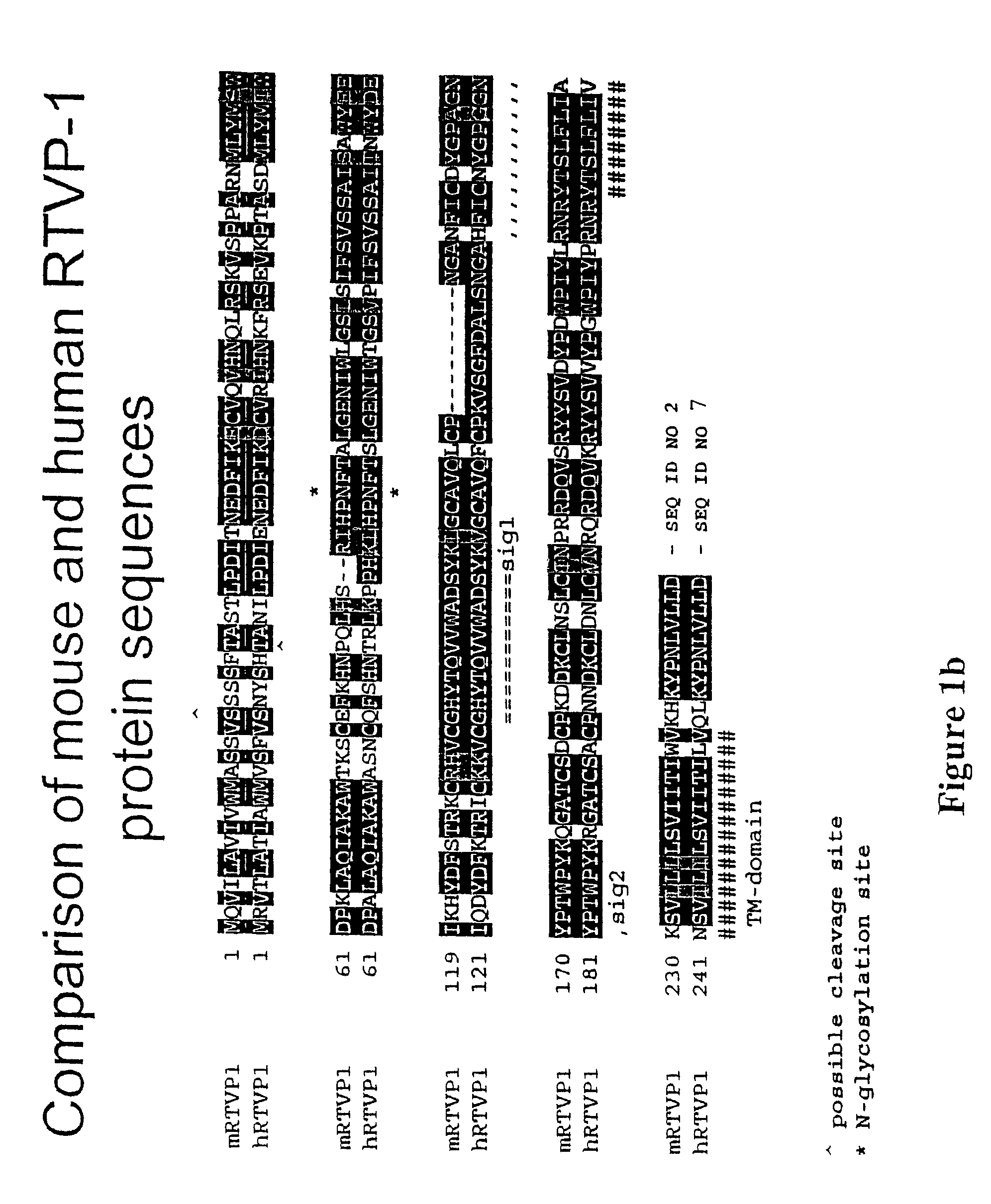
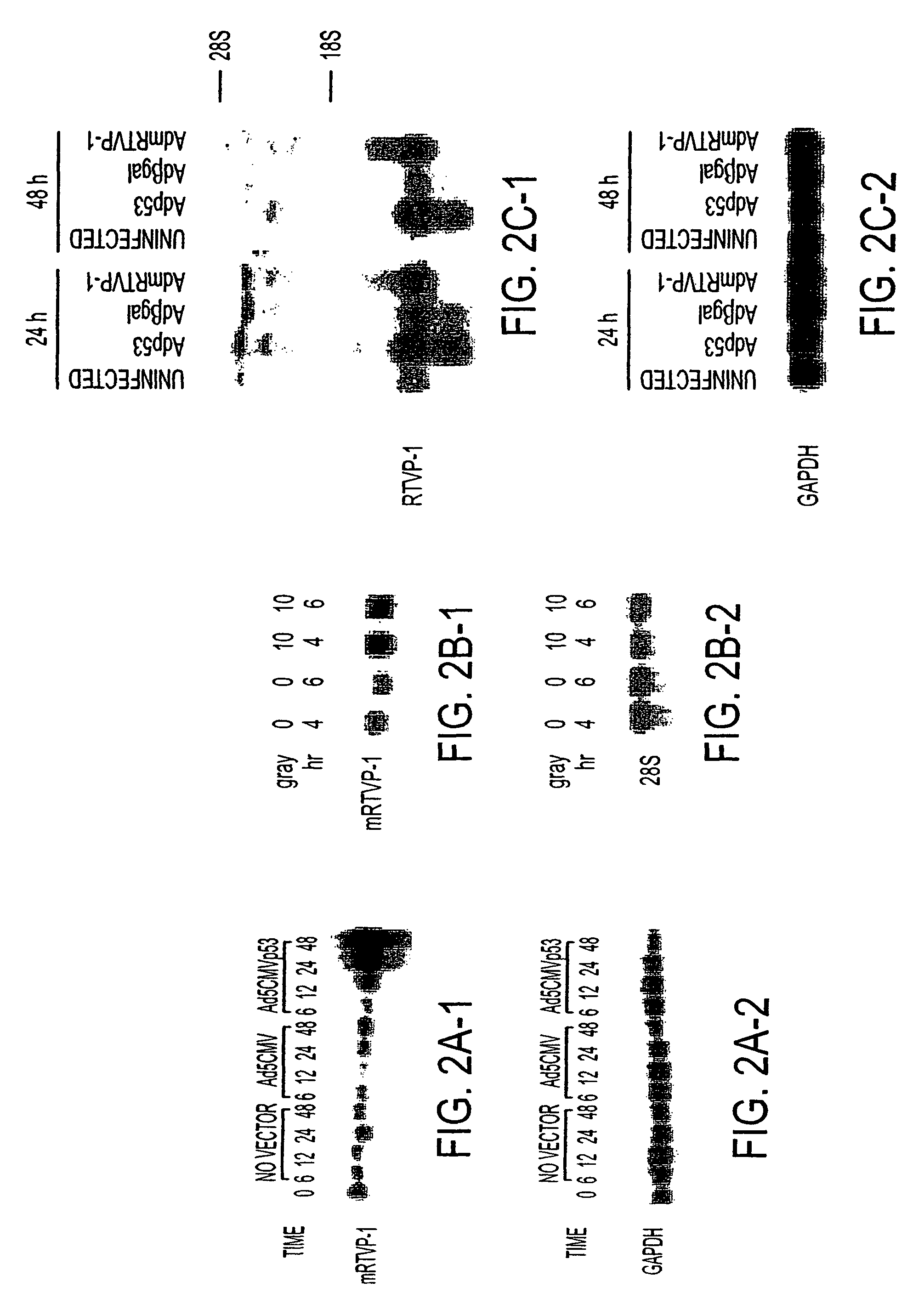
RTVP based compositions and methods for the treatment of prostate cancer
InactiveUS7645452B2Reducing and shutting down RTVP expressionHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseLymphatic Spread
This invention relates to a gene encoding RTVP that has been shown to be up-regulated by p53 using differential display-PCR and subsequently by co-transfection studies. RTVP-1 mRNA is abundant in normal mouse and human prostatic epithelial cells and primary tumors, but is significantly down regulated in metastatic mouse and human prostate cancer. In prostate cancer cells overexpression of the mouse RTVP-1 gene (mRTVP-1) induced apoptosis that was accompanied by increased caspase 8, 9 and 3 activities. mRTVP-1-stimulated apoptosis was also associated with increased levels of bax, bad and activated BID; reduced levels of bcl-2 and bcl-XL; and cytosolic cytochrome c accumulation. Adenoviral-vector-mediated mRTVP-1 expression lead to potent growth suppression and antimetastatic activities in an orthotopic mouse model of prostate cancer in vivo. These therapeutic activities were associated with anti-angiogenic effects and importantly a local and systemic immune response. Accordingly, p53 was linked with suppression of metastasis through its induction of mRTVP-1, which can concurrently induce apoptosis, suppress angiogenesis and stimulate an antitumor immune response. Thus, the invention includes compositions and methods, based on RTVP nucleic acid, polypeptides, and antibodies, for use in the treatment, prevention and detection of neoplastic disease and, specifically, metastatic prostatic neoplasia.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
