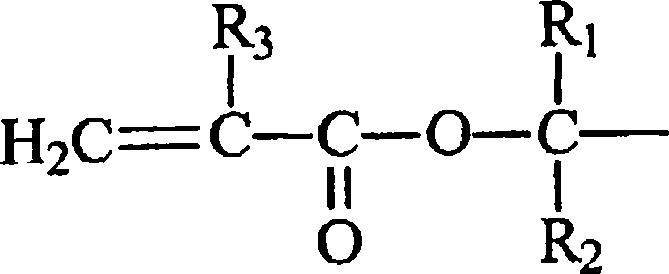
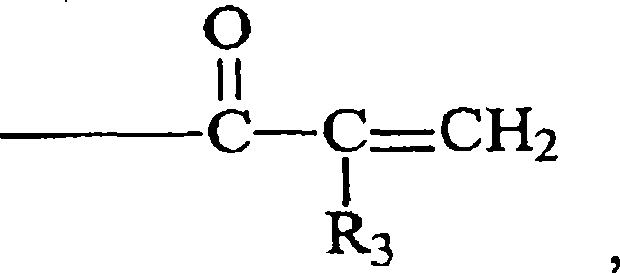
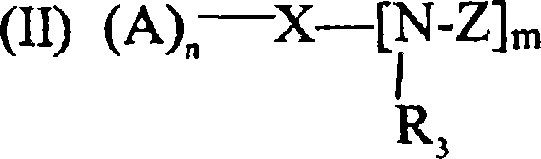Crosslinker for superabsorbent polymers
A technology of cross-linking agent and compound, which is applied in the direction of absorbent pads, medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of increasing uncross-linked polymers, no superabsorbent polymers, and undesirable degree of polymer decomposition, and achieve easy processing Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] In the preparation of the crosslinking agent, an inert polar or nonpolar solvent is suitably used. Examples of suitable solvents include toluene, dichloromethane, chloroform and tetrahydrofuran. Combinations of solvents can be used. The amount of solvent used is not critical as long as it is sufficient to dissolve the reagents. The concentration of reagents in the reaction mixture is preferably from about 0.01 molar to about 10 molar, more preferably from about 0.2 molar to about 4 molar.
[0031] Acryloyl chloride or methacryloyl chloride and reagent (I + ), (II + ) or (III + ) is an exothermic reaction. Therefore, the reaction temperature is preferably controlled so that the temperature does not reach the point where thermal polymerization occurs. The reaction temperature is not critical as long as the reaction can proceed. Preferably, the temperature of the reaction mixture is from about 15°C to about 55°C.
[0032] Any reaction time can be used; however, gen...
Embodiment 1
[0085] A 1 L jacketed, bottom venting reactor was equipped with nitrogen inlet, heat trap, inclined paddle turbine type stirrer and addition funnel. The apparatus was purged with nitrogen overnight before use. The reactor was charged with 200 ml of toluene and 28.3 g (0.27 mol) of 3-methyl-1,3-butanediol. With stirring, 84.3 g (0.83 mol) of triethylamine were added, forming a clear, colorless solution without increasing the temperature. The solution was heated to 35°C. A solution of 109.4 g (1.21 mol) of 96% acryloyl chloride dissolved in 100 ml of toluene was added dropwise. A precipitate formed immediately and the reaction temperature increased. The reaction temperature was maintained between 45°C and 50°C by jacket cooling. When the addition was complete, the mixture was heated at 48°C for 3 hours.
[0086] The mixture was cooled to 35°C and 500 ml of deionized water was added. In order to dissolve the precipitate, the mixture was stirred at 35°C for 45 minutes. The ...
Embodiment 2
[0088] A 500ml 3 neck round bottom flask was equipped with nitrogen inlet, magnetic stir bar, addition funnel, temperature probe and stopper. 150 ml of toluene and 28.3 ml (0.30 mol) of 97% acryloyl chloride were added to the flask. Via syringe, 10.6 ml (0.10 mol) of 3-methyl-1,3-butanediol were added. The resulting solution was heated to 40°C. A solution of 30.6 ml (0.22 mol) of triethylamine in 100 ml of toluene was added at a slow drop rate with vigorous stirring. The reaction was exothermic, with the temperature rising to 50°C. The reaction temperature was maintained at about 50°C by cooling in a water bath. During the addition, a flocculent precipitate formed. When the addition was complete, the slurry was maintained at about 50°C for 2 hours by means of a water bath. After cooling to room temperature, the precipitate was removed by filtration. Volatiles were removed from the filtrate under vacuum to leave a pale yellow, slightly cloudy liquid. The product was diss...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com