Method of producing zinc oxide Fe-doped rare magnetic semiconductor material
A dilute magnetic semiconductor and zinc oxide technology, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, zinc oxide/zinc hydroxide, magnetic film to substrate application, etc., can solve the problem of low solubility limit, difficult realization of ferromagnetism, and low magnetic performance and other issues to achieve the effect of low cost and simple technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
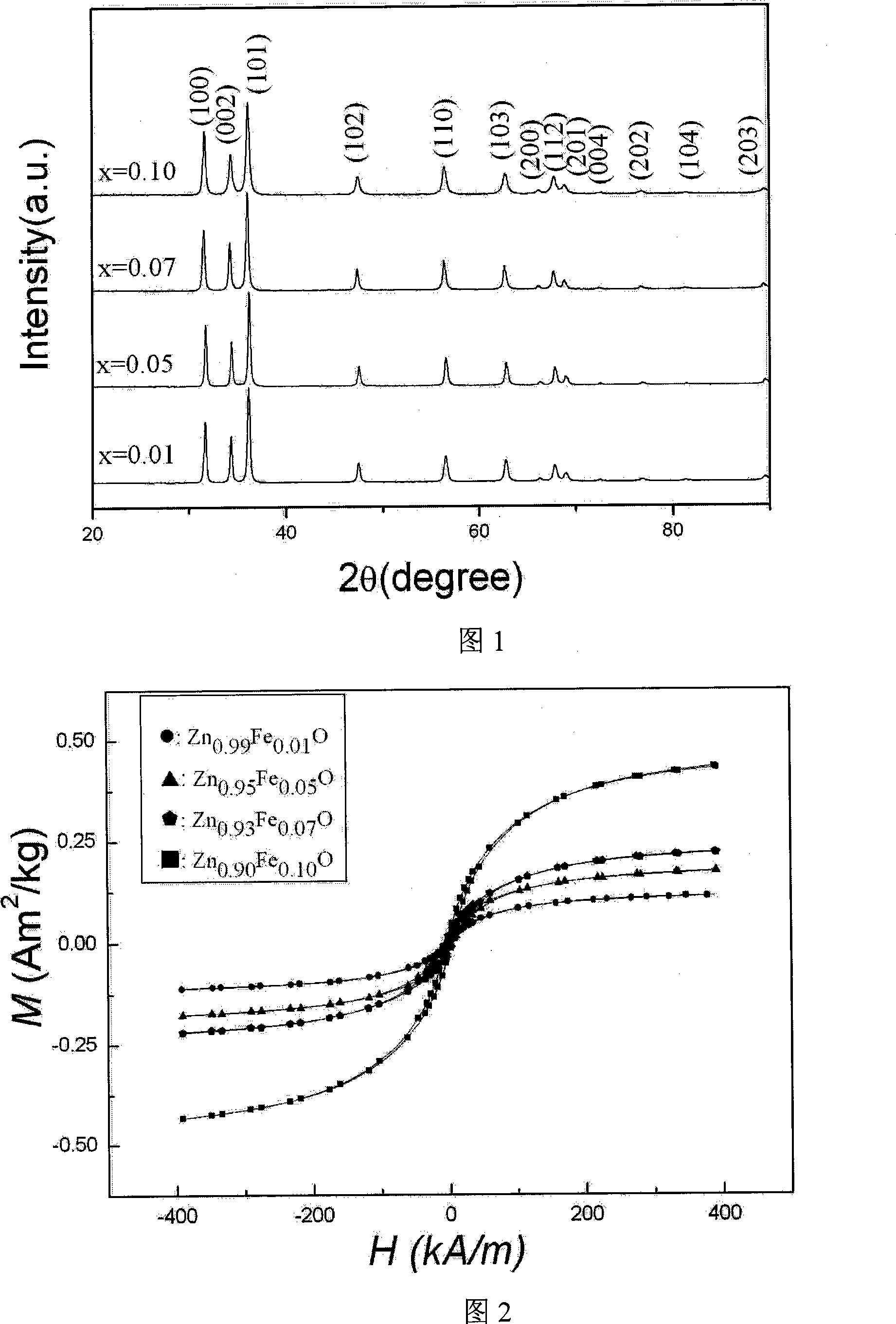
[0025] Example 1: Preparation of ferromagnetic Zn at room temperature 0.99 Fe 0.01 O dilute magnetic semiconductor powder
[0026] 1) Zinc acetate (5.43g) and ferrous acetate (0.06g) with a molar percentage of 99:1 were dissolved in 25ml of ethylene glycol methyl ether, and 0.5ml of ethanolamine was added, and 0.4ml of ferrous acetate was added to the ferrous acetate solution. g of ascorbic acid, made into a solution with a concentration of 0.5mol / L, stirred at room temperature until fully dissolved, then slowly added the ferrous acetate solution into the zinc acetate solution, continued to stir for 12 hours, and left to age for 24 hours to obtain Transparent and uniform sol;
[0027] 2) Place the sol in a vacuum drying oven at 100°C for 12 hours to obtain a gel;
[0028] 3) The gel was heat-treated for 3 hours in an Ar gas environment at 300 ° C, and cooled with the furnace to obtain the desired room temperature ferromagnetic Zn 0.99 Fe 0.01 O dilute magnetic semiconduct...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Preparation of ferromagnetic Zn at room temperature 0.95 Fe 0.05 O dilute magnetic semiconductor powder
[0030] 1) Zinc acetate (5.21g) and ferrous acetate (0.3g) with a molar percentage of 95:5 were dissolved in 25ml of ethylene glycol methyl ether, respectively, and 0.5ml of ethanolamine was added, and 1.8ml was added to the ferrous acetate solution. g ascorbic acid, stirred at room temperature until fully dissolved, then slowly added the ferrous acetate solution into the zinc acetate solution, continued to stir for 15 hours, then left to age for 36 hours to obtain a transparent, uniform sol;
[0031] 2) Place the sol in a vacuum drying oven at 120°C for 18 hours to obtain a gel;
[0032] 3) The gel was heat-treated for 5 hours in an Ar gas environment at 350 ° C, and cooled with the furnace to obtain the desired room temperature ferromagnetic Zn 0.95 Fe 0.05 O dilute magnetic semiconductor powder.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Example 3: Preparation of ferromagnetic Zn at room temperature 0.93 Fe 0.07 O dilute magnetic semiconductor powder
[0034] 1) Zinc acetate (5.1g) and ferrous acetate (0.42g) with a molar percentage of 93:7 were dissolved in 25ml of ethylene glycol methyl ether, respectively, and 0.5ml of ethanolamine was added, and 2.5ml of ferrous acetate was added to the ferrous acetate solution. g ascorbic acid, stirred at room temperature until fully dissolved, then slowly added the ferrous acetate solution into the zinc acetate solution, continued to stir for 12 hours, then left to age for 24 hours to obtain a transparent, uniform sol;
[0035] 2) Place the sol in a vacuum drying oven at 100°C for 12 hours to obtain a gel;
[0036]3) The gel was heat-treated for 3 hours in an Ar gas environment at 300° C., and cooled in a furnace to obtain the desired powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com