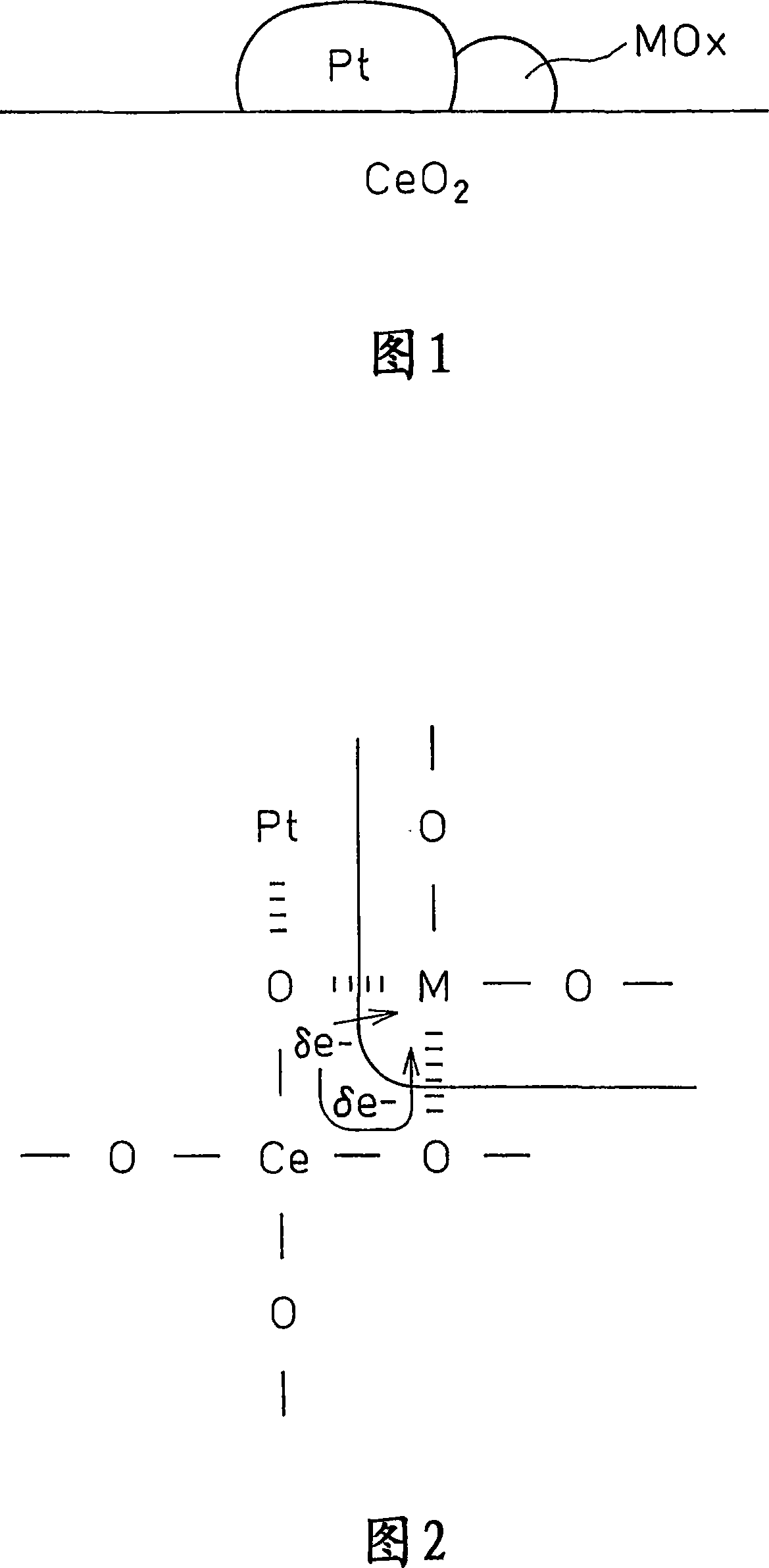
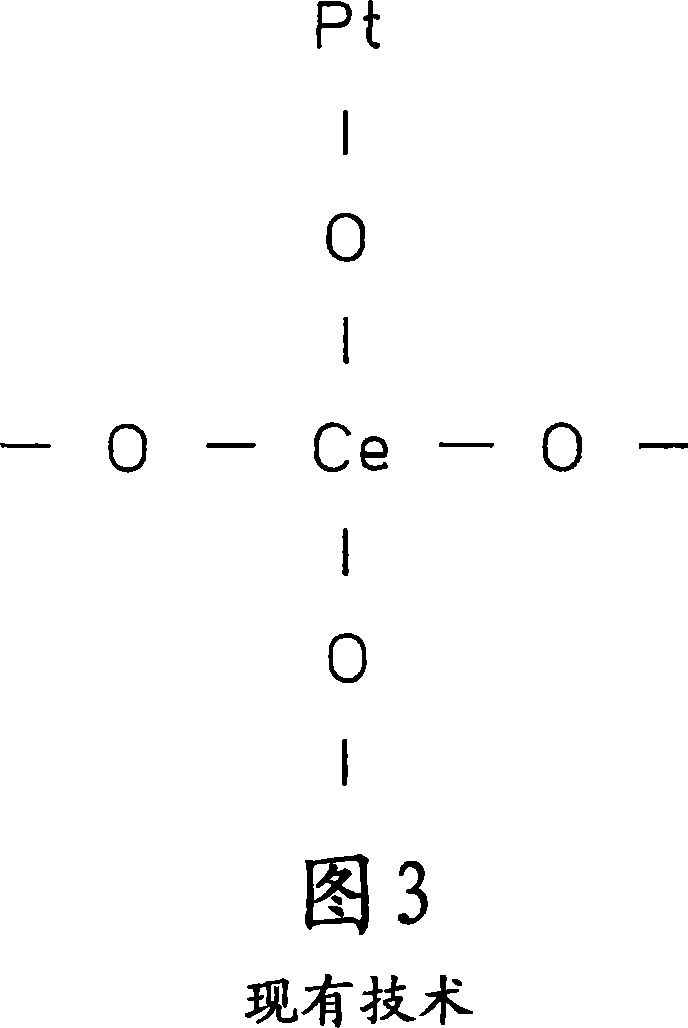Exhaust gas purifying catalyst and process for producing it
A technology for exhaust gas purification and catalyst, which can be used in physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to meet heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] The ceria-zirconia solid solution powder (Ce: Zr (molar ratio) = 1: 1, specific surface area: 70m 2 / g) was dispersed in 6 times the amount (by mass) of distilled water, and the dinitrodiammine platinum solution was added in an amount to obtain a platinum concentration of 1.0% by mass based on the carrier. The resulting solution was mixed for 1 hour, dried at 120° C. to remove water contained in the solution, and the residue was calcined at 500° C. for 2 hours and pulverized in a mortar to obtain a platinum-supporting carrier powder.
[0067] The platinum-supporting carrier powder thus obtained was dispersed in 6 times the amount (by mass) of an aqueous solution of iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate, and the resulting solution was mixed for 1 hour. The iron salt solution contains the amount of iron ions so that the catalyst finally obtained can contain 10% by mass of iron oxide (Fe 2 o 3 ). Then, the water contained in the solution was removed at 120°C, and the residue wa...
Embodiment 2~7
