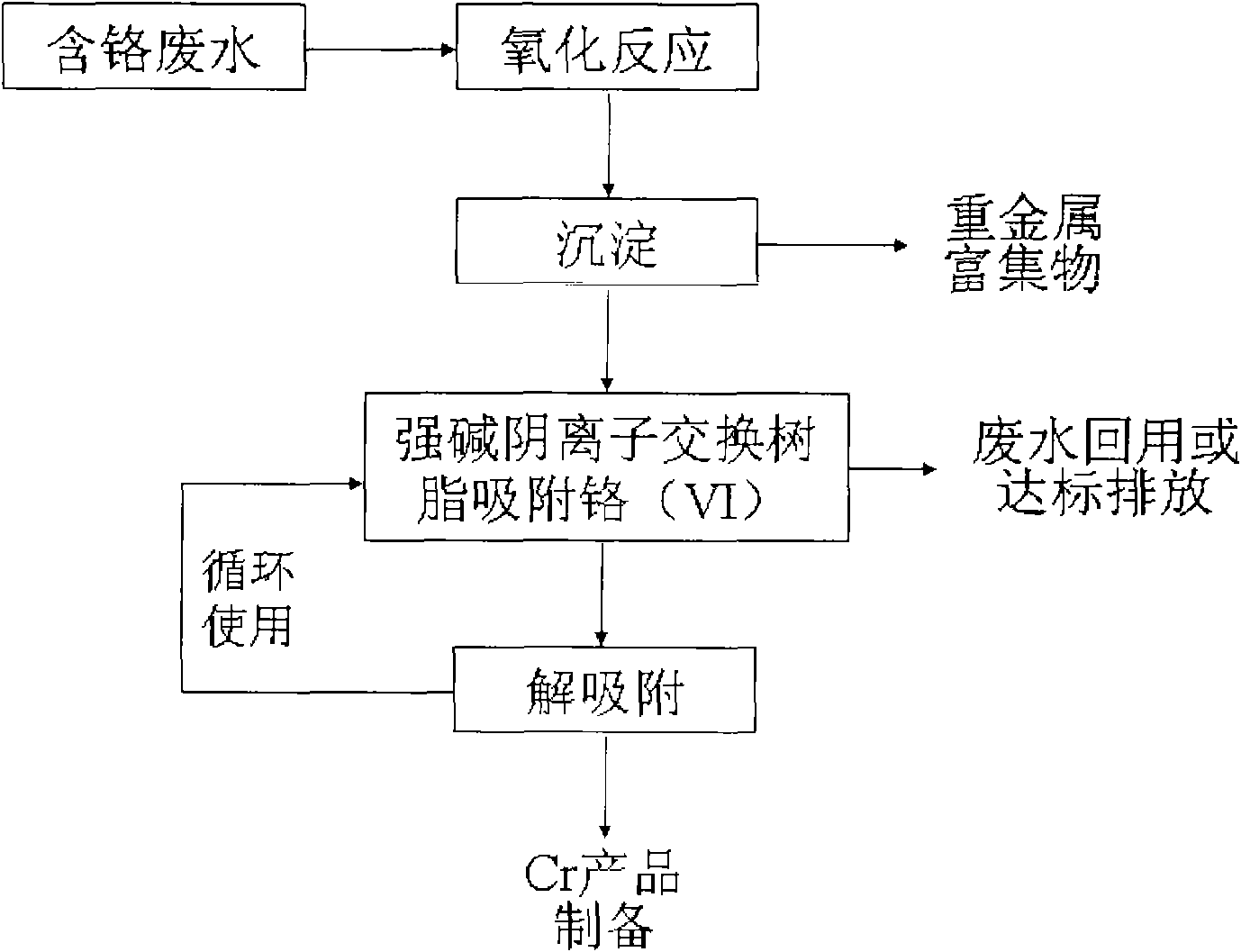
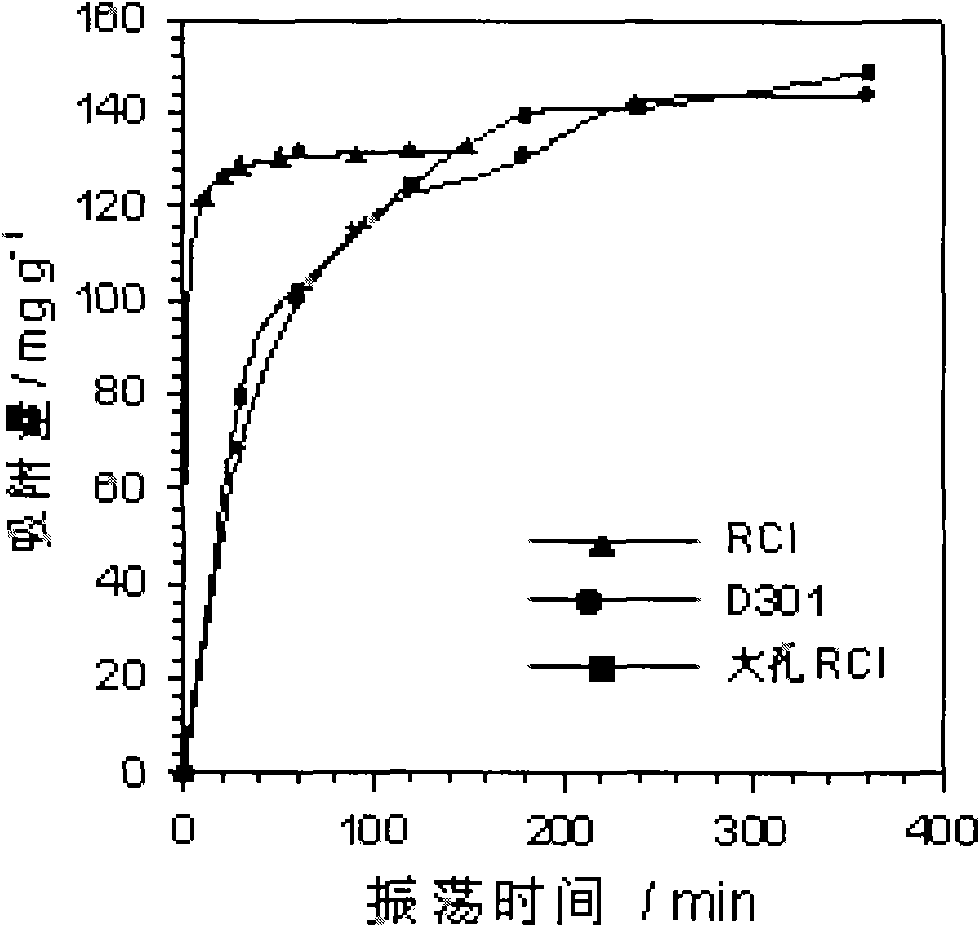
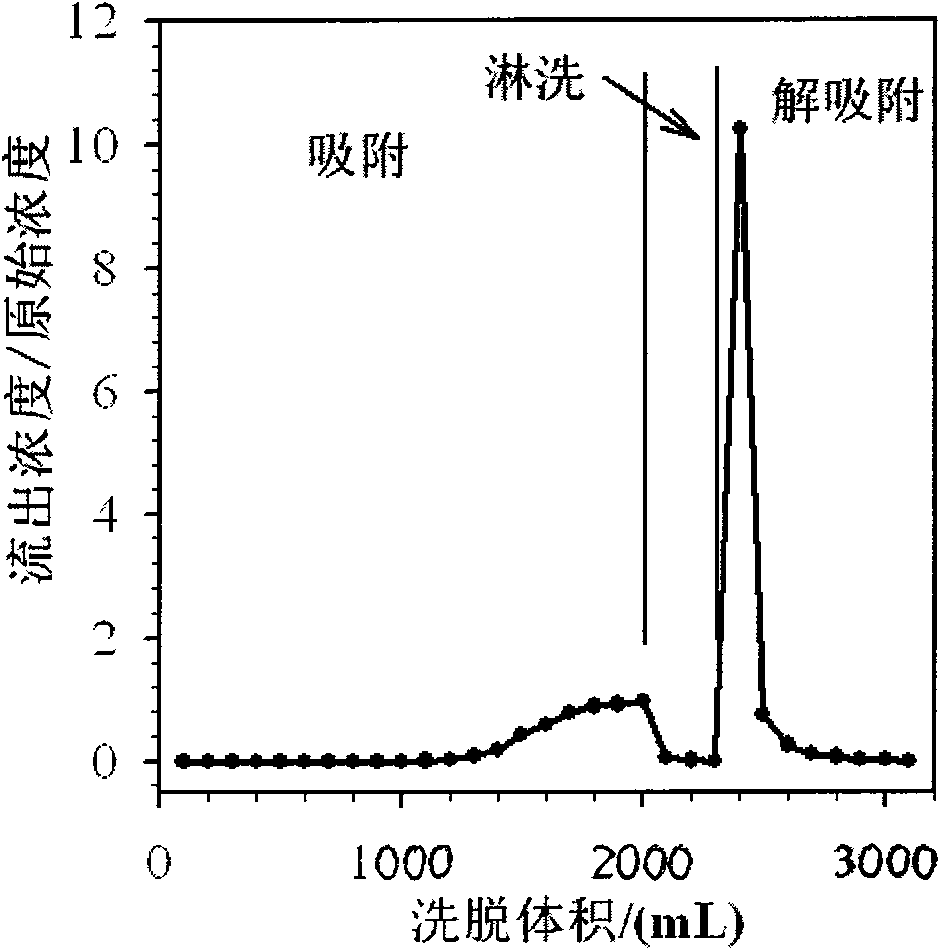
Method for purifying electroplating wastewater and comprehensively utilizing resources
A technology for electroplating wastewater and resources, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chromium compounds, metallurgical wastewater treatment, etc., can solve the problems that restrict the large-scale use of ion exchange technology, high production costs, etc., and achieve significant economic and social benefits, treatment The effect of low cost and stable process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Take 50g of chloromethylated styrene-type macroporous adsorption resin in a three-necked flask, add 300mL of N,N-dimethylformamide, stir at room temperature for 2h, add 16.5g of N-methylimidazole at 40°C for 72h, filter The resin was synthesized and washed with ethanol. The washed resin is vacuum-dried to obtain a chlorine-type macroporous strong base anion-exchange resin containing an imidazole structure.
