Therapeutic hepatitis b vaccine and preparation method and use thereof
A hepatitis B vaccine and therapeutic technology, applied in peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete antiviral treatment and difficult removal, so as to avoid immune escape, strong antigenicity, and overcome less antigenic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Preparation of polypeptide epitope
[0039] The preparation of polypeptides uses the Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis method. First, an amino acid protected by an Fmoc group on the α-amino group is connected to an insoluble carrier through an arm, and then the α-amino group is deprotected, and the amino acid is washed with a solution- Arm - Resin. The second pre-activated α-amino protected amino acid is connected through a coupling reaction. After the condensation reaction is completed, it is washed with a solution, and the deprotection and coupling are repeated until the target peptide is obtained. Finally the peptide-arm-resin is cleaved. Peptide purification, using HPLC method, the crude peptide product is separated and purified by C18 high-pressure column, and the required effluent is tracked and collected by liquid chromatography, the sample peaks are combined, desalted, and freeze-dried to obtain a high-quality peptide. The following takes the prepar...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 Quality Control of Polypeptide Epitopes
[0077] Quality control testing items for peptide epitopes include: appearance, purity and molecular weight.
[0078] Appearance of the polypeptide: the appearance of the prepared epitope peptide should be white powder; chromatographic analysis of the polypeptide: use RP-HPLC to analyze the polypeptide, chromatographic conditions: Waters company C18 chromatographic column (250×4.6mm, 5μm, 10nm). Mobile phase A (acetonitrile with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid). Mobile phase B (water with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid). Linear gradient elution: 0.01 to 20.00min, B from 35% to 50%, flow rate: 1.0ml / min. Detection wavelength: 220nm. Injection volume: 10 μl. Column temperature: room temperature. Quality requirements: purity>98%; mass spectrometry identification of peptides: dissolve the sample into a 0.05 mg / ml solution with 30% acetonitrile aqueous solution. Take 0.51 points on the sample plate, and use 0.5 μl HCCA as the matri...