[0069]In addition to replacing iron (III) nitrate nonahydrate with gallium (III) nitrate, silver nitrate, diammonium molybdate, ammonium tungstate pentahydrate, thallium nitrate and bismuth (III) nitrate pentahydrate, respectively, to implement Example 1 obtains the exhaust gas purification catalyst of embodiment 2~7 in the same manner, so that the catalyst finally obtained can comprise gallium oxide (Ga 2 o 3 ), silver oxide (AgO), molybdenum oxide (MoO 2 ), tungsten oxide (WO 2 ), thallium oxide (Tl 2 o 3 ) or bismuth oxide (Bi 2 o 3 ).
Embodiment 8
[0104] Zirconia powder (amount of added ceria: 2% by mass, specific surface area: 98m2) added with ceria as catalyst carrier 2 / g) was dispersed in 6 times the amount (by mass) of distilled water, and a rhodium nitrate solution (2.7 mass%) was added in an amount to obtain a rhodium concentration of 0.5 mass% based on the support. The resulting solution was mixed for 1 hour, and after removing water contained in the solution at 120° C., the residue was calcined at 500° C. for 2 hours, and then pulverized in a mortar to obtain a rhodium-supporting carrier powder.
[0105] The thus-obtained rhodium-loaded carrier powder was dispersed in 6 times the amount (by mass) of an aqueous solution of iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate, and the resulting solution was mixed for 1 hour. The iron salt solution contains iron ions in such an amount that the final catalyst can have an iron (Fe) rhodium (Rh) ratio (Fe / Rh) of 2.0. Then, the water contained in the solution was removed at 120°C, and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com