Liquid depot formulation
A pre-formulation, non-liquid crystal technology, used in liquid delivery, emulsion delivery, aerosol delivery, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain high phospholipid concentration depot compositions, difficult to sterilize, and delayed "release curve"
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Example 1: Availability of different liquid crystalline phases in reservoirs by choice of composition
[0152] Injectable formulations containing different ratios of phosphatidylcholine ("PC" - Epikuron 200) and glyceryl dioleate (GDO) and EtOH as solvents were prepared to demonstrate that different liquid crystal phase.
[0153] Weigh an appropriate amount of PC and EtOH in a glass bottle, and place the mixture on a shaker until the PC is completely dissolved to form a clear liquid solution. GDO is then added to form an injectable homogeneous solution.
[0154] Each formulation was poured into glass vials and equilibrated with excess water. The phase behavior between cross-polarized light at 25°C was visually inspected. The results are listed in Table 1.
[0155] Table 1
[0156] preparation
PC (wt%)
GDO(wt%)
EtOH (wt%)
h 2 phase in O
A
22.5
67.5
10.0
L 2
B
28.8
61.2
10.0
...
Embodiment 2
[0161] Example 2: In vitro release of water-soluble substances
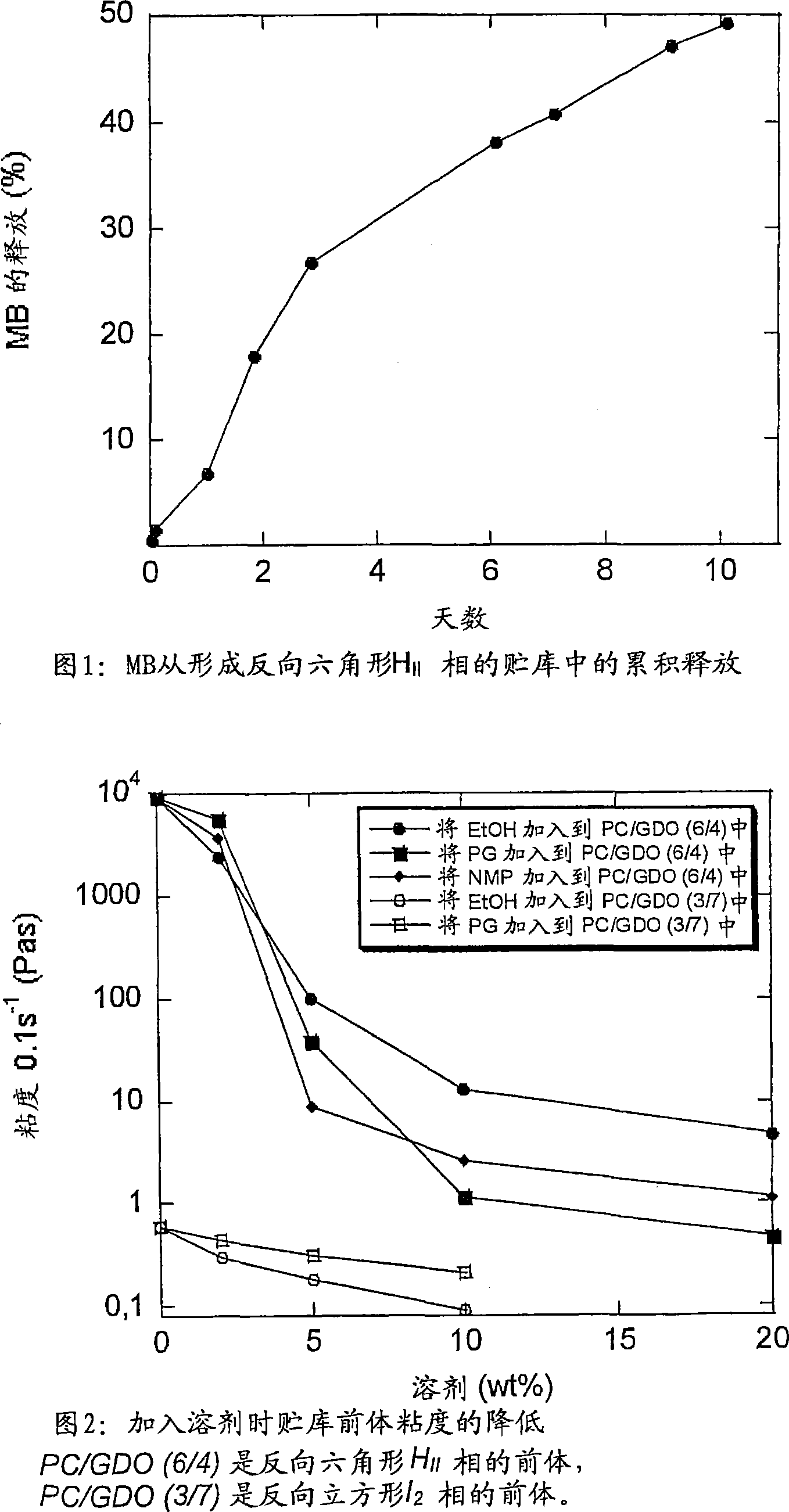
[0162] A water soluble colourant, methylene blue (MB), was dispersed in Formulation C (see Example 1) to a concentration of 11 mg / g formulation. When 0.5 g of this formulation was injected into 100 ml of water, a strongly inverted hexagonal H II Mutually. The absorbance of MB released into the aqueous phase was then measured at 664 nm over a period of 10 days. Release studies were performed at 37°C in Erlenmeyer flasks with magnetic stirring.
[0163] The release profile of MB in the hexagonal phase (see Figure 1) shows that this (and its similar) formulation is a promising storage system. Also, it appears that the formulation gave a low initial release, and the release profile showed that the material could be released for several weeks; only about 50% of the MB was released after 10 days.
Embodiment 3
[0164] Example 3: Viscosity of PC / GDO (6:4) or PC / GDO (3:7) with addition of solvents (EtOH, PG and NMP)
[0165] The PC / GDO / EtOH mixture was prepared according to the method of Example 1. Use a rotary evaporator (vacuum, 40 ° C, 1 h) to remove all or almost all of the EtOH in the mixture, weigh the resulting solid mixture in a glass bottle, and then add 2, 5, 10 or 20% of the solvent (EtOH, propylene glycol (PG) or n-methylpyrrolidone (NMP)). Samples were allowed to equilibrate for several days before viscosity was measured using a Physica UDS200 flow velocity meter at 25°C at a shear rate of 0.1 s-1.
[0166] This example clearly shows the need for a solvent with some depot precursor to obtain an injectable formulation (see Figure 2). Increasing the proportion of PC, the viscosity of the solvent-free PC / GDO mixture increases. Systems with low PC / GDO ratios (more GDO) can be injected with lower concentrations of solvent.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com