Non-copious cooling lower carbon number hydrocarbons separation method containing light gas
A separation method and technology for low-carbon hydrocarbons, which are applied in the fields of oxide conversion to produce olefins and hydrocarbon cracking to produce olefins, and can solve the problems of high energy consumption and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
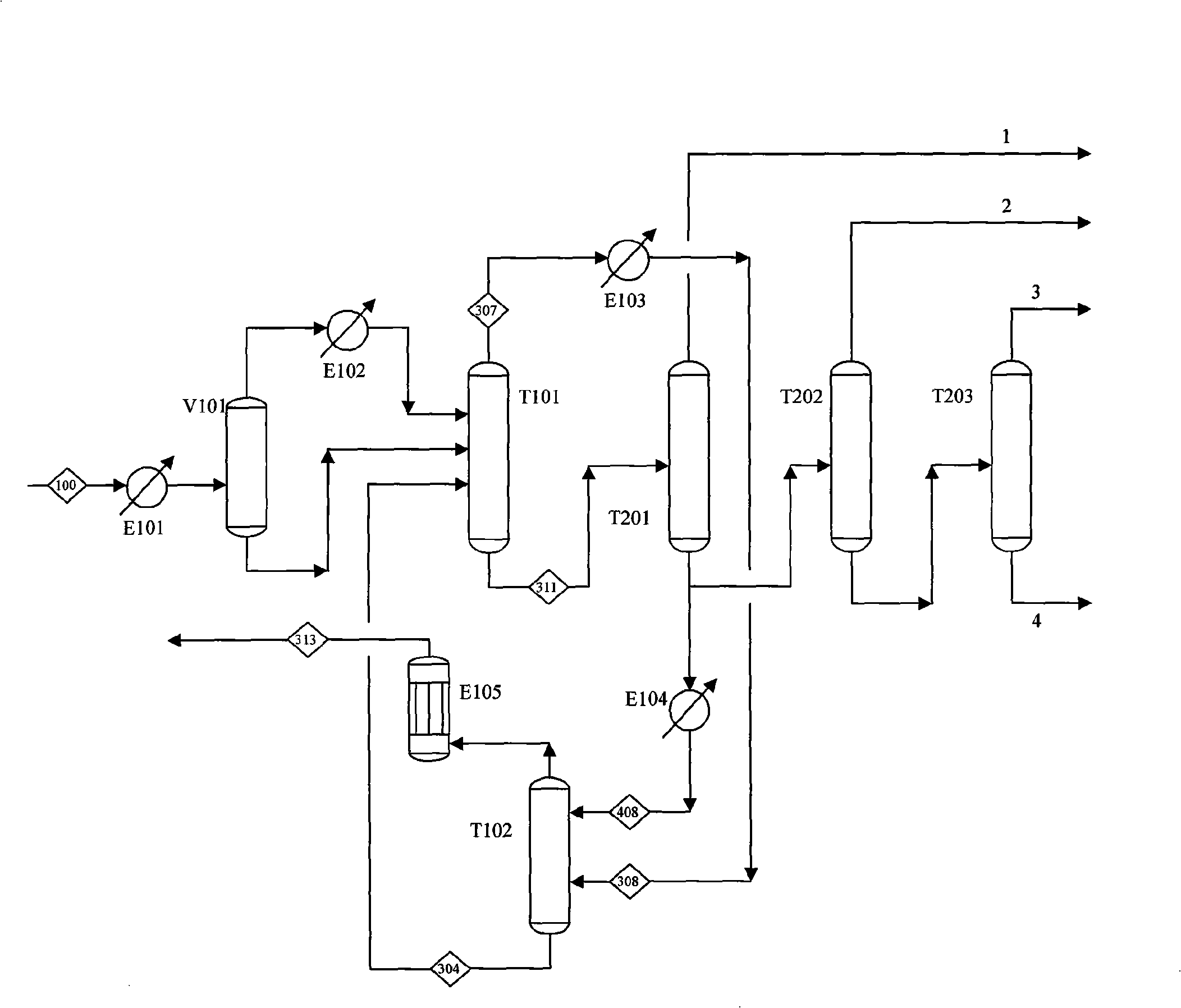
[0054] see process figure 1 , the outlet gas of a reactor enters the separation process after compression, water washing, alkali washing, removal of methanol and drying and dehydration. The gas S100 is cooled to about 10°C by the feed cooler E101 and enters the flash tank V101 for gas-liquid phase separation. The gas-liquid phase is further cooled to 0°C and -20°C by the feed cooler E102 of the pre-cutting tower respectively, and then enters the pre-cutting tower T101. The top product S307 of the pre-cutting tower T101 contains all light gases and ethylene accounting for about 24% of the feed. The output from the tower top enters the absorption tower T102 after being cooled by -60°C ethylene refrigerant in the feed cooler E103 of the oil absorption tower. Absorption tower T102 uses carbon three-based absorbent S408 to absorb carbon two in the feed. The gas at the top outlet of the absorption tower T102 is then cooled with -60°C ethylene refrigerant in the oil absorption tow...