RTVP based compositions and methods for the treatment of prostate cancer
InactiveUS20060057602A1Reducing and shutting down RTVP expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationDiseaseLymphatic Spread
This invention relates to a gene encoding RTVP that has been shown to be up-regulated by p53 using differential display-PCR and subsequently by co-transfection studies. RTVP-1 mRNA is abundant in normal mouse and human prostatic epithelial cells and primary tumors, but is significantly down regulated in metastatic mouse and human prostate cancer. In prostate cancer cells overexpression of the mouse RTVP-1 gene (mRTVP-1) induced apoptosis that was accompanied by increased caspase 8, 9 and 3 activities. mRTVP-1-stimulated apoptosis was also associated with increased levels of bax, bad and activated BID; reduced levels of bcl-2 and bcl-XL; and cytosolic cytochrome c accumulation. Adenoviral-vector-mediated mRTVP-1 expression lead to potent growth suppression and antimetastatic activities in an orthotopic mouse model of prostate cancer in vivo. These therapeutic activities were associated with anti-angiogenic effects and importantly a local and systemic immune response. Accordingly, p53 was linked with suppression of metastasis through its induction of mRTVP-1, which can concurrently induce apoptosis, suppress angiogenesis and stimulate an antitumor immune response. Thus, the invention includes compositions and methods, based on RTVP nucleic acid, polypeptides, and antibodies, for use in the treatment, prevention and detection of neoplastic disease and, specifically, metastatic prostatic neoplasia.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Formulations and methods for control of weedy species
A formulation is provided for application to a host plant to reduce, inhibit or impair one or more of growth and development of the host plant. A method of inhibiting growth plant growth and development is also provided as a means of controlling weedy species. The method comprises: selecting a suitable gene for growth suppression in a target plant; identifying an at least one target site accessible to base pairing in the suitable gene; identifying an at least one divergent site in the at least one target site; designing a construct complementary to the at least one divergent site; adding an at least one RNAi inducer to the construct; and delivering the construct to the target plant.
Owner:TERRAMERA INC
Down-regulation of DNA repair to enhance sensitivity to p53-mediated suppression
InactiveUS20050095226A1Limiting effectEasy to operateHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideGlioblastomaCancer cell apoptosis
The present invention details methods for the treatment of cancer. In particular, it concerns the induction of apoptosis in cancer cells following treatment with inhibitors of DNA repair in combination with p53 gene therapy. Treatment of glioblastoma and breast tumor cells with inhibitors of DNA repair induced growth suppression that was a result of p53-mediated apoptosis. Thus it appears that inhibitors of DNA repair in combination with p53 gene therapy is involved in restoration of p53-mediated apoptosis.
