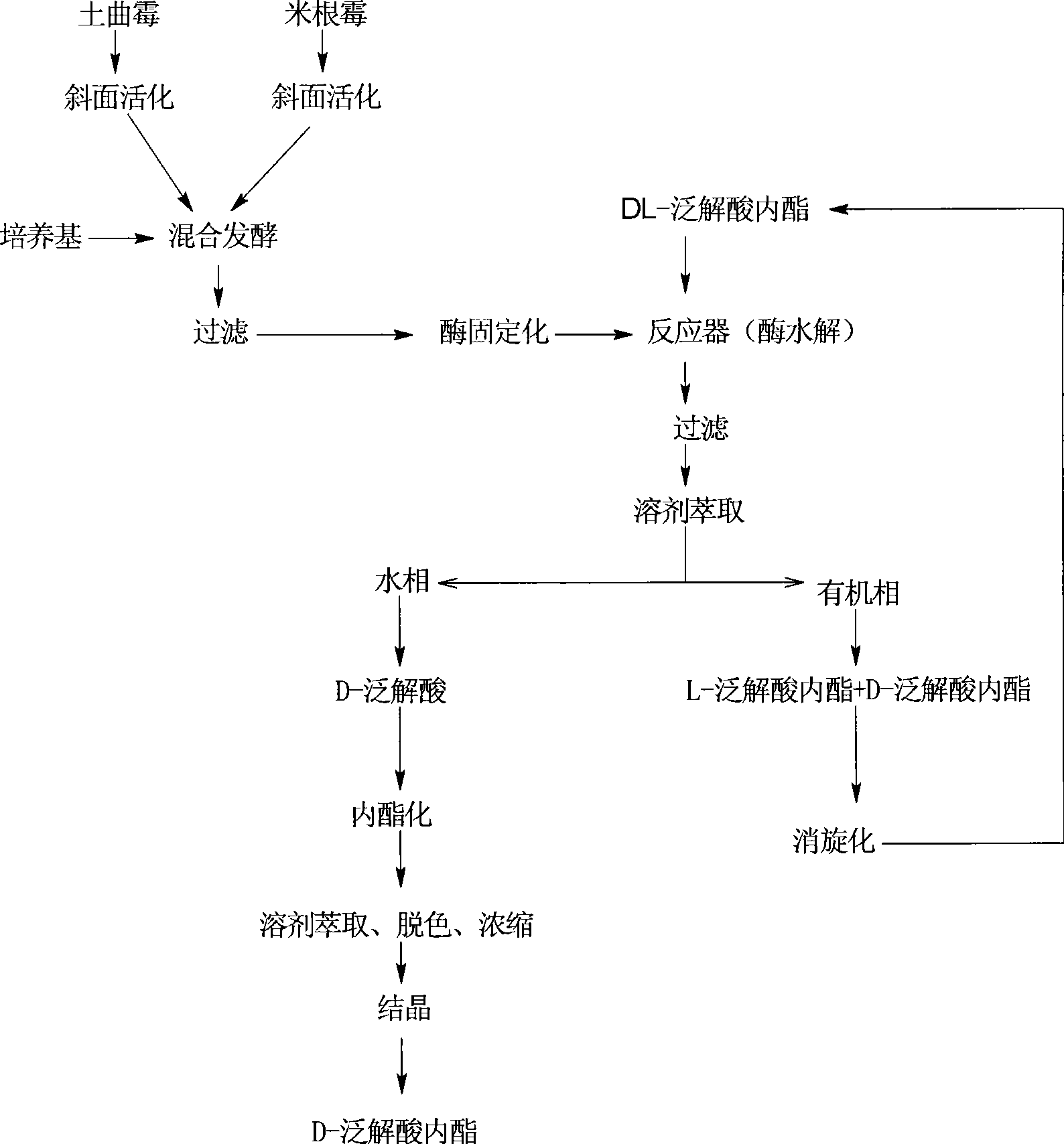Method for preparing D-pantolactone by microbe mixed fermentation method
A pantolactone and mixed fermentation technology, which is applied in the field of microbial mixed fermentation to prepare D-pantolactone, can solve the problems of high total product yield and short hydrolysis time, and achieves short enzymatic conversion time and fermentation time. Short, efficient effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Slope culture: the medium is 160mL of potato juice (20%), 8g of sucrose, 8g of agar, 4g of peptone, 4g of yeast extract, about pH 7.0, set the volume to 800mL, sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, cool down and inoculate after sterilization , with Aspergillusterrus DH-069 as the small bacterium and Rhizopus oryzae QY-022 as the associated bacterium, the inoculum area of the strains Aspergillus terreus and Rhizopus oryzae was 1cm 2 , Cultivated at 26°C for 3 to 6 days, used as slant activated seeds.
