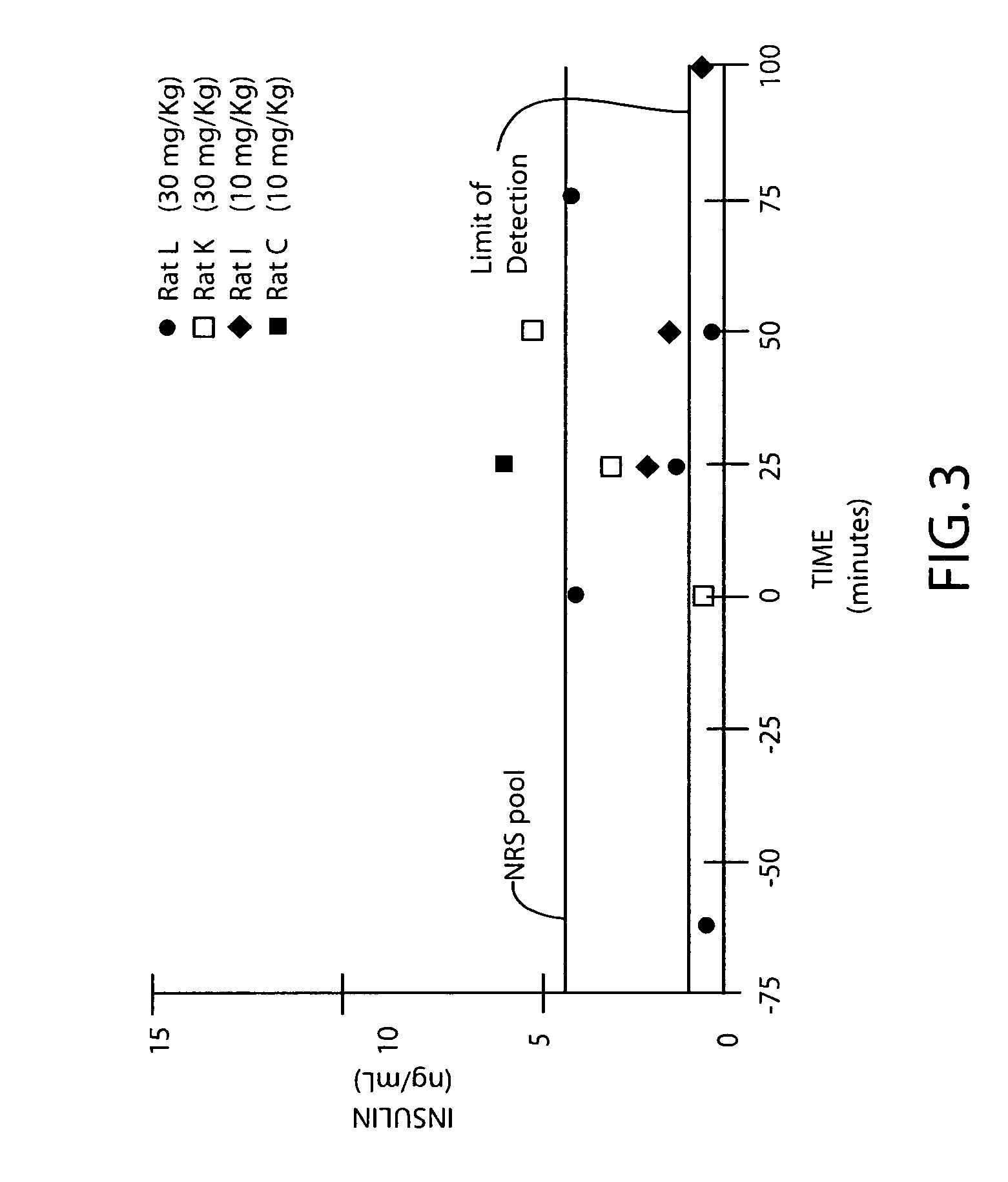
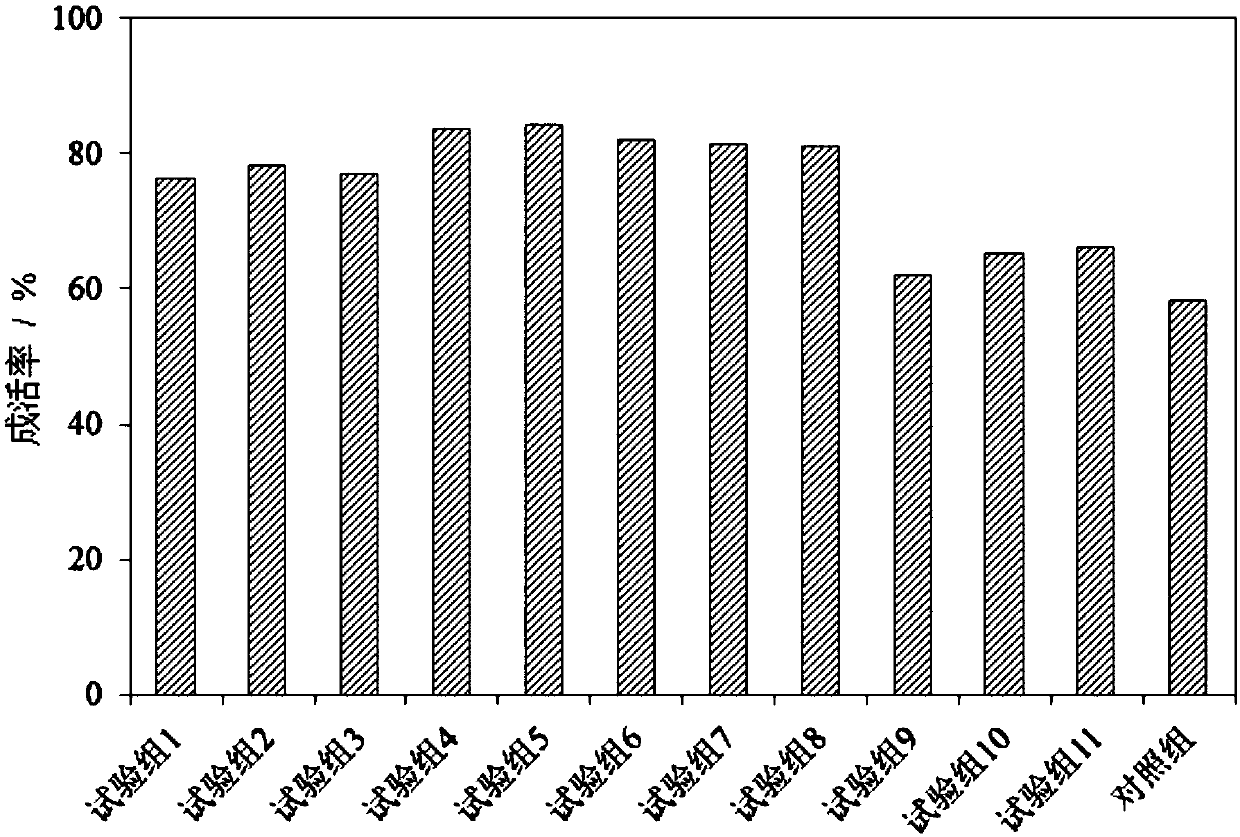
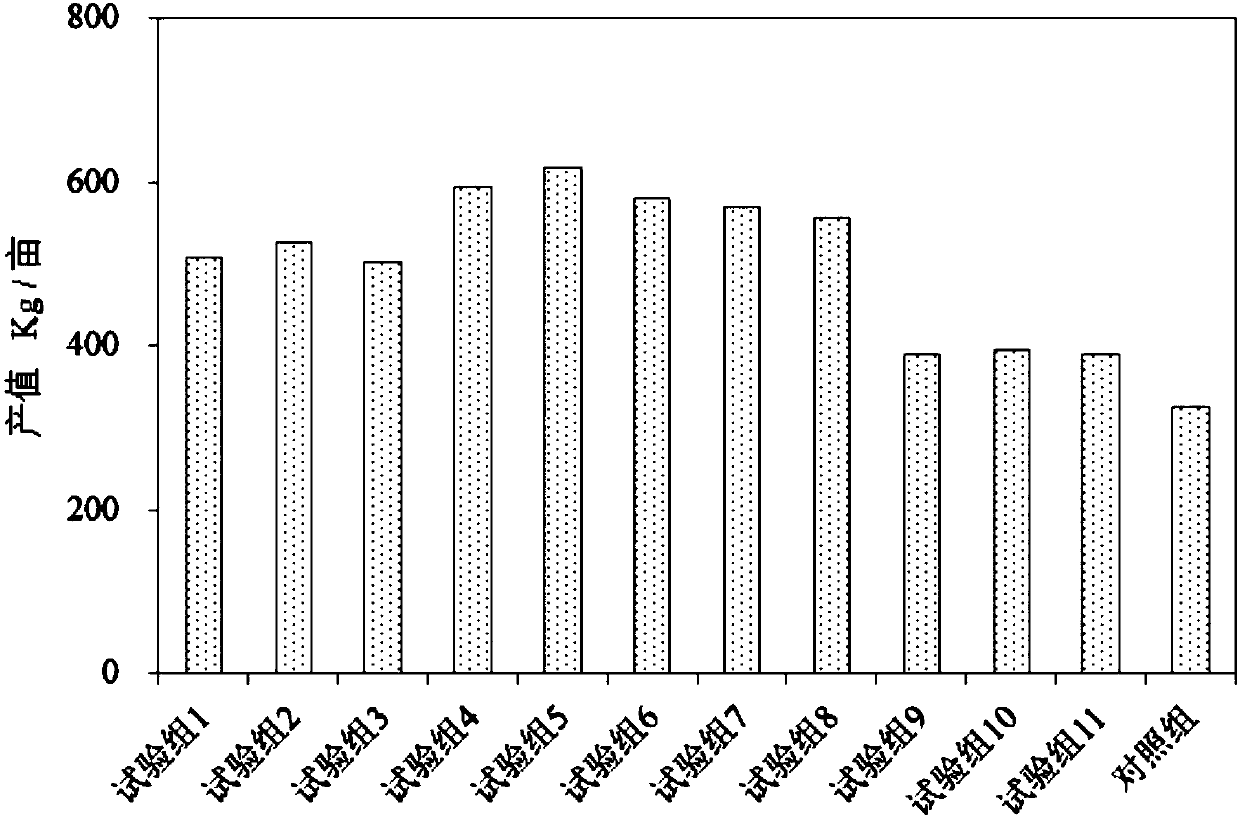
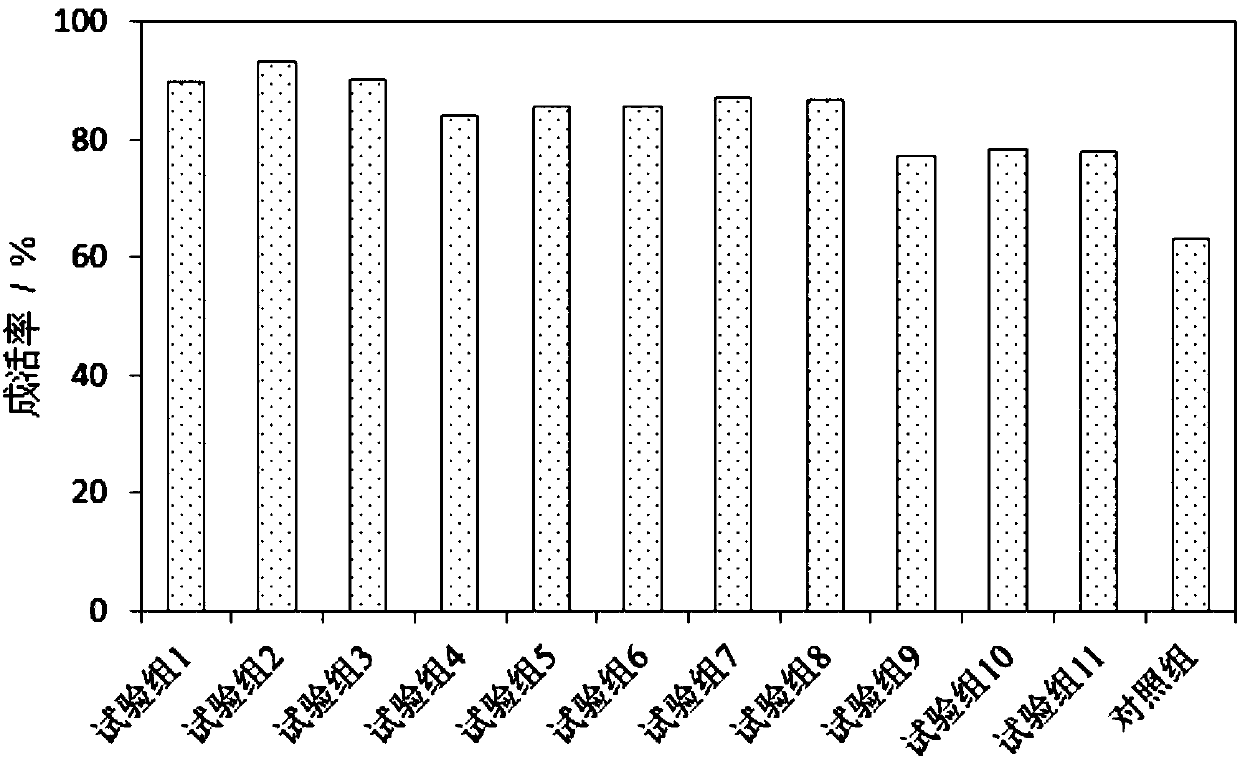
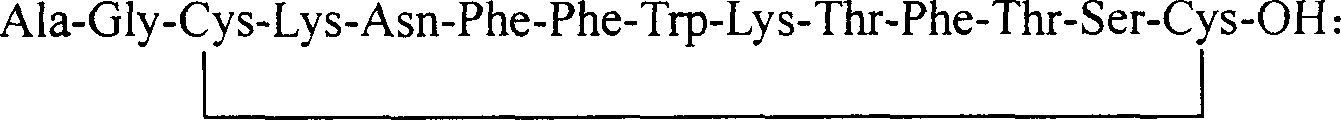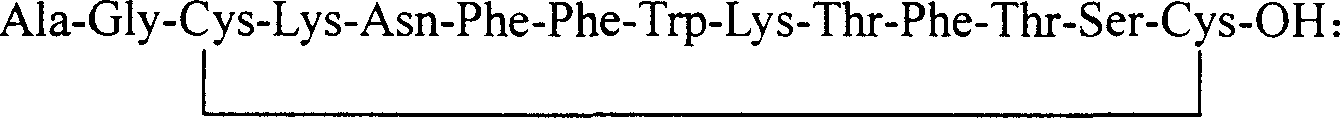Patents
Literature
38 results about "Somatomedin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Somatomedins are a group of proteins produced predominantly by the liver when growth hormones act on target tissue. Somatomedins inhibit the release of growth hormones by acting directly on anterior pituitary and by stimulating the secretion of somatostatin from the hypothalamus.
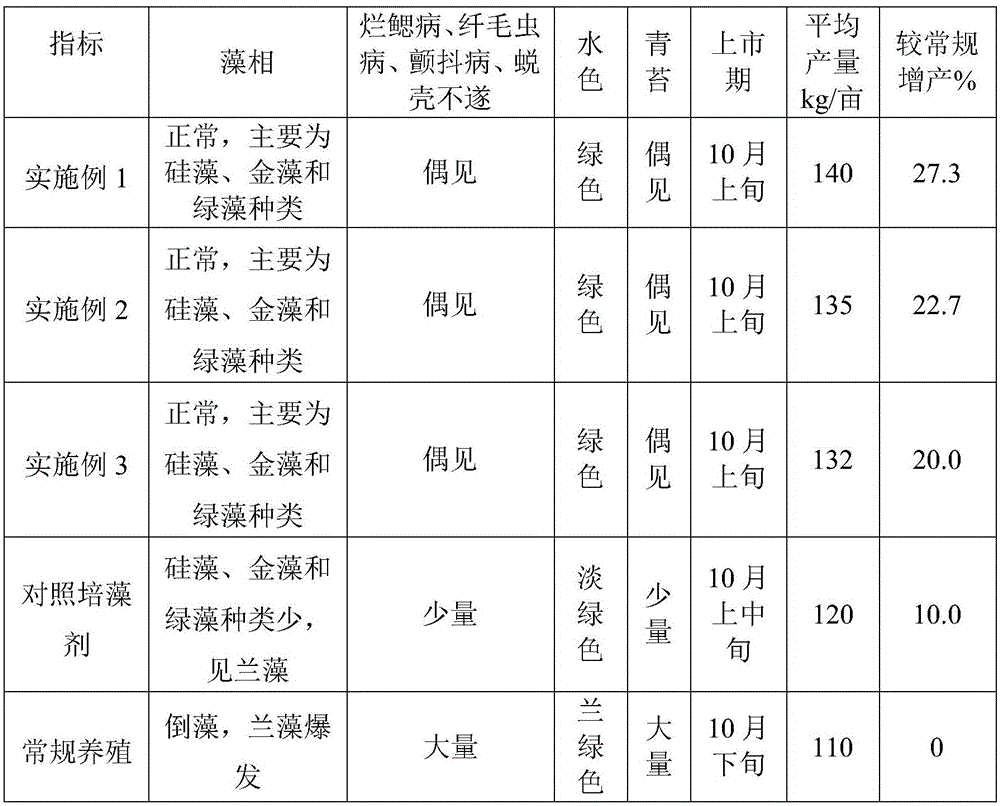
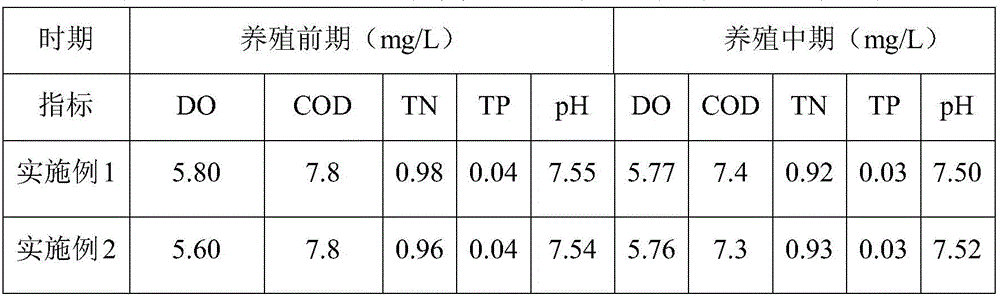
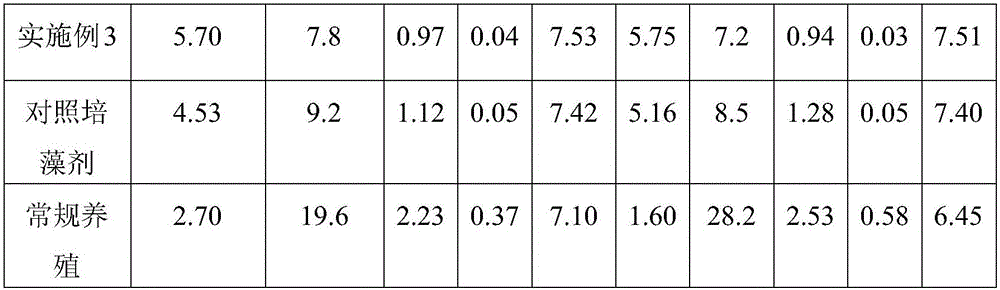
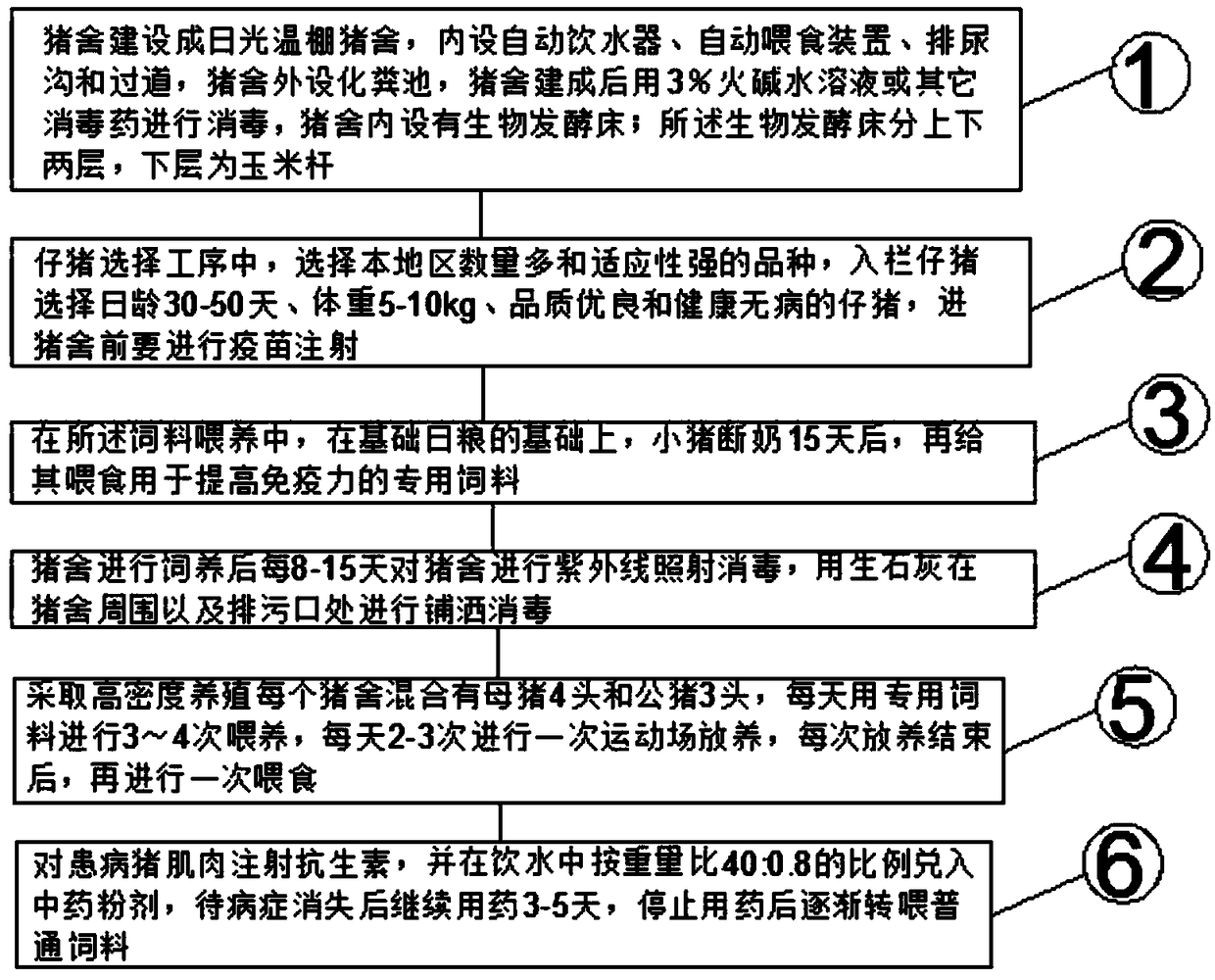
Breeding method for medicinal silky fowl
ActiveCN103858819AImprove survival rateImprove conversion rateAnimal husbandryAnimal scienceFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses a breeding method for medicinal silky fowl. The breeding method mainly comprises the steps of constructing a henhouse, brooding, breeding, disinfecting the henhouse and the like. The survival rate of chicken is greatly increased by adopting the breeding method provided by the invention for breeding silky fowl. According to the breeding method provided by the invention, a microbial technology is effectively combined with an ecological breeding technology, so that a powerful dominant bacterial community is formed in vitro and in vivo of animals under the effects of probiotic stock solution, fodder, drinking water and spraying sanitization, and a pathogenic bacteria colony is restrained and eliminated; a large quantity of nutrition and hormone matters, such as amino acid, protein, vitamin, various bio-chemical enzymes, antibiotics and somatomedin, are secreted and compounded, so that all the organ functions of animal bodies are adjusted and promoted; the feed conversion rate is increased; various functions, such as immunization, nutrition and growth stimulation are generated for the animals; obvious effects, such as preventing and curing diseases, increasing survival rate, promoting growth and breeding, lowering cost, eliminating fecaluria smell, purifying environment and increasing yield and income are achieved.