Owner:GJERSET RUTH
Anticorrosion composition based on mild effect for cosmetics and preparation method of cosmetics
ActiveCN108514539AImprove anti-corrosion performanceGood antibacterial effectGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsCosmetic preparationsAntibacterial activityGrowth suppression
The invention discloses an anticorrosion composition based on a mild effect for cosmetics and a preparation method of the cosmetics. The anticorrosion composition contains the following components inpercentage by weight: 5%-10% of plant extract, 40%-50% of an anticorrosion enhancer and the balance of a pterostilbene derivative, wherein the plant extracts are an aloe extract, a polygonum cuspidatum extract, a grape skin extract and a peanut shell extract. The anticorrosion composition prepared by virtue of the preparation method is mild and non-irritant, does not contain any forbidden and restricted preservative component and formaldehyde release body, can completely support a ''preservative free'' compound system and is high in safety; and the prepared cosmetics has remarkable effects onthe growth suppression of bacteria and mold, has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and strong anticorrosion property, is mild and can be used for a long time.
Owner:广州市腾宇化妆品有限公司
Perfusion medium
PendingUS20200332251A1Increases cell specific productivityImprove productivityCulture processCell culture mediaPerfusion CultureHeterologous
The present disclosure provides a method of culturing mammalian cells, e.g., by perfusion cell culture, expressing a heterologous protein in a cell culture, comprising culturing mammalian cells expressing a heterologous protein in a culture medium comprising an effective amount of one or more lipids or lipid metabolites selected from the group consisting of: linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and prostaglandin E2, or derivatives and / or precursors thereof. The lipids or lipid metabolites or combinations thereof can lead to growth suppression and / or increased productivity with reduced cell bleed. The present disclosure also provides methods for increasing the productivity of a cell culture by culturing the cells in a culture medium comprising an effective amount of one or more lipids or lipid metabolites selected from the group consisting of: linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and prostaglandin E2, or derivatives and / or precursors thereof. The present disclosure also provides culture medium for use in producing therapeutic proteins with increased productivity, wherein the medium comprises one or more lipids or lipid metabolites selected from the group consisting of: linoleic acid, arachidonic acid, and prostaglandin E2, or derivatives and / or precursors thereof.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Phytotoxicity controlling agent for upland farming and phytotoxicity controlling method using the same
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Compositions and methods for treating cancer by modulating HER-2 and EGF receptors
An alternative HER-2 / neu product, herstatin, consists of subdomains I and II from the ectodomain of p185HER-2 and a unique 79 amino acid C-terminus encoded by intron 8. Recombinant herstatin added to cells was found to bind to and inhibit p185HER-2. The effects of ectopic expression of herstatin in combination with either p185HER-2 or with its homolog, the EGF receptor, in several cell lines was studied. Cotransfection of herstatin with HER-2 inhibited p185HER-2 levels and caused an approximate 8-fold reduction in p185 tyrosine phosphorylation. Inhibition of p185HER-2 tyrosine phosphorylation corresponded to a dramatic decline in colony formation by cells that coexpressed p185HER-2 and herstatin. Herstatin also interferred with EGF activation of the EGF receptor in cotransfected cells as demonstrated by impaired receptor tyrosine phosphorylation, reduced receptor down-regulation, and growth suppression. For both p185HER-2 and the EGF receptor, the extent of inhibition was affected by the expression levels of herstatin relative to the receptor. Herstatin is an autoinhibitor of p185HER-2 and expands its inhibitory activity to another member of the group I family of receptor tyrosine kinases, the EGF receptor. Herstatin blocked the activated Akt-mediated EGF survival signal, as well as transforming growth factor alpha (TGFα)-mediated EGF receptor activation, survival signal and proliferation signal. Purified recombinant herstatin specifically inhibited human carcinoma cells that over-express HER-2, and was effectively absorbed into the blood of intraperitoneally injected mice, where it was not proteolytically degraded and was present for between one and three hours.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Preparation method of plant growth promoting and weeding mixture
InactiveCN109548783AEfficient killingPromote growthBiocideAnimal repellantsGrowth plantMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a plant growth promoting and weeding mixture. The plant growth promoting and weeding mixture is obtained by mixing a microbial agent, a herbicide and water in a ratio of 1: 1: 80, the plant growth promoting and weeding mixture is used for weeding, the soil is improved, and the soil fertility is enhanced. Compared with the prior art, the plant growthpromoting and weeding mixture has the following effects that weeds can be killed, and meanwhile, the damage of the herbicide to crops is avoided, the growth suppression of the herbicide on the crops is eliminated, the fertilizer efficiency can be increased, and the soil is improved, so that the yield of the crops can be increased, and the quality of the crops can be improved.
