Fenton and Fenton-like reaction catalyst regeneration and reclamation method
A catalyst and reaction technology, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical/physical processes, etc., can solve problems such as obstacles to popularization and application, and achieve the goals of avoiding secondary pollution, good industrial application prospects, and reducing consumption Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
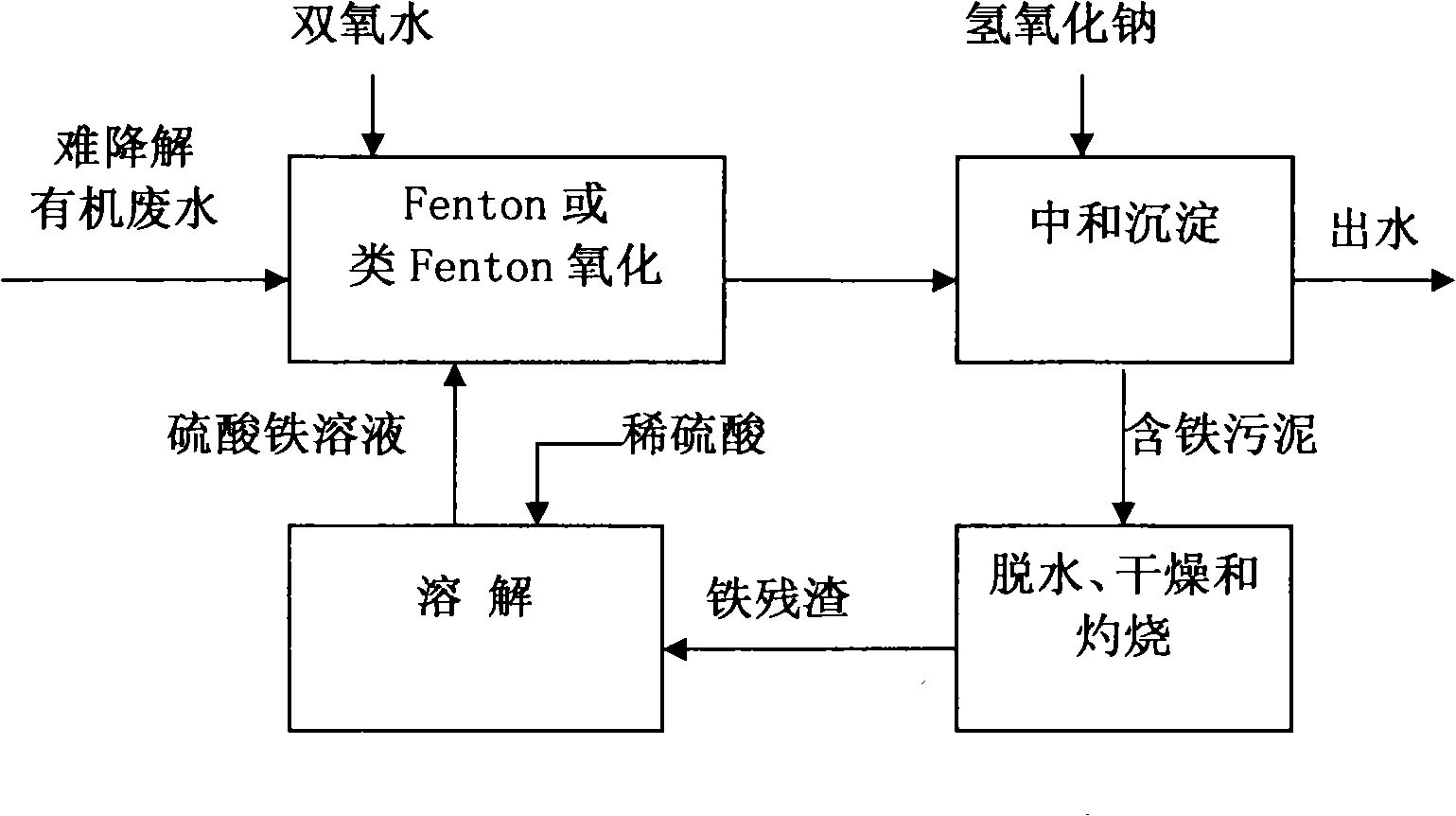
[0021] Example 1 Treatment of fine chemical wastewater containing refractory organics such as nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene by Fenton reagent oxidation method
[0022] Step 1. Use Fenton reagent oxidation method to pretreat fine chemical wastewater: add 1mmol FeSO per liter of wastewater 4 ·7H 2 O, 10mmol H 2 O 2 After stirring and reacting for 480 minutes under the condition of the initial pH value of 3.5, the pH of the reaction solution was adjusted to 7.5 with 6mol / L NaOH solution, and the solution was allowed to settle for 2 hours. The supernatant was drained by siphoning to obtain iron-containing contamination. mud;
[0023] The COD of the fine chemical wastewater before the reaction was 1200 mg / L, the COD of the wastewater after the reaction was 372 mg / L, and the COD removal rate was 69%.
[0024] Step 2: Dehydrate the iron-containing sludge by vacuum filtration, and place the resulting filter cake in an oven at 105±1℃ to dry until the moisture content is 5%; then place the...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Treatment of fine chemical wastewater containing refractory organics such as nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene by Fenton-like reagent oxidation method
[0030] Step 1. Use Fenton-like reagent oxidation method to pre-treat fine chemical wastewater: add 1mmol of fresh Fe per liter of wastewater 2 (SO 4 ) 3 , 10mmol H 2 O 2 After stirring and reacting for 480 minutes under the condition of the initial pH value of 3.5, the pH of the reaction solution was adjusted to 7.5 with 6mol / L NaOH solution, and the solution was allowed to settle for 2 hours. The supernatant was drained by siphoning to obtain iron-containing contamination. mud;
[0031] The COD of the fine chemical wastewater before the reaction was 1200 mg / L, the COD of the wastewater after the reaction was 492 mg / L, and the COD removal rate was 59%.
[0032] Steps 2 and 3 are the same as in Example 1.
[0033] Step 4. Add the regenerated iron sulfate solution to the above-mentioned fine chemical wastewater to repl...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Treatment of fine chemical wastewater containing refractory organics such as nitrobenzene and chlorobenzene by Fenton-like reagent oxidation method
[0037] Steps 1, 3, and 4 are the same as in Example 2, and Step 2 is as follows:
[0038] Step 2. Dehydrate the iron-containing sludge by vacuum filtration, and place the resulting filter cake in an oven at 120±1℃ to dry until the moisture content is 9%; then place the dried iron-containing sludge Burn in a muffle furnace at 500°C for 10 minutes to obtain iron residue. At this time, the removal rate of organic matter (TOC) in the iron residue is 97%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com