[0038] Enzyme production culture: the medium is 1% sucrose, 0.5% peptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 0.5% corn steep liquor, about pH 7.0, the liquid volume is 100mL / 500mL triangular flask, sterilized at 121°C for 30 minutes, after sterilization Cool and inoculate separately, and cultivate at 26°C for 3 to 5 days as a fermented enzyme liquid.
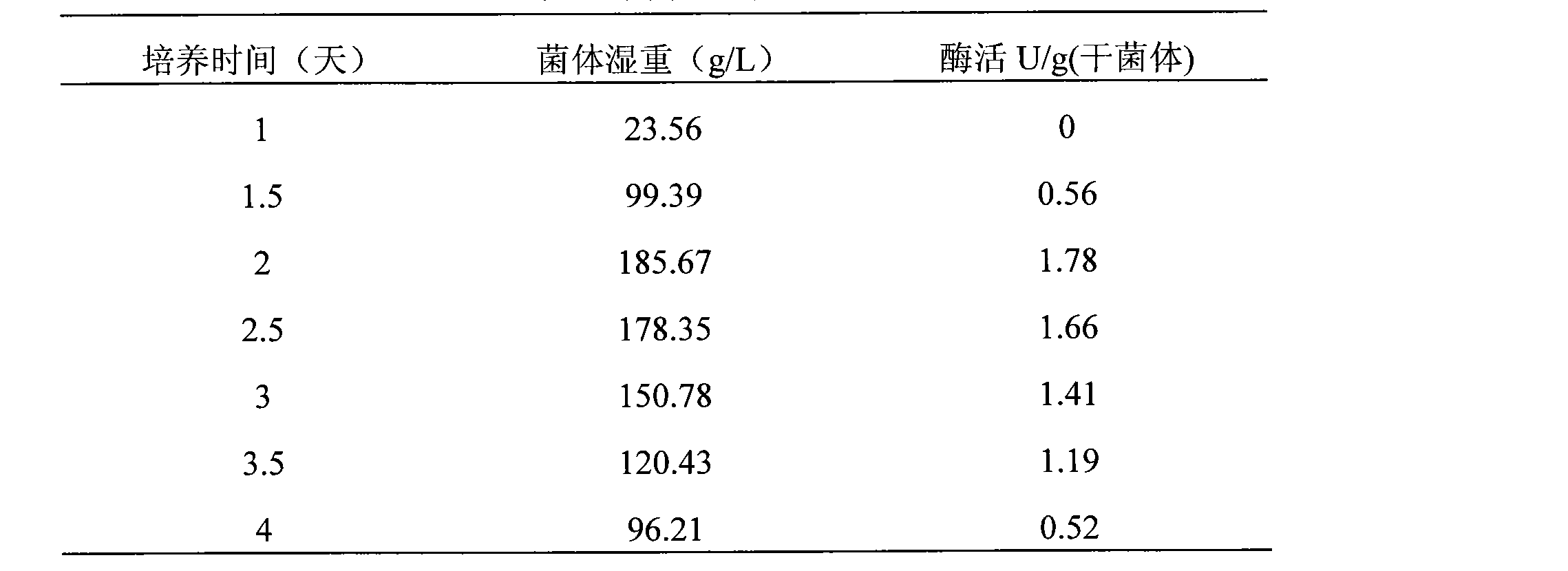
[0039] The shake flask experiment results are as follows (Table 1). It can be seen from Table 1 that the enzyme activity reached the hig...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The chemically synthesized DL-pantoacid lactone was used as the substrate, with 50mmol CaCl 2 The aqueous solution is prepared into a 30% concentration as the substrate: add the wet thallus prepared by the method of Example 1, the addition amount is 0.3U / g pantothenolactone, put it on a shaking table at 26°C, react at 160r / min, and take samples every 20min High-pressure liquid chromatography analysis and specific rotation determination, and the pH of the reaction solution was adjusted to 7.0 with concentrated ammonia water, and the enzymatic hydrolysis time was 5 hours. The mycelium filtered out after the reaction was finished was added with a new reaction substrate to continue the reaction. This was repeated and reused 8 times. The obtained enzymatic hydrolysis results are shown in Table 2. The results in Table 2 show that after repeated 8 times of enzymatic hydrolysis, the obtained enzyme conversion rate is about 40%, and the specific rotation of the product D-pantola...
Embodiment 3
[0048] According to example 1 method, ferment and produce enzyme, get wet mycelium 100g, press water: mycelia: glutaraldehyde=25: 3: 0.5, keep stirring 4~6 hours under 4 ℃, after immobilization finishes, weigh The immobilized mycelium that weighs about 100g left and right, with this immobilized mycelium, carry out enzymatic hydrolysis by the example 2 method. The results of repeated batch enzymatic hydrolysis for 10 times are shown in Table 3.
[0049] Table 3 Results of repeated batch enzyme transformation of immobilized cells
[0050] conversions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Conversion rates(%) 39.9 41.9 43.4 41.7 41.1 41.9 40.9 42.8 42.3 41.2
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific rotation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com