Clear liquid complex fertilizer special for high concentration drip irrigation and method of preparing the same
A compound fertilizer and high-concentration technology, applied in the direction of urea compound fertilizer, nitrogen fertilizer, potash fertilizer, etc., can solve the problem that phosphate fertilizer cannot be topdressed, and achieve the effect of solving the shallow root system of crops, improving nutrition and reducing the amount of phosphate fertilizer used.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) In Reactor 1: Dissolve 42 parts of urea in 20 parts of hot water at 80°C, add 9 parts of 82% (V / V) liquid phosphoric acid and 10 parts of potassium chloride in sequence, and keep the temperature to obtain fertilizer liquid A .
[0026] (2) In reactor 2: dissolve 6 parts of fulvic acid in 10 parts of water, then add 2.5 parts of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, 1 part of zinc sulfate heptahydrate, 1.5 parts of boric acid, and heat to 40 ° C to fully Dissolved to obtain fertilizer solution B.
[0027] (3) In the reactor 3: Pour the fertilizer solution B into the fertilizer solution A, keep it at 80°C for 30 minutes, stir evenly after the reaction is complete, without precipitation, cool to 25°C, and obtain a yellow clear liquid that is the finished product liquid Fertilizer, ready for canning.
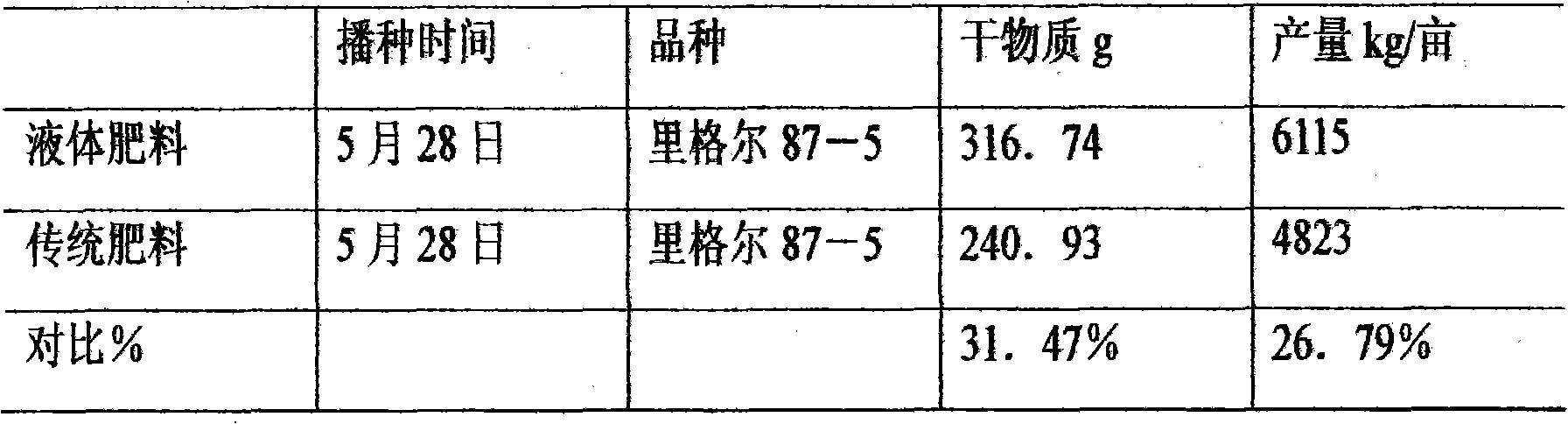
[0028] Three representative soils in Xinjiang were selected: sandy soil, loamy soil and sandy loam soil for simulation experiments. Each pot is filled with 3.5 kg of soil, and...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) In Reactor 1: Dissolve 41 parts of urea in 20 parts of 80°C hot water, add 10 parts of 84% (V / V) liquid phosphoric acid and 9 parts of potassium chloride in sequence, and keep the temperature to obtain fertilizer solution A .
[0033] (2) In reactor 2: dissolve 5 parts of fulvic acid in 10 parts of water, then add 2.5 parts of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, 2 parts of zinc sulfate heptahydrate, and 1.5 parts of boric acid, and heat to 42°C to fully Dissolved to obtain fertilizer solution B.
[0034] (3) In the reactor 3: Pour the fertilizer solution B into the fertilizer solution A, keep the reaction at 85°C for 50 minutes, stir evenly after the reaction is complete, there is no precipitation, and after cooling, a yellow clear liquid is obtained, which is the finished liquid fertilizer, that is Can be canned.
[0035]A representative calcareous loam soil in Xinjiang was selected for the simulation experiment. Each pot is filled with 20 kg of soil, and fertilizers ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) Reactor 1: Dissolve 43 parts of urea in 17 parts of 90°C hot water, add 9.5 parts of 85% (V / V) liquid phosphoric acid and 9 parts of potassium chloride in sequence, and keep the temperature to obtain fertilizer solution A.
[0040] (2) Reactor 2: Dissolve 5-6 parts of fulvic acid in 10 parts of water, then add 2-2.5 parts of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate heptahydrate, 1.5 parts of boric acid, and heat to 45°C to fully dissolve to obtain fertilizer solution B.
[0041] (3) Reactor 3: Pour the fertilizer solution B into the fertilizer solution A, keep it at 90°C for 30 minutes, stir evenly after the reaction is complete, without precipitation, and after cooling, a yellow clear liquid is obtained, which is the finished liquid fertilizer, ready for canning Pack.
[0042] Four different fertilizer treatments and one blank control were set up in the experiment: 1. All base fertilizer of traditional fertilizer, 2. All base fertilizer of liquid fe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com