Owner:王曼
Method for producing seaweed protein feed through synergistic effect of enzymolysis and fermentation
InactiveCN103549130AImprove conversion utilizationImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyAnimal feeding stuffDrug biological activityFermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing a seaweed protein feed through the synergistic effect of enzymolysis and fermentation. The method comprises the steps of fully mixing seaweed residue (the water content is 38%) and a feed enzyme preparation according to a certain proportion and performing the enzymolysis for 4-7h with the pH of 6.2-7.0 at the temperature being 35-45 DEG C to obtain a seaweed residue-feed enzyme preparation mixture; inoculating compound microorganisms and performing solid fermentation. The method has a simple process and is easy to operate; an external source is added to degrade a cellulose preparation to produce nutrition beneficial to microbial growth through the enzymolysis and make up the deficiency of enzyme produced by using the compound microorganisms, so as to stabilize the solid fermentation process and the product quality, greatly reduce the content of cellulose and increase the protein content; the seaweed protein feed is rich in multiple minerals, bioactive constituents and unknown somatomedin, and can be used as a protein feed for livestock and poultry and an aquatic feed; the method provides a technical support for growing tensions on developing novel protein resources and relieving a feed protein source.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV FOR THE NATITIES +1
Ecological organic fertilizer
InactiveCN102838390AGood conditionImprove biological characteristicsBacillus licheniformisChemical condition
The invention discloses an ecological organic fertilizer comprising a base material and a nutrient solution according to a weight ratio of (800-1200):1; the base material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0-90 parts of pig manure, 0-6 parts of chicken manure, 0-8 parts of bean dregs, 0-4 parts of wheat bran, 0-3 parts of sugar, 0-2 parts of distillers' grains, 0-19 parts of brewer's grain and 0-4 parts of corn starch, wherein all the parts by weight cannot be zero simultaneously; the nutrient solution comprises lactobacillus series, yeast group series, photosynthetic bacteria series, gram positive actinomycete groups, fermentation series filamentous bacteria, bacillus subtilis, bacillus natto, lactobacillus plantarum, bacillus licheniformis, high-activity enzyme and somatomedin. With the adoption of the ecological organic fertilizer, the physical and chemical conditions and the biological characteristic of soil are effectively improved, the soil is aged, and the green manure supply property and the buffer property of the soil are enhanced; the organic fertilizer is rich in organic substance and various nutrient elements to provide nutrition for crops, and thus, the organic fertilizer can promote the growth of the crops and improve the quality of agricultural products; and the organic fertilizer is beneficial to crop absorption, so that the utilization ratio of the fertilizer is increased.
Owner:CHENGDU JIAJIAMEI FOOD
Compositions and Methods for Growth of Pluripotent Cells
InactiveUS20090087907A1Low costEasy to presentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSomatomedinGenotype
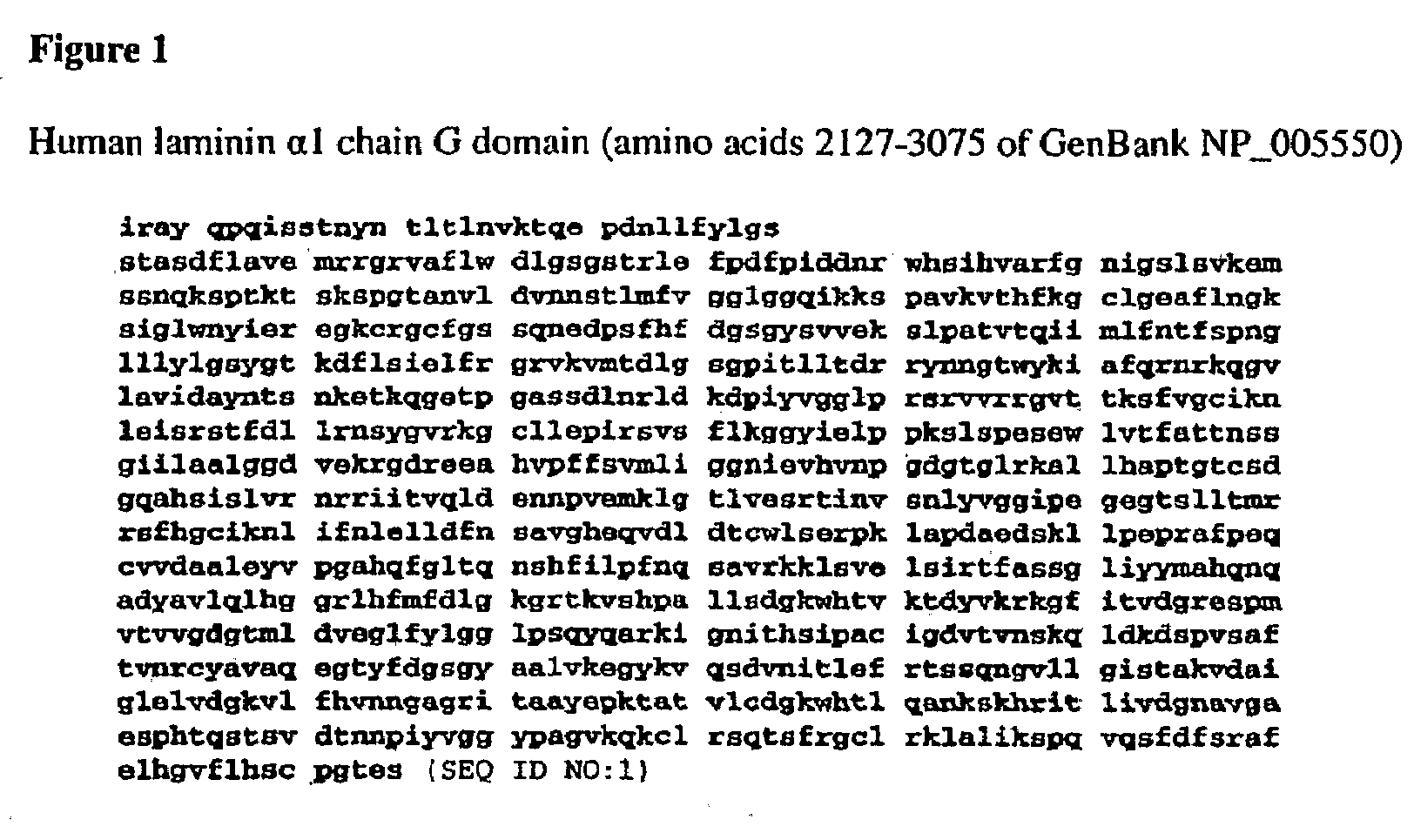
A method of propagating embryonic stem (ES) cells in an undifferentiated state, while maintaining both the pluripotency and the cells normal genotype is disclosed. The method comprises using recombinantly produced protein domains to attach human embryonic stem cells to the surface of a bioreactor. The ES cells are supplied with nutrients while they held in place by the recombinantly produced protein domains which may be chosen from Laminin G domain, Fibronectin domain 2, Fibronectin domain 3, Nidogen G2 domain, Nidogen G3 domain, Vitronectin somatomedin B domain, and Vitronectin somatomedin C terminal domain. Useful molecules are characterized by a high binding affinity for hES cells and a molecular weight of about 50 kDa±20%.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Preparation method of synthesizing growth chalone from solid phase polypeptide
InactiveCN1923851AConvenient sourceReduce usageSomatostatinsPeptide preparation methodsHydrogen fluorideSomatomedin
The invention discloses a chalone preparing method of solid-phase polypeptide, which comprises the following steps: adopting 2-chloride-trityl resin, 4-methyl trityl resin or 4-methoxyl trityl resin as raw material; connecting amino acid with protective group according to solid-phase synthetic method; obtaining protected octapeptide resin; removing Fmoc-protective group sequently; stripping side-chain protective group; cutting peptide to obtain reduced aoqu-peptide; oxidizing through air under pH 7-11 condition; separating and purifying rought product through C18 (C8) column to produce exquisite.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA +1
Biological additive for animal feed and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101637219AImprove conversion rateAdjust and improve organ functionAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a biological additive for animal feed, which comprises the components of bacillus subtilis solution, yeast solution, lactic acid bacteria solution, acetic acid bacteria solution, beer yeast solution and vegetable lactic acid bacteria solution in a ratio of 0.4-1:1:0.6-1.5:0.6-1.5:0.6-1.5:0.3-0.7. After being mixed with the feed and drinking water and entering intestinal canals of animals, the biological additive can build a free dominant species with beneficial bacteria in the intestinal canals so as to inhibit and kill harmful pathogenic bacteria; and simultaneously, a great deal of nutrients such as amino acids, proteins, vitamins, biochemical enzymes, antibiotics, somatomedins and the like are secreted and synthesized, so that the functions of all organs of the animal body are adjusted and improved, the feed conversion rate is improved, the animals are stimulated to generate immunity, to be nourished, to grow and the like, and the effects of deodorizing manure, preventing and controlling diseases, improving survival rate, enforcing growth and breeding, cleaning the environment, improving economic benefits and the like can be achieved.