Embodiment 2
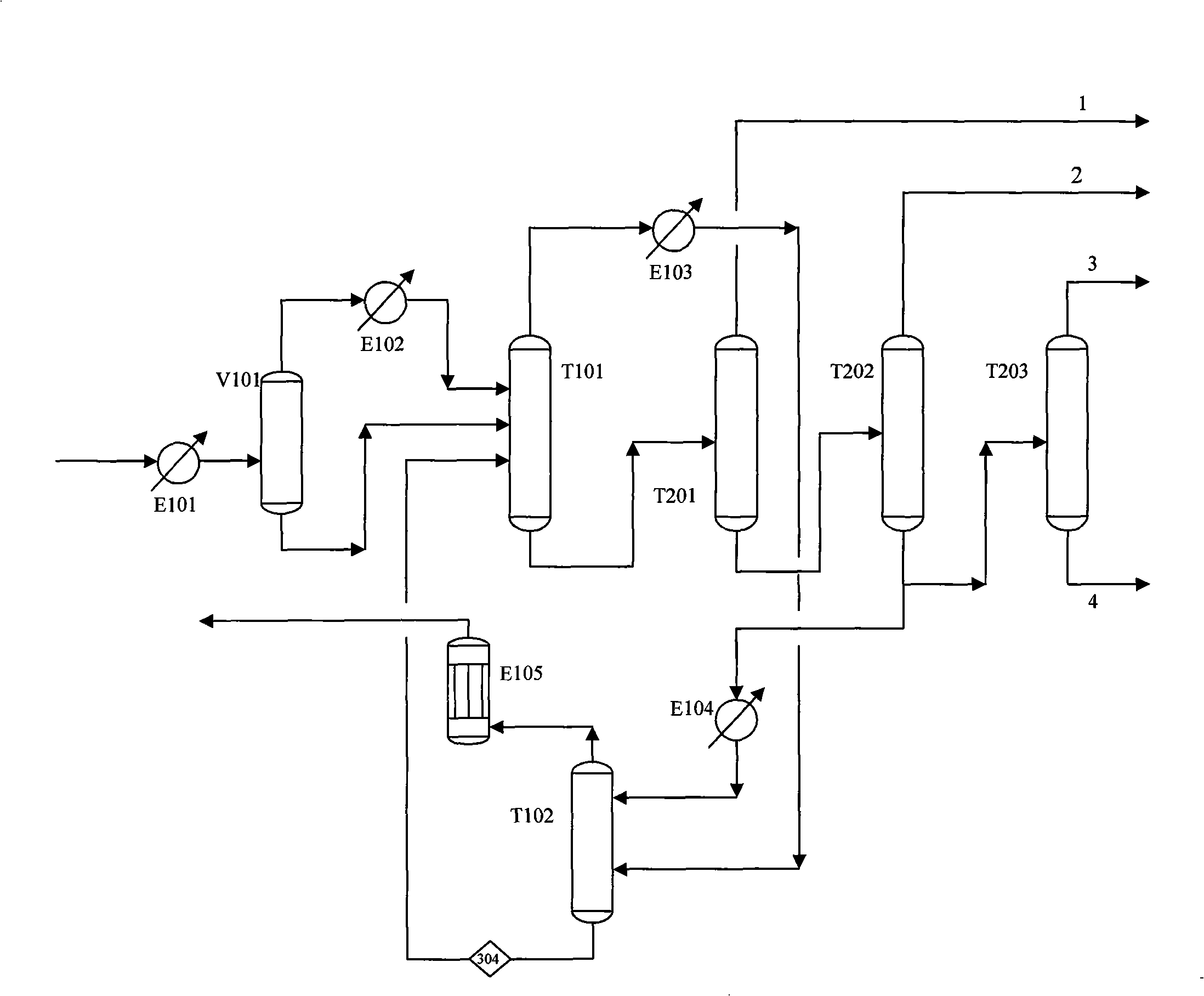
[0059] see process image 3, the outlet gas of a reactor enters the separation process after compression, water washing, alkali washing, removal of methanol and drying and dehydration. The gas S100 is cooled to about 10°C by the feed cooler E101 and enters the flash tank V101 for gas-liquid phase separation. The gas-liquid phase is further cooled to 0°C and -19°C by the feed cooler E102 of the pre-cutting tower respectively, and then enters the pre-cutting tower T101. The top product S308 of the pre-cutting tower T101 contains all light gases and ethylene accounting for about 27% of the feed, and enters the absorption tower T102 after being cooled in the feed cooler E103 of the oil absorption tower with -60°C ethylene refrigerant. The absorption tower T102 uses an absorbent (S408) with carbon five as the main component to absorb carbon two in the feed. The discharge S311 of the pre-cutting tower T101 tower kettle is C2, C3 and heavier products, which are directly sent to the...
