Routing plate processing technique
A processing technology, engraving and milling technology, applied in the direction of wood processing equipment, manufacturing tools, thin wood chip manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of unreasonable density distribution, high formaldehyde emission, low board strength, etc., to reduce pre-curing time, Stable mechanical properties and reduced formaldehyde emission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
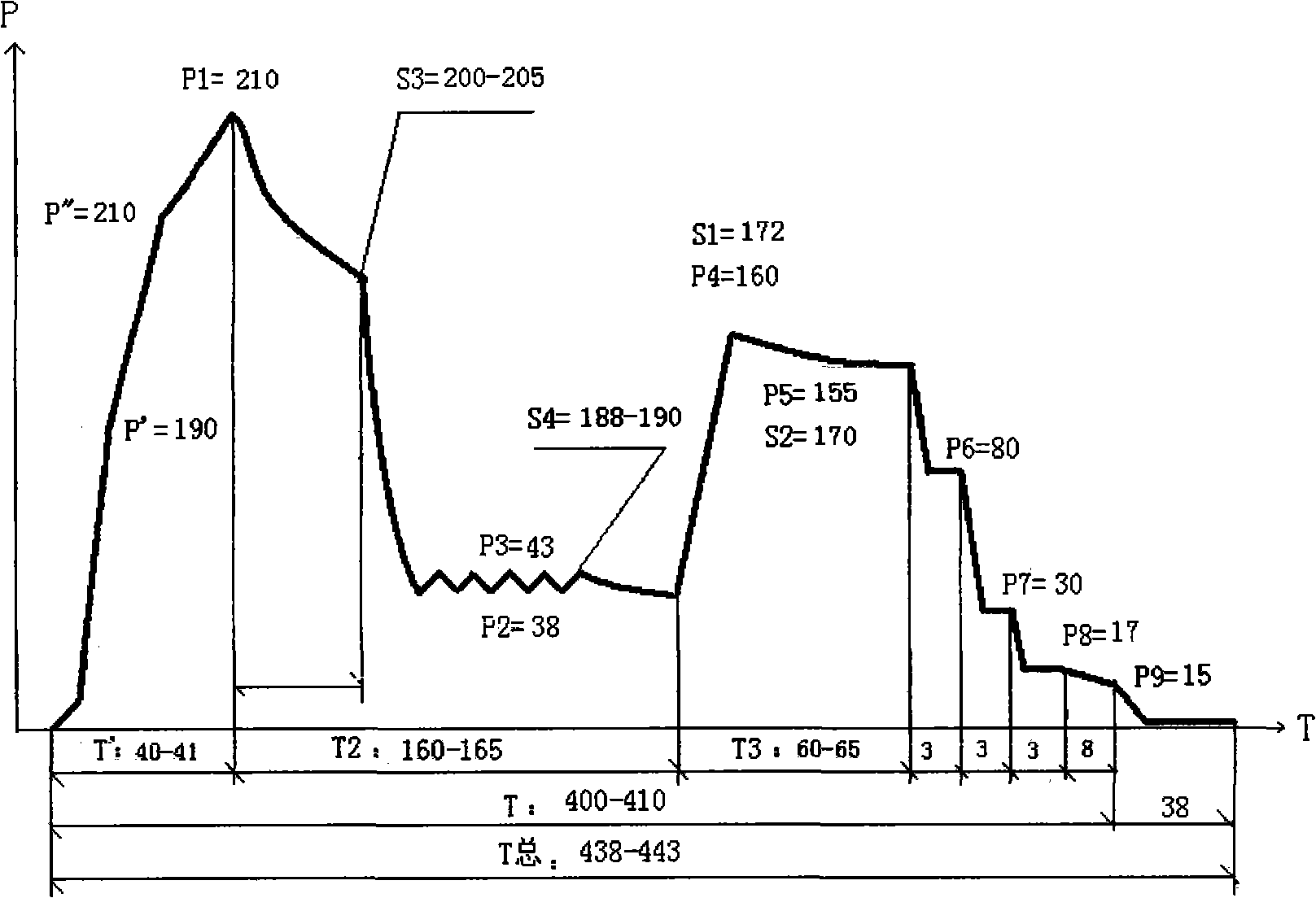
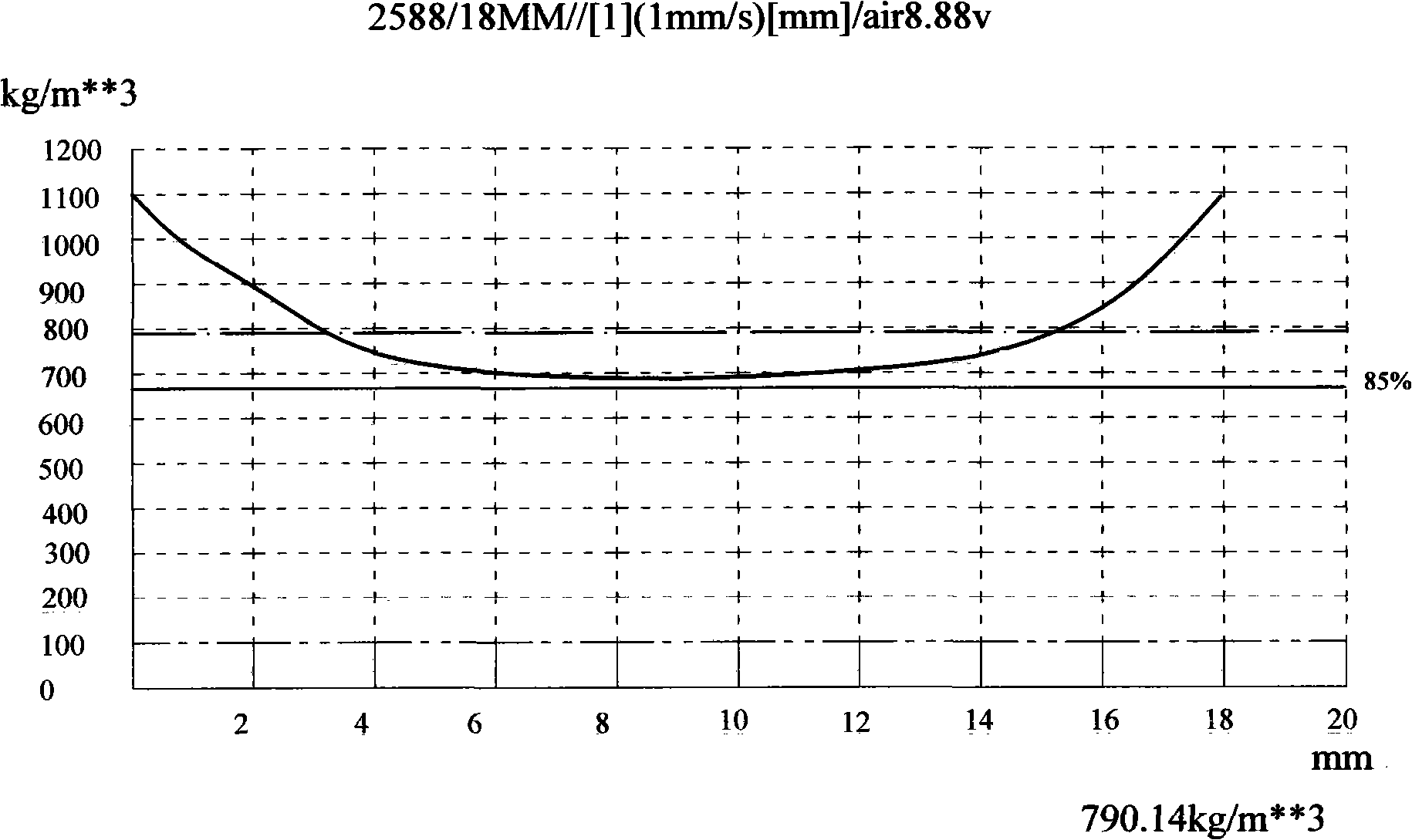
[0011] A milling board processing technology, the processing steps are: chipping and screening of wood: chipping tree species with similar specific gravity into wood chips of uniform size; pre-cooking and steaming: pre-cooking the chipped wood chips with saturated steam Cook for 3 minutes, the pre-cooking temperature is 90°C, and then cook for 3 minutes, the cooking temperature is 165°C; fiber separation: defibrate the cooked wood chips through a thermal mill, and the obtained wood fibers have ≥36 meshes accounting for the total fiber weight 10% of the total fiber weight, ≤200 meshes accounted for 5% of the total fiber weight; preparation of E1 grade urea-formaldehyde glue: After heating the formaldehyde in the container to 30°C, add NaOH with a mass concentration of 30% to adjust the pH value to 8.5; add the first batch of urea , the amount added is 35% of the mass of formaldehyde. After stirring until the temperature is balanced, measure the pH value to 8.3-8.5; heat up to 65...
Embodiment 2
[0013]A milling board processing technology, the processing steps are: chipping and screening of wood: chipping tree species with similar specific gravity into wood chips of uniform size; pre-cooking and steaming: pre-cooking the chipped wood chips with saturated steam Cook for 5 minutes, the pre-cooking temperature is 100°C, and then cook for 5 minutes, the cooking temperature is 175°C; fiber separation: defibrate the cooked wood chips through a thermal mill, and the obtained wood fibers have ≥36 meshes accounting for the total fiber weight 20%, ≤200 mesh accounts for 10% of the total fiber weight; preparation of E1 grade urea-formaldehyde glue: After heating the formaldehyde in the container to 35°C, add NaOH with a mass concentration of 30% to adjust the pH value to 8.8; add the first batch of urea , the amount added is 35% of the mass of formaldehyde. After stirring until the temperature is balanced, measure the pH value to 8.5; heat up to 65-83°C, measure the pH value at 7...