Owner:戴志南
Culture method of probiotics and application thereof
ActiveCN108753677AImprove heat resistanceGood acid resistance ie chemical resistanceBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffFood additiveSomatomedin
The invention discloses a culture method of probiotics. The method comprises the following steps: adding a porous material into a culture medium containing somatomedin for promoting reproduction of probiotics, ensuring that the volume ratio of the culture medium to the porous material is 1: 100, and inoculating the probiotics into the culture medium, so as to perform culture and realize probioticsculture. The obtained probiotics can be applied to products of preparation of food, food additives, medicine and feed or environmental protection treatment. The obtained probiotics has excellent heatresistance, acid resistance and drug resistance, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of food, medicine, feed and environmental protection.
Owner:ZHONGKE YIKANG BEIJING BIOTECH CO LTD
Microorganism promoted live pig breeding method
InactiveCN103766283AImprove conversion rateAdjust and improve organ functionAnimal housingBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a microorganism promoted live pig breeding method. The method mainly comprises the steps of building a pigsty, cushioning the pigsty, selecting piglets, carrying out breeding management, disinfecting the pigsty and the like. According to the invention, a microorganism technology and an ecological breeding technology are combined, so that stock solution of probiotics forms powerful dominant bacterial communities inside and outside animals along with packing, feeds, drinking water and spraying sanitization and pathogenic bacterial communities are inhibited and eliminated; and meanwhile, a great quantity of nutrition and hormone substances, such as amino acid, proteins, vitamins, various biochemical enzymes, antibiotics and somatomedin, are secreted and synthesized so as to regulate and improve functions of each organ of an animal organism, improve a feed conversion rate, generate various effects of immunization, nutrition, growth stimulation and the like on animals and implement the obvious effects of preventing and treating diseases, improving the survival rate, promoting growth and breeding, reducing cost, removing odor of manure and urine, purifying the environment, increasing both production and income and the like.
Owner:曲靖市麒麟区天源实业有限公司
Abstraction of pilose antler releasing somatomedin (DEER GHRF) and preparation method thereof
The present invention relates to process of extracting growth hormone release factor (GHRF) from pilose antler. The process includes the following steps: 1. crushing pilose antler and leaching to obtain leached liquid; 2. ultrafiltering the leached liquid and collecting the pilose antler extract of molecular weight 1-10 kDa; and 3. high efficiency liquid chromatography on the pilose antler extract and collecting component containing GHRF of pilose antler. The present invention also relates to the pilose antler extract with rich GHRF, and its application in medicine, food, cosmetics, feed, etc.
Owner:王利忠
Lactic acid bacteria contained tomato cultivation medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104521709AQuality improvementBioloigcal waste fertilisersGrowth substratesDiseaseDecomposition
The invention discloses a lactic acid bacteria contained tomato cultivation medium and a preparation method thereof. The cultivation medium is characterized in that the medium comprises, by weight, 30% of rice hulls, 10% of sword bean vines, 20% of cucumber stems, 10% of rhodospirillum, 30% of river sand, 0.1% of fermentation microflora I and 0.1% of fermentation microflora II. According to the preparation method of the cultivation medium, agricultural organic wastes are smashed and subjected to solid state fermentation and decomposition for 24 hours at high temperature and high speed, and plant lactobacillus is added to perform uniform mixing. By means of the lactic acid bacteria contained tomato cultivation medium and the preparation method thereof, the cultivation medium is safe, environmental friendly, and poisonless and tasteless, seedling wilting and root rotting can not occur after direct usage, dinitrogenase, active amino acids and nutrients of plant somatomedin are contained, tomato root stock diseases such as root rot, damping off and sheath blight can be prevented, and aflatoxin produced during usage of the rice hulls can be removed.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA WEILONG INFORMATION TECH
Preparation method for algae-culturing agent for aquaculture
InactiveCN106083297APromote growth and reproductionTo increase productionBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersShrimpSomatomedin
The invention discloses a preparation method for an algae-culturing agent for aquaculture. According to the method, chicken manure, bean cake, fish meat and other organic materials and an EM active calcium solution with powerful functions are subjected to co-fermentation by employing a micro-ecology theory according to the growth characteristic of algae, during fermentation, a large amount of ionic-state and chelated-state algae somatomedin, nutritive salts, trace elements and minerals, and a special mixing and pelletizing technology is employed for preparing the algae-culturing agent. Concrete steps of the preparation method comprise (1) anaerobic fermentation; (2) aerobic fermentation; and (3) pelletization. The prepared algae-culturing agent for aquaculture possesses advantages of comprehensive nutrition, good algae culturing effect and the like, and is applicable to growth of algae in water of breeding fish, shrimps, crabs and shells and improvement of water quality.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
Method for cultivating ganoderma and collecting ganoderma spore powder
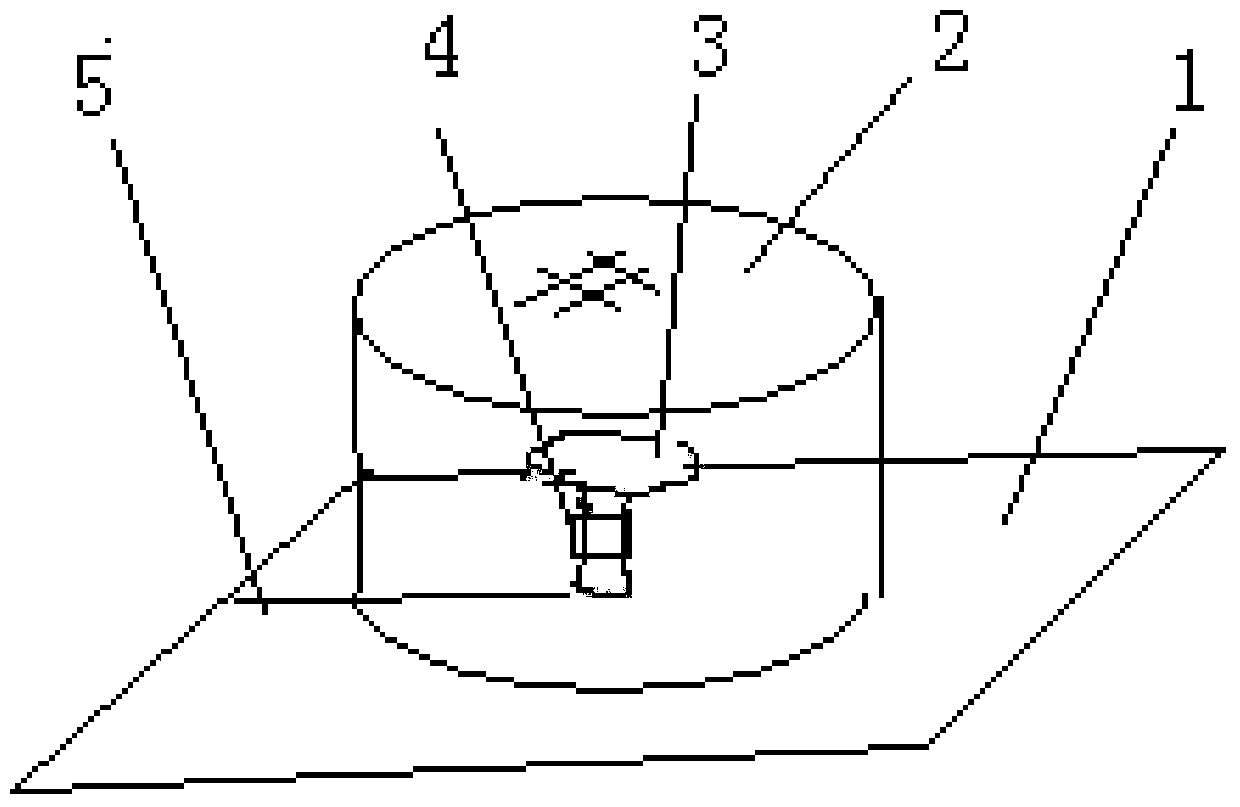
Provided is a method for cultivating ganoderma and collecting ganoderma spore powder. The method comprises the steps that pure broad-leaved tree basswood serves as a culture medium, a ganoderma variety is selected, when ganoderma sporophores enter the mature period and begin to generate spore powder, a paper pad is inserted into and padded at the root of each ganoderma sporophore, each paper pad is horizontally clamped and inserted into the root of the ganoderma sporophore through a sheared seam sheared in advance, and then tea filter paper or air-permeable non-woven fabric or gauze tubes are arranged; at the ganoderma cover powder appearing period, ganoderma stalks are wrapped by an absorber impregnated with a 100-500 mg / 1000 mL of somatomedin gibberellin solution, wherein the absorber is cotton or sponge or fiber or fabric, the outer layer of the absorber is provided with rectangular plastic film which wraps the absorber into a cylinder, and absorption of the stalks is guaranteed; a ganoderma cylinder is wrapped with the wrapped cylinder of the absorber through upper and lower omega-shaped plastic or steel wire clips at the initial period or imminent critical period.
