Cellulose/ soy protein composite sponge and preparing method thereof
A technology of soybean protein and composite sponge is applied in the fields of biomedical materials and polymers to achieve the effect of simple production process and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Embodiment 1 (comparative example)
[0024] Pre-cool 7wt% sodium hydroxide / 12wt% urea aqueous solution (96.4g) to -12°C, take it out and place it at room temperature (below 20°C), quickly put 3.6g of dry cotton linter cellulose into it, and stir thoroughly A 3.6 wt% cellulose solution was prepared. After centrifugation and degassing, place it in a -20°C refrigerator, transfer it to a -80°C refrigerator after 24 hours, place it in a -80°C refrigerator for 24 hours, freeze-dry, treat with dilute acetic acid, and rinse with water to obtain pure cellulose sponge.
Embodiment 2
[0026]In 100g of the 3.6wt% cellulose solution in Example 1, add 4g of a 10wt% soybean protein solution while stirring, and continue stirring for 20min to obtain a mixed solution after the addition is complete. After the cellulose / soybean protein mixed solution was centrifuged and degassed, the cellulose / soybean protein composite sponge was prepared according to the method of Example 1. The soybean protein content in the composite sponge is 10wt%.
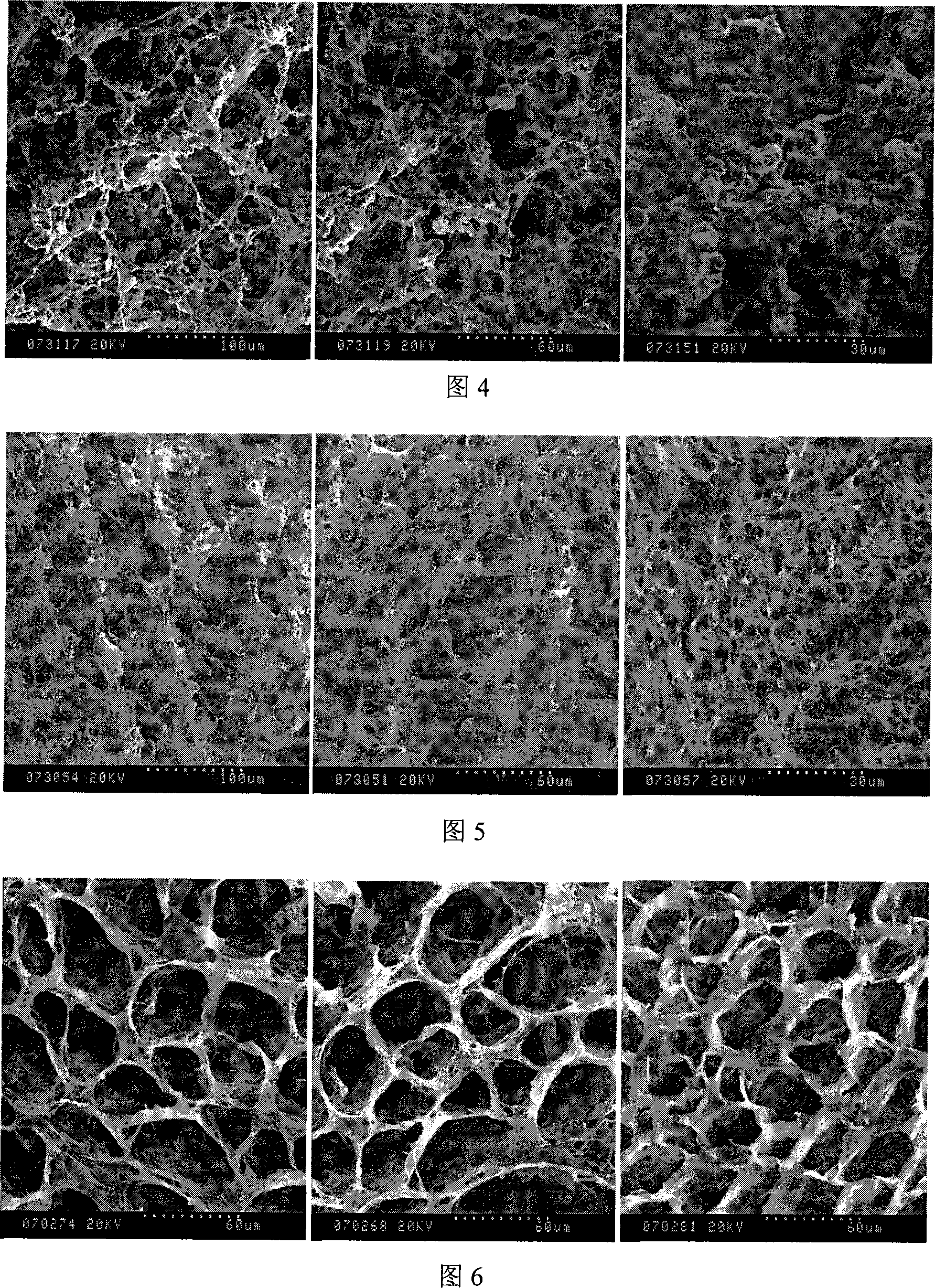
[0027] Fig. 1 is the SEM photograph of the sponge obtained in Example 1 and Example 2, that is, the SEM photograph of the composite sponge with 10 wt% of pure cellulose sponge and soybean protein respectively. The sponge is a porous structure with irregular pore shapes and different sizes.
Embodiment 3
[0029] The composite sponges obtained in Examples 1 and 2 were implanted into SPF grade SD rats subcutaneously and intramuscularly after conventional autoclaving, and were raised after suturing the surgical wound. The samples were taken out during the operation, and observed by light microscope and scanning electron microscope to preliminarily evaluate the biocompatibility of the material.
[0030] Fig. 2 is the light microscope pictures of the cellulose / soybean protein composite sponge obtained in this example (soybean protein solid content is 10wt%) implanted in rats for 1, 3 and 5 months respectively. After 1 month, the spongy material was clearly visible, and a small amount of cells and tissues entered the interior of the spongy material. After 3 months, part of the composite sponge still existed, but the amount of cells and tissues entering the material increased significantly. After 5 months, the composite sponge has basically disappeared, and the tissue has occupied th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com