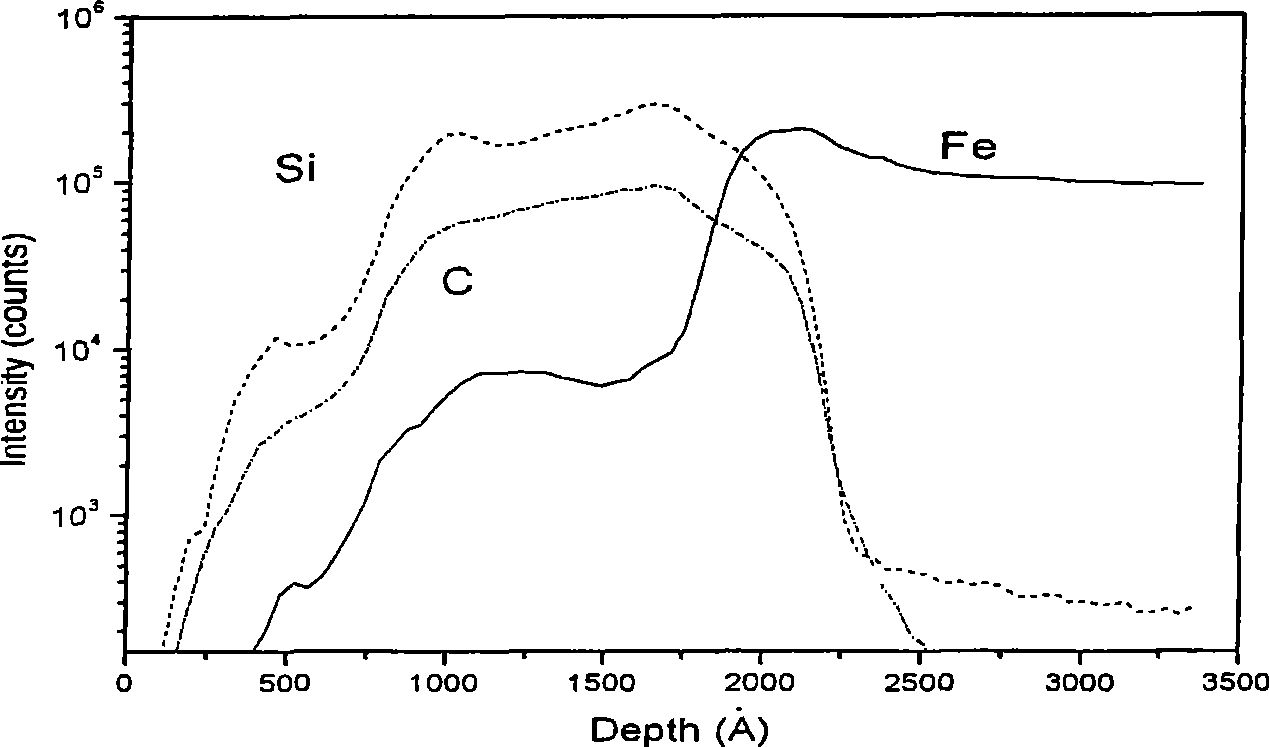
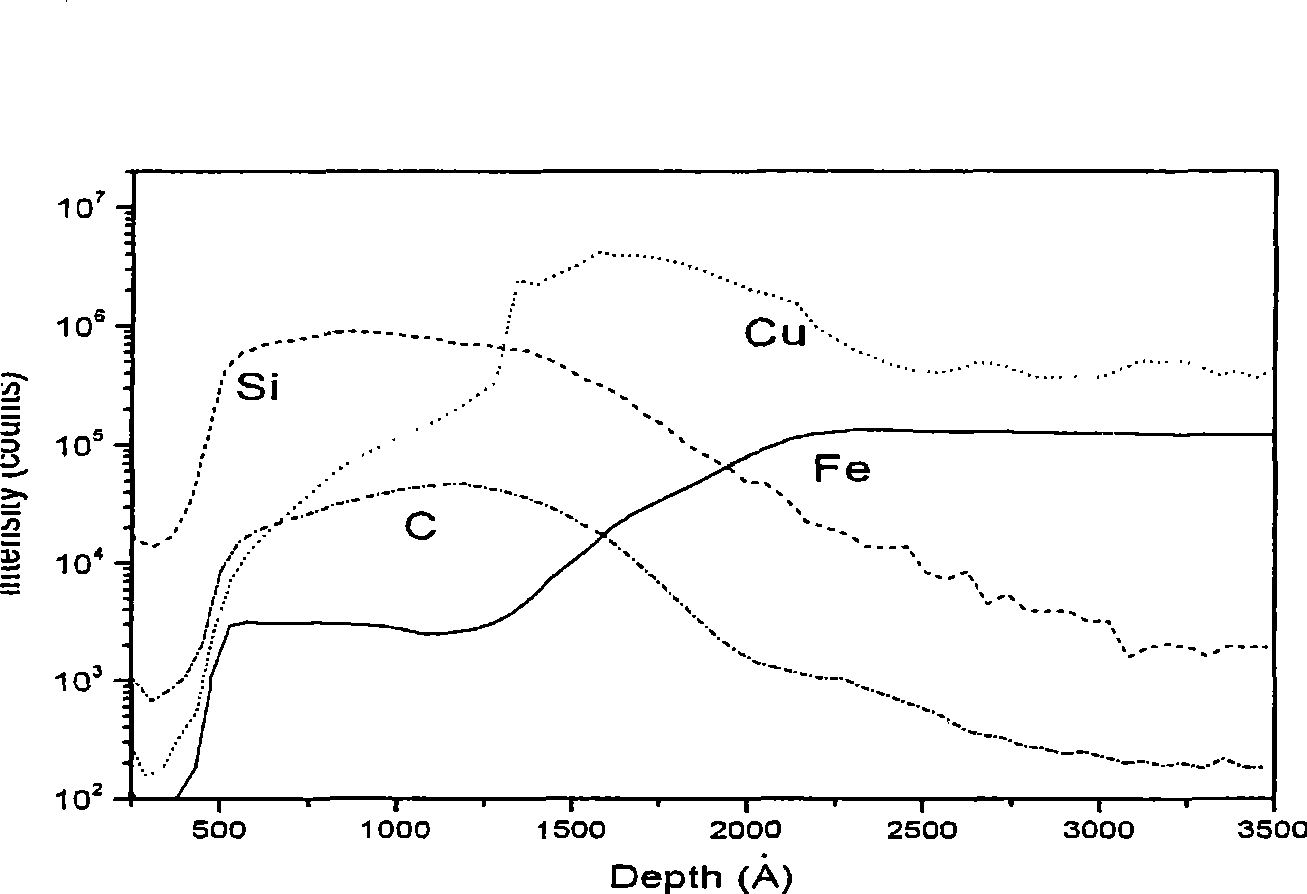
Method for improving adhesive performance of SiC-C hydrogen (tritium) resistance coatings to matrix metal material
A substrate and coating technology, applied in the field of nuclear technology and application, to achieve the effect of improving the interface structure and improving the interface bonding performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment example 1
[0017] 1) The stainless steel material is used as the substrate. After the surface of the substrate is conventionally ground and polished, it is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and deionized water, dried, and then placed in a vacuum studio.
[0018] 2) The background vacuum reaches 6×10 -4 After Pa, use Ar first + The ion beam sputters and cleans the sample at an angle of 45 degrees, Ar + The ion beam energy is 3-5keV, and the beam current is 5-10mA.
[0019] 3) Deposit a Cu layer with a thickness of 20nm by DC magnetron sputtering, use argon ion bombardment to mix Cu and Fe elements, Ar + The ion energy is 40keV, the dose is 1×10 16 ions / cm 2 .