Owner:浙江品高生物科技有限公司
Cob-free silage corn fermentation technology
InactiveCN107259084AExpand sourceImprove palatabilityAnimal feeding stuffAnimal fodder preservationDiseaseMoisture
The invention relates to a cob-free silage corn fermentation technology which concretely comprises the following steps: harvesting corns when corn plants at least have 3 green leaves respectively, crushing the corns until the particle size length is smaller than 3cm when the moisture is 62-75 percent, and adding a lactic acid bacteria fermentation solution to carry out primary packaging; adding a Lubaokang acid agent, carrying out pit storage, and keeping the water content be 62-75 percent, wherein the compaction density reaches 700kg / m<3> or above, and the dry matter density reaches 220kg / m<3> or above; and after sealing fermentation, opening a pit for secondary packaging, wherein an amount of film wrapping layers for packaging is 4-8. The invention aims at providing a method for treating corn stalks and can provide good-quality silage feeds; the silage feeds contain a great amount of beneficial substances, such as amino acid, organic acid, polysaccharides, various vitamins, various enzymes, somatomedin, antibiotics, anti-disease substances, easily absorbed by livestock, so that the feed source is expanded, grain feeds are saved, the problem of environmental pollution caused by stalks is solved at the same time, the production cost is lowered, and the economic benefit is increased.
Traditional Chinese medicine feed additive for preventing and treating swine erythema disease
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine feed additive for preventing and treating swine erythema disease. In the formula, selection of traditional Chinese medicine is targeted, the combination of different drugs conditions the function of the swine from the whole body to local parts, and supplementation of trace elements is realized. According to the invention, the traditional Chinese medicine feed additive is prepared based on the aspect of promoting the digestive absorption function of the swine in combination with antibiosis, inflammation diminishment, virus killing and detoxification, and has good weight increment effect. Mint oil has the effects of cooling, detoxification and skin care, thereby finally reducing formation of bacterium and inflammation fungus and pustule and effectively preventing swine erythema disease. The technical scheme of the invention is formed by repeated test and allocation of 12-year swine raising experience and meets the theory of traditional Chinese medicine; and furthermore, the additive provided by the invention contains multiple somatomedins, thereby being capable of effectively improving meat quality, enhancing resistance, strengthening immunity, and having good effect in preventing swine erythema disease.
Owner:SHANDONG NEW HOPE LIUHE GROUP
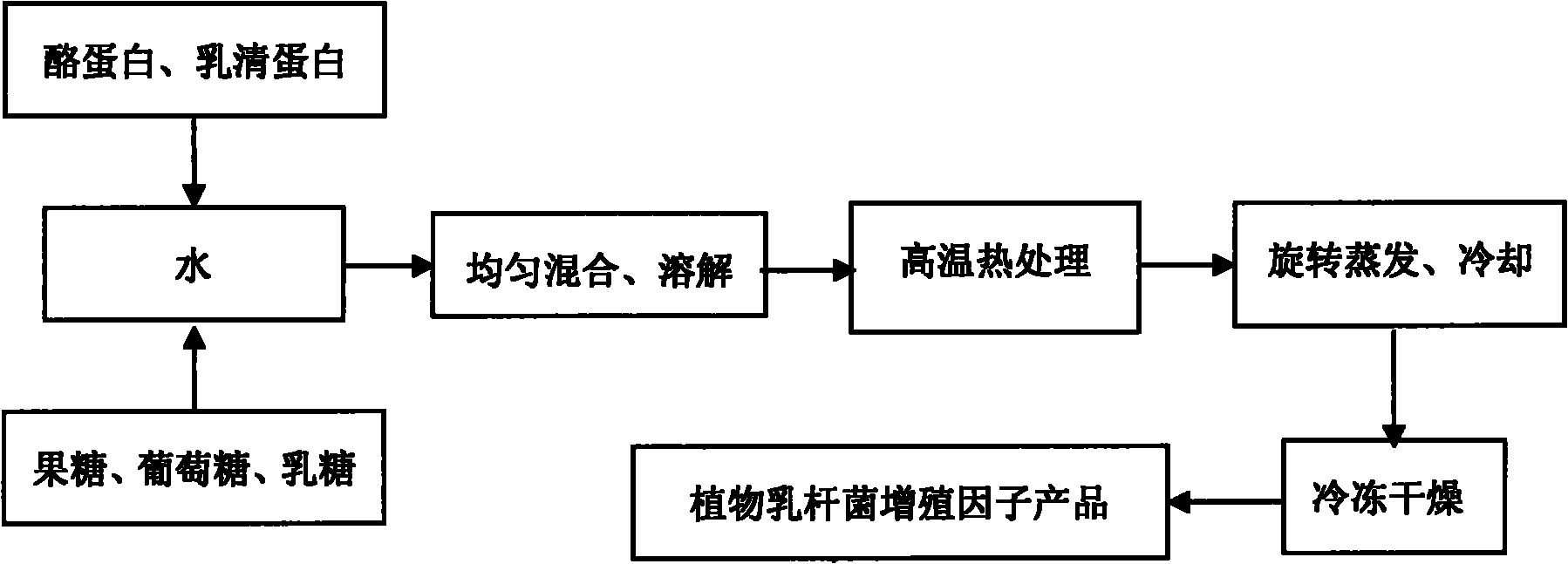
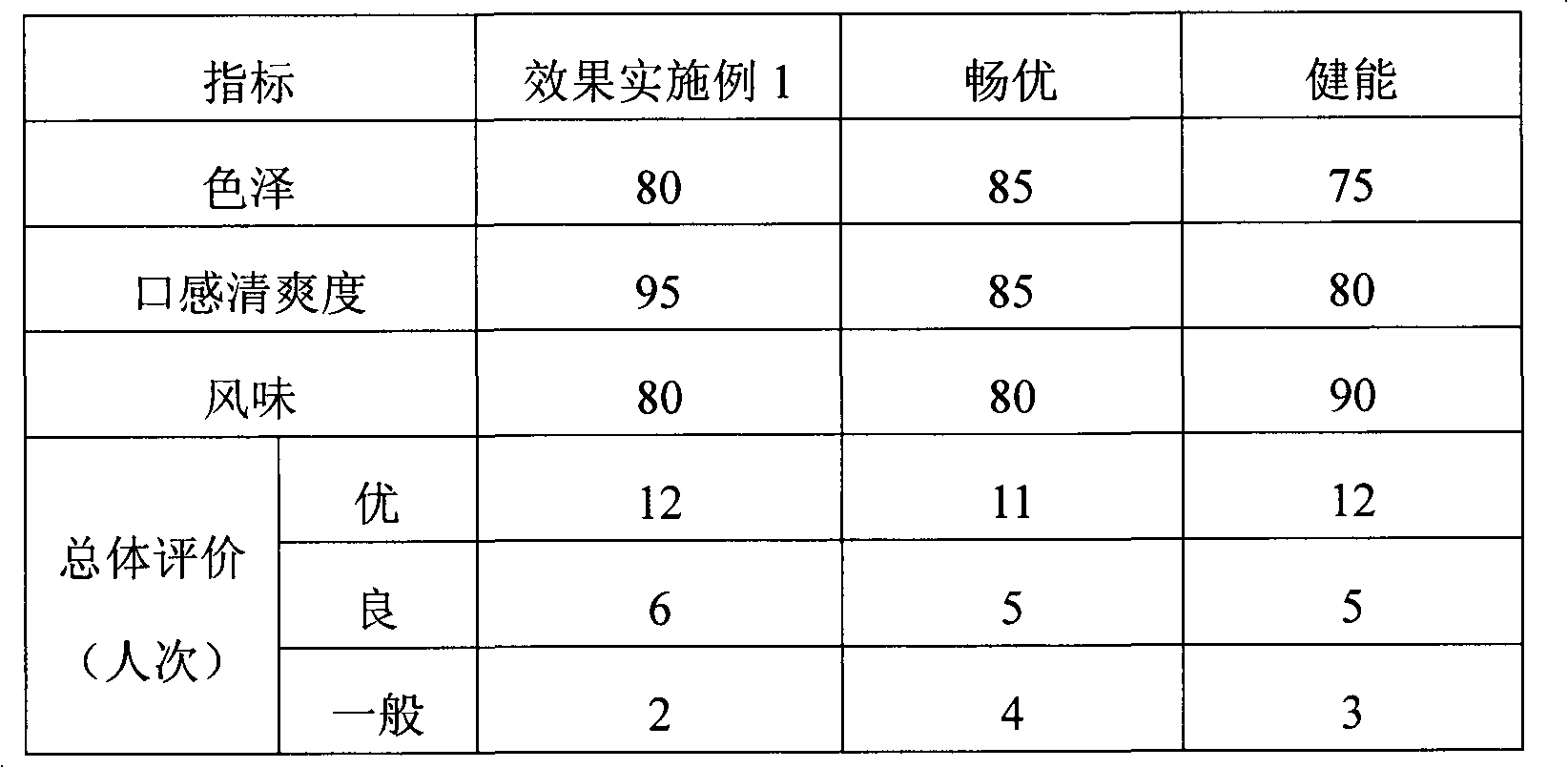
Lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin as well as raw material composition, preparation method and application thereof
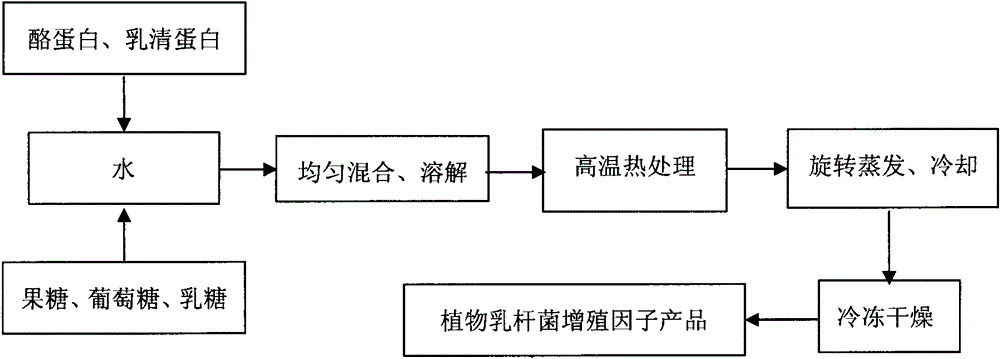
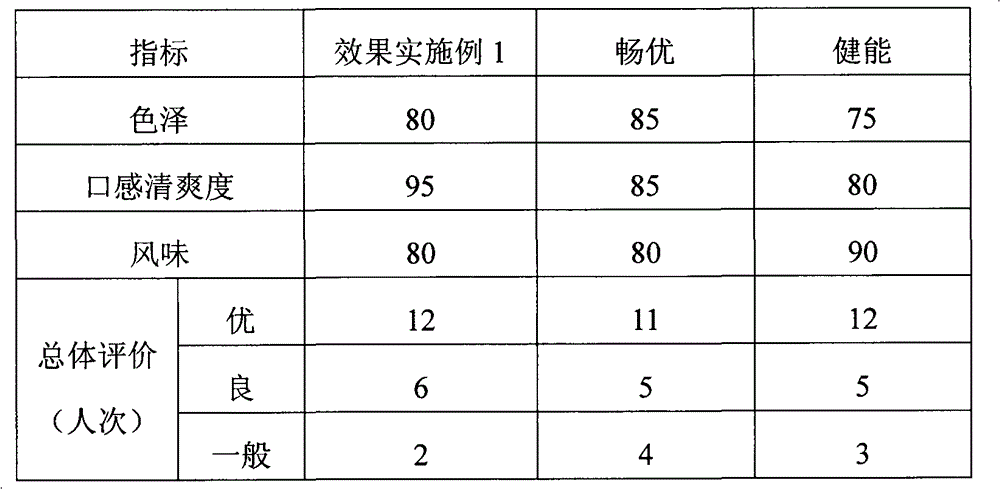
ActiveCN103103145APromote rapid proliferationEase of industrial applicationMilk preparationBacteriaCow milkingSomatomedin
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin as well as a raw material composition, a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin comprises revertose, water and casein and / or whey protein. The preparation method of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin comprises the steps of uniformly mixing and dissolving the raw material composition of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin; and then, performing high temperature thermal treatment at temperature higher than 90 DEG C for more than 10 minutes. The invention further discloses application of lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin in preparing lactobacillus plantarum containing fermented milk. The somatomedin can be used as a fermenting promoter in cow milk of lactobacillus plantarum to promote lactobacillus plantarum to proliferate quickly and massively in the fermentation process of lactobacillus plantarum, thereby being favorable for application of lactobacillus plantarum in fermented dairy.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD CO LTD
