Identification of pathogens
A pathogen and identification method technology, which is applied in the field of identification of pathogens infected by body fluids, to achieve the effects of reducing recovery care, accelerating treatment, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] Example 1: Sample-reference strain
[0096] All reference strains tested in this study were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) or the "Deutsche Sammlung für Mikroorganismen und Zellkultur" (DSMZ). In addition to reference strains, probe specificity and sensitivity were tested with clinical isolates that had been identified by classical microbiological methods. For long-term storage, store all bacterial strains in 50% glycerol stock solutions at -80°C. For most experiments a pure culture was used of a number of bacteria / ml obtained by culturing each microorganism in Caso broth overnight at 37°C and finally adjusting the concentration of microorganisms / ml using Mc Farland standard # 0.5. Microarray testing of the following bacteria: Escherichia coli (ATCC 35218, EC5, EC17, 81617, 68933, 68307), Enterobacter aerogenes (DSMZ 30053, 12676), Enterobacter cloacae (26385, 79232, 93840, 12720, 74892 ), Klebsiella pneumoniae (25809, 85813, 26385, 13253), ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Embodiment 2: the design of oligonucleotide probe
[0098] Probe design and analysis was performed with the ARB software package (Ludwig et al., 2004). Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequences of selected pathogenic bacteria and yeasts were downloaded from GenBank at the NCBI homepage (www.ncbi.nlm.ni-h.gov) and uploaded to the ARB software package to create sequences comprising more than 27,000 16S The rDNA sequence also has a database of more than 7,000 18S rDNA sequences to detect possible mismatches with eukaryotic sequences.
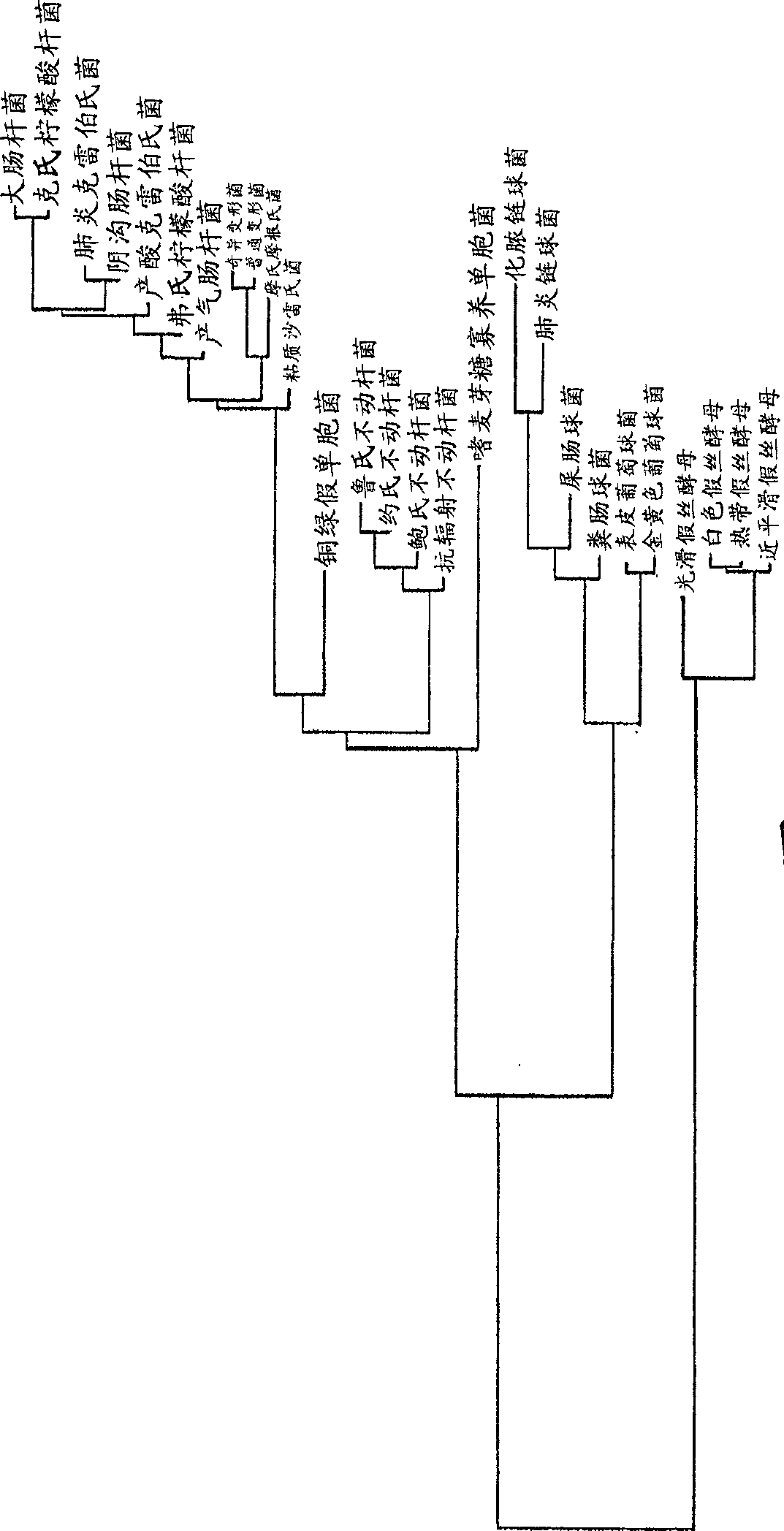
[0099] After aligning the new sequence to a pre-existing database, the dendrogram is calculated using the neighbor joining method (see figure 1 ).
[0100]Use of probe design functions (including variable parameter settings such as probe length (20 bases), maximum non-group hits, G+C content, melting temperature, and minimum hairpin loop) , according to the results of the ARB software, probes for the species and the selected genus were designed.
...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Embodiment 3: the preparation of microarray
[0122] Oligonucleotide probes were from VBC Genomics (Austria). Five thymine residues were added at the 5' end of each oligonucleotide as a spacer. To ensure covalent attachment to reactive aldehyde groups on the microarray surface (CSS-100 Silylated Slides, Cel Associates, USA), the probes were 5' amino modified. Probes were printed onto silanized glass slides at different concentrations (50 μM, 20 μM and 10 μM in 3x SSC and 1.5 M betaine monohydrate) by a contact arrayer (Omnigrid, GeneMachines) while conditioning the air. Humidity is between 55 and 60%.
[0123] Six copies of each probe were printed per microarray. Spotting was performed with a SMP3 needle (TeleChem, USA) to obtain a spot size of 100 μm in diameter.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com