Method of manufacturing fatty acid ethyl esters from triglycerides and alcohols
a technology of triglycerides and alcohols, which is applied in the direction of fatty acid chemical modification, fatty oil/acid recovery from waste, fatty oil/fat refining, etc., can solve the problems of putting a strain on the transformation cost and all these specifications are not always useful
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
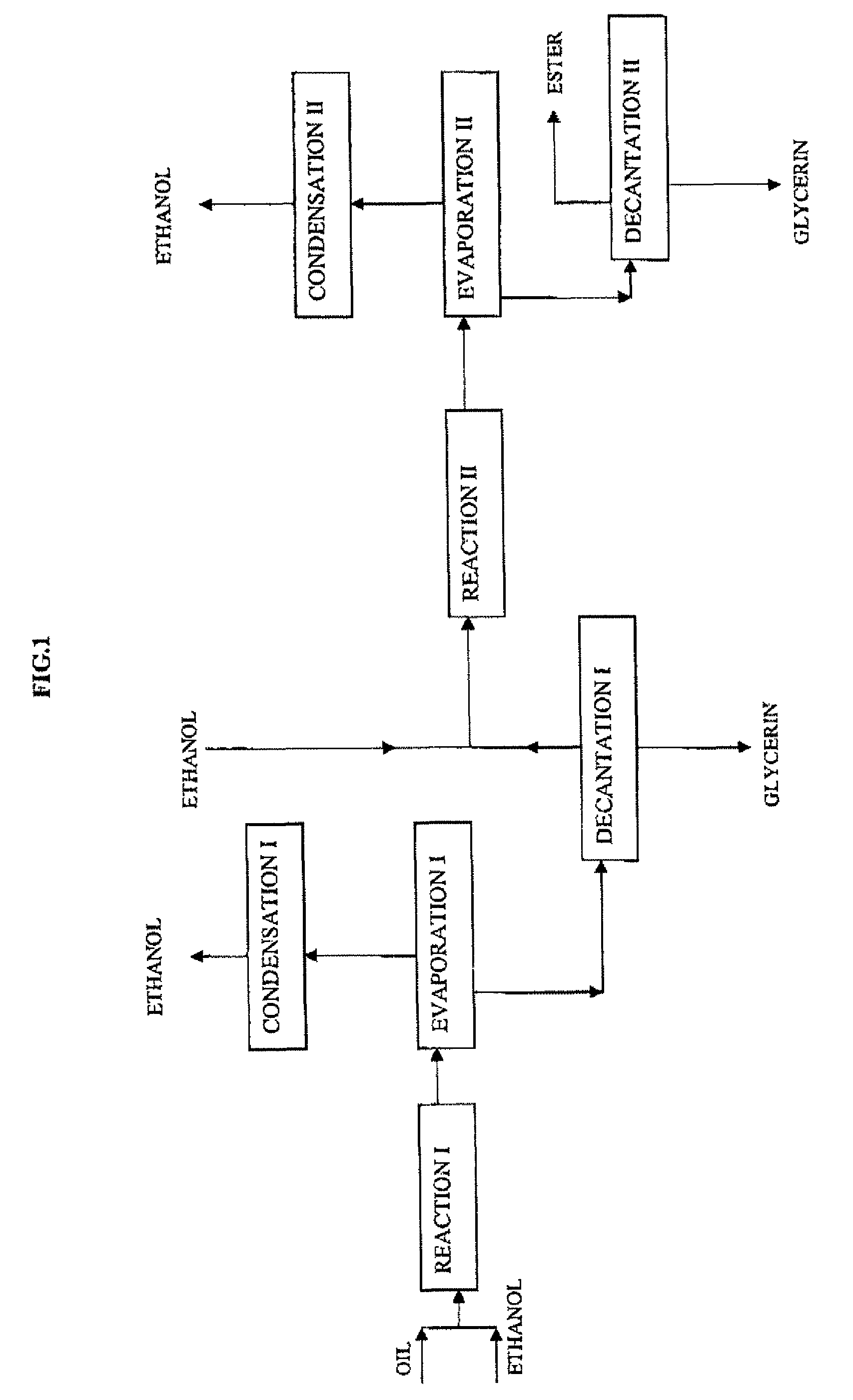
[0061]100 g colza oil and 100 g ethanol are fed at 200° C. and at a LHSV of 0.25 h−1 (volume of oil per volume of catalyst and per hour) into a fixed-bed reactor containing 110 ml of a catalyst consisting of a mixed zinc aluminate oxide.
[0062]After a residence time of about 110 minutes, a mixture consisting of about 93.2% by mass of ethyl esters, 3.7% by mass of monoglycerides, the 100% complement being made up of triglycerides, diglycerides, sterols and sterol esters, is obtained. This composition is not compatible with the specifications required by the EN 14214 standard for use of this product as a fuel, at least as regards the proportions of esters and of monoglycerides. The reaction therefore has to be continued to improve the conversion.