[0020] 3) A SiC-C coating with a thickness of 40nm is deposited by intermediate frequency magnetron sputtering, the conditions are: beam current 150mA, voltage 500-600V, duty cycle 62.5%, and then the coating is bombarded with an argon ion beam from the vertical direction, and the ion energy is 40keV, bombardment dose 1×10 ...
Embodiment example 2
[0023] 1) The stainless steel material is used as the substrate. After conventional grinding and polishing, ultrasonic cleaning and drying, the surface of the substrate is placed in a vacuum studio.
[0024] 2) The background vacuum reaches 6×10 -4 After Pa, the sample is cleaned by sputtering by electron beam heating and scanning. The energy of the electron beam is 20KeV, and the current density of the electron beam is about 8×10 4 W / cm 2 , scanning speed is 5mm / min
[0025] 3) Deposit a Cu layer with a thickness of 10nm by the method of intermediate frequency magnetron sputtering, and then bombard it with argon ions, the energy of Ar+ ions is 30keV, and the dose is 1×10 16 ions / cm 2 .
[0026] 3) A SiC-C coating with a thickness of 40nm is deposited by intermediate frequency magnetron sputtering, the conditions are: beam current 150mA, voltage 500-600V, duty cycle 80%, and then the coating is bombarded with an argon ion beam from the vertical direction, and the ion energ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com