Glucose dehydrogenase
A technology of glucose dehydrogenase and glucose concentration, applied in the direction of enzyme, enzyme stabilization, oxidoreductase, etc., to achieve the effect of high-efficiency production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
[0197] In the first embodiment, the present invention is a eukaryotic-derived glucose dehydrogenase that catalyzes the following reaction.
[0198] D-glucose + electron transport substance (oxidized form) →
[0199] D-glucono-δ-lactone + electron transport substance (reduced form)
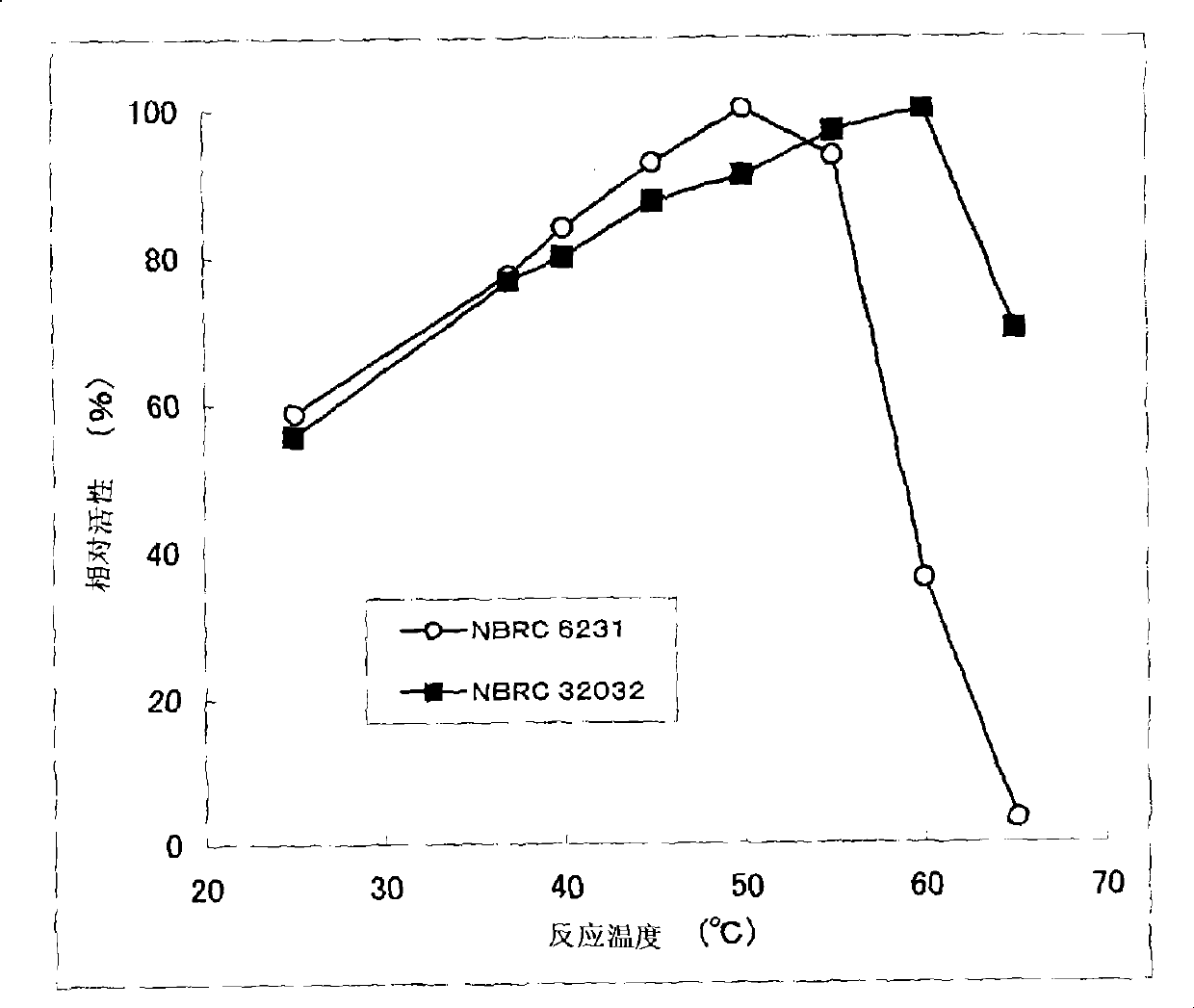
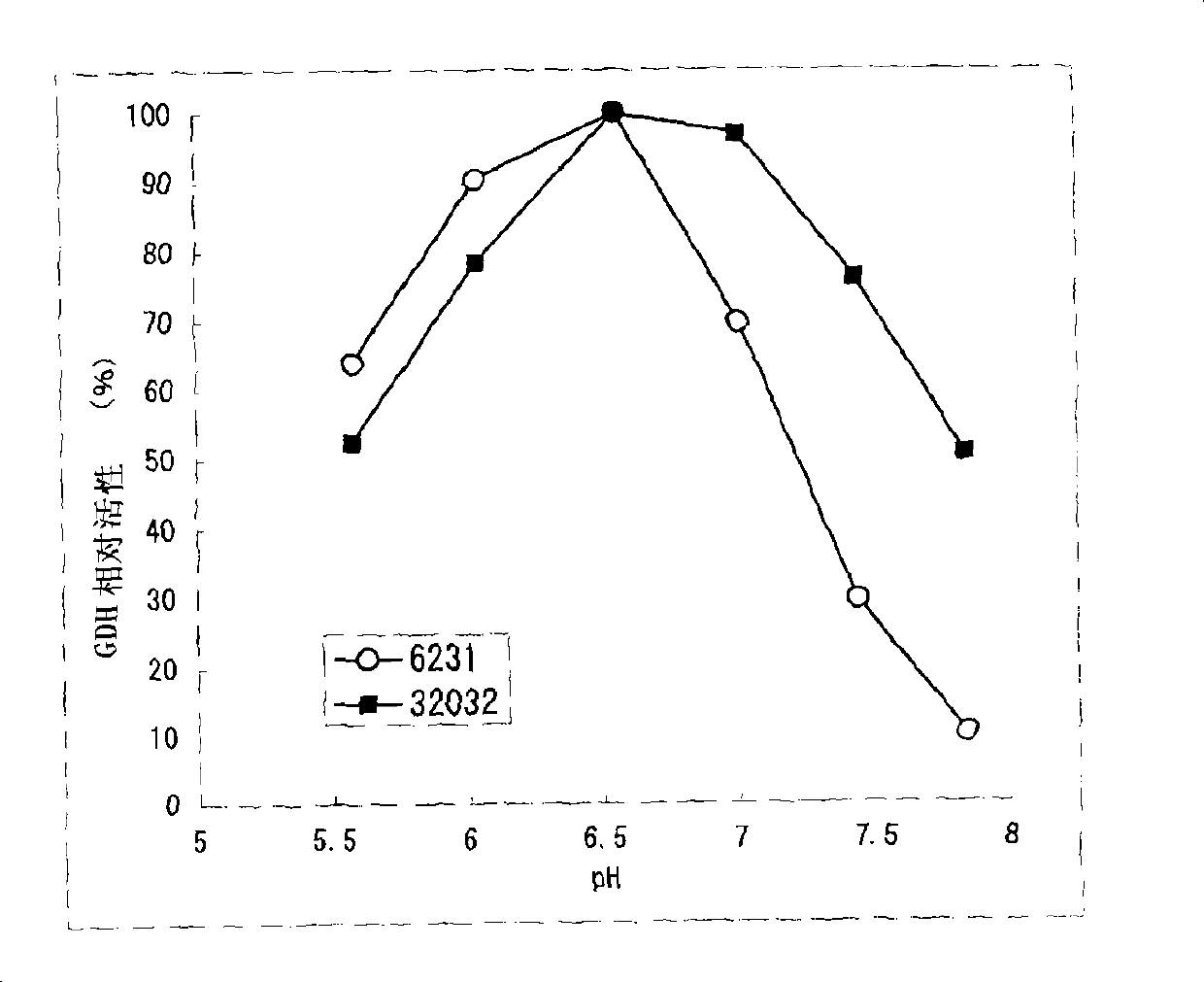
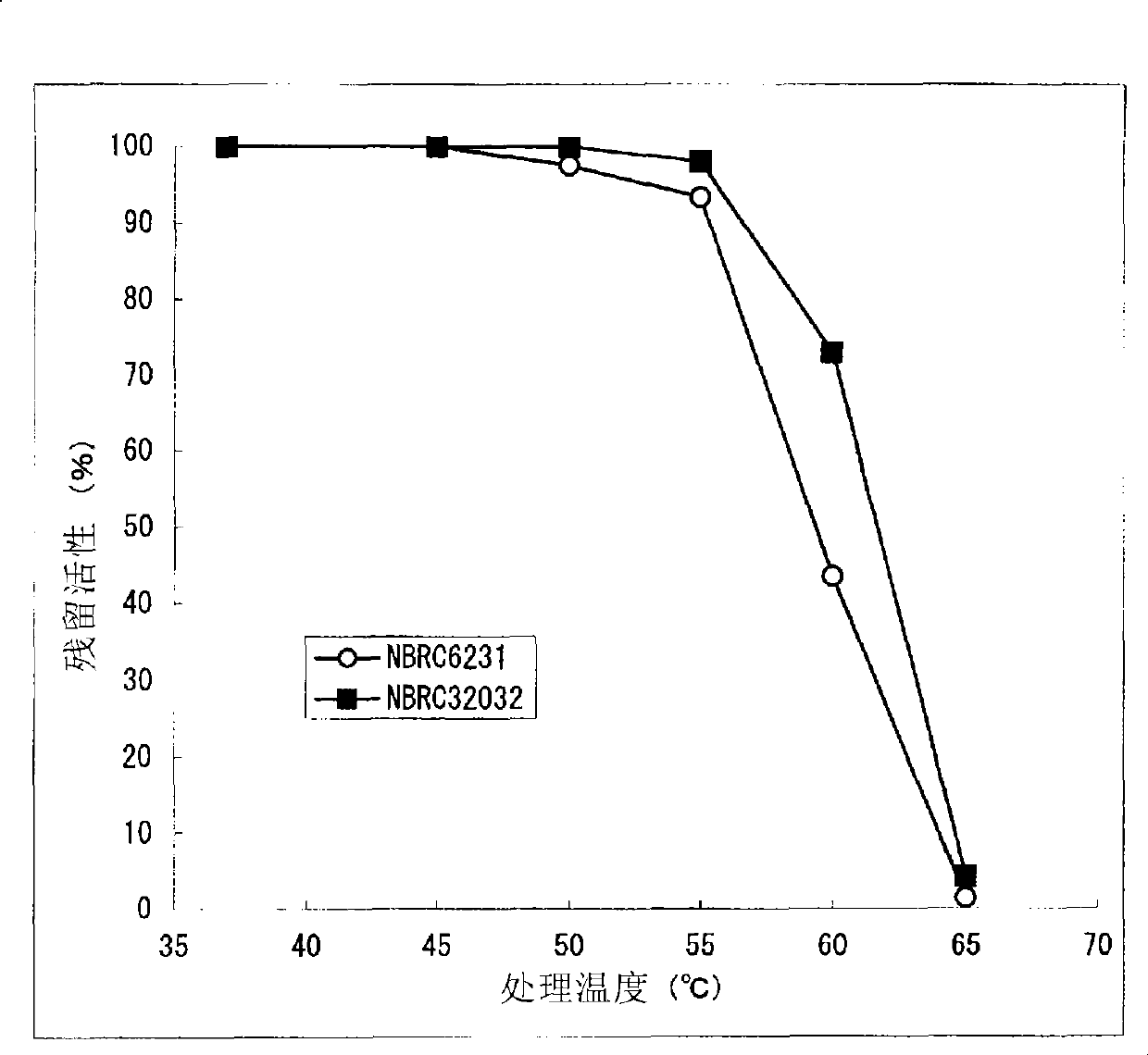
[0200] The present invention is characterized by high heat resistance, which is different from the known eukaryotic-derived GDH in this point. Compared with the residual activity of Aspergillus terreus-derived GDH, which is excellent in stability among known eukaryotic-derived glucose dehydrogenases, after heating at 55°C for 15 minutes (residual activity when the activity before heating treatment is 100%) rate) was 60%, whereas the residual activity of the GDH of the present invention after heat treatment at 55°C