Preparation method of biological feed additive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
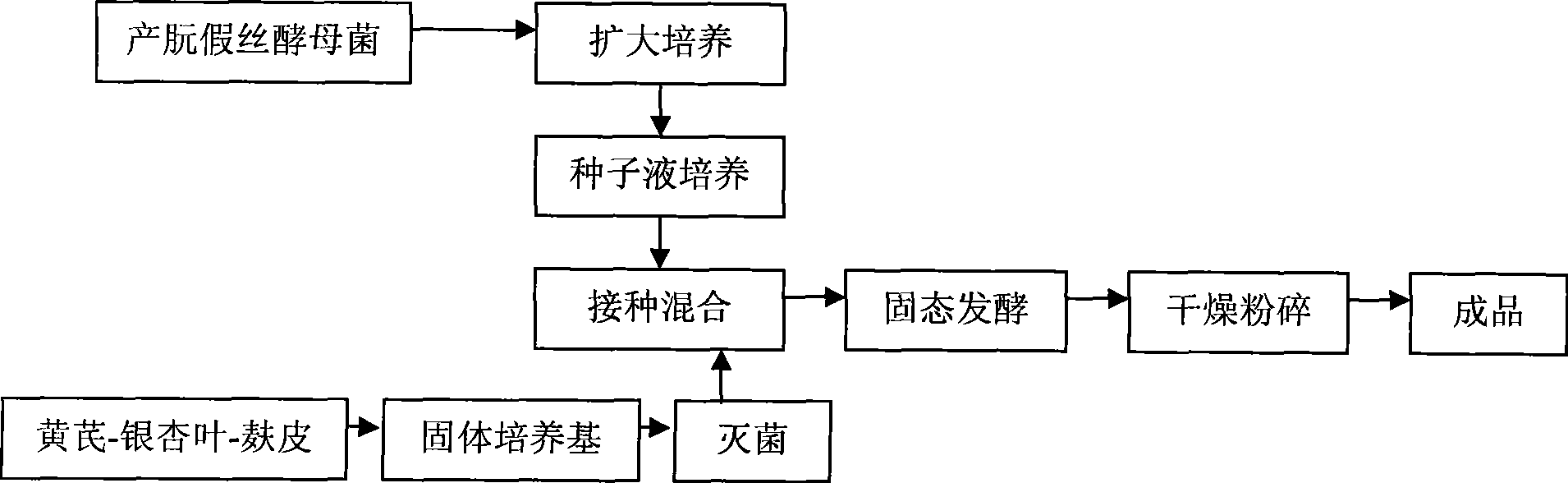
Image
Examples
preparation Embodiment 1
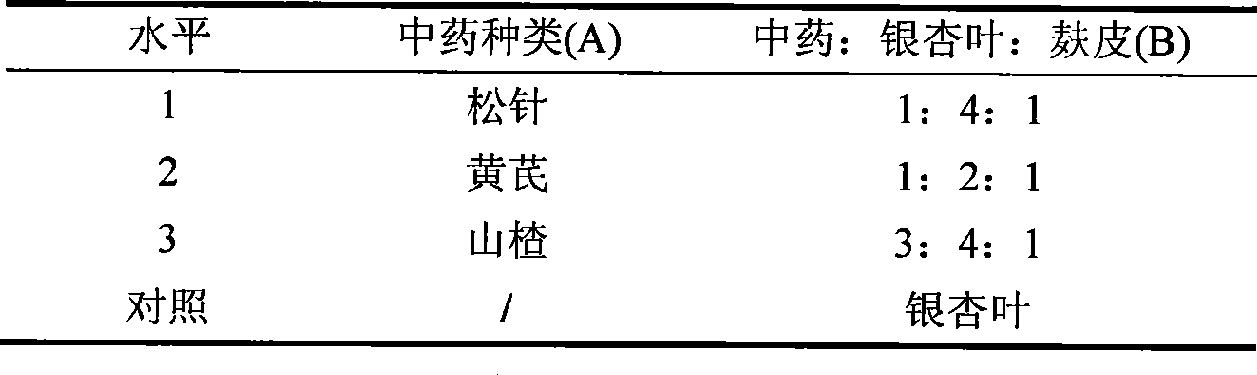
[0025] 1. Select pine needles, astragalus, and hawthorn three kinds of traditional Chinese medicines and mix them with ginkgo leaves for fermentation, and select appropriate Chinese medicines and their ratios with ginkgo leaves and bran.
[0026] 2. The experiment adopts a two-factor completely randomized design, a control is set, a total of 10 treatments are repeated 3 times, and the experimental design is shown in Table 1.
