Polyethyleneglycol modified aprotinin and preparation thereof
A technology of polyethylene glycol and aprotinin, which is applied in the field of chemically modified aprotinin and its preparation, can solve the problems of short half-life and achieve the effects of improving specific activity, low immunogenicity and good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Aprotinin modified with methoxypolyethylene glycol succinimidyl propionate 5000 (mPEG-SPA-5000)
[0060] Choice of reaction temperature: Take 2ml of 1.0mg / ml aprotinin solution, add 2ml of phosphate buffer to make the pH of the solution 7.0, then add 4.0mg of mPEG-SPA-5000 solid, dissolve, mix well, take 0.3 for each ml was placed in 4 test tubes with stoppers, and then placed at 4°C, 10°C, 25°C and 37°C for 30 minutes to stop the reaction. Compare the modification rate and determine the modification condition. The results showed that polyethylene glycol-modified aprotinin could be obtained at these temperatures, and the modification rate was the highest at 25°C. See Table 1 for specific data.
[0061] Table 1: Effects of different temperatures on the modification rate of aprotinin
[0062] temperature 4℃ 10℃ 25℃ 37℃ Modification rate (%) 28 24 46 38
[0063] Choice of reaction time: Take 2ml of 1.0mg / ml aprotinin solution, add 2ml of phosp...
Embodiment 2
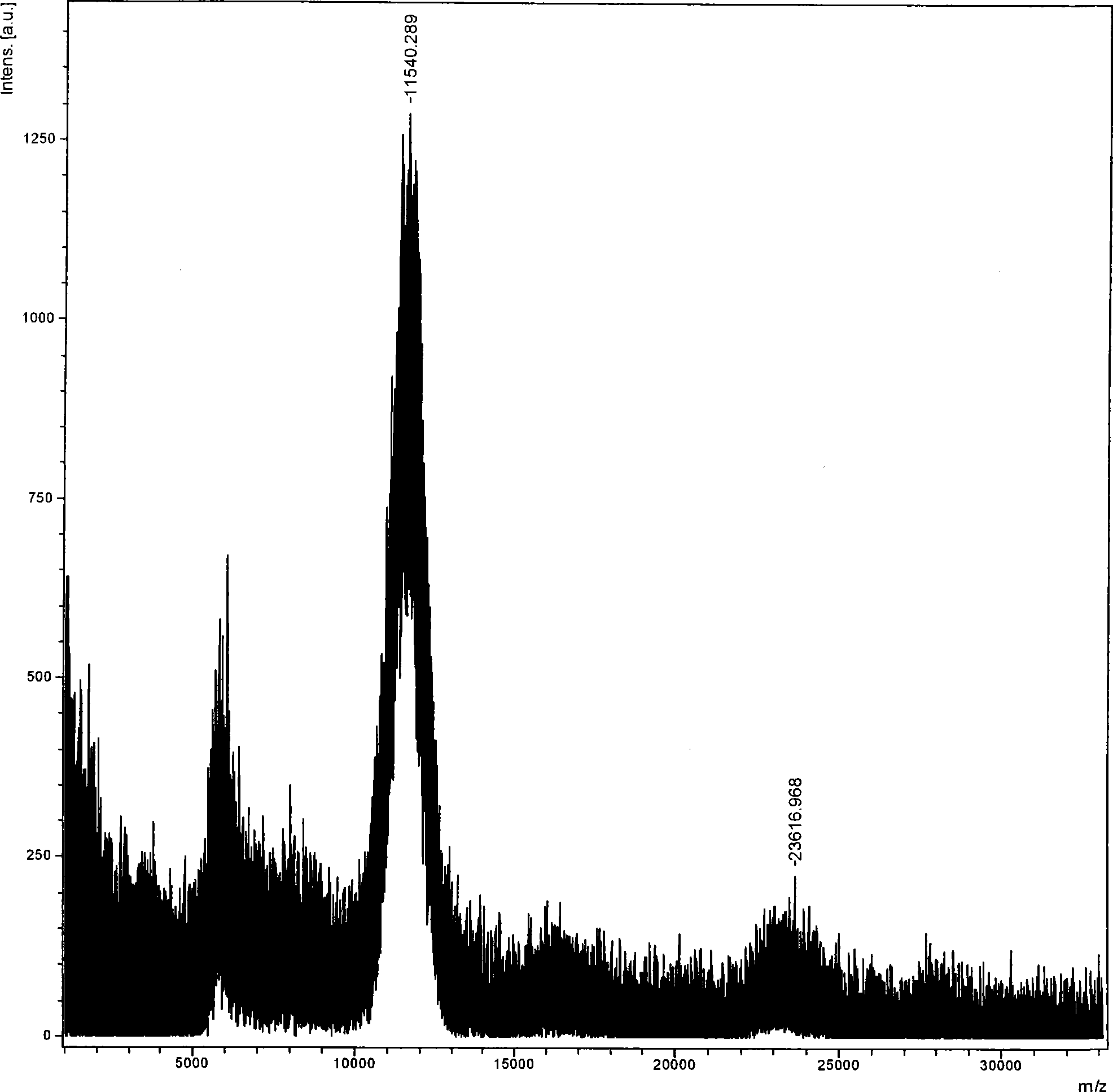
[0070] Isolation, Purification and Identification of Polyethylene Glycol Modified Aprotinin
[0071] Take 10ml of 1.0mg / ml aprotinin solution, add about 5ml of phosphate buffer to make the pH of the solution 7.0, then add 16mg of mPEG-SPA-5000 solid, dissolve, mix well, react at 25°C for 30min, add 3 g of glycine solids terminated the reaction.