for 15 minutes was 90% or more. Furthermore, the GDH of the present invention preferably maintains GDH activity even after being treated at 60°C for 15 minutes, more preferably the resi...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0247] In order to achieve the above object, the present inventors discovered a gene DNA presumed to be glucose dehydrogenase using the NCBI database.
[0248] The DNA (gene) containing the nucleotide sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 7 is predicted from the NCBI database, includes DNA (gene) encoding glucose dehydrogenase derived from Aspergillus oryzae RIB40 strain, and is a genomic gene sequence without removing introns.
[0249] The DNA (gene) containing the base sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 8 is a genome gene sequence in which introns are removed from SEQ ID NO: 7.
[0250] The gene encoding a protein having the amino acid sequence described in SEQ ID NO: 9 represents the entire sequence of the glucose dehydrogenase gene predicted from the NCBI database.
[0251] The present inventors predicted that DNA (gene) encoding a protein having glucose dehydrogenase activity derived from Aspergillus oryzae can be easily identified from Non-Patent Documents 1 to 4, NCBI database...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0289] The method for producing GDH, one of the embodiments of the present invention, is characterized in that, in the method for recombinantly producing GDH from filamentous bacteria, by introducing a mutation into the signal peptide sequence present in its N-terminal region, compared with before introducing the mutation Increased expression of the target enzyme.
[0290] As a result of the inventors' diligent efforts to obtain a large yield of GDH protein, in order to achieve the above object, first of all, using the genome information of Aspergillus oryzae in the above invention, the gene DNA that is the source of the change was found to be glucose dehydrogenase. gene DNA.
[0291] Using the NCBI database, the present inventors discovered gene DNA presumed to be FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase.
[0292] The present inventors expected that identification of DNA (gene) encoding a protein having glucose dehydrogenase activity can be easily performed from Non-Patent Docume...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com