[0045] Stir 1 g of chlorine-type macroporous strong base anion exchange resin containing imidazole structure in deionized water for 2 h, then add 20 mL of sodium sulfate solution with a molar concentration of 2 mol / L and shake for 10 h until the reaction is complete, filter the resin, and then use deionized The filtered resin is washed with water to remove excess sulfate ions to obtain a sulfate-type macroporous strong base anion exchange resin containing an imidazole structure.
[0046] Stir 1 g of chlorine-type macroporous strong base anion exchange resin contain...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Taking the wastewater of an electroplating factory as the research object, the test results of the main components are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from the table that the wastewater contains a large amount of Cr(III), Cr(VI) and other valuable heavy metal elements, and direct discharge causes environmental pollution. Pollution, recovery of valuable heavy metal elements can produce certain economic benefits.
[0049] Table 1 Main components of electroplating chromium-containing wastewater
[0050] Pollutant name
Cr(V)
Cr(total)
Cu
Zn
Ni
Fe
Al
Concentration (mg / L)
250
344
28.92
16.61
8.589
134.6
5.063
[0051] Chromium (III) is oxidized to chromium (VI): Take 2L of chromium-containing wastewater, use NaOH to adjust the pH value of the wastewater to 13.00, and then add 10.8 mmol of hydrogen peroxide to oxidize the chromium (III) in the wastewater to chromium (VI).
[0052] ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] According to the method of Example 2, in the step of recovering valuable heavy metal resources such as copper and nickel, the pH value is adjusted to 8.00 with hydrochloric acid, so that heavy metal elements such as zinc, copper, nickel and iron in the wastewater are converted into hydroxide precipitation, and the filtrate after precipitation The contents of zinc, copper, nickel, iron, and aluminum in it are 0.13mg / L, 0.22mg / L, 0.41mg / L, 0.69mg / L, and 0.21mg / L respectively.
[0057] The filtrate in the step of adsorbing chromium (VI) on the strongly basic anion exchange resin is adjusted to pH 4.00 with hydrochloric acid. According to Example 2, the secondary adsorption columns are used in series, so that the Cr(VI) content in the wastewater after ion exchange treatment is less than 0.1 mg / L.
[0058] In the step of preparing the chromium product, the sodium chromate solution is prepared by a soluble barium chloride precipitation method to prepare the barium chromate pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com