Owner:上海康地源生物科技有限公司
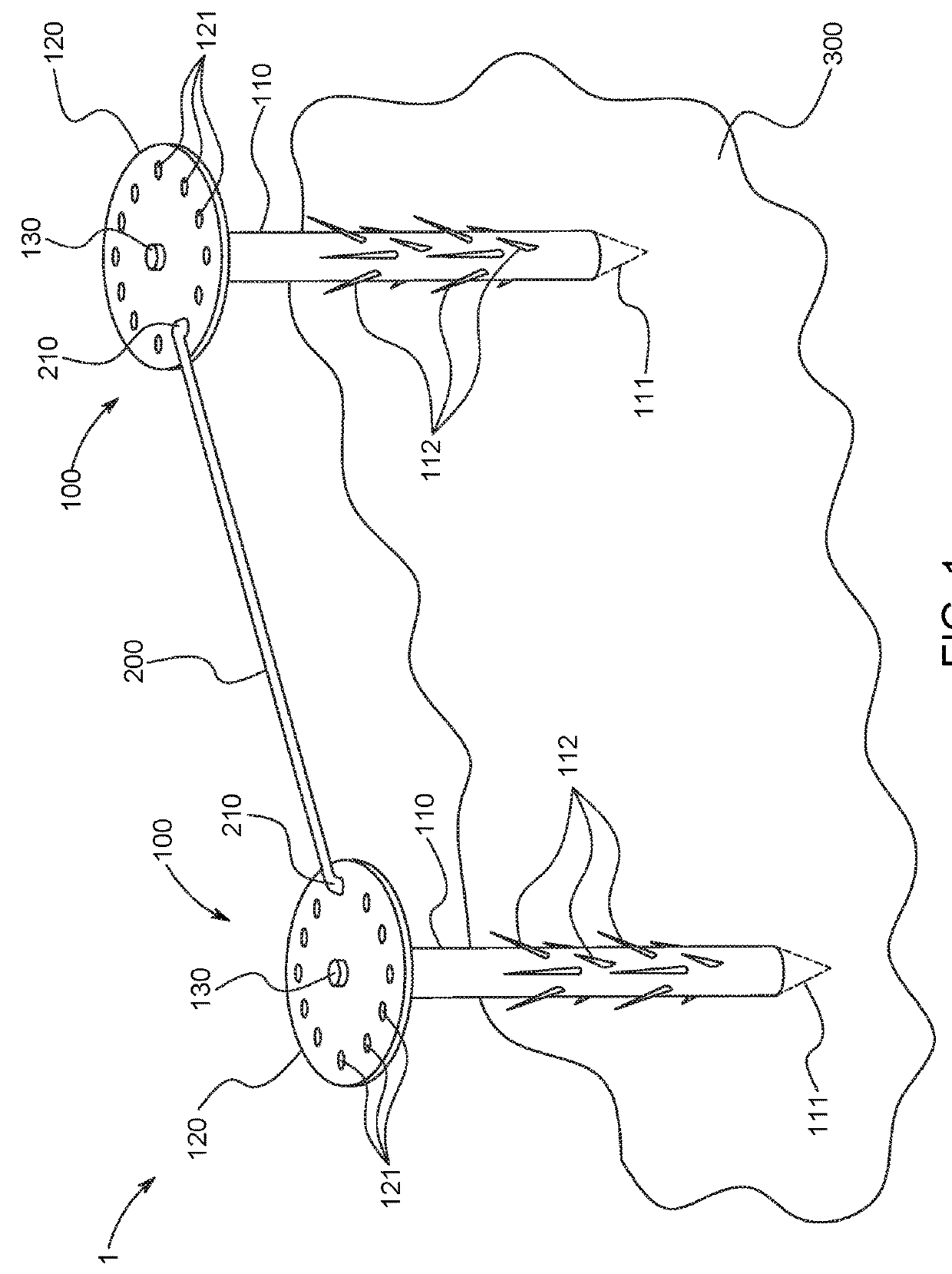
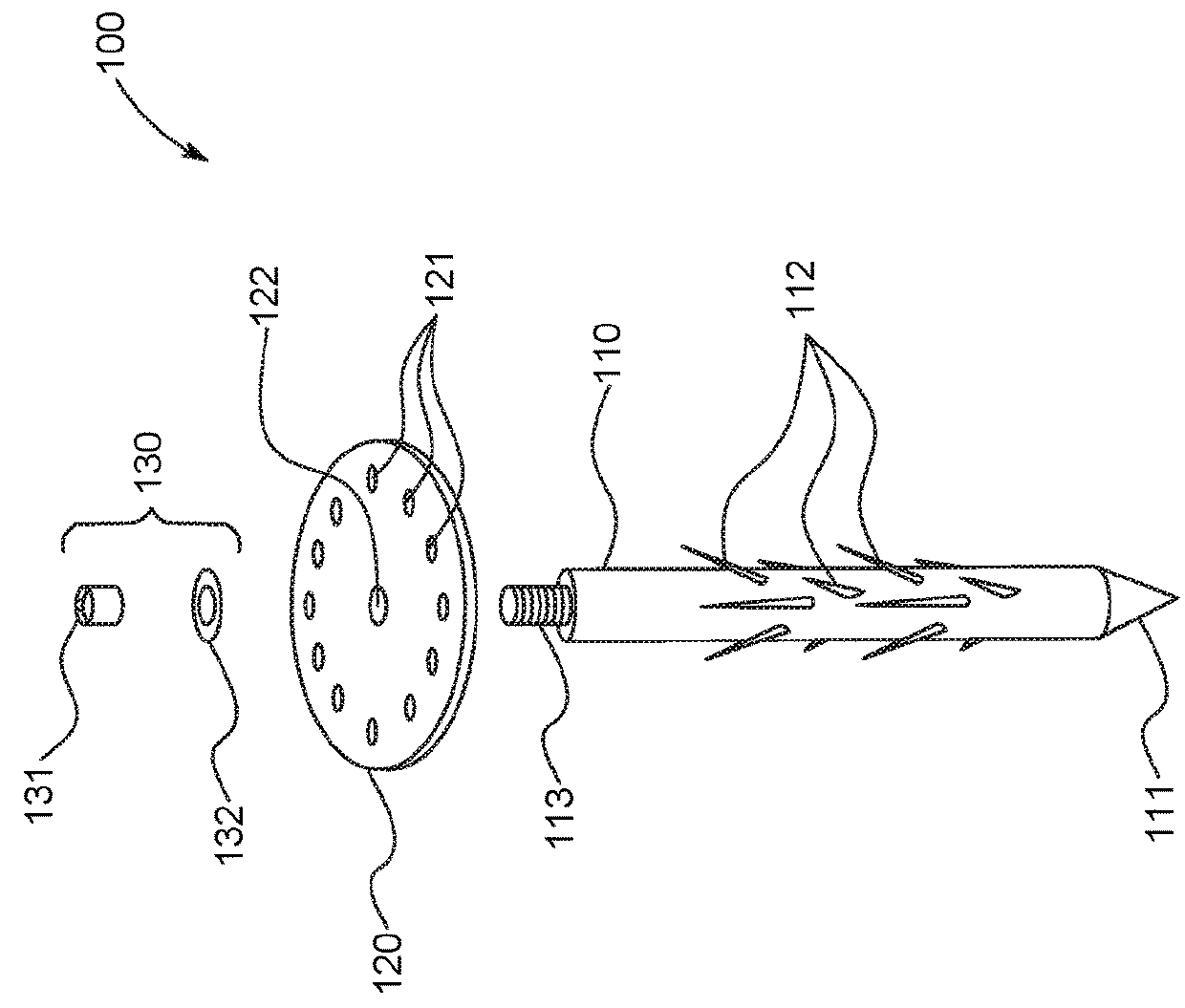
Weed growth suppression device
A weed growth suppression device, including a first spike assembly to be inserted at least partially into a surface, a second spike assembly to be inserted at least partially into the surface, and a rod to connect the first spike assembly to the second spike assembly.
Owner:SCHALLER SANDY
RTVP based compositions and methods for the treatment of prostate cancer
InactiveUS7824685B2Reducing and shutting down RTVP expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseLymphatic Spread
This invention relates to a gene encoding RTVP that has been shown to be up-regulated by p53 using differential display-PCR and subsequently by co-transfection studies. RTVP-1 mRNA is abundant in normal mouse and human prostatic epithelial cells and primary tumors, but is significantly down regulated in metastatic mouse and human prostate cancer. In prostate cancer cells overexpression of the mouse RTVP-1 gene (mRTVP-1) induced apoptosis that was accompanied by increased caspase 8, 9 and 3 activities. mRTVP-1-stimulated