Process for separating bio-oil via solvent with high boiling point
A high-boiling solvent, bio-oil technology, applied in lignin derivatives, chemical instruments and methods, petroleum industry, etc., can solve problems such as pollution of the environment, avoid pollution, reduce economic costs, and improve environmental friendliness and safety. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
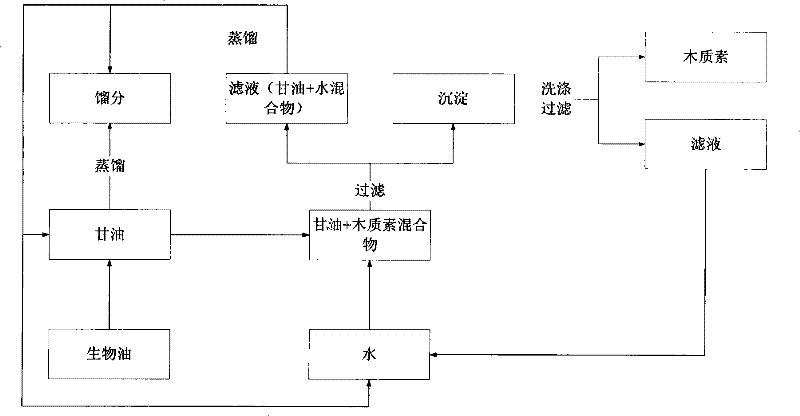
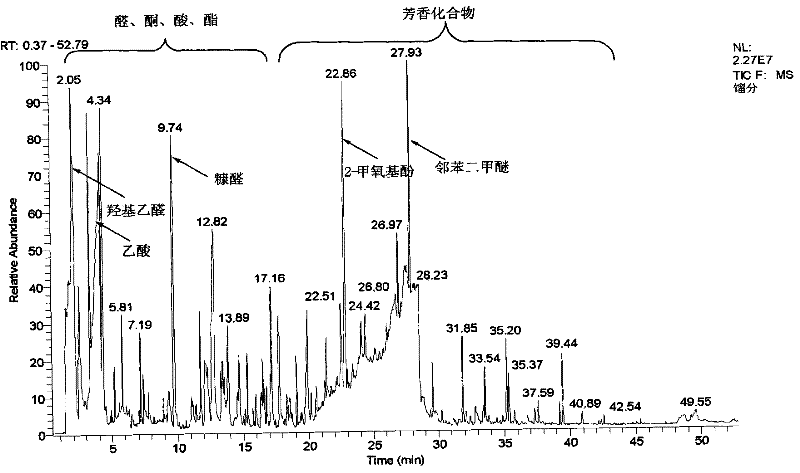
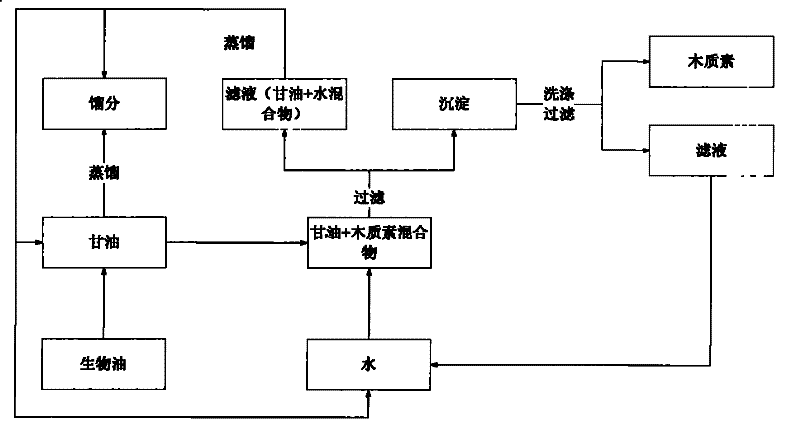
[0017] Take 60g of glycerin, heat it to 230°C under stirring, control the temperature between 230-250°C, add 30g of bio-oil drop by drop through the constant pressure dropping funnel, and drop it for about 30 minutes, collect the fraction until no liquid flows out. A mixture of 18.55 g of fractions and residual glycerin was obtained, the water content of the fraction was 51.5wt.%, and the content of glycerin was 16.21wt.%, that is, a fraction of 51.80wt.% was obtained from bio-oil. The obtained fraction is analyzed by GC-MS, and the GC-MS spectrogram is shown in figure 2 ; Fractions containing aldehydes, ketones, acids, esters and aromatic compounds.
[0018] Cool the remaining glycerol mixture to 80°C, add it dropwise to 40ml deionized water, and keep stirring, a large amount of brown precipitates are precipitated, and centrifuged to obtain the precipitates and glycerin filtrate; the precipitates are washed twice with 15ml deionized water, centrifuged Separation and vacuum ...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Considering that the fractions in Example 1 contain a relatively high concentration of glycerin, in order to avoid glycerol from entering the fractions, the distillation temperature was controlled between 200-220° C., and the method of suction filtration was used instead of centrifugation to increase the recovery rate of glycerin. Other operations of the separation process were the same as in Example 1 to obtain 47.11wt.% fraction and 29.77wt.% lignin, wherein the fraction had a moisture content of 55.02wt.% and a glycerin content of 1.21wt.%. It can be seen that lowering the temperature to between 200-220°C can effectively reduce the glycerol content in the fraction.
[0022] At the same time, 58.10 g of crude glycerol was recovered, and the glycerol content was 81.32wt.%, that is, the recovery rate of pure glycerin was 78.74wt.%. Part of the glycerin was transferred to the washing liquid, and after being enriched to a certain concentration, it could be recovered by dis...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Using 58.10 g of crude glycerin recovered in Example 2 as a solvent, 30 g of bio-oil was separated, and the separation process was the same as that of Example 2 to obtain 52.05 wt.% fraction and 34.92 wt.% lignin. 53.85 g of crude glycerin was recovered, and the recovery rate of crude glycerin was 92.69 wt.%. This example demonstrates that the recovered crude glycerol can be recycled, and the fraction and lignin yields are slightly higher than pure glycerol. This is caused by the solubility of glycerol to some components in bio-oil, and the recycling of glycerol can eliminate this effect and improve the product yield.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com