Embodiment 3
[0015] A milling board processing technology, the processing steps are: chipping and screening of wood: chipping tree species with similar specific gravity into wood chips of uniform size; pre-cooking and steaming: pre-cooking the chipped wood chips with saturated steam Cook for 4 minutes, the pre-cooking temperature is 95°C, and then cook for 4 minutes, the cooking temperature is 170°C; fiber separation: defibrate the cooked wood chips through a thermal mill, and the obtained wood fibers have ≥36 meshes accounting for the total fiber weight 15% of the fiber, ≤200 meshes accounted for 8% of the total fiber weight; preparation of E1 grade urea-formaldehyde glue: After heating the formaldehyde in the container to 33°C, add NaOH with a mass concentration of 30% to adjust the pH value to 8.7; add the first batch of urea , the amount added is 35% of the mass of formaldehyde. After stirring until the temperature is balanced, measure the pH value to 8.4; heat up to 65-83°C, measure th...
PUM
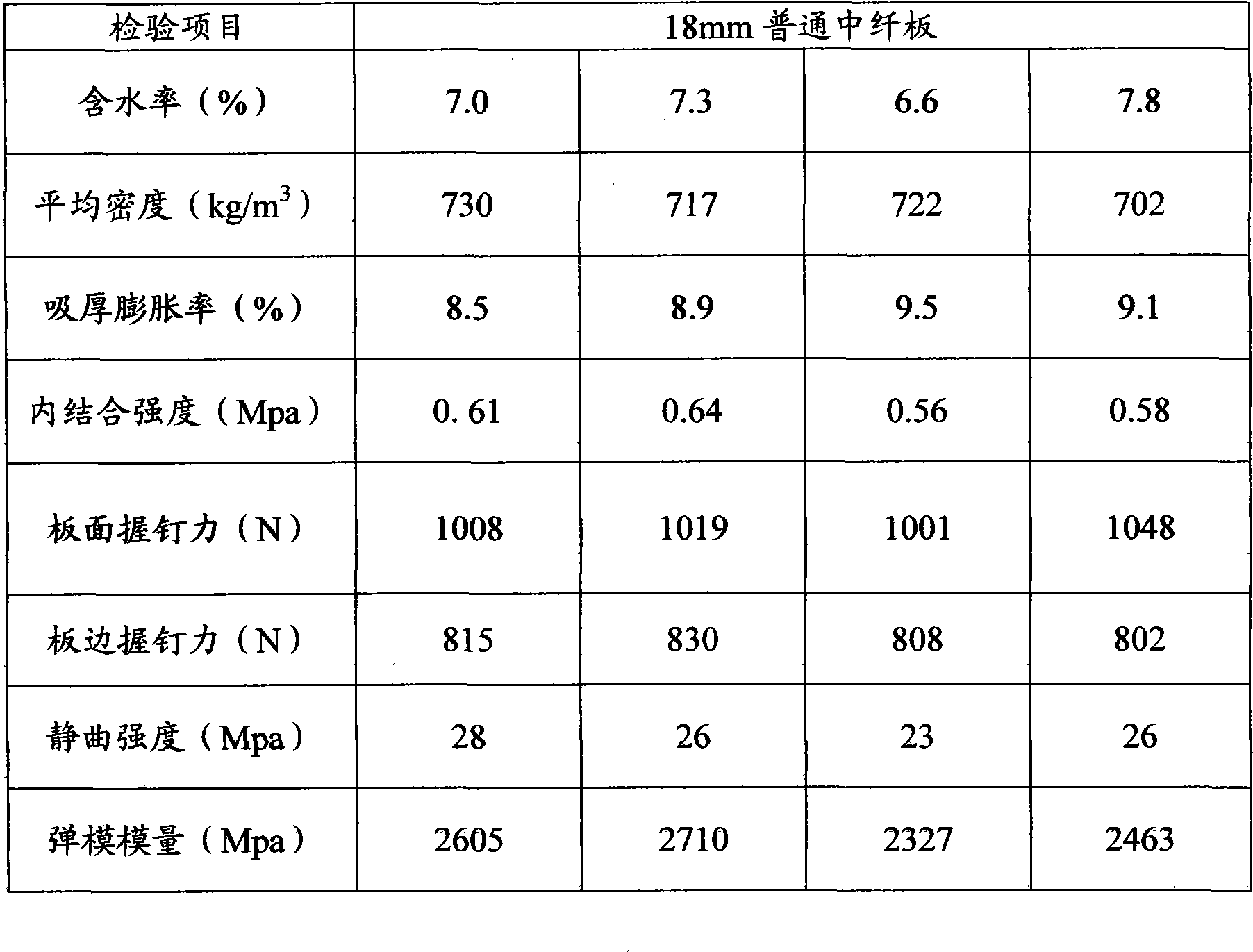
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Static bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Static bending strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com