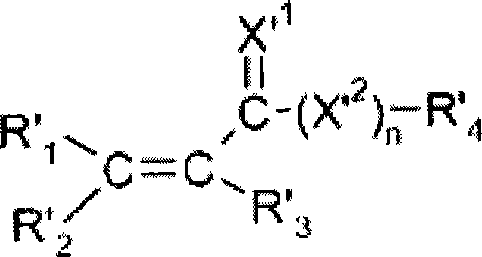
Radiation curable hybrid composition and process
A radiation curing, compound technology, applied in dyeing low-molecular-weight organic compound processing, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to remove hydroxide groups, unsuitable for visual communication, etc., to achieve the effect of high refractive index
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0177] Example 1 (Non-Halogenated Nanocomposite and Coating Formulation)
[0178] Step 1.1
[0179] Bisphenylacetic acid (120 g from Alfa) was dissolved in 200 g of glacial acetic acid, and the mixture was stirred and heated to 50°C. Contains about 20.0% ZrO 2 A dispersion (500 g) of nanoparticles (average diameter approximately 5 nm, purchased from Nyacol, see table below) in acetic acid and water was added dropwise to the acid mixture. After the addition of nanoparticles, 14.45 g of surface modifier NZ-33 (see table below) was added dropwise with continued stirring. Volatile components were removed from the resulting mixture under gradually reduced pressure while maintaining the overall temperature at 50 to 60°C.
[0180] Step 1.2
[0181] Once no significant condensation of the volatile components is observed, 320 g of 2-phenoxyethylacrylic acid (commercially available from Cytec under the registered trademark 114), the mixture is subjected to gradual depressurizat...
example 2
[0185] Example 2 (Halogenated Nanocomposites and Coating Formulations)
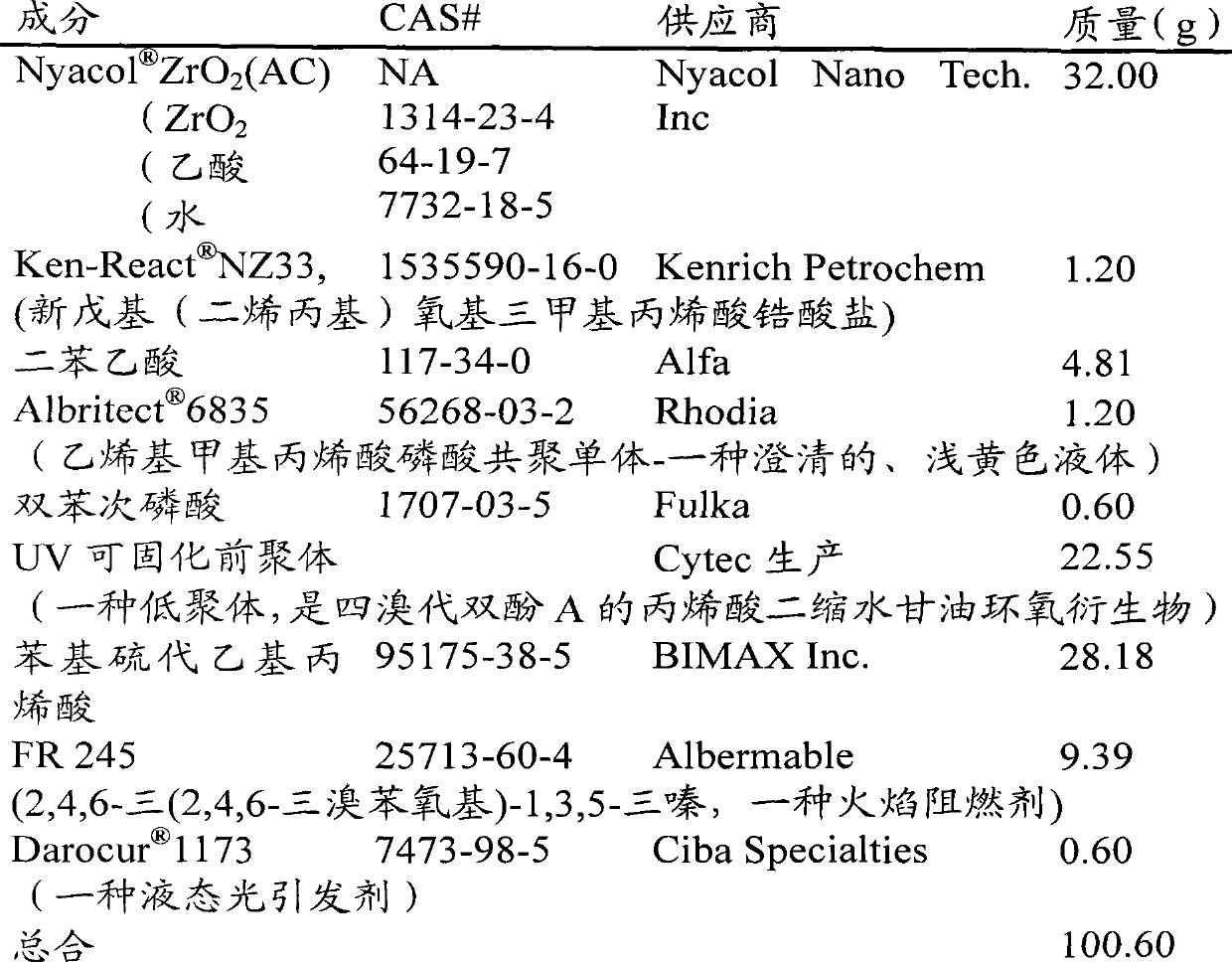
[0186] In addition to UV-curable ex-polymers are 150 Brominated analogues of epoxy acrylic acid (ie bisphenol A moiety substituted by 4 bromine-containing groups) (prepared by the applicant), Example 2 was prepared in a manner similar to that described in Example 1. The ingredients used to prepare this product are listed in the table below.
[0187] Table 1
[0188]
[0189] The product properties are as follows, Refractive Index (measured with a refractometer from Fischer Scientific Co) = 1.5851. Clear liquid with >99% solids.
[0190] Coated film from Example 2.
[0191] Example 2 (20g) and 0.6g 1173 (a traditional photoinitiator), and the coating film was applied to the substrate of PET film by the traditional method of applicator roll. The coating was UV cured in four passes at 100 ft / min under two medium pressure mercury H lamps to form a film coating with a refractive index of 1.6120 (me...
example 3
[0192] Example 3 (Non-Halogenated Sulfur-Containing Nanocomposites and Coating Formulations)
[0193] The following surface modifiers were mixed: 1-benzoylacetone (0.26g); bisphenylacetic acid (2.55g); bisphenylphosphinic acid (0.26g) and (0.26 g, see table). The mixture was completely dissolved (3.33 g) with acetic acid (51 g) at 60°C to form a surface modifier solution.
[0194] The aqueous dispersion of nanoparticles (42.5 g) was stirred. This dispersion contains 20% by mass of zirconia nanoparticles, 12% by mass of acetic acid and 68% by mass of water, which can be used as ZrO 2 Obtained from Nyacol Nano Technologies.
[0195] The surface modifier solution was slowly added to the stirred nanoparticle dispersion to obtain a mixture with a viscosity of about 20 cp at 25°C after addition. The mixture was then heated to 60° C., stirred with a Rotovap and left for 2 hours without decompression. The mixture was then heated in a Rotovap to remove acetic acid and water unde...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com