apoptosis was also associated with increased levels of bax, bad and activated BID; reduced levels of bcl-2 and bcl-XL; and cytosolic cytochrome c accumulation. Adenoviral-vector-mediated mRTVP-1 expression lead to potent growth suppression and antimetastatic activities in an orthotopic mouse model of prostate cancer in vivo. These therapeutic activities were associated with anti-angiogenic effects and importantly a local and systemic immune response. Accordingly, p53 was linked with suppression of metastasis through its induction of mRTVP-1, which can concurrently induce apoptosis, suppress angiogenesis and stimulate an antitumor immune response. Thus, the invention includes compositions and methods, based on RTVP nucleic acid, polypeptides, and antibodies, for use in the treatment, prevention and detection of neoplastic disease and, specifically, metastatic prostatic neoplasia.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Methods, apparatus and system for providing source-drain epitaxy layer with lateral over-growth suppression
At least one method, apparatus and system disclosed herein for suppressing over-growth of epitaxial layer formed on fins of fin field effect transistor (finFET) to prevent shorts between fins of separate finFET devices. A set of fins of a first transistor is formed. The set of fins comprises a first outer fin, an inner fin, and a second outer fin. An oxide deposition process is performed for depositing an oxide material upon the set of fins. A first recess process is performed for removing a portion of oxide material. This leaves a portion of the oxide material remaining on the inside walls of the first and second outer fins. A spacer nitride deposition process is performed. A spacer nitride removal process is performed, leaving spacer nitride material at the outer walls of the first and second outer fins. A second recess process is performed for removing the oxide material from the inside walls of the first and second outer fins. An epitaxial layer deposition processed upon the set of fins. A portion of the lateral over-growth of epitaxial layer on the outer walls of the first and second outer fins is suppressed by the spacer nitride material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com