Amphiphilic oligomers
InactiveUS20050181976A1Promote absorptionGood componentPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesAmpicillinDaunorubicin
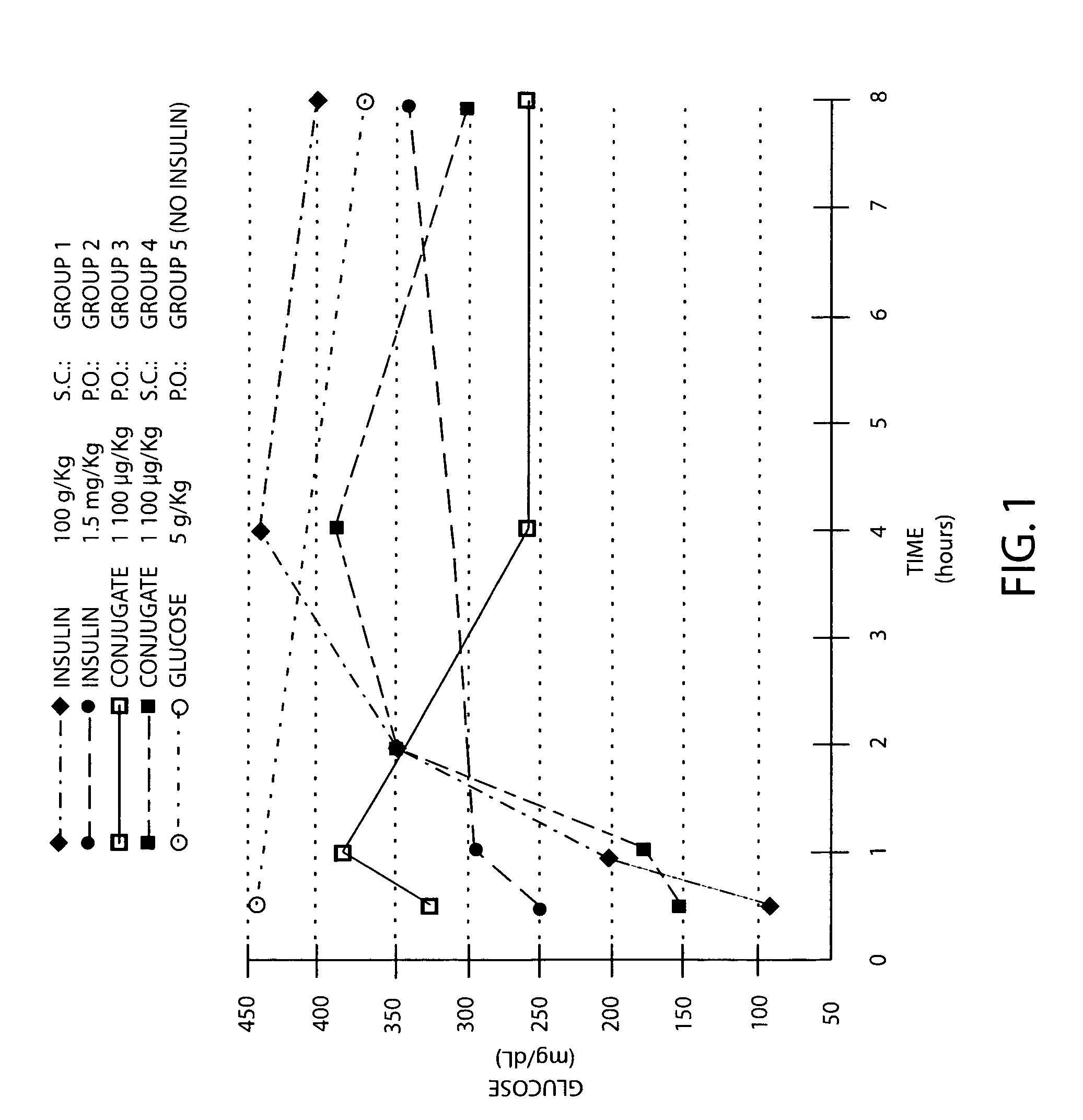
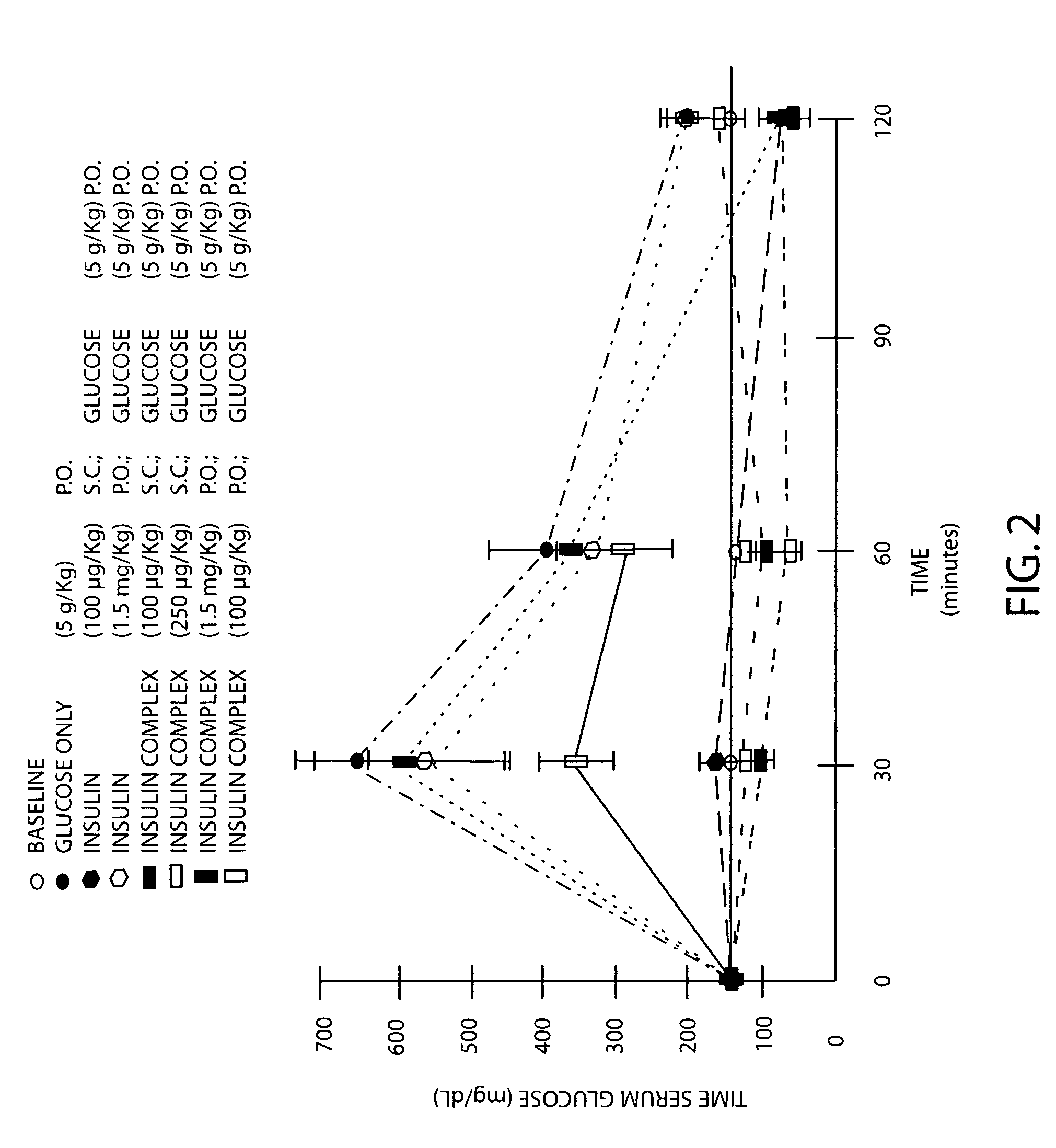
A therapeutic formulation comprising a microemulsion of a therapeutic agent in free and / or conjugatively coupled form, wherein the microemulsion comprises a water-in-oil (w / o) microemulsion including a lipophilic phase and a hydrophilic phase, and has a hydrophilic and lipophilic balance (HLB) value between 3 and 7, wherein the therapeutic agent may for example be selected from the group consisting of insulin, calcitonin, ACTH, glucagon, somatostatin, somatotropin, somatomedin, parathyroid honnone, erythropoietin, hypothalamic releasing factors, prolactin, thyroid stimulating hormones, endorphins, enkephalins, vasopressin, non-naturally occurring opioids, superoxide dismutase, interferon, asparaginase, arginase, arginine deaminease, adenosine deaminase, ribonuclease, trypsin, chymotrypsin, papain, Ara-A (Arabinofuranosyladenine), Acylguanosine, Nordeoxyguanosine, Azidothym id ine, Didesoxyadenosine, Dideoxycytidine, Dideoxyinosine Floxuridine, 6-Mercaptopurine, Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, or I-darubicin, Erythromycin, Vancomycin, oleandomycin, Ampicillin; Quinidine and Heparin. In a particular aspect, the invention comprises an insulin composition suitable for parenteral as well as non-parenteral administration, preferably oral or parenteral administration, comprising insulin covalently coupled with a polymer including (i) a linear polyalkylene glycol moiety and (ii) a lipophilic moiety, wherein the insulin, the linear polyalkylene glycol moiety and the lipophilic moiety are conformationally arranged in relation to one another such that the insulin in the composition has an enhanced in vivo resistance to enzymatic degradation, relative to insulin alone. The microemulsion compositions of the invention are usefully employed in therapeutic as well as non-therapeutic, e.g., diagnostic, applications.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
High-efficient activated biological fermentation bait for aquatic product, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a high-efficient activated biological fermentation bait for an aquatic product, and a preparation method and application thereof. The high-efficient activated biological fermentation bait for the aquatic product is prepared from the raw materials in percentage by weight: 30 to 45 percent of imported fish meal, 25 to 45 percent of fermented soybean meal, 0 to 30 percent of enzymolysis protein, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of small peptide, 1 to 5 percent of bacillus subtilis, 2 to 8 percent of bacillus coagulans, 0 to 5 percent of saccharomycetes, 0.1 to 1 percent of digestive enzyme, 0.5 to 2 percent of organic acid, and 0.5 to 2 percent of somatomedin. According to the high-efficient activated biological fermentation bait for the aquatic product, no any antibiotic is added,various cultures are organically combined, and flora advantages of the various cultures are fully played, so that not only can a digestive tract disease be prevented, but also fish and shrimp can be promoted to grow and gain weight, and the aim of complex synergism is achieved; in addition, the balance of the intestinal flora of the fish and shrimp can be improved and maintained, and the bait canbe directly applied to fish and shrimp cultivation.