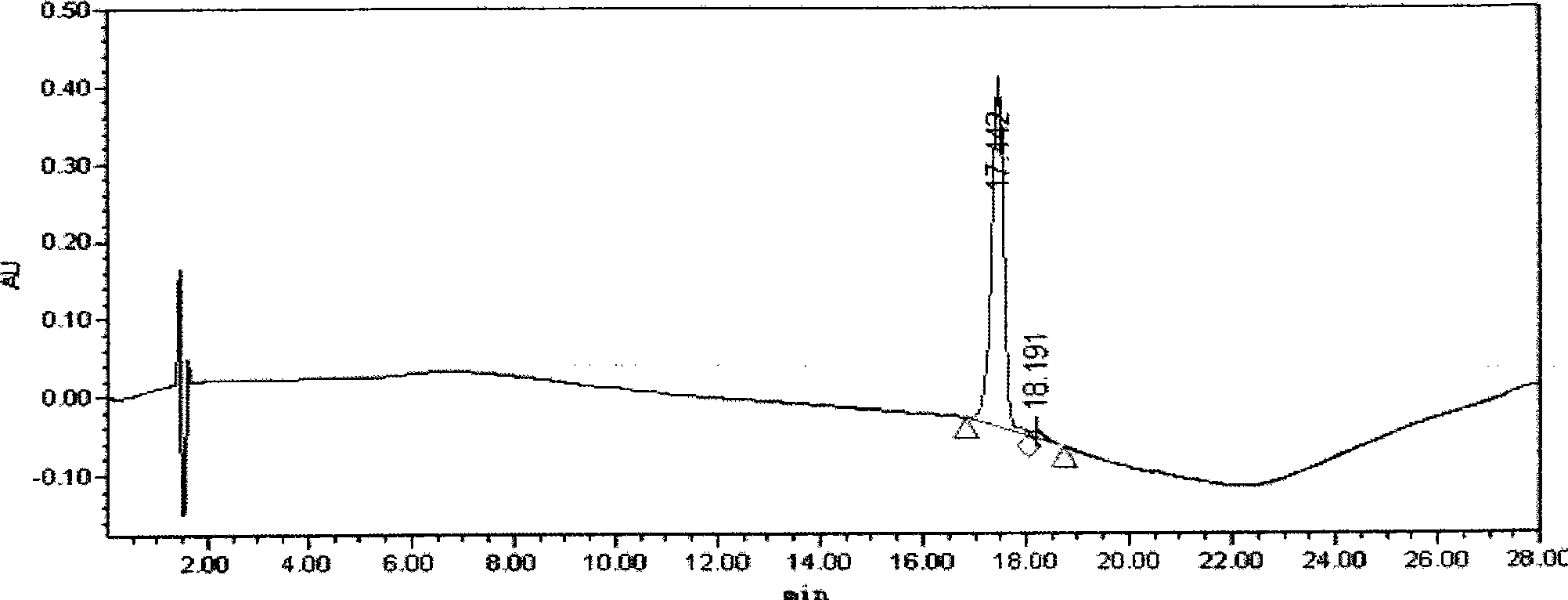
[0072] The above reaction solution was taken, dialyzed against 0.05 mol / L, Tris-HCl buffer solution with pH 6.0, concentrated to 5 ml with an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 3000, and separated on a column. The chromatographic conditions are as follows:
[0073] Chromatography medium: SOURCE 30S
[0074] Column volume: 5ml
[0075] Flow rate: 3.0ml / min
[0076] Column equilibration: equilibrate 5 times column volume with 0.05mol / L, Tris-HCl (starting buffer) with pH 6.0
[0077] Sample volume: 5ml
[0078] Elution: First use 3 times the column volume of starting buffer to elute the unadsorbed part, an...
Embodiment 3
[0083] Determination of biological potency of aprotinin and polyethylene glycol-modified aprotinin (method see Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2005 Part II: aprotinin)
[0084] According to the titer determination method of aprotinin in Pharmacopoeia, the titer of aprotinin and polyethylene glycol-modified aprotinin was determined, and then the specific activity (U / mg) of the sample was calculated. The titer test showed that the specific activity of the polyethylene glycol-modified aprotinin not only did not decrease, but also increased nearly 1-fold. The specific results are shown in Table 4.
[0085] Table 4 Aprotinin and polyethylene glycol-modified aprotinin biopotency assay results
[0086]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com