[0027] Table 1 Two-factor complete random design table
[0028]
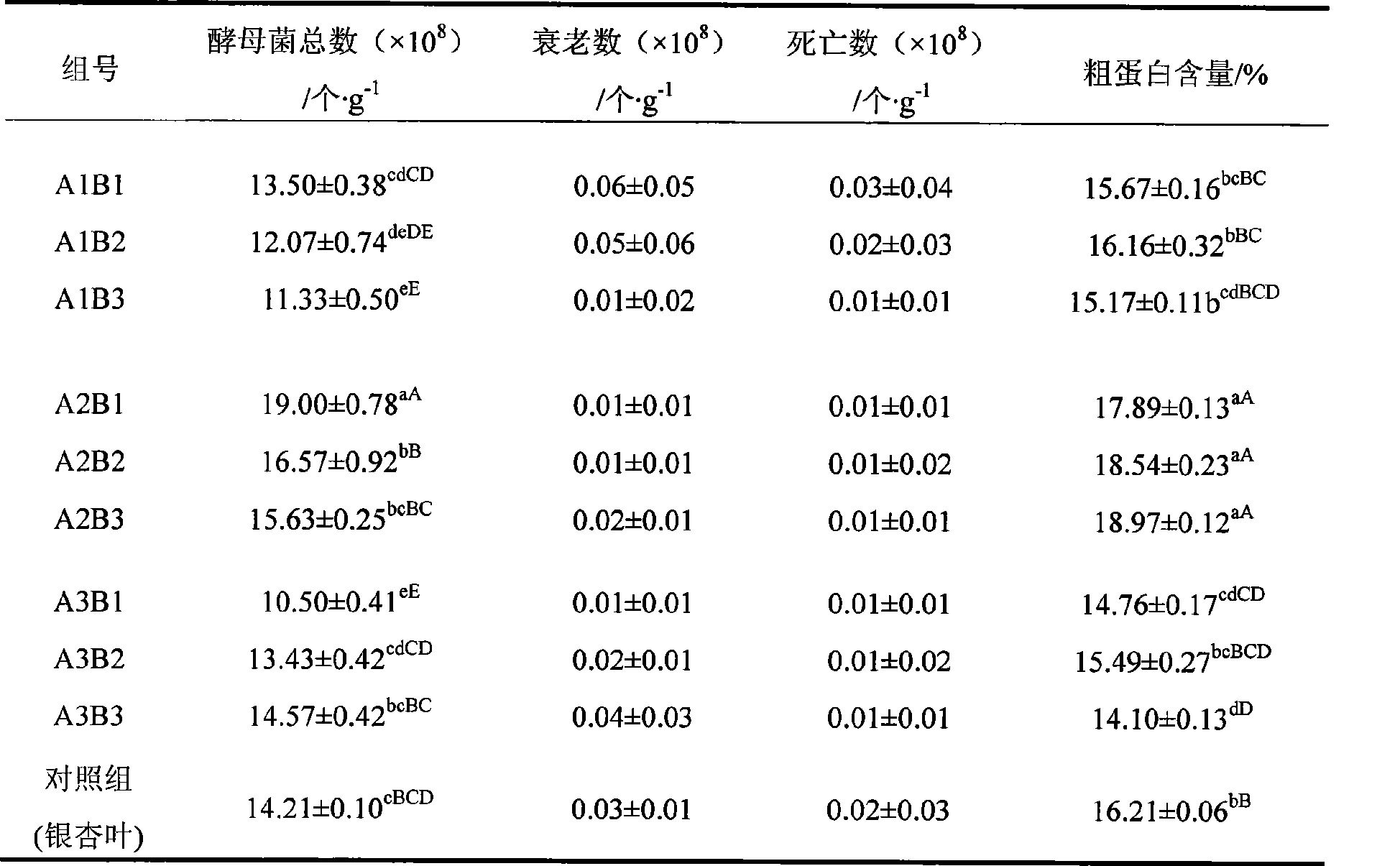
[0029] Table 2 Fermentation comparison of different traditional Chinese medicine-Ginkgo biloba combinations
[0030]
[0031] Note: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), and different uppercase letters indicate extremely significant differences (P<0.01).
[0032] 3. The test results show that the effect of fermenting with Astragalus-Ginkgo biloba-bran as the fermentation raw material is better (Table 2). The fermented product of pine needles-gingko ...
preparation Embodiment 2
[0037] 1. Transfer the strain of Candida rutans to the slant medium and culture it at 28°C for 20 hours. The above-mentioned slant medium is PDA medium. The preparation process is as follows: After 200g of potatoes are boiled in water, add 20g of sucrose and 10g of agar , mix well, add water to make up to 1000mL.
[0038] 2. Inoculate the Candida utilis obtained in step (1) into the liquid seed medium on a clean bench, and culture on a shaker (28° C., 200 rpm) for 24 hours. The preparation process of the liquid seed medium is as follows: 20 g of glucose, 10 g of peptone, and 10 g of yeast extract are dissolved in water, and then the volume is adjusted to 1000 mL with water. Liquid culture is based on sterilization at 121°C for 20 minutes. The content of saccharomycetes in the gained seed culture liquid is 9 * 10 9 pc / mL, stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for 1 month.
[0039] 3. Dry and grind astragalus, ginkgo leaves, and bran into fine powder, sift through a 40-mesh sieve, ...
preparation Embodiment 3
[0045] 1. Transfer the strain of Candida rutans to the slant medium and culture it at 25°C for 24 hours. The above slant medium is PDA medium. The preparation process is as follows: Cut 200g of potatoes into small pieces and boil them in water And maintain for 20-30 minutes, filter with double-layer gauze to get potato juice, add 15g of sucrose and stir to dissolve, then add 20g of agar, continue to heat until the agar is completely melted and becomes transparent, and finally add water to make up to 1000mL.
[0046] 2. Inoculate the Candida utilis obtained in step (1) into the liquid seed medium on a clean bench, and culture it on a shaking table (25° C., 200 rpm) for 30 h. The formula of the liquid seed medium is: glucose 20g, peptone 6g, yeast extract 10g, dissolve in distilled water and dilute to 1000mL. Liquid culture is based on sterilization at 121°C for 20 minutes. The content of saccharomycetes in the gained seed culture liquid is 6 * 10 9 pc / mL, stored in a refriger...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com