Owner:广东渔赞臣生物科技有限公司
Method for breeding live pigs
InactiveCN109287571AImprove conversion rateImprove the level of epidemic preventionFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseFeed conversion ratio
The invention discloses a method for breeding live pigs. The method comprises the steps of pigsty building, piglet selection, feed feeding, pigsty disinfection, feeding management and disease management, and is characterized in that a pigsty is internally provided with a biological fermentation bed; the biological fermentation bed is divided into an upper layer and a lower layer, the lower layer is corn stalks, and the upper layer comprises at least raw wood chips, soil and salt; a mixture of sodium chloride, brown sugar and probiotics strains is added into the upper layer, and pigs can enterthe pigsty after 8-12 days when the temperature is controlled at 65-80%. The method for breeding the live pigs has the advantages that probiotics enter a live pig body along with feed, the formation of dominant florae is also facilitated, a large amount of amino acid, protein, vitamins and various biochemical enzymes, antibiotics, somatomedin and other nutrition and hormone substances are secretedand synthesized to adjust and improve the function of each organ of an animal body, improve the feed conversion rate, and have a variety of effects on the pigs, such as immunity, nutrition and growthstimulation, special feed for improving the immunity of the live pigs is adopted so that the immunity of the live pigs can be effectively improved, and the incidence of the live pigs is reduced.
Owner:贺琪
Recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine secreting bacteria resuscitation somatomedin and application thereof
InactiveCN101862450ASecretion persistsStable growth curveAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesGrowth Factor Gene
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine secreting bacteria resuscitation somatomedin and application thereof. The recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine uses the bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine as host cell. An exogenous expression vector carrying out transfection on the host cell is an expression vector comprising a bacteria resuscitation somatomedin genetic fragment. The recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine can continuously secrete Rpf factors with bioactivity and can induce a humoral immunity response level and a cellular immune response level. An antibody which is generated by aiming at the exogenous Rpf can interdict the stimulating effect of the Rpf to MTB. The level of inducing IFN-gamma of the recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine is superior to that of BCG. The recombinant bacillus calmette-guerin vaccine is applied to preparation of a preventive immunity vaccine for MTB infection and / or MTB inapparent infection.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Step-degrdeable bioactive implanting material comprising growth promotion factor
InactiveCN100381181CPromote proliferation and differentiationPromote growthSurgeryProsthesisSomatomedinGrowth promotion
The present invention relates to a bioactive implant material which can be stepwise degraded and contains somatomedin. It is basically formed from medical quick degradable high-molecular component containing somatomedin and medical slow degradable high-molecular component containing biomimetic apatite by means of blending or copolymerization mode, in which the medical quick degradable high-molecular component containing somatomedin can be quickly degraded and can release somatomedin in the implanted initial stage, and the medical slow degradable high-molecular component containing biomimetic apatite can provide relative stable active scaffold for new bone formation and growth, and can be slowly degraded after the new bone is formed and matured.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Alfalfa feed for tortoise
Owner:DALIAN NATIONALITIES UNIVERSITY
Fermented feed capable of improving laying performance and egg quality of laying hens
InactiveCN104938868AIncrease feed intakeIncrease profitAnimal feeding stuffSodium bicarbonateAnimal science
The invention discloses a fermented feed capable of improving the laying performance and the egg quality for laying hens. The fermented feed comprises the following raw materials by weight: 58-63.7 percent of corn, 17-20 percent of soya bean meal, 1-1.5 percent of fish meal, 3-5 percent of bran, 1.5 percent of bone meal, 4-7.67 percent of seashells, 0.3 percent of salt, 0.15 percent of methionine, 0.1 percent of trace elements, 0.03 percent of decavitamin, 0.05 percent of sodium bicarbonate, and 0.1-0.15 percent of enzyme-rich probiotics for poultry; the fermented feed is prepared by adding 380-460 kg of water in each ton of feed, and hermetically fermenting for 24-48 h before feeding. The fermented feed has the advantages that the feed intake of the laying hens is increased, the feed utilization rate is increased, the fermented feed does not contain antibiotics, but contains probiotics, such as viable bacteria, enzymes and oligopeptides, of various somatomedin, can improve the intestinal environment of poultry, enhances the immunity, can also promote the oocyte development and increase the spawning quantity, improves the laying rate, enhances the egg quality, and besides, can also reduce the pollution to surrounding environment, and brings remarkable economic, social and ecological benefits to locals applying the fermented feed.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANCHENG SCI GRP
Preparation method of slow-release organic fertilizer rich in beneficial components such as somatomedin
InactiveCN106467417AImprove biological activityImprove nutritional compositionClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersSomatomedinWater flow
At present, use of fertilizers in quantity leads to continuous decline of soil fertility and severe salinization. Nutrients required in soil during use of organic fertilizers in quantity flow away with water during the irrigation process, thus leading to nutrition shortage. Then, growth of plants and crops is severely influenced. Thus, a slow release technology of nutrient elements which are needed for soil is badly in need. The invention discloses a biochar organic fertilizer containing rich nutrient elements. The slow release period of nutrient elements is long, and adsorption quantity is large. By the method, soil fertility can be enhanced, and application amount of fertilizers can be greatly reduced. Therefore, preservation of cultivated land is realized, and the purpose of sustainable utilization of cultivated land is achieved.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
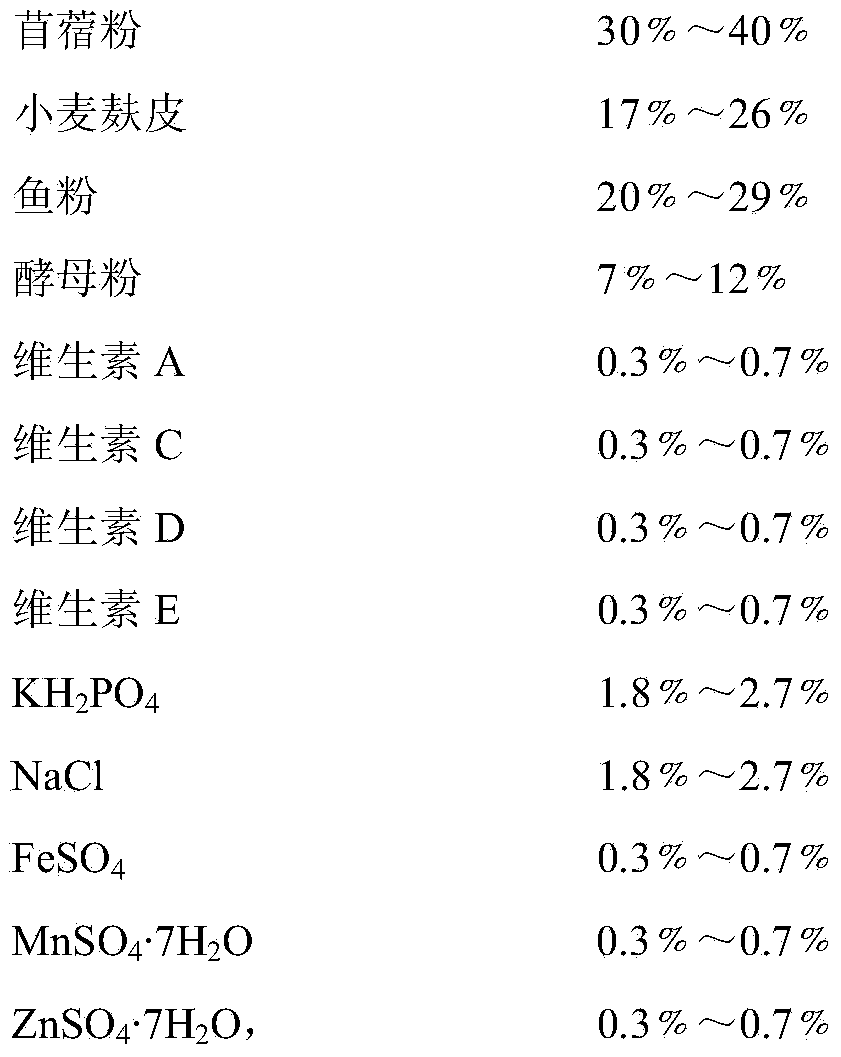
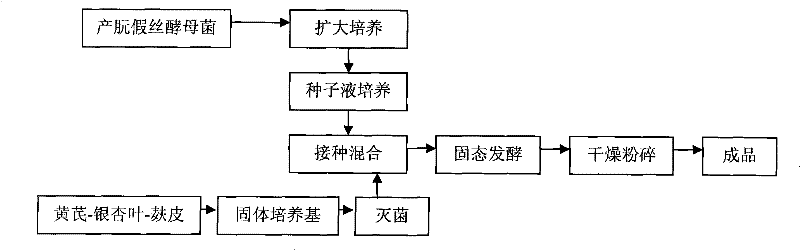
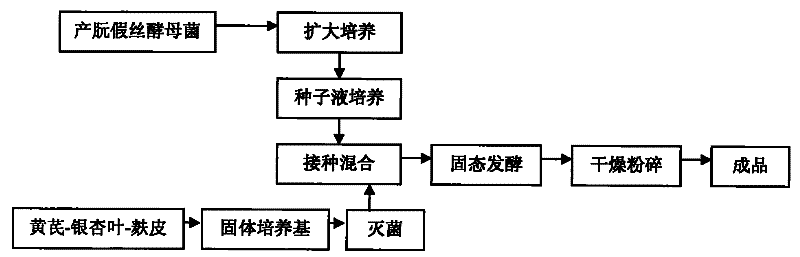
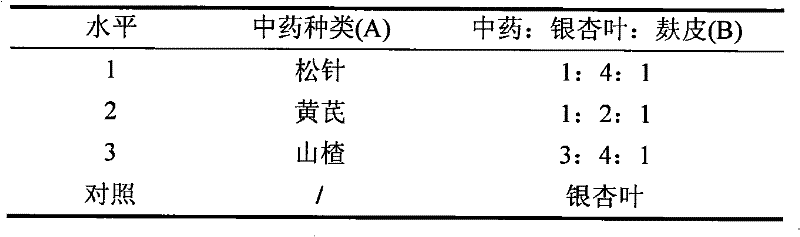
Preparation method of biological feed additive
InactiveCN101543259BThe experimental results are consistentGood effectAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologySucrose
The invention relates to a preparation method of biological feed additive which is used for livestock and poultry breeding and can effectively enhance the breeding speed and quality. The preparation method of the biological feed additive is as follows: pulverizing milk veteh, ginkgo leaf and bran into powder, evenly mixing the powder with nutrient fluid to prepare solid culture medium, and fermenting the mixture by Candida utilis to obtain the biological feed additive, wherein the mass ratio of the milk veteh, the ginkgo leaf and the bran is 1:2-4:1; and the preparation method of the nutrient fluid is as follows: dissolving 2.47-3g of cane sugar, 3.29-4g of NH42SO4, 2g of KH2PO4 and 0.5g of MgSO4.7H2O into water and metering the volume to be 100mL with water. The biological feed additive prepared has high nutrition, is rich in amylase, vitamins, minerals, digestive enzyme, somatomedin and relatively complete amino acid, has good palatability and can effectively enhance the breeding speed and quality.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A method for cultivating ganoderma and collecting ganoderma spore powder