[0063]To carry out a second catalysis stage, it is necessary to remove all or part of the glycerin formed during the first stage in order to shift the reaction equilibrium. An excess ethanol flash is readily obtained by expansion by going from ...
example 2
According to the Invention
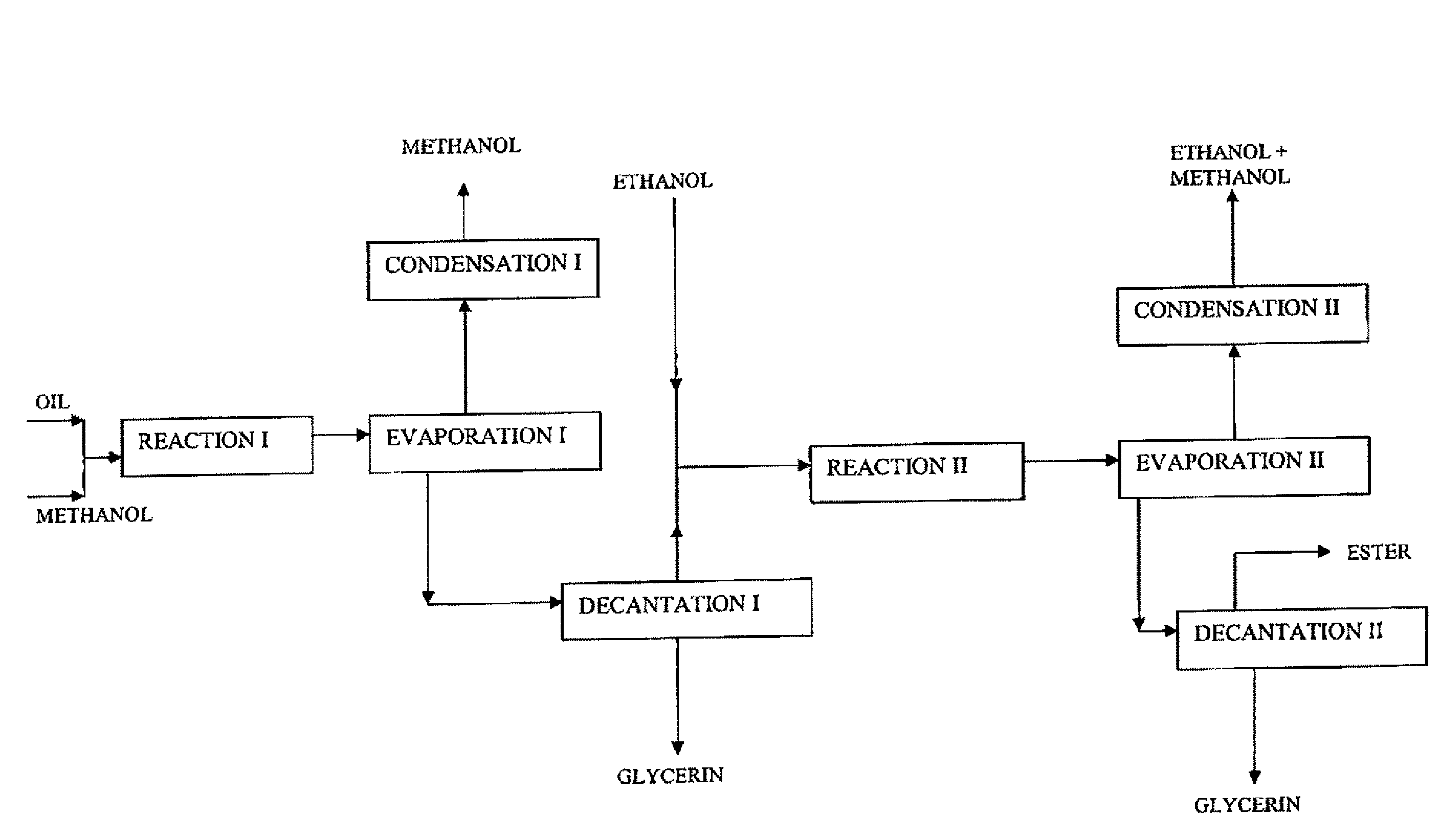
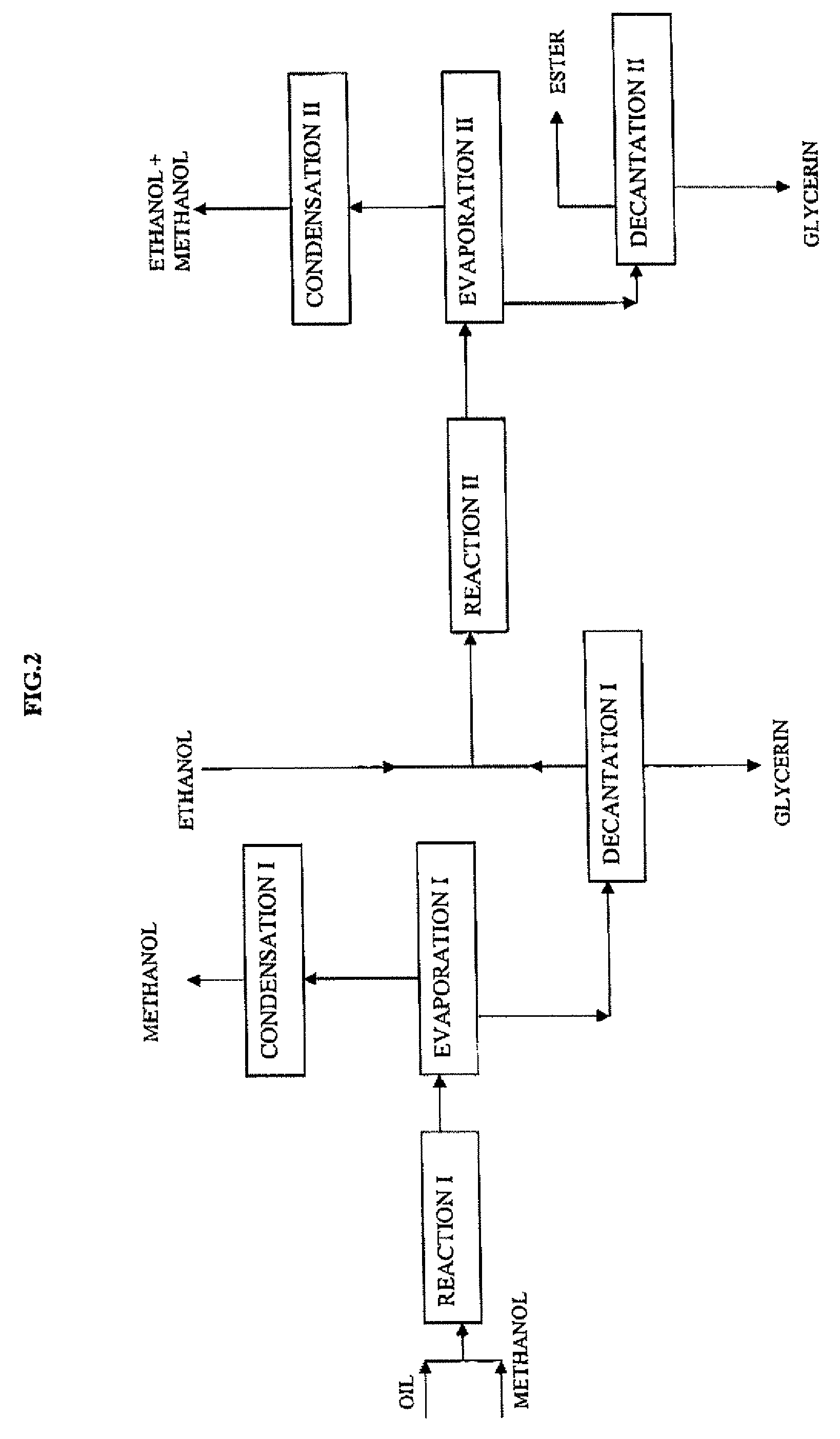
[0066]This example describes the operating conditions of the method involving a first transesterification stage wherein the alcohol used is methanol and a second stage wherein the alcohol used is ethanol. The flowsheet is given in FIG. 2.
[0067]As in example 1, 100 g colza oil and this time 100 g methanol are fed into a fixed-bed reactor containing 110 ml of the same catalyst, at 200° C., at a LHSV of 0.5 h−1 (volume of oil per volume of catalyst and per hour), i.e. a reaction time of 55 minutes. The composition of the reaction mixture at the end of this reaction time is of the order of 93.9% by mass of methyl esters and 3.4% by mass of monoglycerides, the 100% complement consisting of residual triglycerides, diglycerides, sterols and sterol esters.
[0068]The next stage consists in removing all of the excess methanol, in decanting the glycerin formed, then in continuing the operation by means of a second reaction stage wherein the ester phase is fed with etha...
example 3
Comparative
[0073]25 g colza oil, 25 g ethanol and 1 g of the catalyst described in example 1 are fed into a 100-ml autoclave reactor equipped with a stirring system and with a temperature and pressure control device. The medium is brought to 200° C. under stirring. The pressure reaches 32 bar (3.2 MPa).
[0074]A sample is taken from the liquid phase after a 7-hour reaction. After ethanol filtration and evaporation, the medium is allowed to settle. No phase separation is observed, which indicates a negligible free glycerol formation. The ethyl ester concentration is determined by steric exclusion chromatography. It is 23.8% by mass.
[0075]At this stage, 20 g of the product obtained above, 20 g ethanol and 1 g of the catalyst described in example 1 are fed into a 100-ml autoclave reactor equipped with a stirring system and with a temperature and pressure control device. The medium is brought to 200° C. under stirring. The pressure reaches 32 bar (3.2 MPa).
[0076]A sample is taken from the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com