Embodiment 3
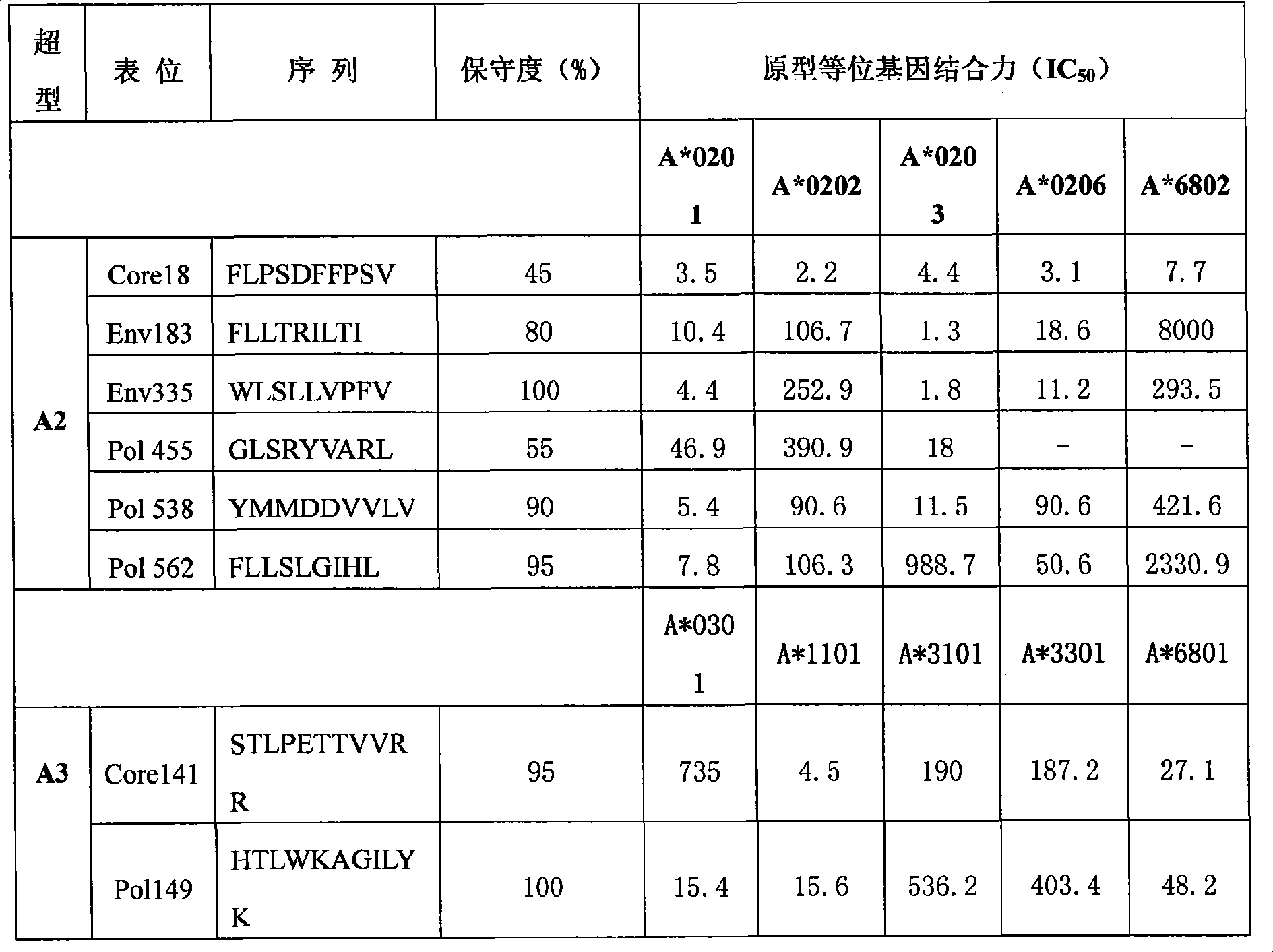
[0081] Example 3 Screening of polypeptide epitopes
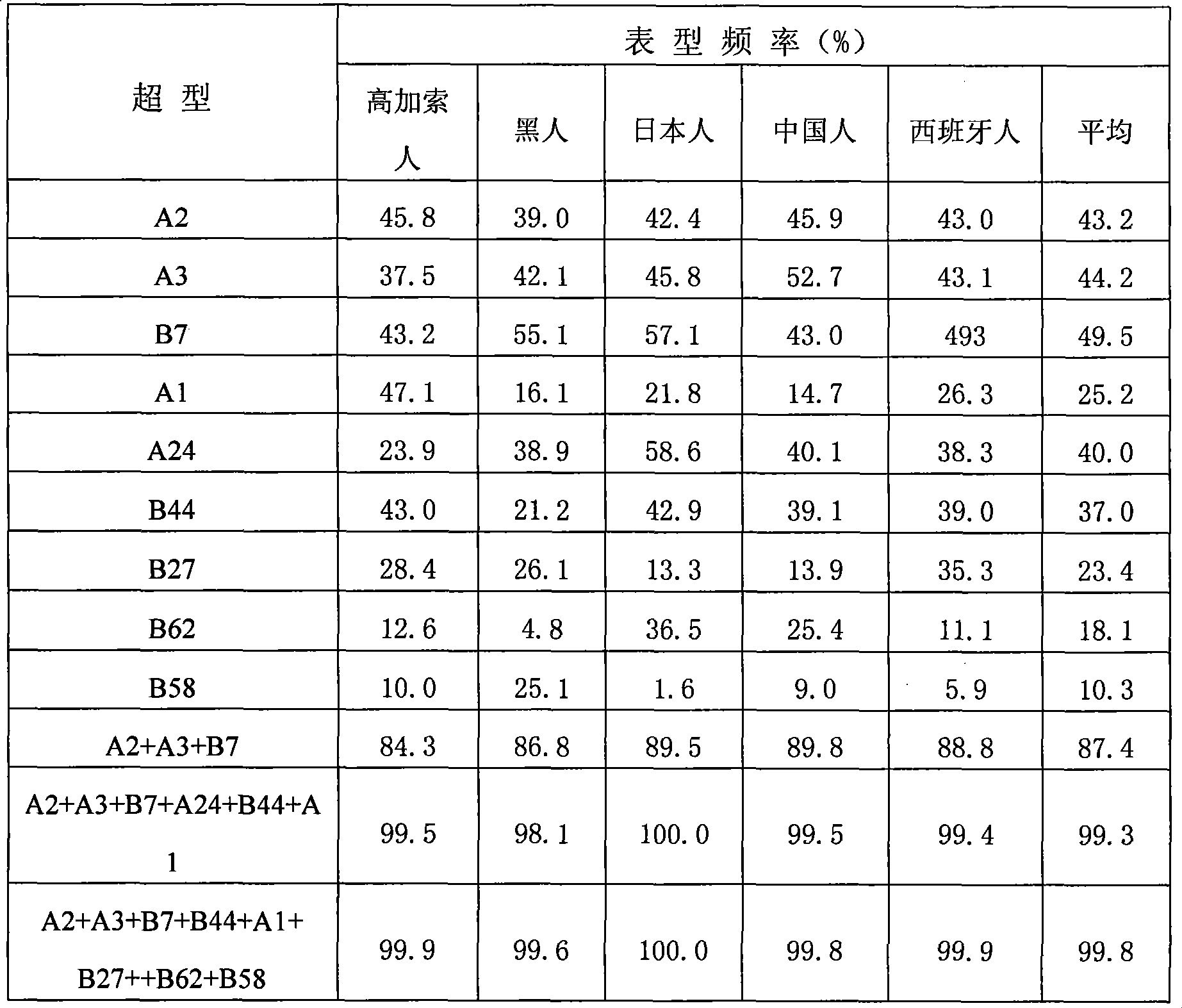
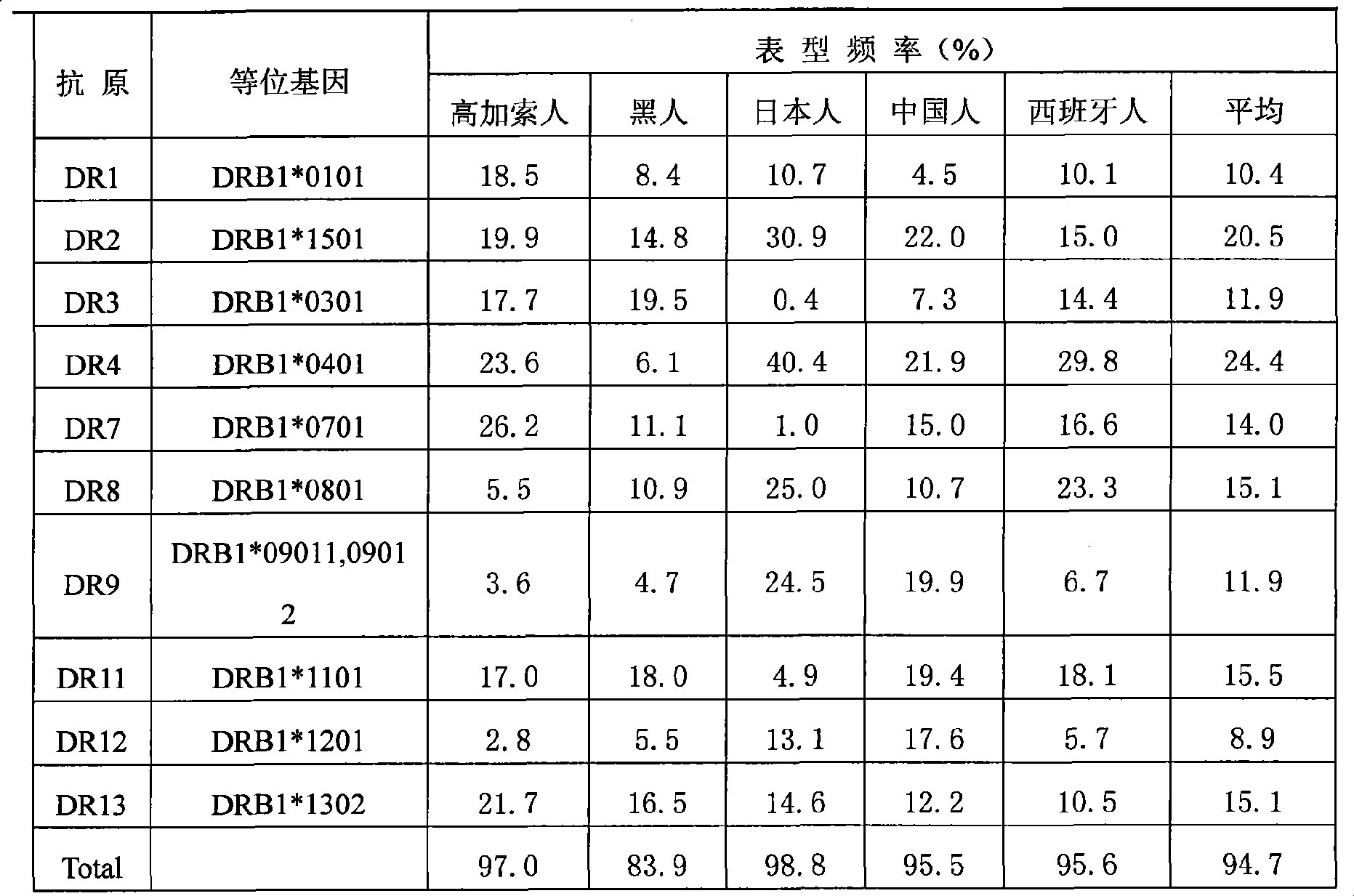
[0082] At present, the design of hepatitis B therapeutic vaccine tends to cover most of the population. Only in this way can it be effective for most of the population and have better commercial value. Broad coverage can be achieved by selecting epitope peptides with high affinity to HLA supertypes that are highly expressed in the overall population.
[0083] HLA class I molecules can bind to multiple overlapping but independent peptides. According to the characteristics of the bound peptides, most HLA class I molecules can be classified into several major HLA class I supertypes. By examining the ability of these epitopes to bind to all or most HLA molecules of a specific supertype, the epitopes required for the preparation of effective multi-epitope vaccines can be screened. Selecting the population with the widest coverage and targeted selection of the most common HLA supertypes in some populations is conducive to the rat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com