Comprehensive resources treatment method of waste circuit board
A technology of discarded circuit boards and comprehensive resources, applied in the direction of sustainable waste treatment, solid waste management, electronic waste recycling, etc., can solve the problems of large investment, toxicity, and harmfulness, and achieve high metal recovery rate, low investment, and low cost Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
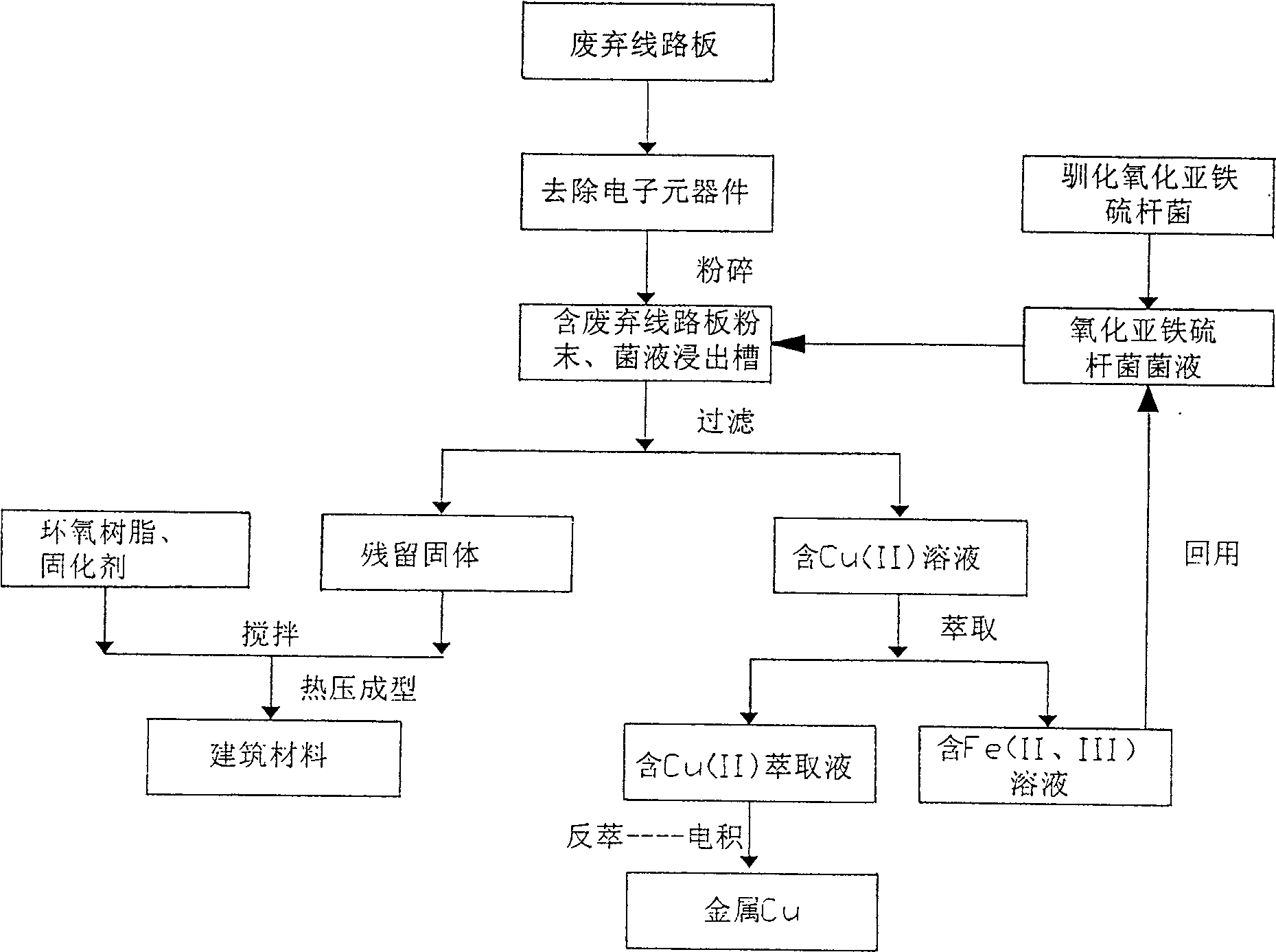
Image
Examples
example 1
[0048] a. Acclimatize the Thiobacillus ferrooxidans used in leaching waste circuit board metal Cu, add CuSO in the 9K liquid culture medium (that is, the substratum prepared with the formula in the present invention) of inoculating Thiobacillus ferrooxidans 4 ·5H 2 O, when the solution changes from blue-green to dark green, re-inoculate the domesticated Thiobacillus ferrooxidans and increase CuSO 4 ·5H 2 The dosage of O, after several times of transfer and acclimation culture, enables the leaching Thiobacillus ferrooxidans to adapt to the culture environment containing high concentration of Cu ions, and its tolerance level reaches 6-8g Cu ions. 2+ / L.
[0049] b. Inoculate the Thiobacillus ferrooxidans liquid through domestication in the 1# container (volume is 4L) that fills 9K culture medium solution, inoculum size is 10% (volume ratio), and solution is stirred, stirring speed is 100r / min, cultured for 2 days, at this time the solution turned reddish brown. The iron ion...
example 2
[0058] a. Acclimatize Thiobacillus ferrooxidans for leaching metal Cu in waste circuit boards, add CuSO to the 9K liquid medium inoculated with Thiobacillus ferrooxidans 4 ·5H 2 O, when the solution changes from blue-green to dark green, re-inoculate the domesticated Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, and increase the dosage of CuSO4·5H2O. It can adapt to the culture environment containing high concentration of Cu ions, and its tolerance can reach 10-13g Cu 2+ / L.
[0059] b. Inoculate the Thiobacillus ferrooxidans liquid through domestication in the 1# container (volume is 4L) that fills 9K culture medium solution, inoculum size is 14% (volume ratio), and solution is stirred, and stirring speed is 80r / min, cultured for 1 day, at this time the solution turned reddish brown. The iron ions in the solution are basically Fe 3+ The amount of microorganisms in the bacterial solution measured by the lipophosphorus method is 8n mol P / mL, and the oxidation-reduction potential of the solut...
example 3
[0068] a. acclimation and leaching the Microspirillum ferrooxidans used for metal Cu in the discarded circuit board, adding CuSO in the 9K liquid medium (that is, the medium prepared with the formula in the present invention) of Microspirillum ferrous oxides inoculated 4 ·5H 2 O, when the solution changes from blue-green to dark green, re-inoculate the domesticated Microspirillum ferrooxidans, and increase CuSO 4 ·5H 2 The amount of O added, after several times of transfer and domestication, made the leaching Microspirilla ferrooxidans adapt to the culture environment containing high concentrations of Cu ions, and its tolerance reached 12-15g Cu ions. 2+ / L.
[0069] B. fill the 1# container (volume is 4L) of 9K substratum solution inoculation through domesticated Microspiral ferrooxidans bacterium liquid, inoculum size is 5% (volume ratio), and solution is stirred, stirring speed is 120r / min, cultured for 3 days, at this time the solution turned reddish brown. The iron io...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flexural strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com