Embodiment 3
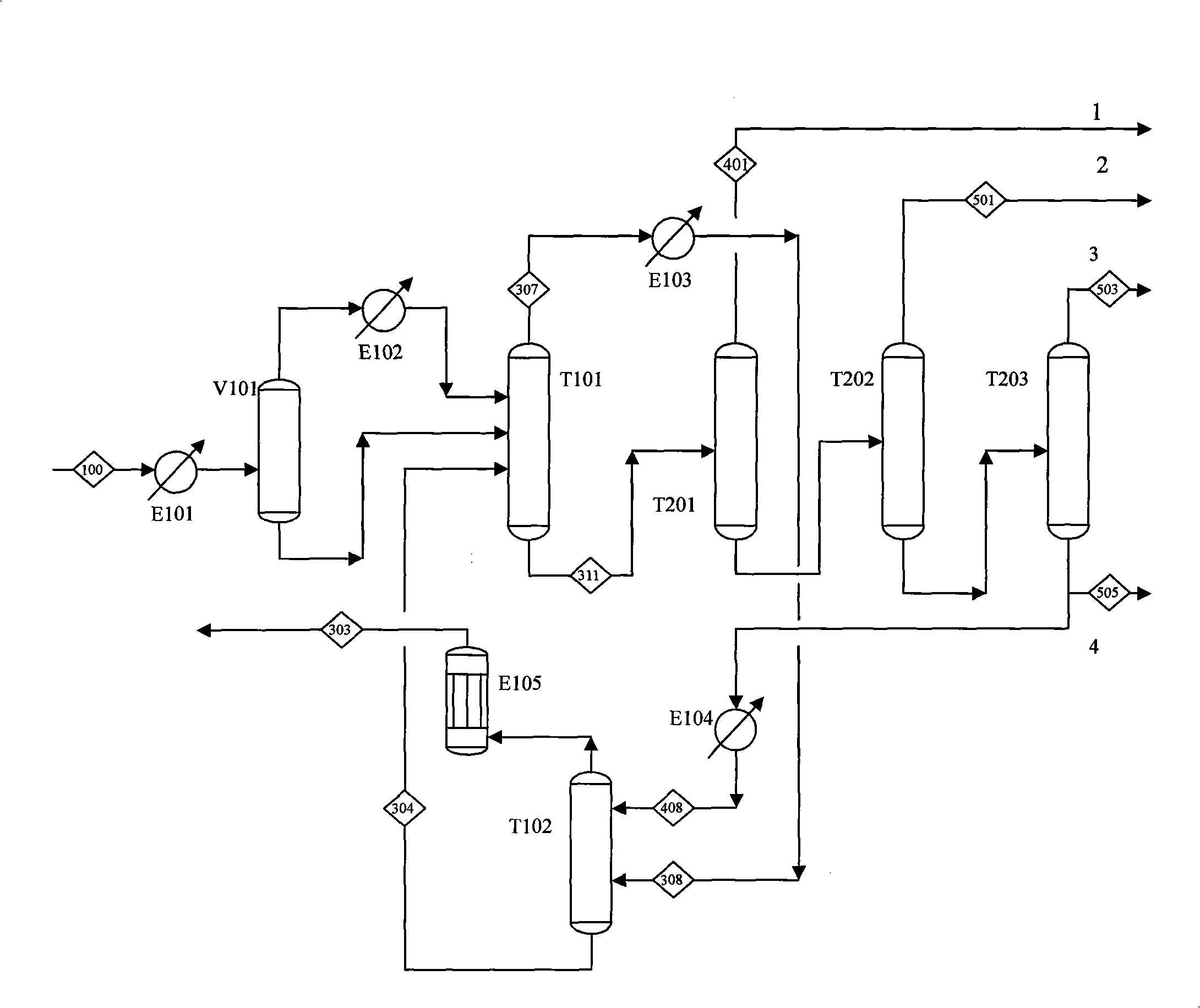
[0065] see process Figure 4 , the outlet gas S100 of a certain reactor enters the high-pressure depropanizer T202A after being compressed, washed with water, washed with alkali, dried and dehydrated. The top gas of the high depropanizer T202A is further pressurized to 3.6Mpa and then enters the acetylene hydrogenation reactor to remove alkynes. The material after removing acetylene is cooled to 2°C to obtain a gas-liquid two-phase, and the gas-liquid phase is further cooled separately. The gas phase enters the pre-cutting tower T101, and the liquid phase is divided into two parts, one part is used as the reflux of the high-pressure depropanizer T202A, and the other part is fed into the pre-cutting tower T101. The top product of the pre-cutting tower T101 is sent to the absorption tower T102 after cooling S308. The tower uses carbon three as an absorbent to absorb the carbon two hydrocarbons in the top product of the pre-cutting tower. The gas at the top of the absorption tow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com