Catalytic cracking method
A catalytic cracking and nano-catalyst technology, applied in the field of catalytic cracking, can solve the problems of low utilization rate, frequent regeneration, easy carbon formation, etc., and achieve the effect of increased utilization rate, simple method and reduced dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Taking Yanhua naphtha as raw material, its composition is as follows (w%):
[0042] C4-1.85, C5 6.96, C6 21.29, C7 19.29, C8 23.66, C9 16.04, C10 7.40, C11 2.61, C12 0.64. Among them, 26.18 normal alkanes, 33.66 isoparaffins, 27.35 naphthenes, 0.20 olefins, 12.35 aromatics, and 0.26 unknowns.
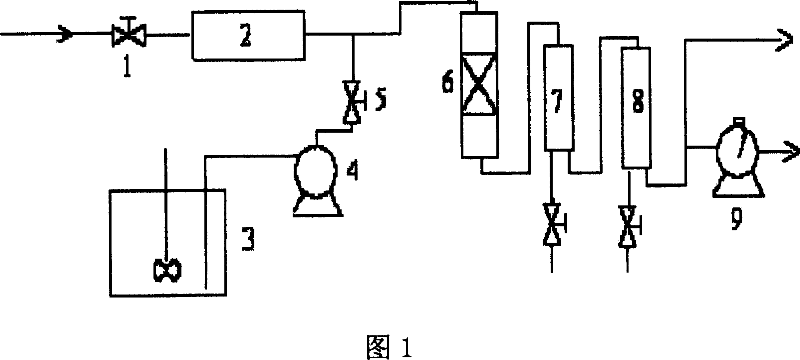
[0043] Naphtha with a water-to-oil ratio of 1 enters the preheater 2 at a flow rate of 0.3g / min, and the water liquid containing 700ppm nano-sized alumina is fed into the preheater through the peristaltic pump 4 at a flow rate of 0.3g / min under stirring 2 and the pipeline between reactor 6. The catalytic cracking reaction was carried out at 785°C, and gas samples were taken every 0.5hr to analyze its composition. After about 1 hour of reaction, the cumulative amounts of gaseous and liquid phase products were metered. The reaction results and yields of main products in the gas phase are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0048] Except that the catalytic cracking reaction was carried out at 790° C., other reaction conditions were the same as in Example 1. Table 2 shows the reaction results and yields of main products in the gas phase.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Taking Yanhua naphtha as raw material, its composition is as follows (% by weight):
[0054] C4-1.85, C5 6.96, C6 21.29, C7 19.29, C8 23.66, C9 16.04, C10 7.40, C11 2.61, C12 0.64. Among them, 26.18 normal alkanes, 33.66 isoparaffins, 27.35 naphthenes, 0.20 olefins, 12.35 aromatics, and 0.26 unknowns.
[0055] Make the naphtha that water-oil ratio is 1 enter preheater 2 with the flow rate of 0.3g / min, the ZSM-5 molecular sieve (particle diameter<160 order) containing 700ppm alkaline earth metal modification is stirred under stirring with 0.1g / min The flow of min is added into the pipeline between the preheater 2 and the reactor 6 through the peristaltic pump 4 . Catalytic cracking reactions were carried out at 750°C, and gas samples were taken every 0.5hr to analyze its composition. After about 1 hour of reaction, the cumulative amounts of gaseous and liquid phase products were metered. The reaction results and yields of main products in the gas phase are shown in Ta...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com