ActiveCN106069194BReduce browning rateQuality improvementHarvestersCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologySomatomedin
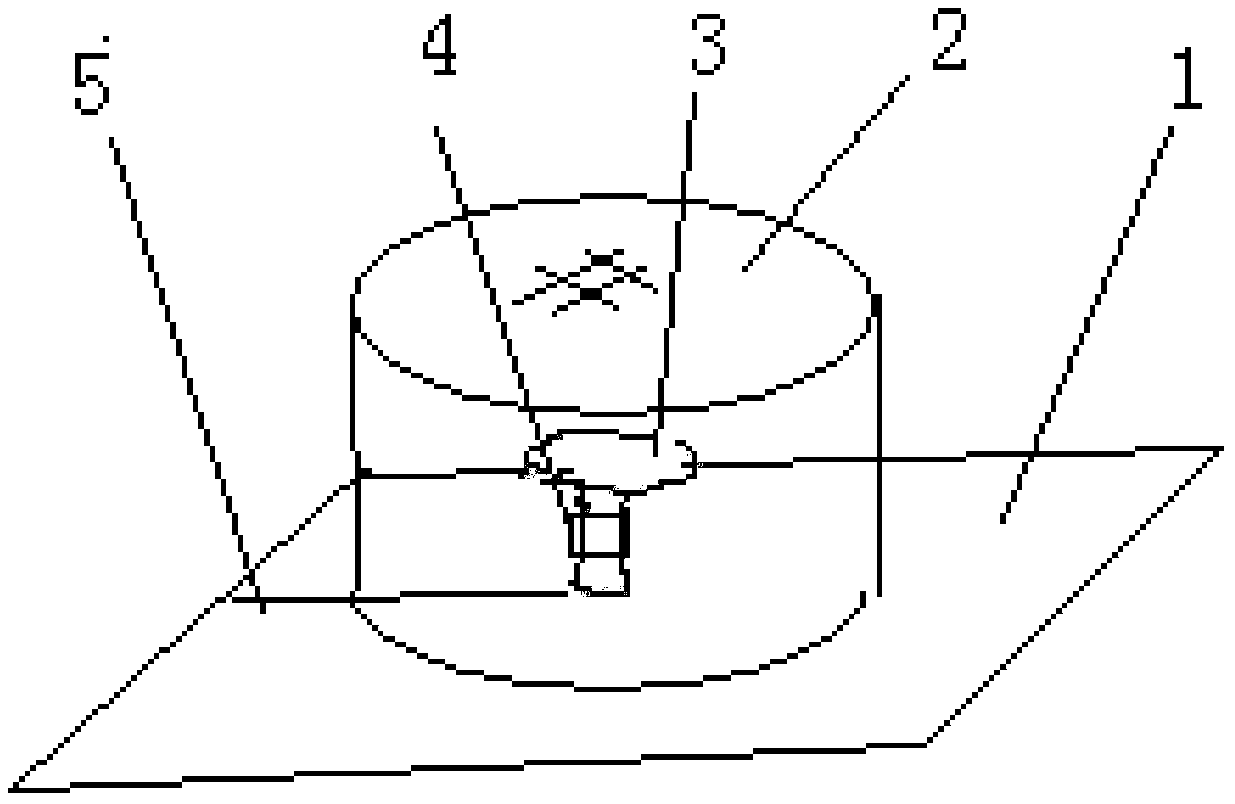
Provided is a method for cultivating ganoderma and collecting ganoderma spore powder. The method comprises the steps that pure broad-leaved tree basswood serves as a culture medium, a ganoderma variety is selected, when ganoderma sporophores enter the mature period and begin to generate spore powder, a paper pad is inserted into and padded at the root of each ganoderma sporophore, each paper pad is horizontally clamped and inserted into the root of the ganoderma sporophore through a sheared seam sheared in advance, and then tea filter paper or air-permeable non-woven fabric or gauze tubes are arranged; at the ganoderma cover powder appearing period, ganoderma stalks are wrapped by an absorber impregnated with a 100-500 mg / 1000 mL of somatomedin gibberellin solution, wherein the absorber is cotton or sponge or fiber or fabric, the outer layer of the absorber is provided with rectangular plastic film which wraps the absorber into a cylinder, and absorption of the stalks is guaranteed; a ganoderma cylinder is wrapped with the wrapped cylinder of the absorber through upper and lower omega-shaped plastic or steel wire clips at the initial period or imminent critical period.
Owner:浙江品高生物科技有限公司
Lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin as well as raw material composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103103145BPromote rapid proliferationEase of industrial applicationMilk preparationBacteriaCow milkingSomatomedin
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin as well as a raw material composition, a preparation method and application thereof. The raw material composition of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin comprises revertose, water and casein and / or whey protein. The preparation method of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin comprises the steps of uniformly mixing and dissolving the raw material composition of the lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin; and then, performing high temperature thermal treatment at temperature higher than 90 DEG C for more than 10 minutes. The invention further discloses application of lactobacillus plantarum somatomedin in preparing lactobacillus plantarum containing fermented milk. The somatomedin can be used as a fermenting promoter in cow milk of lactobacillus plantarum to promote lactobacillus plantarum to proliferate quickly and massively in the fermentation process of lactobacillus plantarum, thereby being favorable for application of lactobacillus plantarum in fermented dairy.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD CO LTD
Method for producing seaweed protein feed through synergistic effect of enzymolysis and fermentation
InactiveCN103549130BImprove conversion utilizationImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyAnimal feeding stuffDrug biological activityFermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing a seaweed protein feed through the synergistic effect of enzymolysis and fermentation. The method comprises the steps of fully mixing seaweed residue (the water content is 38%) and a feed enzyme preparation according to a certain proportion and performing the enzymolysis for 4-7h with the pH of 6.2-7.0 at the temperature being 35-45 DEG C to obtain a seaweed residue-feed enzyme preparation mixture; inoculating compound microorganisms and performing solid fermentation. The method has a simple process and is easy to operate; an external source is added to degrade a cellulose preparation to produce nutrition beneficial to microbial growth through the enzymolysis and make up the deficiency of enzyme produced by using the compound microorganisms, so as to stabilize the solid fermentation process and the product quality, greatly reduce the content of cellulose and increase the protein content; the seaweed protein feed is rich in multiple minerals, bioactive constituents and unknown somatomedin, and can be used as a protein feed for livestock and poultry and an aquatic feed; the method provides a technical support for growing tensions on developing novel protein resources and relieving a feed protein source.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV FOR THE NATITIES +1
Biological additive for animal feed and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101637219BImprove conversion rateAdjust and improve organ functionAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a biological additive for animal feed, which comprises the components of bacillus subtilis solution, yeast solution, lactic acid bacteria solution, acetic acid bacteria solution, beer yeast solution and vegetable lactic acid bacteria solution in a ratio of 0.4-1:1:0.6-1.5:0.6-1.5:0.6-1.5:0.3-0.7. After being mixed with the feed and drinking water and entering intestinal canals of animals, the biological additive can build a free dominant species with beneficial bacteria in the intestinal canals so as to inhibit and kill harmful pathogenic bacteria; and simultaneously, a great deal of nutrients such as amino acids, proteins, vitamins, biochemical enzymes, antibiotics, somatomedins and the like are secreted and synthesized, so that the functions of all organs of the animal body are adjusted and improved, the feed conversion rate is improved, the animals are stimulated to generate immunity, to be nourished, to grow and the like, and the effects of deodorizing manure, preventing and controlling diseases, improving survival rate, enforcing growth and breeding, cleaning the environment, improving economic benefits and the like can be achieved.
Owner:戴志南
Production process of probiotics colony additive for pig breeding feed
InactiveCN107988098ARealize prevention and controlRealize developmentFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyOrganic acid
The invention discloses a production process of a probiotics colony additive for a pig breeding feed. The process comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a culture primary enlarge cultivation solution; 2) preparing a culture secondary enlarge cultivation solution; and 3) inoculating the culture and carrying out drying and production. The invention also provides an application of the probioticscolony additive in pig feeds. 100-300g of probiotics colony additive is added into every 50kg of the pig feed. The probiotics colony additive can help the establishment of intestinal tracts of the pigs and maintain dominant bacterial communities and promote the pigs to generate various biological active substances such as various digestive enzymes, vitamins, organic acids and somatomedin. The pigs are healthy in intestinal tract and good in digestive absorption naturally, and the weight gain is obvious.
Owner:FOSHAN CHUANSUO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A serum-free culture system for epidermal cell culture
ActiveCN105132357BIncrease the number ofHigh activityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsHigh cellCuticle
Owner:NOVAPRINT THERAPEUTICS SUZHOU CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com